Introduction
Biliary tract cancer has a poor prognosis because it
is often diagnosed at an advanced stage and is often unresectable.
If an early diagnosis of this malignancy is possible, the prognosis
might improve (1). Again, it is
often difficult to differentiate malignant biliary tract strictures
and benign biliary strictures: Such as primary sclerosing
cholangitis, IgG4-associated sclerosing cholangitis and Mirrizi
syndrome (2). It is important to
distinguish biliary tract cancer from benign biliary disease
because the treatment strategies and prognoses differ. In patients
with a biliary stricture, endoscopic retrograde
cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a common pathological diagnostic
method that allows the use of several techniques for tissue
sampling, including bile aspiration cytology, brush cytology, and
forceps biopsy. The specificities of the pathological examination
of tissue obtained by ERCP for biliary strictures are almost 100%,
thus, obtaining histological or cytological evidence is very
important to determine the therapeutic strategies in these
patients. However the sensitivities of bile aspiration cytology,
brush cytology, and forceps biopsy for biliary strictures are 6–72%
(3,4), have not been satisfactory. Therefore,
improvement of the sensitivity for diagnosing biliary tract cancer
is needed.
Mucins, which are produced by various epithelial
cells, are high molecular weight glycoproteins with
oligosaccharides attached to serine or threonine residues of the
mucin core protein backbone by O-glycosidic linkages. The human
mucin (MUC) family consists of members designated MUC1 to MUC21.
Mucins are also expressed in pancreatico-biliary neoplasm included
biliary tract cancer. Furthermore, MUC expression pattern might
reflect the cell differentiation type of biliary tract cancer like
pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinus neoplasms, for example,
gastric type presents a MUC1-/MUC2-/MUC5AC+/MUC6-profile,
intestinal type presents a MUC1-/MUC2+/MUC5AC+/MUC6-profile, and
pancreatico-biliary type presents a MUC1+/MUC2-/MUC5AC+/MUC6+
profile (5,6).
Sialylated carbohydrate antigen KL-6, a type of
Mucin 1, cell surface associated (MUC1), was investigated and was
suggested to have a significant relationship with a worse tumor
behavior, especially cancer cell invasion and metastasis in
gastrointestinal, hepatic, pancreatico-biliary and ampullary
cancers (7–9). Although the KL-6 concentration of serum
for intrahepatic ductal adenocarcinoma and pancreatic juice for
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma was useful in diagnosing
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (10–12),
there have not been any studies about the clinical benefits of
measuring the KL-6 concentration of bile for diagnosing biliary
tract cancer. In the present study, the usefulness of the KL-6
concentration of bile for diagnosis of biliary tract cancer was
examined.
Patients and methods
A total of 43 patients with biliary disease were
enrolled prospectively between October 2011 and January 2014 at our
hospital. The diagnosis of biliary tract cancer was based on the
pathological diagnosis of bile aspiration cytology, transpapillary
forceps biopsy, endoscopic ultrasound fine needle aspiration
(EUS-FNA) or surgical specimen. Patients without a malignant
disease had a final benign diagnosis based on clinical and
radiological follow-up data for at least 6 months. This study was
performed according to the guidelines described in the Helsinki
Declaration for biomedical research involving human subjects. The
study protocol was approved by the institutional review board of
Tottori University. Written informed consent was obtained from all
participating subjects.
The 43 patients with biliary disease included 28 men
and 15 women: Age range, 34–88 years; mean age, 72.6 years
(Table I). A malignant lesion was
present in 25 patients and a benign lesion was present in 18
patients.
 | Table I.Patients' characteristics with benign
biliary disease and patients with biliary tract cancer. |
Table I.
