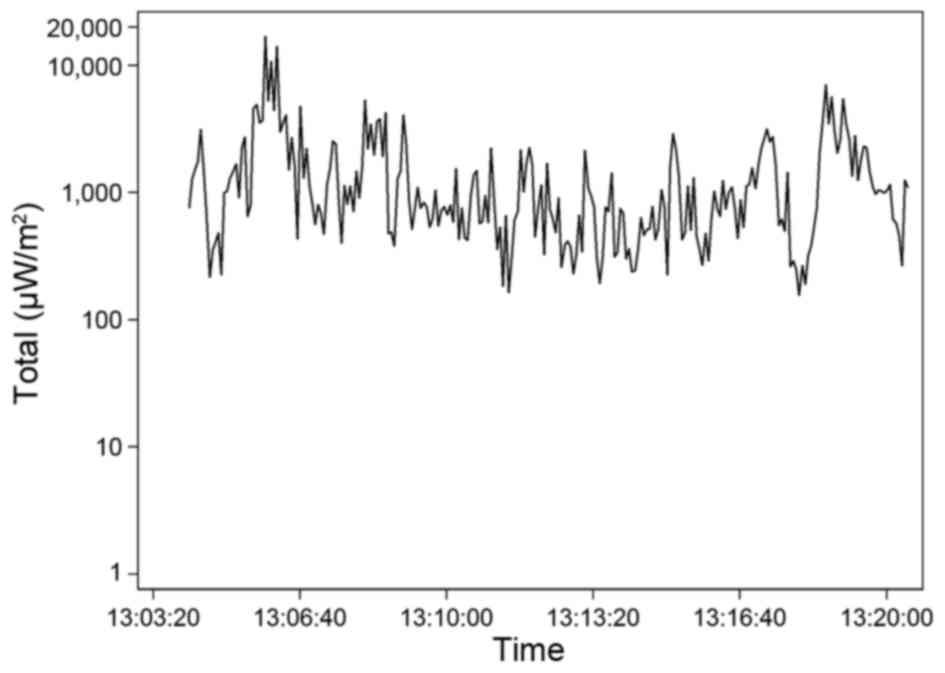
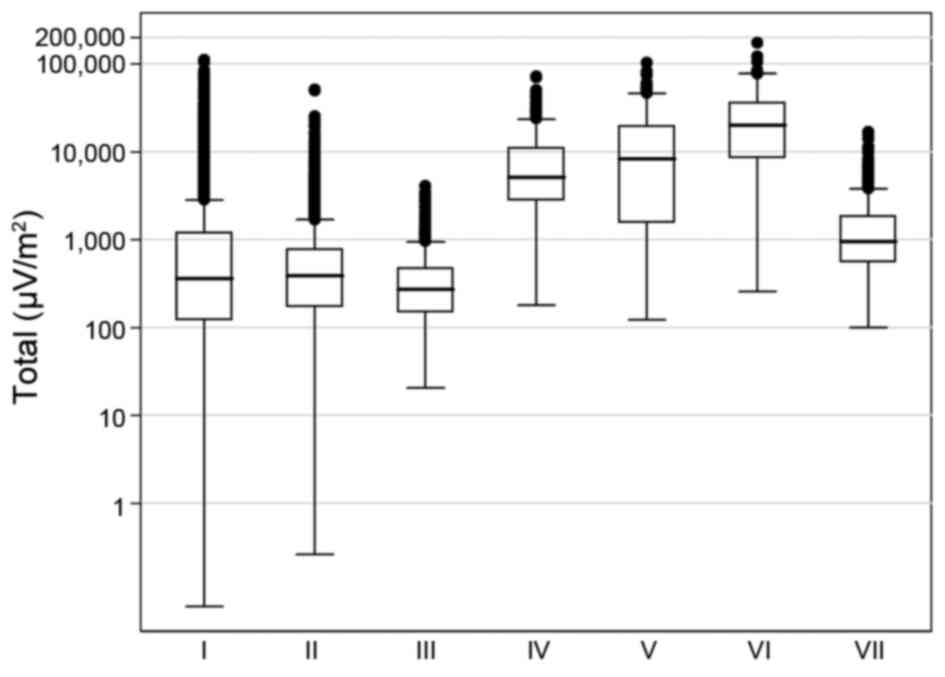
|
1
|
Hardell L, Koppel T, Carlberg M, Ahonen M
and Hedendahl L: Radiofrequency radiation at Stockholm Central
Railway Station in Sweden and some medical aspects on public
exposure to RF fields. Int J Oncol. 49:1315–1324. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guidelines for limiting exposure to
time-varying electric, magnetic, and electromagnetic fields (up to
300 GHz). International Commission on Non-Ionizing Radiation
Protection. Health Phys. 74:494–522. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
ICNIRP statement on the ‘Guidelines for
limiting exposure to time-varying electric, magnetic and
electromagnetic fields (up to 300 GHz)’. Health Phys. 97:257–258.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hedendahl L, Carlberg M and Hardell L:
Electromagnetic hypersensitivity-an increasing challenge to the
medical profession. Rev Environ Health. 30:209–215. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
BioInitiative Working Group, .
