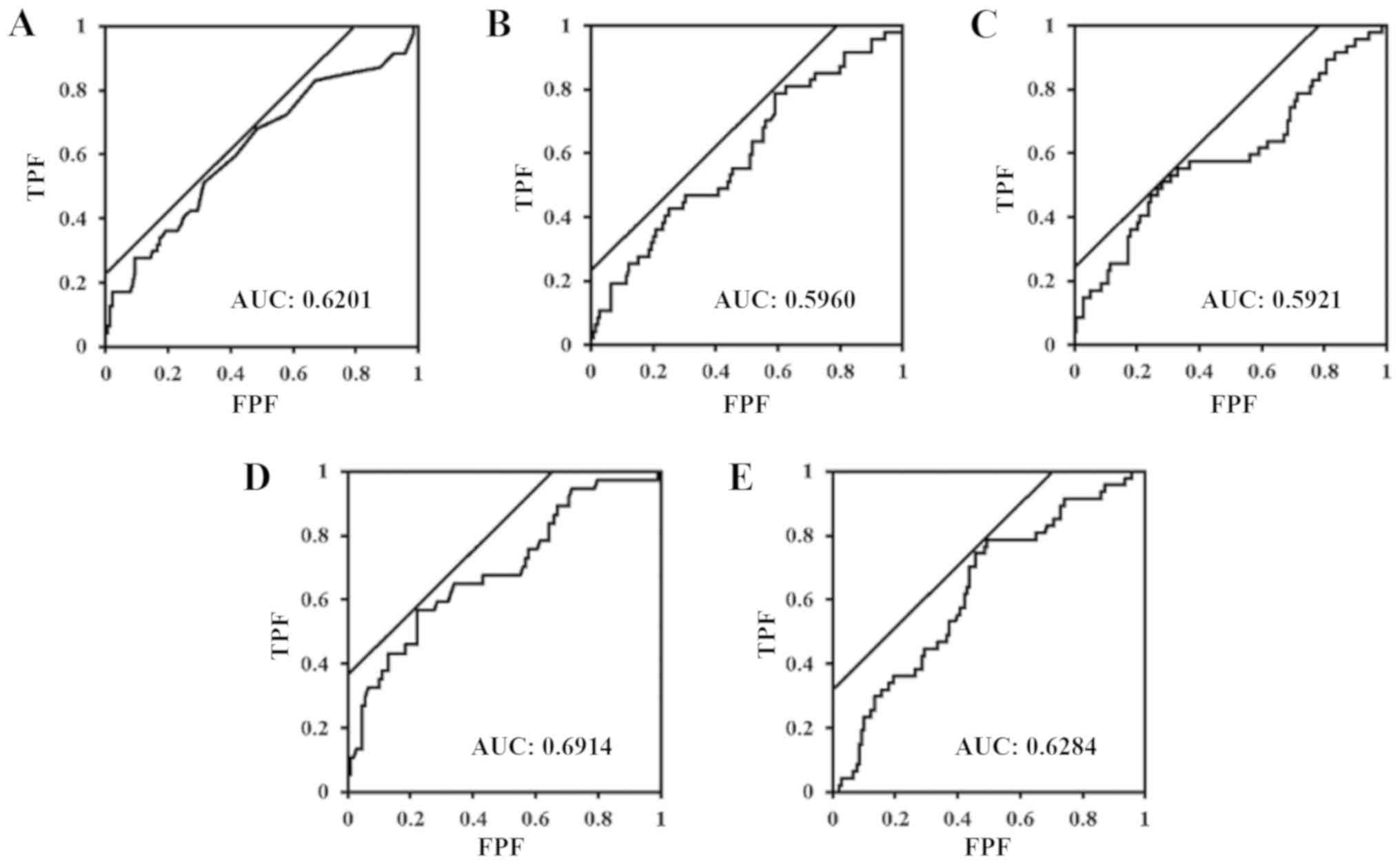
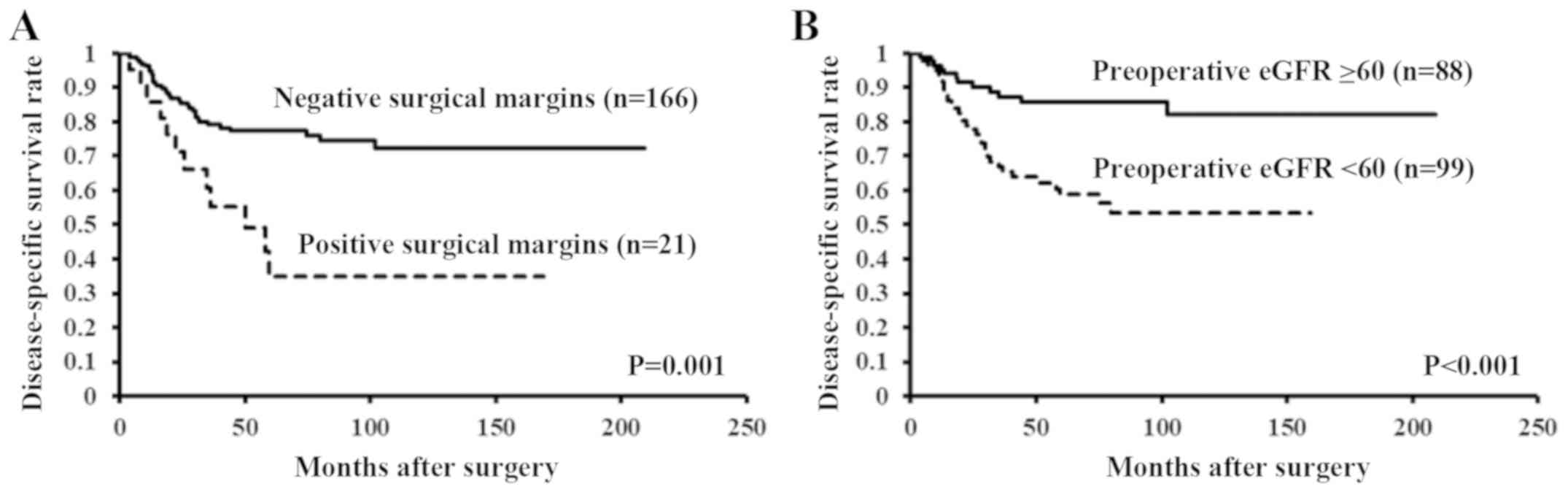
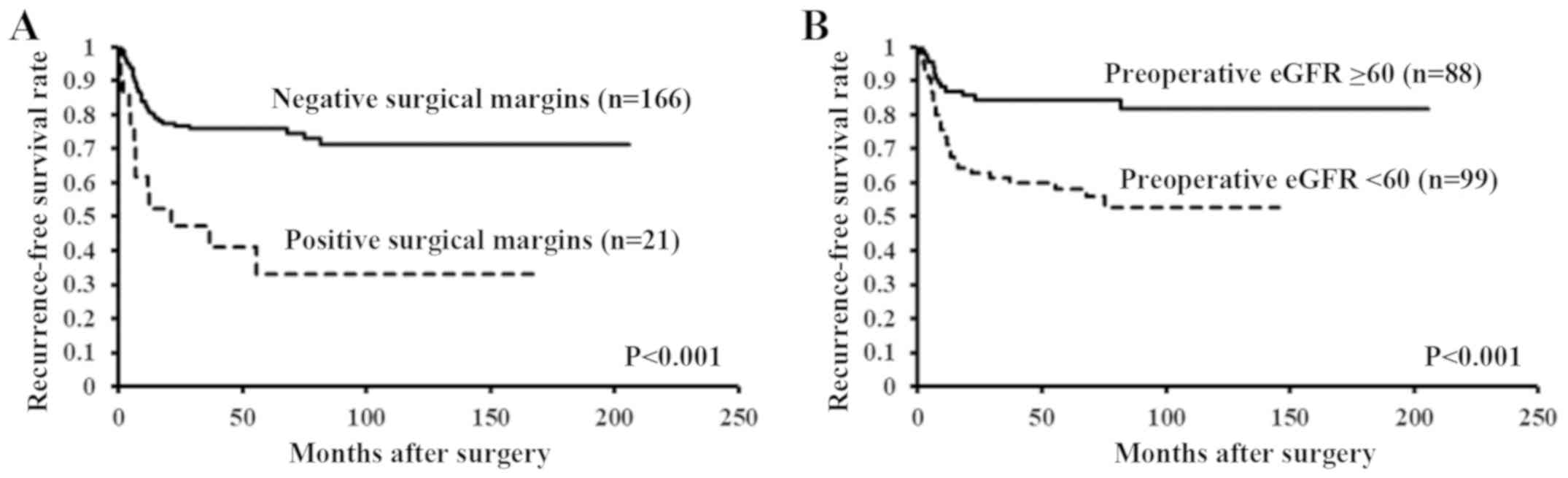
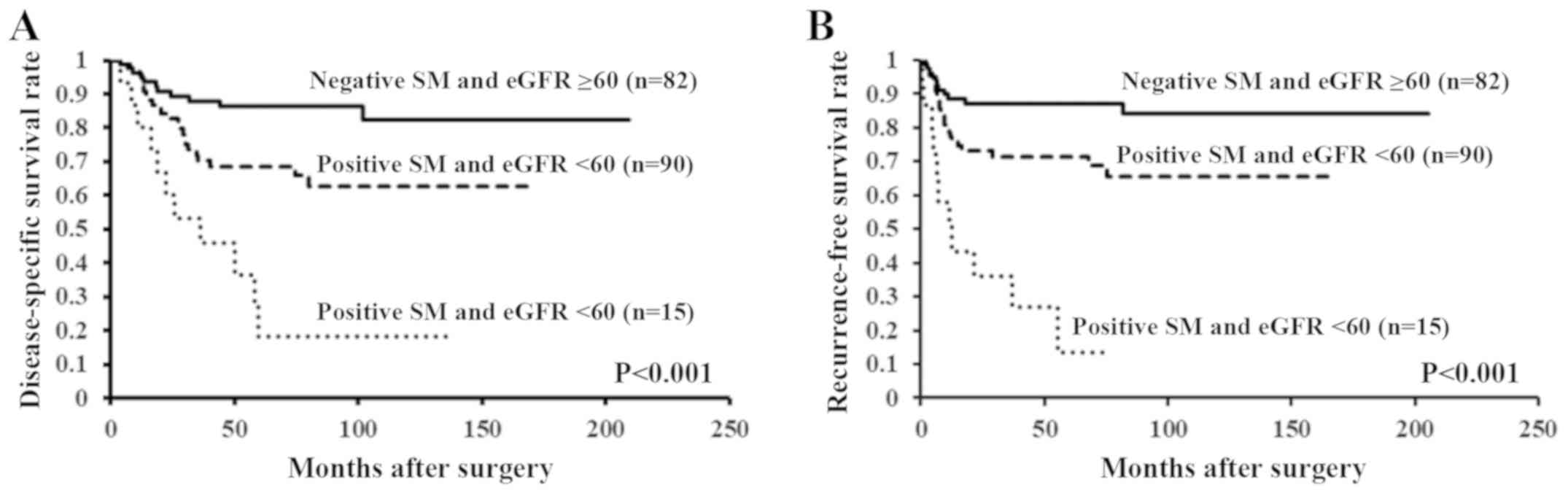
|
1
|
Babjuk M, Böhle A, Burger M, Capoun O,
Cohen D, Compérat EM, Hernández V, Kaasinen E, Palou J, Rouprêt M,
et al: EAU Guidelines on non-muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma
of the bladder: Update 2016. Eur Urol. 71:447–461. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Miller K and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Munoz JJ and Ellison LM: Upper tract
urothelial neoplasms: Incidence and survival during the last 2
decades. J Urol. 164:1523–1525. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cosentino M, Palou J, Gaya JM, Breda A,
Rodriguez-Faba O and Villavicencio-Mavrich H: Upper urinary tract