Patients' characteristics with benign
biliary disease and patients with biliary tract cancer.
|
| Benign biliary
disease (n=18) | Biliary tract cancer
(n=25) | P-value |
|---|
| Mean age, year | 69.8 (42–88) | 74.6 (51–87) | 0.07a |
| Number of patients
(M/F) | 18 (13/5) | 25 (15/10) | 0.41b |
| Mean size of tumor,
mm | – | 36.3 (7–100) | – |
| Tumor marker
(serum) |
|
|
|
| CEA,
ng/ml | 4.2 (1.2–13.5) | 20.6 (0.8–337.7) | 0.979a |
| CA19-9,
U/ml | 36.6 (3.7–187.8) | 483.0 (4.7–4939) | <0.01a |
| KL-6, U/ml | 260.5 (133–412) | 830.7 (144–8176) | 0.16a |
We performed ERCP and transpapillary bile aspiration
cytology. Cytodiagnosis of the specimens was performed by
Papanicolaou's method. A lateral-viewing duodenoscope (JF260V;
Olympus Optical Co., Ltd, Tokyo, Japan) was used to carry out ERCP.
Bile was collected by aspirating through a biliary catheter from
the bile duct during ERCP by using a cannula (M00535700; Boston
Scientific Corporation, Natick, MA, USA), and a 0.035-inch
hydrophilic guide-wire (M00556051; Boston Scientific Corporation).
Over the guide-wire, the cannula was advanced into the bile duct.
The guide-wire was then withdrawn, and bile was collected using a
syringe with the tip of the cannula in the bile duct. The aspirated
specimen was then evaluated.
Afterwards, the bile was centrifuged at 1,710 × g
for 5 min, the pellet was subjected to cytological examination, and
a supernatant was used for measuring the KL-6 concentration. Human
KL-6 levels were determined in duplicate with a PICOLUMI KL-6 kit
(EIDIA, Tokyo, Japan), and an electrochemiluminescence immunoassay
(ECLIA) specific for human KL-6.
We compared the KL-6 concentration of bile in the
biliary tract cancer group with the benign biliary disease group.
We also evaluated the utility of measuring the KL-6 concentration
of bile for use in the diagnosis of biliary tract cancer.
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed using
StatFlex ver. 6.0 for Windows software (Artech Co, Ltd., Osaka,
Japan). Categorical variables were compared by using the Chi-square
test. Continuous variables were compared by using the Mann-Whitney
U-test. Comparisons of the mean KL-6 concentration of bile
between biliary tract cancer and benign biliary disease were
performed by using the Mann-Whitney U-test. All values are
expressed as means ± standard deviation or means with interquartile
ranges. P<0.05 was considered significant. The diagnostic power
of KL-6 concentration of bile was assessed by using a
receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves analysis. Optimal
cut-off levels for KL-6 of bile were determined according to Youden
index, and positive and negative predictive values were evaluated
using these cut-off values.
Results
The patients with biliary disease characteristics
are shown in Table I. The malignant
group included 11 perihilar bile duct adenocarcinoma, 8 distal bile
duct adenocarcinoma and 6 gallbladder adenocarcinoma. The growth
pattern types of biliary tract cancer were 4 mass-forming type, 9
intraductal type and 12 periductal type, respectively. The benign
group included 9 benign biliary strictures, 1 pancreaticobiliary
maljunction, 2 chronic cholecystitis, 1 adenomyomatosis of
gallbladder, 3 adenoma of the papilla and 2 papillitis of
Vater.
There was no significant difference in age and sex
between the malignant group and the benign group. The median level
of serum CA19-9 in the malignant group was significantly higher
than that in the benign group. There were no significant
differences in the level of serum CEA and KL-6 between the
malignant group and the benign group.