BioInitiative Report: A Rationale for a Biologically-based Public
Exposure Standard for Electromagnetic Fields (ELF and RF). Sage C
and Carpenter DO: Bioinitiative. 2007 http://www.bioinitiative.org/table-of-contents/October
3–2016.
|
|
6
|
BioInitiative Working Group, .
BioInitiative 2012. A Rationale for a Biologically-based Public
Exposure Standard for Electromagnetic Fields (ELF and RF). Sage C
and Carpenter DO: Bioinitiative. 2012 http://www.bioinitiative.org/table-of-contents/October
3–2016.
|
|
7
|
Szmigielski S, Szudzinski A, Pietraszek A,
Bielec M, Janiak M and Wrembel JK: Accelerated development of
spontaneous and benzopyrene-induced skin cancer in mice exposed to
2450-MHz microwave radiation. Bioelectromagnetics. 3:179–191. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cleary SF, Liu LM and Merchant RE: Glioma
proliferation modulated in vitro by isothermal radiofrequency
radiation exposure. Radiat Res. 121:38–45. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cleary SF, Liu LM and Merchant RE: In
vitro lymphocyte proliferation induced by radio-frequency
electromagnetic radiation under isothermal conditions.
Bioelectromagnetics. 11:47–56. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chou CK, Guy AW, Kunz LL, Johnson RB,
Crowley JJ and Krupp JH: Long-term, low-level microwave irradiation
of rats. Bioelectromagnetics. 13:469–496. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Repacholi MH, Basten A, Gebski V, Noonan
D, Finnie J and Harris AW: Lymphomas in E mu-Pim1 transgenic mice
exposed to pulsed 900 MHZ electromagnetic fields. Radiat Res.
147:631–640. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Utteridge TD, Gebski V, Finnie JW,
Vernon-Roberts B and Kuchel TR: Long-term exposure of E-mu-Pim1
transgenic mice to 898.4 MHz microwaves does not increase lymphoma
incidence. Radiat Res. 158:357–364. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hardell L, Eriksson M, Carlberg M,
Sundström C and Mild KH: Use of cellular or cordless telephones and
the risk for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Int Arch Occup Environ Health.
78:625–632. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Linet MS, Taggart T, Severson RK, Cerhan
JR, Cozen W, Hartge P and Colt J: Cellular telephones and
non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 119:2382–2388. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Carlberg M, Hedendahl L, Ahonen M, Koppel
T and Hardell L: Increasing incidence of thyroid cancer in the
Nordic countries with main focus on Swedish data. BMC Cancer.
16:4262016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lauer O, Frei P, Gosselin MC, Joseph W,
Röösli M and Fröhlich J: Combining near- and far-field exposure for
an organ-specific and whole-body RF-EMF proxy for epidemiological
research: A reference case. Bioelctromagnetics. 34:366–374. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lu M and Wu XY: Study of specific
absorption rate (SAR) induced in human endocrine glands for using
mobile phones. IEEE Asia-Pacific International Symposium on
Electromagnetic Compatibility (APEMC). 1084–1086. 2016.
|
|
18
|
Tillmann T, Ernst H, Streckert J, Zhou Y,
Taugner F, Hansen V and Dasenbrock CT: Indication of cocarcinogenic
potential of chronic UMTS-modulated radiofrequency exposure in an
ethylnitrosourea mouse model. Int J Radiat Biol. 86:529–541. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lerchl A, Klose M, Grote K, Wilhelm AF,
Spathmann O, Fiedler T, Streckert J, Hansen V and Clemens M: Tumor
promotion by exposure to radiofrequency electromagnetic fields
below exposure limits for humans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
459:585–590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wyde M, Cesta M, Blystone C, Elmore S,
Foster P, Hooth M, Kissling G, Malarkey D, Sills R, Stout M, et al:
Report of Partial Findings from the National Toxicology Program
Carcinogenesis Studies of Cell Phone Radiofrequency Radiation in
Hsd: Sprague Dawley® SD rats (Whole Body Exposures).