urothelial cell carcinoma: Location as a predictive factor for
concomitant bladder carcinoma. World J Urol. 31:141–145. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Seisen T, Granger B, Colin P, Léon P,
Utard G, Renard-Penna R, Compérat E, Mozer P, Cussenot O, Shariat
SF and Rouprêt M: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
clinicopathologic factors linked to intravesical recurrence after
radical nephroureterectomy to treat upper tract urothelial
carcinoma. Eur Urol. 67:1122–1133. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Novara G, De Marco V, Dalpiaz O, Galfano
A, Bouygues V, Gardiman M, Martignoni G, Patard JJ, Artibani W and
Ficarra V: Independent predictors of contralateral metachronous
upper urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma after
nephroureterectomy: Multi-institutional dataset from three European
centers. Int J Urol. 16:187–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li WM, Shen JT, Li CC, Ke HL, Wei YC, Wu
WJ, Chou YH and Huang CH: Oncologic outcomes following three
different approaches to the distal ureter and bladder cuff in
nephroureterectomy for primary upper urinary tract urothelial
carcinoma. Eur Urol. 57:963–969. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matas AJ, Simmons RL, Kjellstrand CM,
Buselmeier TJ and Najarian JS: Increased incidence of malignancy
during chronic renal failure. Lancet. 1:883–886. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cengiz K: Increased incidence of neoplasia
in chronic renal failure (20-year experience). Int Urol Nephrol.