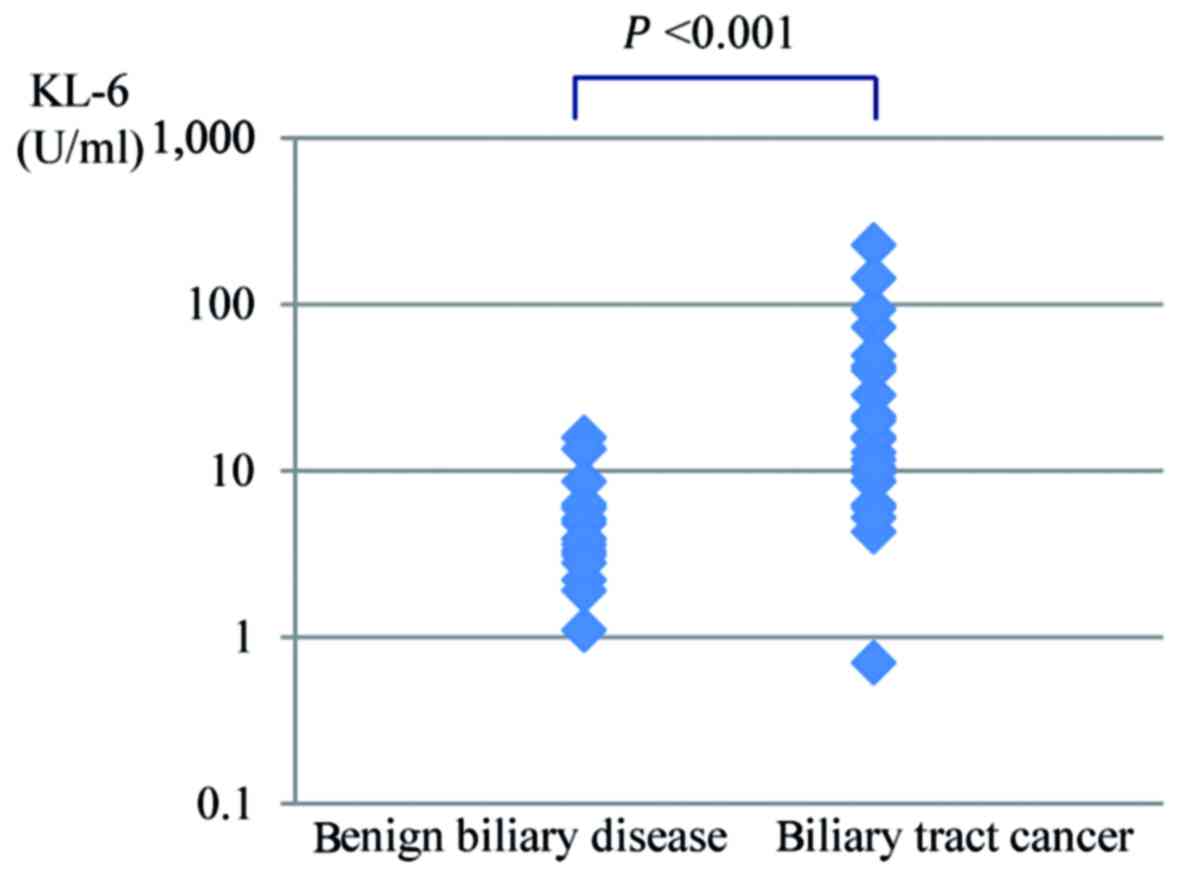
The KL-6 concentration of bile in the malignant
group and the benign group are shown in Fig. 1. The average KL-6 concentration of
bile was significantly higher for biliary tract cancer (34.6±51.6
U/ml) than for benign biliary disease (5.2±3.9 U/ml,
P<0.001).
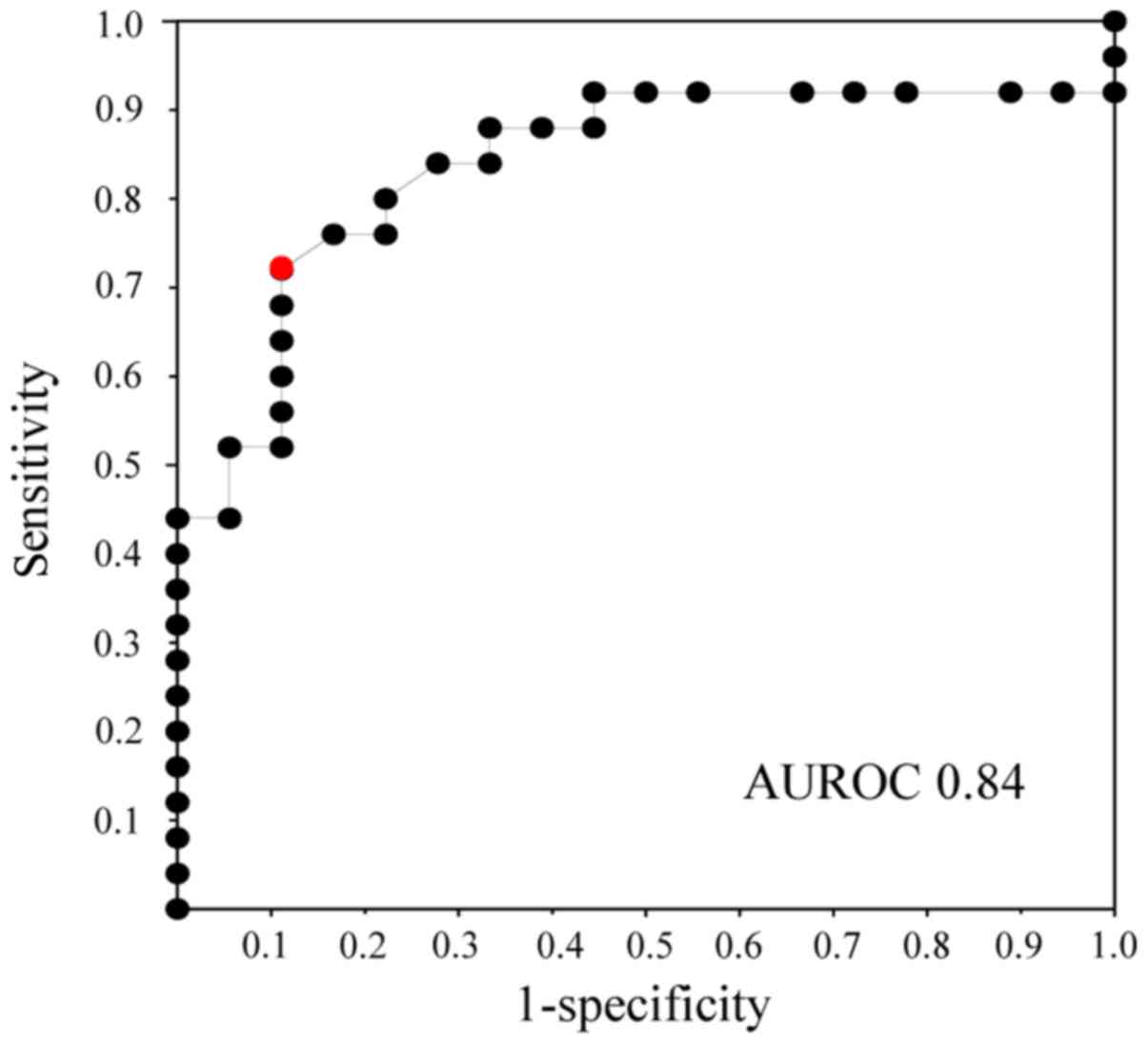
The ROC curves for bile KL-6 concentration showed
that the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve
(AUROC) had a value of 0.84 between biliary tract cancer and benign
biliary disease (Fig. 2). According
to the ROC curves, the cut-off value of bile KL-6 for the diagnosis
of biliary tract cancer was estimated to be 8.6 U/ml.
Compared with bile KL-6 in patients with benign
biliary disease, the cut-off value of bile KL-6 for the diagnosis
of biliary tract cancer was associated with a sensitivity,
specificity, positive predictive values, negative predictive
values, and accuracy of 72, 89, 90, 70 and 79%, respectively
(Tables II and III).
 | Table II.The cut-off levels of bile KL-6 for
biliary tract cancer. |
Table II.
The cut-off levels of bile KL-6 for
biliary tract cancer.