Draft 5-19-2016. US National Toxicology Program (NTP). 2016
http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/055699http://biorxiv.org/content/biorxiv/early/2016/05/26/055699.full.pdfOctober
3–2016.
|
|
21
|
Lai H and Singh NP: Acute low-intensity
microwave exposure increases DNA single-strand breaks in rat brain
cells. Bioelectromagnetics. 16:207–210. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hardell L, Näsman Å, Påhlson A, Hallquist
A and Mild K Hansson: Use of cellular telephones and the risk for
brain tumours: A case-control study. Int J Oncol. 15:113–116.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hardell L, Mild K Hansson, Påhlson A and
Hallquist A: Ionizing radiation, cellular telephones and the risk
for brain tumours. Eur J Cancer Prev. 10:523–529. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hardell L, Hallquist A, Mild KH, Carlberg
M, Påhlson A and Lilja A: Cellular and cordless telephones and the
risk for brain tumours. Eur J Cancer Prev. 11:377–386. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hardell L, Mild KH and Carlberg M: Further
aspects on cellular and cordless telephones and brain tumours. Int
J Oncol. 22:399–407. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baan R, Grosse Y, Lauby-Secretan B, El
Ghissassi F, Bouvard V, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Islami F,
Galichet L and Straif K; WHO International Agency for Research on
Cancer Monograph Working Group, : Carcinogenicity of radiofrequency
electromagnetic fields. Lancet Oncol. 12:624–626. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of
Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, . 102. Non-Ionizing Radiation, Part 2
Radiofrequency Electromagnetic Fields. International Agency for
Research on Cancer; Lyon, France: 2013 http://monographs.iarc.fr/ENG/Monographs/vol102/mono102.pdfOctober
3–2016
|
|
28
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Mild K Hansson:
Pooled analysis of two case-control studies on use of cellular and
cordless telephones and the risk for malignant brain tumours
diagnosed in 1997–2003. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 79:630–639.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Mild K Hansson:
Pooled analysis of two case-control studies on the use of cellular
and cordless telephones and the risk of benign brain tumours
diagnosed during 1997–2003. Int J Oncol. 28:509–518.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Mild K Hansson:
Pooled analysis of case-control studies on malignant brain tumours
and the use of mobile and cordless phones including living and
deceased subjects. Int J Oncol. 38:1465–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brain tumour risk in relation to mobile
telephone use: Results of the INTERPHONE international case-control
study. Int J Epidemiol. 39:675–694. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Acoustic neuroma risk in relation to
mobile telephone use: Results of the INTERPHONE international
case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol. 35:453–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cardis E, Armstrong BK, Bowman JD, Giles
GG, Hours M, Krewski D, McBride M, Parent ME, Sadetzki S, Woodward
A, et al: Risk of brain tumours in relation to estimated RF dose
from mobile phones: Results from five Interphone countries. Occup
Environ Med. 68:631–640. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F and
Mild KH: Pooled analysis of case-control studies on acoustic
neuroma diagnosed 1997–2003 and 2007–2009 and use of mobile and
cordless phones. Int J Oncol. 43:1036–1044. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M, Söderqvist F and
Mild KH: Case-control study of the association between malignant
brain tumours diagnosed between 2007 and 2009 and mobile and
cordless phone use. Int J Oncol. 43:1833–1845. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hardell L, Carlberg M and Mild K Hansson:
Use of mobile phones and cordless phones is associated with
increased risk for glioma and acoustic neuroma. Pathophysiology.
20:85–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Mobile phone and
cordless phone use and the risk for glioma-Analysis of pooled
case-control studies in Sweden, 1997–2003 and 2007–2009.
Pathophysiology. 22:1–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Coureau G, Bouvier G, Lebailly P,
Fabbro-Peray P, Gruber A, Leffondre K, Guillamo JS, Loiseau H,
Mathoulin-Pélissier S, Salamon R and Baldi I: Mobile phone use and
brain tumours in the CERENAT case-control study. Occup Environ Med.
71:514–522. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hardell L and Carlberg M: Using the Hill
viewpoints from 1965 for evaluating strengths of evidence of the
risk for brain tumors associated with use of mobile and cordless
phones. Rev Environ Health. 28:97–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hill AB: The environment and disease:
Association or causation? Proc R Soc Med. 58:295–300.
1965.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yakymenko I, Tsybulin O, Sidorik E,
Henshel D, Kyrylenko O and Kyrylenko S: Oxidative mechanisms of
biological activity of low-intensity radiofrequency radiation.