33:121–126. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stewart JH: Cancers of the kidney and
urinary tract in patients on dialysis for end-stage renal disease:
Analysis of data from the United states, Europe, and Australia and
New Zealand. J Am Soc Nephrol. 14:197–207. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ito K, Kuroda K, Asakuma J, Hamada S,
Tasaki S, Tasaki S, Sato A, Horiguchi A, Seguchi K and Asano T:
Preoperative risk factors for extraurothelial recurrence in
patients with ureteral cancer treated with radical
nephroureterectomy. J Urol. 191:1685–1692. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuroda K, Asakuma J, Horiguchi A, Tasaki
S, Yoshii H, Sato A, Ito K, Seguchi K, Sumitomo M and Asano T:
Prognostic factors for upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma
after nephroureterectomy. Urol Int. 88:225–231. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bolenz C, Shariat SF, Fernández MI,
Margulis V, Lotan Y, Karakiewicz P, Remzi M, Kikuchi E, Zigeuner R,
Weizer A, et al: Risk stratification of patients with nodal
involvement in upper tract urothelial carcinoma: Value of
lymph-node density. BJU Int. 103:302–306. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sobin L, Gospodarowicz M and Wittekind C:
TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours. (7th). 2009.
|
|
15
|
John E, Guido S, Jonathan E and Isabell S:
Pathology and Genetics: Tumours of the Urinary System and Male
Genital System (IARC WHO Classification of Tumours). 2004.
|
|
16
|
Qu JL, Qu XJ, Li Z, Zhang JD, Liu J, Teng
YE, Jin B, Zhao MF, Yu P, Shi J, et al: Prognostic model based on
systemic inflammatory response and clinicopathological factors to
predict outcome of patients with Node-Negative gastric cancer. PLoS
One. 10:e01285402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuksel OH, Akan S, Uukmez A, Yildirim C,
Sahin A and Verit A: Preoperative glasgow prognostic score as a
predictor of primary bladder cancer recurrence. Mol Clin Oncol.
5:201–206. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Imai E, Horio M, Nitta K, Yamagata K,
Iseki K, Tsukamoto Y, Ito S, Makino H, Hishida A and Matsuo S:
Modification of the modification of diet in renal disease (MDRD)
Study equation for Japan. Am J Kidney Dis. 50:927–937. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang M, Jeong CW, Kwak C, Kim HH and Ku
JH: Preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio can significantly
predict mortality outcomes in patients with non-muscle invasive
bladder cancer undergoing transurethral resection of bladder tumor.
Oncotarget. 8:12891–12901. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Uemura K, Kawahara T, Yamashita D, Jikuya
R, Abe K, Tatenuma T, Yokomizo Y, Izumi K, Teranishi JI, Makiyama
K, et al: Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts prognosis in
castration-resistant prostate cancer patients who received
cabazitaxel chemotherapy. Biomed Res Int. 2017:75386472017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gunes A, Yigit M, Tok L and Tok O:
Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in patients with nonarteritic
anterior Ischemic optic neuropathy. Korean J Ophthalmol.