| Cut-off | Sensitivity | 1-Specificity | PPV | NPV | Lielihood ratio | Odds ratio | Youden-index |
|---|
| 225.100 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | – | 0.4186 | – | – | 0.0000 |
| 142.400 | 0.0400 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4286 | – | – | 0.0400 |
| 92.600 | 0.0800 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4390 | – | – | 0.0800 |
| 72.500 | 0.1200 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4500 | – | – | 0.1200 |
| 49.000 | 0.1600 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4615 | – | – | 0.1600 |
| 42.200 | 0.2000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4737 | – | – | 0.2000 |
| 40.000 | 0.2400 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.4865 | – | – | 0.2400 |
| 28.300 | 0.2800 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5000 | – | – | 0.2800 |
| 21.200 | 0.3200 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5143 | – | – | 0.3200 |
| 20.000 | 0.3600 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5294 | – | – | 0.3600 |
| 15.900 | 0.4000 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5455 | – | – | 0.4000 |
| 15.800 | 0.4400 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5625 | – | – | 0.4400 |
| 15.400 | 0.4400 | 0.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.5484 | 7.9200 | 13.3571 | 0.4400 |
| 13.500 | 0.5200 | 0.0556 | 0.9286 | 0.5862 | 9.3600 | 18.4167 | 0.4644 |
| 12.800 | 0.5200 | 0.1111 | 0.8667 | 0.5714 | 4.6800 | 8.6667 | 0.4089 |
| 11.600 | 0.5600 | 0.1111 | 0.8750 | 0.5926 | 5.0400 | 10.1818 | 0.4489 |
| 10.400 | 0.6000 | 0.1111 | 0.8824 | 0.6154 | 5.4000 | 12.0000 | 0.4889 |
| 9.800 | 0.6400 | 0.1111 | 0.8889 | 0.6400 | 5.7600 | 14.2222 | 0.5289 |
| 8.700 | 0.6800 | 0.1111 | 0.8947 | 0.6667 | 6.1200 | 17.0000 | 0.5689 |
| 8.600 | 0.7200 | 0.1111 | 0.9000 | 0.6957 | 6.4800 | 20.5714 | 0.6089 |
| 6.300 | 0.7600 | 0.1667 | 0.8636 | 0.7143 | 4.5600 | 15.8333 | 0.5933 |
| 6.200 | 0.7600 | 0.2222 | 0.8261 | 0.7000 | 3.4200 | 11.0833 | 0.5378 |
| 6.000 | 0.8000 | 0.2222 | 0.8333 | 0.7368 | 3.6000 | 14.0000 | 0.5778 |
| 5.900 | 0.8400 | 0.2778 | 0.8077 | 0.7647 | 3.0240 | 13.6500 | 0.5622 |
| 5.200 | 0.8400 | 0.3333 | 0.7778 | 0.7500 | 2.5200 | 10.5000 | 0.5067 |
| 5.100 | 0.8800 | 0.3333 | 0.7857 | 0.8000 | 2.6400 | 14.6667 | 0.5467 |
| 4.800 | 0.8800 | 0.3889 | 0.7586 | 0.7857 | 2.2629 | 11.5238 | 0.4911 |
| 4.300 | 0.8800 | 0.4444 | 0.7333 | 0.7692 | 1.9800 | 9.1667 | 0.4356 |
| 3.900 | 0.9200 | 0.4444 | 0.7419 | 0.8333 | 2.0700 | 14.3750 | 0.4756 |
| 3.600 | 0.9200 | 0.5000 | 0.7186 | 0.8182 | 1.8400 | 11.5000 | 0.4200 |
| 3.300 | 0.9200 | 0.5556 | 0.6970 | 0.8000 | 1.6560 | 9.2000 | 0.3644 |
| 3.100 | 0.9200 | 0.6667 | 0.6571 | 0.7500 | 1.3800 | 5.7500 | 0.2533 |
| 2.800 | 0.9200 | 0.7222 | 0.6389 | 0.7143 | 1.2739 | 4.4231 | 0.1978 |
| 2.200 | 0.9200 | 0.7778 | 0.6216 | 0.6667 | 1.1829 | 3.2857 | 0.1422 |
| 1.900 | 0.9200 | 0.8889 | 0.5897 | 0.5000 | 1.0350 | 1.4375 | 0.0311 |
| 1.100 | 0.9200 | 0.9444 | 0.5750 | 0.3333 | 0.9741 | 0.6765 | −0.0244 |
| 0.700 | 0.9200 | 1.0000 | 0.5610 | 0.0000 | 0.9200 | 0.0000 | −0.0800 |
| 0.000 | 0.9600 | 1.0000 | 0.5714 | 0.0000 | 0.9600 | 0.0000 | −0.0400 |
 | Table III.Diagnostic ability of KL-6
measurement of bile for differentiating biliary tract cancer from
benign biliary disease. |
Table III.