Electromagn Biol Med. 35:186–202. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bolte JF, Maslanyj M, Addison D, Mee T,
Kamer J and Colussi L: Do car-mounted mobile measurements used for
radio-frequency spectrum regulation have an application for
exposure assessments in epidemiological studies? Environ Int.
86:75–83. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Estenberg J and Augustsson T: Extensive
frequency selective measurements of radiofrequency fields in
outdoor environments performed with a novel mobile monitoring
system. Bioelectromagnetics. 35:227–230. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Joseph W, Frei P, Röösli M, Thuróczy G,
Gajsek P, Trcek T, Bolte J, Vermeeren G, Mohler E, Juhász P, et al:
Comparison of personal radio frequency electromagnetic field
exposure in different urban areas across Europe. Environ Res.
110:658–663. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bolte JF and Eikelboom T: Personal
radiofrequency electromagnetic field measurements in The
Netherlands: Exposure level and variability for everyday
activities, times of day and types of area. Environ Int.
48:133–142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Urbinello D, Joseph W, Verloock L, Martens
L and Röösli M: Temporal trends of radio-frequency electromagnetic
field (RF-EMF) exposure in everyday environments across European
cities. Environ Res. 134:134–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Aerts S, Deschrijver D, Verloock L, Dhaene
T, Martens L and Joseph W: Assessment of outdoor radiofrequency
electromagnetic field exposure through hotspot localization using
kriging-based sequential sampling. Environ Res. 126:184–191. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Verlock L, Joseph W, Goeminne F, Martens
L, Verlaek M and Constandt K: Assessment of radiofrequency
exposures in schools, homes, and public places in Belgium. Health
Phys. 107:503–513. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Calvente I, Fernández MF, Pérez-Lobato R,
Dávila-Arias C, Ocón O, Ramos R, Ríos-Arrabal S, Villalba-Moreno J,
Olea N and Núñez MI: Outdoor characterization of radio frequency
electromagnetic fields in a Spanish birth cohort. Environ Res.
138:136–143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gonzalez-Rubio J, Najera A and Arribas E:
Comprehensive personal RF-EMF exposure map and its potential use in
epidemiological studies. Environ Res. 149:105–112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Eberhardt JL, Persson BR, Brun AE, Salford
LG and Malmgren LO: Blood-brain barrier permeability and nerve cell
damage in rat brain 14 and 28 days after exposure to microwaves
from GSM mobile phones. Electromagn Biol Med. 27:215–229. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Salford LG, Brun AE, Eberhardt JL,
Malmgren L and Persson BR: Nerve cell damage in mammalian brain
after exposure to microwaves from GSM mobile phones. Environ Health
Perspect. 111:881–883, A408. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Nittby H, Brun A, Eberhardt J, Malmgren L,
Persson BR and Salford LG: Increased blood-brain barrier
permeability in mammalian brain 7 days after exposure to the
radiation from a GSM-900 mobile phone. Pathophysiology. 16:103–112.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Sirav B and Seyhan N: Effects of GSM
modulated radio-frequency electromagnetic radiation on permeability
of blood-brain barrier in male & female rats. J Chem Neuroanat.
75:123–127. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tang J, Zhang Y, Yang L, Chen Q, Tan L,
Zuo S, Feng H, Chen Z and Zhu G: Exposure to 900 MHz
electromagnetic fields activates the mkp-1/ERK pathway and causes
blood-brain barrier damage and cognitive impairment in rats. Brain
Res. 1601:92–101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Nittby H, Grafström G, Tian DP, Malmgren
L, Brun A, Persson BR, Salford LG and Eberhardt J: Cognitive
impairment in rats after long-term exposure to GSM-900 mobile phone
radiation. Bioelectromagnetics. 29:219–232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Grafström G, Nittby H, Brun A, Malmgren L,
Persson BR, Salford LG and Eberhardt J: Histopathological
examinations of rat brains after long-term exposure to GSM-900
mobile phone radiation. Brain Res Bull. 77:257–263. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Fragopoulou A, Samara A, Antonelou MH,
Xanthopoulou A, Papadopoulou A, Vougas K, Koutsogiannopoulou E,
Anastasiadou E, Stravopodis DJ, Tsangaris GT and Margaritis LH:
Brain proteome response following whole body exposure of mice to
mobile phone or wireless DECT base radiation. Electromagn Biol Med.