31:159–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kasuga J, Kawahara T, Takamoto D, Fukui S,
Tokita T, Tadenuma T, Narahara M, Fusayasu S, Terao H, Izumi K, et
al: Increased neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with
disease-specific mortality in patients with penile cancer. BMC
Cancer. 16:3962016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li CE, Chien CS, Chuang YC, HP T and CH K:
Chronic kidney disease as an important risk factor for tumor
recurrences, progression and overall survival in primary
non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Int Urol Nephrol. 48:993–999.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kim YW, Kim WT, Yun SJ, Lee SC, Kim WJ, Ha
YS, Park YH, Kang SH, Hong SH, Kwon TG, et al: Preoperative chronic
kidney disease status is an independent prognostic factor in
patients with renal cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 22:4098–4103.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tollefson MK, Boorjian SA, Gettman MT,
Rangel LJ, Bergstralh EJ and Karnes RJ: Preoperative estimated
glomerular filtration rate predicts overall mortality in patients
undergoing radical prostatectomy. Urol Oncol. 31:1483–1488. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morizane S, Yumioka T, Yamaguchi N, Masago
T, Honda M, Sejima T and Takenaka A: Risk stratification model,
including preoperative serum C-reactive protein and estimated
glomerular filtration rate levels, in patients with upper urinary
tract urothelial carcinoma undergoing radical nephroureterectomy.
Int Urol Nephrol. 47:1335–1341. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li CC, Chang TH, Wu WJ, Ke HL, Huang SP,
Tsai PC, Chang SJ, Shen JT, Chou YH and Huang CH: Significant
predictive factors for prognosis of primary upper urinary tract
cancer after radical nephroureterectomy in Taiwanese patients. Eur
Urol. 54:1127–1134. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu CF, Chang PL, Chen CS, Chuang CK, Weng
HH and Pang ST: The outcome of patients on dialysis with upper
urinary tract transitional cell carcinoma. J Urol. 176:477–481.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu HS, Hwang JE, Chung HS, Cho YH, Kim MS,
Hwang EC, Oh KJ, Kim SO, Jung SI, Kang TW, et al: Is preoperative
chronic kidney disease status associated with oncologic outcomes in
upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma? A multicenter propensity
score-matched analysis. Oncotarget. 8:66540–66549. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li WM, Li CC, Ke HL, Wu WJ, Huang CN and
Huang CH: The prognostic predictors of primary ureteral
transitional cell carcinoma after radical Nephroureterectomy. J
Urol. 182:451–458. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ou JH, Pan CC, Lin JS, Tzai TS, Yang WH,
Chang CC, Cheng HL, Lin YM and Tong YC: Transitional cell carcinoma
in dialysis patients. Eur Urol. 37:90–94. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chang CH, Yang CM and Yang AH: Renal
diagnosis of chronic hemodialysis patients with urinary tract
transitional cell carcinoma in Taiwan. Cancer. 109:1487–1492. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen KS, Lai MK, Huang CC, Chu SH and Leu
ML: Urologic cancers in uremic patients. Am J Kidney Dis.
25:694–700. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kato S, Chmielewski M, Honda H,
Pecoits-Filho R, Matsuo S, Yuzawa Y, Tranaeus A, Stenvinkel P and
Lindholm B: Aspects of immune dysfunction in end-stage renal
disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 3:1526–1533. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vamvakas S, Bahner U and Heidland A:
Cancer in end-stage renal disease: Potential factors involved. Am J
Nephrol. 18:89–95. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stopper H, Meysen T, Bockenforde A, Bahner
U, Heidland A and Vamvakas S: Increased genomic damage in
lymphocytes of patients before and after long-term maintenance
hemodialysis therapy. Am J Kidney Dis. 34:433–437. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Song X, Zhang GM, Ma XC, Luo L, Li B, Chai
DY and Sun L: Comparison of preoperative neutrophil-lymphocyte,
lymphocyte-monocyte, and platelet-lymphocyte ratios in patients
with upper urinary tract urothelial carcinoma undergoing radical
nephroureterectomy. Onco Targets Ther. 9:1399–1407. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Keller CR, Odden MC, Fried LF, Newman AB,
Angleman S, Green CA, Cummings SR, Harris TB and Shlipak MG: Kidney
function and markers of inflammation in elderly persons without
chronic kidney disease: The health, aging, and body composition
study. Kidney Int. 71:239–244. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Colin P, Ghoneim TP, Nison L, Seisen T,
Lechevallier E, Cathelineau X, Ouzzane A, Zerbib M, Long JA,
Ruffion A, et al: Risk stratification of metastatic recurrence in
invasive upper urinary tract carcinoma after radical
nephroureterectomy without lymphadenectomy. World J Urol.
32:507–512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Allard CB, Alamri A, Dason S, Farrokhyar
F, Matsumoto ED and Kapoor A: The method of bladder cuff excision
during laparoscopic radical nephroureterectomy does not affect
oncologic outcomes in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. World J
Urol. 31:175–181. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|