Diagnostic ability of KL-6
measurement of bile for differentiating biliary tract cancer from
benign biliary disease.
|
| Optimal cut-off
values,% | Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | PPV, % | NPV, % | Accuracy, % |
|---|
| KL-6, U/ml | 8.6 | 72 | 89 | 90 | 70 | 79 |
Table IV summarizes
the diagnostic ability of bile aspiration cytology and/or KL-6
analysis to differentiate biliary tract cancer from benign biliary
disease. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value,
negative predictive value, and accuracy of bile aspiration cytology
alone were 80, 100, 100, 78, and 88%, respectively. Of the
remaining 5 patients who remained undiagnosed by cytological
assessment, the KL-6 concentration of bile was measured in all 5
(100%) patients. Adding the KL-6 concentration of the bile
aspiration cytology diagnosis significantly increased the
sensitivity of bile aspiration cytology by 20.0% (P=0.018).
 | Table IV.Diagnostic ability of bile aspiration
cytology and/or KL-6 measurement of bile for differentiating
biliary tract cancer from benign biliary disease. |
Table IV.
Diagnostic ability of bile aspiration
cytology and/or KL-6 measurement of bile for differentiating
biliary tract cancer from benign biliary disease.
|
| Sensitivity, % | Specificity, % | PPV, % | NPV, % | Accuracy, % |
|---|
| KL-6
measurement | 72 | 89 | 90 | 70 | 79 |
|
| (18/25) | (16/18) | (18/20) | (16/23) | (34/43) |
| Bile aspiration
cytology | 80 | 100 | 100 | 78 | 88 |
|
| (20/25) | (18/18) | (20/20) | (18/23) | (38/43) |
| Bile aspiration
cytology | 100a | 89 | 93 | 100 | 95 |
| And/or KL-6
measurement | (25/25) | (16/18) | (25/27) | (15/15) | (41/43) |
Six patients (14.0%) in this study developed
complications following bile aspiration cytology during ERCP. Mild
pancreatitis occurred at a rate of 9.3% (4/43) and cholangitis
occurred at a rate of 4.7% (2/43). All were resolved with
conservative treatment. No serious complications such as
perforation or hemorrhages were observed. There was no procedure
related mortality.
Discussion
Although ERCP plays an important role in the
diagnosis for biliary stricture, the sensitivity is not enough.
Recent studies showed that the sensitivity of bile aspiration
cytology, biliary brush cytology and forceps biopsy for malignant
biliary strictures were 41.6, 45.0, and 48.1%, respectively. A
combination of both modalities only modestly increased the
sensitivity to 59.4%. Both techniques are almost 100% specific
(3,4). Furthermore, the incidence rates of
post-ERCP complication, which were reported as 4.0–6.9%, including
pancreatitis (2.6–3.5%), bleeding (0.3–1.3%), and perforation
(0.1–0.6%), can not be ignored (13,14).
Recently, the high sensitivity (80%) and the low
complication rate (bleeding 1.0%, biliary peritonititis 0.3%) of
EUS-FNA for the diagnosis of malignant biliary strictures were
reported (15–17). Meanwhile small lesions, especially
the lesions present with wall thickening, are more difficult to
sample by using EUS-FNA. In addition, the possibility for needle
tract seeding in resectable cases is unresolved (18).
ERCP is a common method for tissue sampling in
patients with biliary strictures by bile aspiration cytology,
biliary brush cytology and forceps biopsy. A recent study showed
that the sensitivity and accuracy of bile aspiration cytology for
malignant biliary strictures were 41.6 and 67.7%, respectively
(3). Navaneenthan et al
reported that the sensitivities of transpapilary brush cytology and
forceps biopsy in diagnosing malignant biliary strictures were 45.0
and 48.1%, respectively. A combination of both modalities only
modestly increased the sensitivity to 59.4%. Both techniques are
almost 100% specific (4). Bile
aspiration cytology is easier and safer than brush cytology and
forceps biopsy, which are technically difficult and carry some
degree of complication. Therefore, bile aspiration cytology during
ERCP is an effective method for the cytological diagnosis of
biliary tract cancer, although the sensitivity is inadequate.