31:250–274. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Dasdag S, Akdag MZ, Erdal ME, Erdal N, Ay
OI, Ay ME, Yilmaz SG, Tasdelen B and Yegin K: Effects of 2.4 GHz
radiofrequency radiation emitted from Wi-Fi equipment on microRNA
expression in brain tissue. Int J Radiat Biol. 91:555–561. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Dasdag S, Tas M, Akdag MZ and Yegin K:
Effect of long-term exposure of 2.4 GHz radiofrequency radiation
emitted from Wi-Fi equipment on testes functions. Electromagn Biol
Med. 34:37–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Avendaño C, Mata A, Samiento CA Sanchez
and Doncel GF: Use of laptop computers connected to internet
through Wi-Fi decreases human sperm motility and increases sperm
DNA fragmentation. Fertil Steril. 97:39–45.e2. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Akdag MZ, Dasdag S, Canturk F, Karabulut
D, Caner Y and Adalier N: Does prolonged radiofrequency radiation
emitted from Wi-Fi devices induce DNA damage in various tissues of
rats? J Chem Neuroanat. 75:116–122. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Burlaka A, Tsybulin O, Sidorik E, Lukin S,
Polishuk V, Tsehmistrenko S and Yakymenko I: Overproduction of free
radical species in embryonal cells exposed to low intensity
radiofrequency radiation. Exp Oncol. 35:219–225. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Megha K, Deshmukh PS, Banerjee BD,
Tripathi AK and Abegaonkar MP: Microwave radiation induced
oxidative stress, cognitive impairment and inflammation in brain of
Fischer rats. Indian J Exp Biol. 50:889–896. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Megha K, Deshmukh PS, Ravi AK, Tripathi
AK, Abegaonkar MP and Banerjee BD: Effect of low-intensity
microwave radiation on monoamine neurotransmitters and their key
regulating enzymes in rat brain. Cell Biochem Biophys. 73:93–100.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Megha K, Deshmukh PS, Banerjee BD,
Tripathi AK, Ahmed R and Abegaonkar MP: Low intensity microwave
radiation induced oxidative stress, inflammatory response and DNA
damage in rat brain. Neurotoxicology. 51:158–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Deshmukh PS, Nasare N, Megha K, Banerjee
BD, Ahmed RS, Singh D, Abegaonkar MP, Tripathi AK and Mediratta PK:
Cognitive impairment and neurogenotoxic effects in rats exposed to
low-intensity microwave radiation. Int J Toxicol. 34:284–290. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Deshmukh PS, Banerjee BD, Abegaonkar MP,
Megha K, Ahmed RS, Tripath AK and Mediratta PK: Effect of low level
microwave radiation exposure on cognitive function and oxidative
stress in rats. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 50:114–119.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Gerner C, Haudek V, Schandl U, Bayer E,
Gundacker N, Hutter HP and Mosgoeller W: Increased protein
synthesis by cells exposed to a 1,800-MHz radio-frequency mobile
phone electromagnetic field, detected by proteome profiling. Int
Arch Occup Environ Health. 83:691–702. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Markovà E, Malmgren LO and Belyaev IY:
Microwaves from mobile phones inhibit 53BP1 focus formation in
human stem cells more strongly than in differentiated cells:
Possible mechanistic link to cancer risk. Environ Health Perspect.
118:394–399. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Khurana VG, Hardell L, Everaert J,
Bortkiewicz A, Carlberg M and Ahonen M: Epidemiological evidence
for a health risk from mobile phone base stations. Int J Occup
Environ Health. 16:263–267. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Levitt BB and Lai H: Biological effects
from exposure to electromagnetic radiation emitted by cell tower
base stations and other antenna arrays. Environ Rev. 18:369–395.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Buchner K and Eger H: Changes of
clinically important neurotransmitters under the influence of
modulated RF fields-A long-term study under real-life conditions.
Umwelt-Medizin-Gesellschaft. 24:44–57. 2011.
|
|
74
|
Augner C, Hacker GW, Oberfeld G, Florian
M, Hitzl W, Hutter J and Pauser G: Effects of exposure to GSM
mobile phone base station signals on salivary cortisol,
alpha-amylase, and immunoglobulin A. Biomed Environ Sci.
23:199–207. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Eskander EF, Estefan SF and Abd-Rabou AA:
How does long term exposure to base stations and mobile phones
affect human hormone profiles? Clin Biochem. 45:157–161. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Carpenter DO and Sage C: Setting prudent
public health policy for electromagnetic field exposures. Rev
Environ Health. 23:91–117. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Hardell L and Sage C: Biological effects
from electromagnetic field exposure and public exposure standards.
Biomed Pharmacother. 62:104–109. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Starkey SJ: Inaccurate official assessment
of radiofrequency safety by the Advisory Group on Non-ionising
Radiation. Rev Environ Health. 31:493–503. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|