Tang et al reported that KL-6 mucin, one kind
of MUC1, was positive in biliary tract cancer tissues (10). Xu et al also reported KL-6
might be involved in tumor cell adhesion and invasion in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (9).
These reports mean that there is the potential for an increase in
bile KL-6 concentration in patients with biliary tract cancer. So,
we considered the KL-6 concentration of bile measurement in
patients with biliary disease might be helpful to diagnose biliary
tract cancer.
In the current study, a high KL-6 concentration of
bile was seen in 72% of patients with biliary tract cancer. The
sensitivity of bile aspiration cytology for the diagnosis of
biliary tract cancer was significantly improved by adding the bile
KL-6 concentration although bile aspiration cytology showed
favorable sensitivity for biliary tract cancer in the present
study. If the sensitivity of bile aspiration cytology for biliary
tract cancer was as low as that of ERCP-guided tissue sampling in
recent studies, the measurement of bile KL-6 concentration might
have improved the diagnostic ability of bile cytology for biliary
tract cancer more. Biliary tract cancer whose bile cytology results
were inconclusive or negative could be diagnosed exactly by
combining the bile KL-6 measurements with the bile cytology
results. Because the high-accuracy of bile aspiration cytology for
biliary tract cancer was evaluated in the present study, the
diagnostic ability of the combination of bile aspiration cytology
and bile KL-6 concentration was not significantly higher than that
of bile aspiration cytology only. We thought that the sensitivity
of bile KL-6 concentration might be better than that of bile
aspiration cytology if the diagnostic ability of bile aspiration
cytology for biliary tract cancer was low. However, a high
concentration of bile KL-6 was also seen in 11% of patients with
benign biliary disease because the specificity of KL-6 of bile was
inadequate. These findings suggest that further examinations such
as trasnpapilary brush cytology, forceps biopsy, cholangioscopy,
and EUS-FNA are necessary when bile aspiration cytology specimens
are negative and the KL-6 concentration of bile is increased.
The other benefit of the measurement of bile KL-6 is
that it does not affect the diagnostic ability of bile aspiration
cytology because the KL-6 concentration was evaluated by using the
supernatant of bile from which the cell pellet was removed for
cytological examination.
There were no significant differences in the level
of serum KL-6 between the biliary tract cancer group and the benign
biliary disease group in this study although the elevation of serum
KL-6 mucin levels in patients with cholangiocarcinoma was reported
in previous study (11). The reason
of this discrepancy might be involved in MUC1 gene polymorphisms
which are associated with serum KL-6 levels (19). The association between bile KL-6 and
MUC1 gene polymorphisms was uncertain, more study is needed.
The present study has some limitations. Firstly,
this study was a single-center study with small number of cases.
Secondly, the in-vivo and in-situ experiments of KL-6
were not evaluated. Thirdly, this sample size is insufficient to
conclude that KL-6 as a diagnostic factor in biliary tract cancers.
Fourthly, if we checked KL-6 level by using samples from cancer
adjunct tissue, we might improve the accuracy of the central
conclusion. Finally, other biliary tract neoplasms, such as
neuroendocrine tumors, and para-biliary malignant tumors which may
cause biliary strictures, such as pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
were not evaluated.
In conclusion, the KL-6 concentration of bile may
strengthen the sensitivity of bile cytology for biliary tract
cancer.
References
|
1
|
Ishihara S, Horiguchi A, Miyakawa S, Endo
I, Miyazaki M and Takada T: Biliary tract cancer registry in Japan
from 2008 to 2013. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 23:149–157. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wakai T, Shirai Y, Sakata J, Maruyama T,
Ohashi T, Korira PV, Ajioka Y and Hatakeyama K: Clinicopathological
features of benign biliary strictures masquerading as biliary
malignancy. Am Surg. 78:1388–1391. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Burnett AS, Calvert TJ and Chokshi RJ:
Sensitivity of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
standard cytology: 10-y review of the literature. J Surg Res.
184:304–311. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Navaneethan U, Njei B, Lourdusamy V,
Konjeti R, Vargo JJ and Parsi MA: Comparative effectiveness of
biliary brush cytology and intraductal biopsy for detection of
malignant biliary strictures: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 81:168–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yonezawa S, Higashi M, Yamada N, Yokoyama
S and Goto M: Significance of mucin expression in pancreatobiliary
neoplasms. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 17:108–124. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moschovis D, Bamias G and Delladetsima I:
Mucins in neoplasms of pancreas, ampulla of Vater and biliary
system. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 8:725–734. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Inagaki Y, Xu H, Nakata M, Seyama Y,
Hasegawa K, Sugawara Y, Tang W and Kokudo N: Clinicopathology of
sialomucin: MUC1, particularly KL-6 mucin, in gastrointestinal,
hepatic and pancreatic cancers. Biosci Trends. 3:220–232.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tang W, Inagaki Y, Kokudo N, Guo Q, Seyama
Y, Nakata M, Imamura H, Sano K, Sugawara Y and Makuuchi M: KL-6
mucin expression in carcinoma of the ampulla of Vater: Association
with cancer progression. World J Gastroenterol. 11:5450–5454. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu HL, Inagaki Y, Seyama Y, Sugawara Y,
Kokudo N, Nakata M, Wang FS and Tang W: Expression of KL-6 mucin, a
human MUC1 mucin, in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and its
potential involvement in tumor cell adhesion and invasion. Life
Sci. 85:395–400. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tang W, Guo Q, Qu X, Inagaki Y, Seyama Y,
Midorikawa Y, Gai R, Kokudo N, Sugawara Y, Nakata M and Makuuchi M:
KL-6 mucin is a useful immunohistochemical marker for
cholangiocarcinoma. Oncol Rep. 17:737–741. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu H, Inagaki Y, Tang W, Guo Q, Wang F,
Seyama Y, Midorikawa Y, Gai R, Kokudo N, Sugawara Y, et al:
Elevation of serum KL-6 mucin levels in patients with
cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatogastroenterology. 55:2000–2004.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Matsumoto K, Takeda Y, Harada K, Onoyama
T, Kawata S, Horie Y, Sakamoto T, Ueki M, Miura N and Murawaki Y:
Clinical impact of the KL-6 concentration of pancreatic juice for
diagnosing pancreatic masses. Biomed Res Int. 2015:5283042015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cotton PB, Garrow DA, Gallagher J and
Romagnuolo J: Risk factors for complications after ERCP: A
multivariate analysis of 11,497 procedures over 12 years.
Gastrointest Endosc. 70:80–88. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G,
Niro G, Valvano MR, Spirito F, Pilotto A and Forlano R: Incidence
rates of post-ERCP complications: A systematic survey of
prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol. 102:1781–1788. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sadeghi A, Mohamadnejad M, Islami F,
Keshtkar A, Biglari M, Malekzadeh R and Eloubeidi MA: Diagnostic
yield of EUS-guided FNA for malignant biliary stricture: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc.
83:290–8.e1. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Weilert F, Bhat YM, Binmoeller KF, Kane S,
Jaffee IM, Shaw RE, Cameron R, Hashimoto Y and Shah JN: EUS-FNA is
superior to ERCP-based tissue sampling in suspected malignant
biliary obstruction: Results of a prospective, single-blind,
comparative study. Gastrointest Endosc. 80:97–104. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
De Moura DT, Moura EG, Bernardo WM, De
Moura ET, Baracat FI, Kondo A, Matuguma SE and Artifon EL:
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography versus endoscopic
ultrasound for tissue diagnosis of malignant biliary stricture:
Systematic review and meta-analysis. Endosc Ultrasound. Nov
8–2016.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
18
|
Heimbach JK, Sanchez W, Rosen CB and Gores
GJ: Trans-peritoneal fine needle aspiration biopsy of hilar
cholangiocarcinoma is associated with disease dissemination.
HPB(Oxford). 13:356–360. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bonella F, Long X, Ohshimo S, Horimasu Y,
Griese M, Guzman J, Kohno N and Costabel U: MUC1 gene polymorphisms
are associated with serum KL-6 levels and pulmonary dysfunction in
pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 11:482016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|