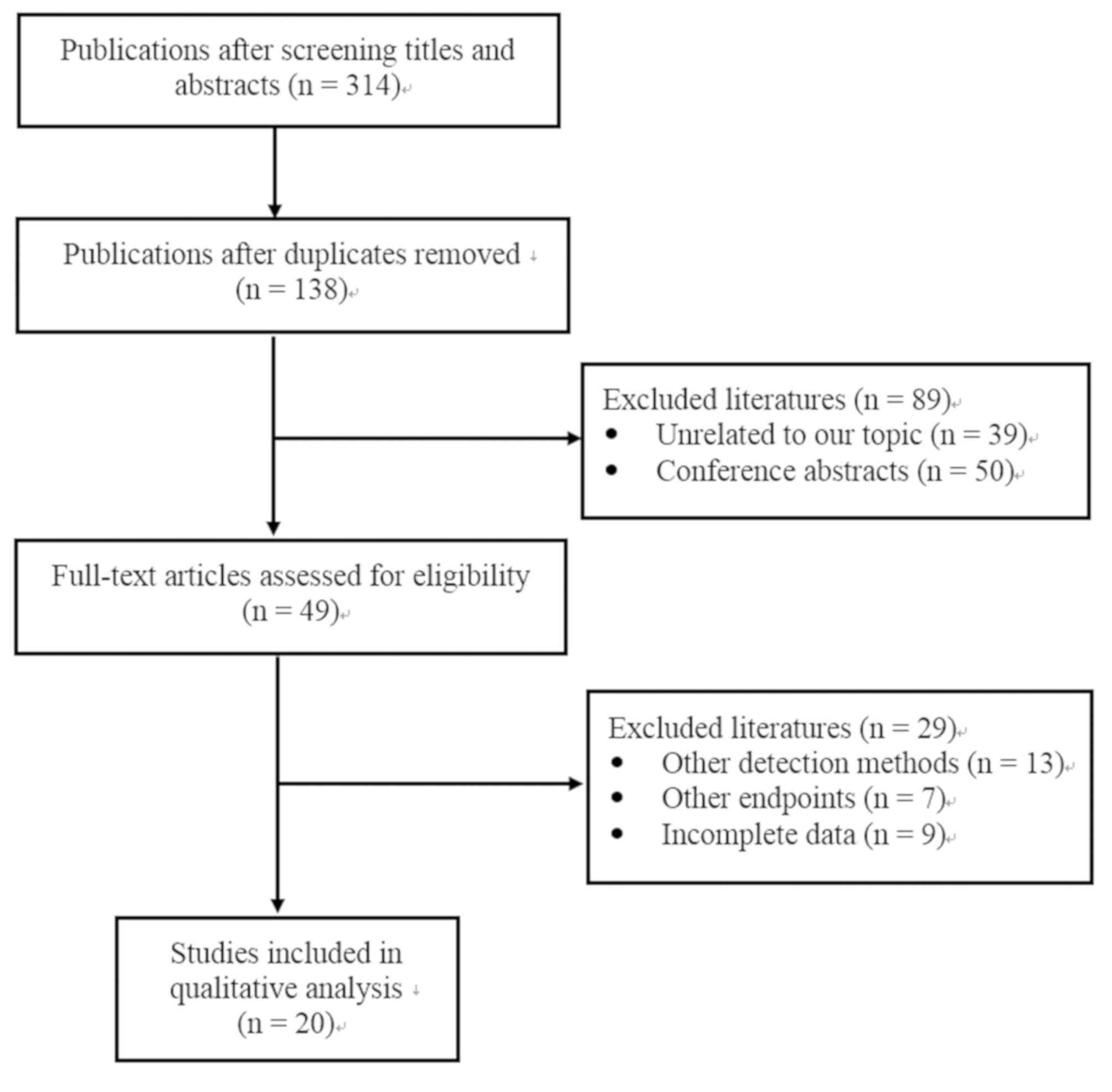
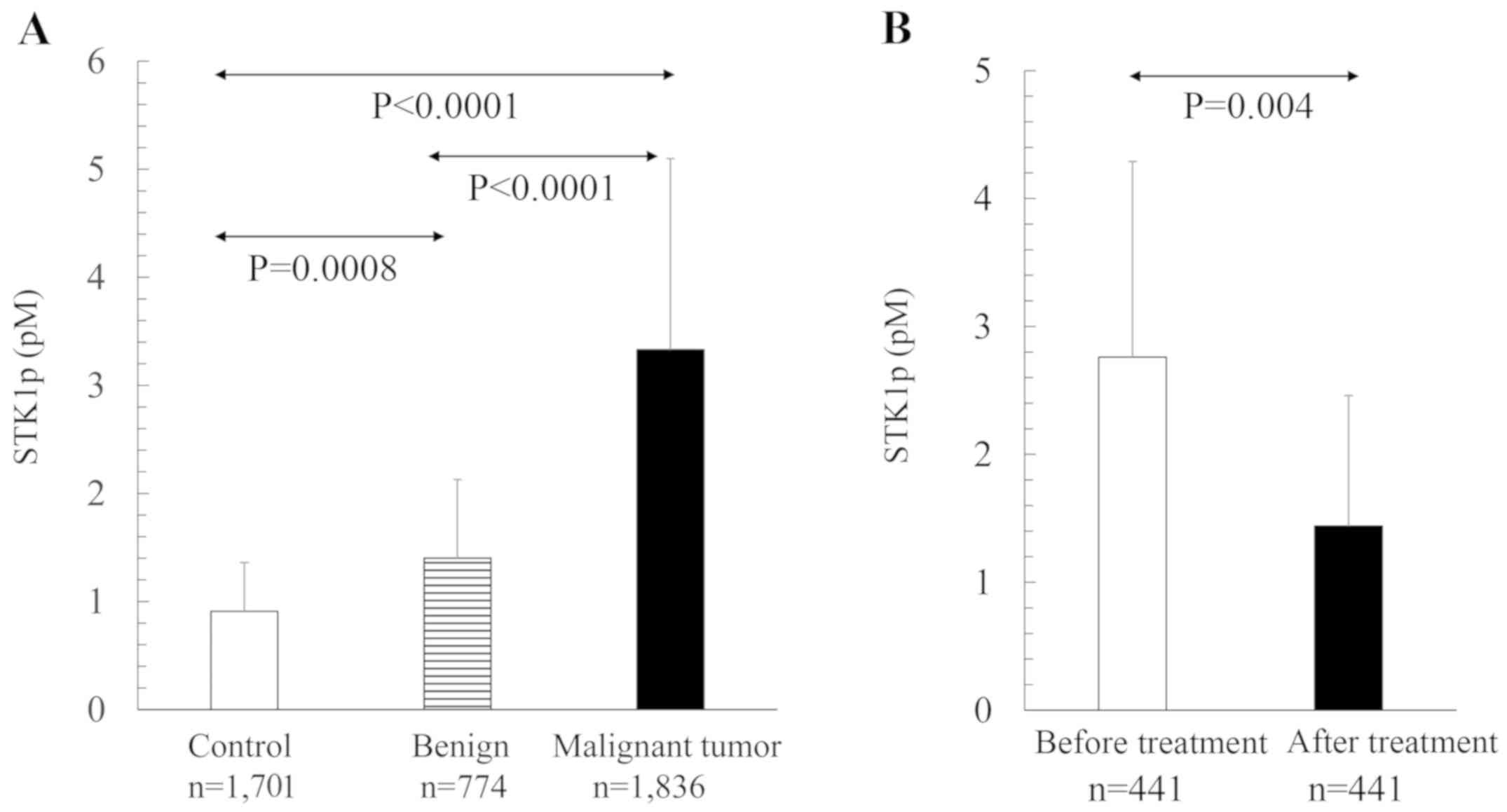
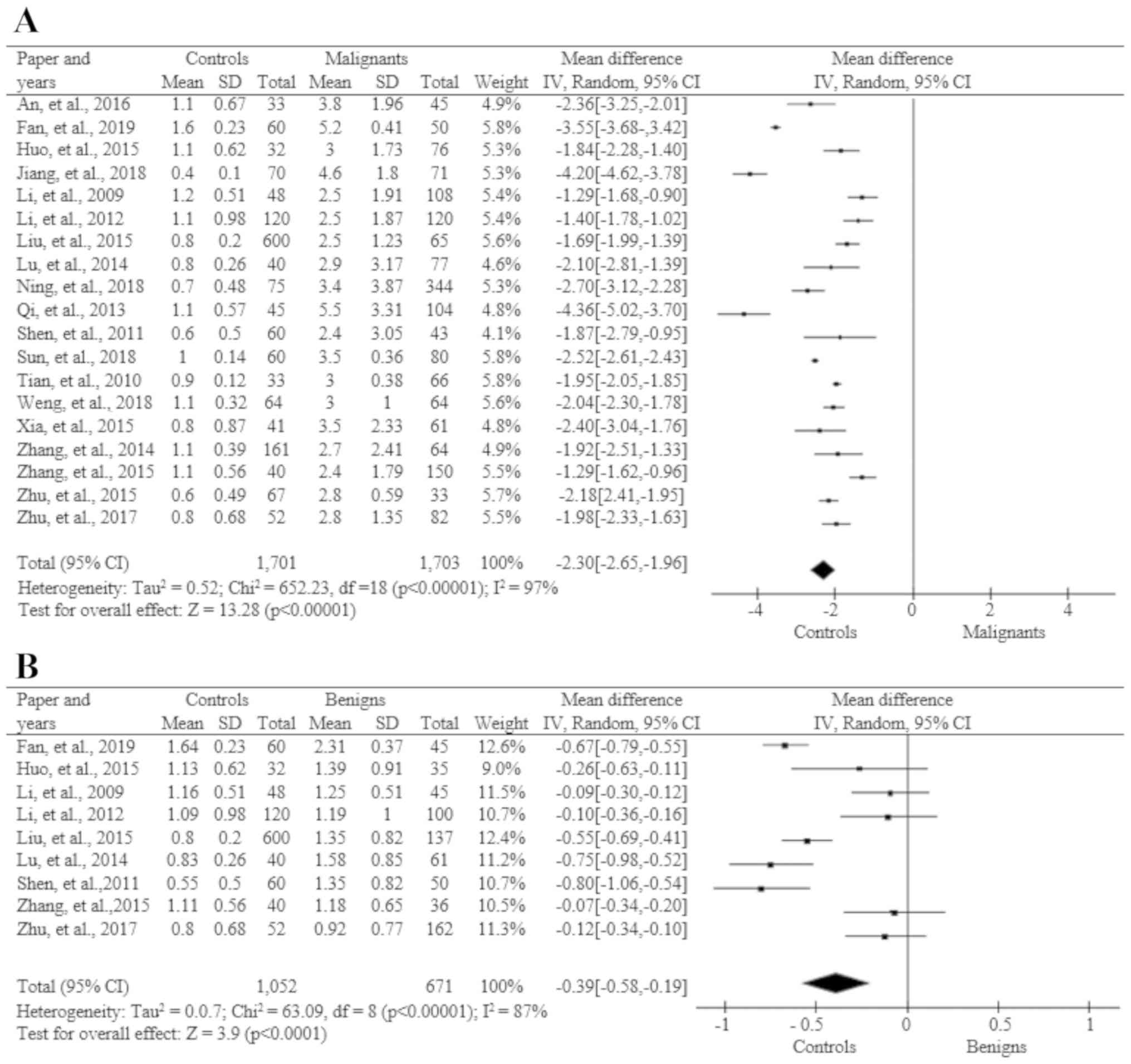
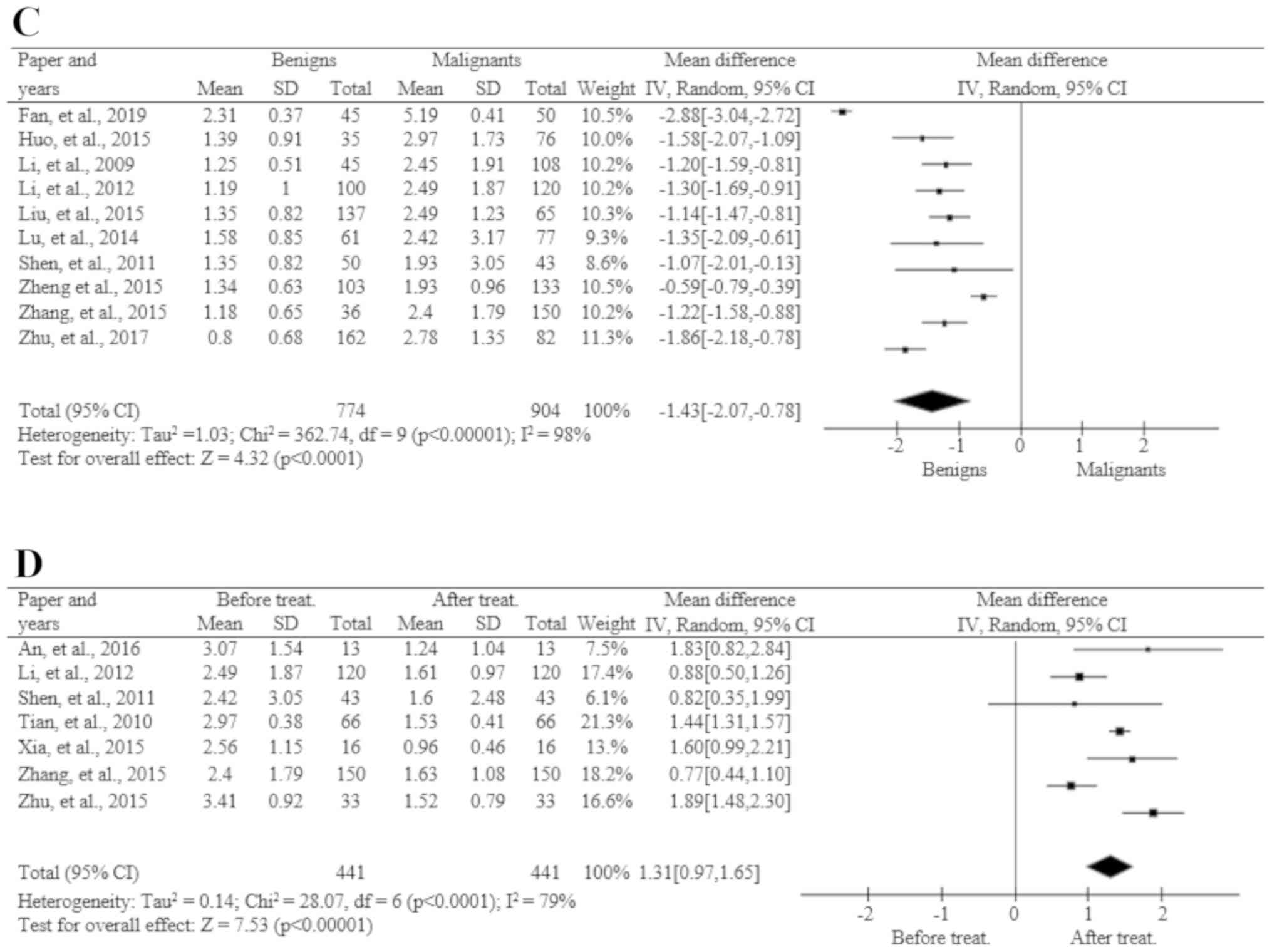
|
1
|
Boyle P and Levin B: World Cancer Report
2008. International Agency for Research on Cancer; Distributed by
WHO Press, c2008, International Agency for Research on Cancer.
France, Publisher: Lyon: Geneva, 2008.
|
|
2
|
Stewart BW and Wild CP: World Cancer
Report 2014. International Agency for Research on Cancer; World
Health Organization. France, Publisher Lyon, 2014.
|
|
3
|
Stewart BW, Bray F, Forman D, Ohgaki H,
Straif K, Ullrich A and Wild CP: Cancer prevention as part of
precision medicine: ‘Plenty to be done’. Carcinogenesis. 37:2–9.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Huxley RR, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Clifton P,
Czernichow S, Parr CL and Woodward M: The impact of dietary and
lifestyle risk factors on risk of colorectal cancer: A quantitative
overview of the epidemiological evidence. Int J Cancer.
125:171–180. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, Zhang S, Zeng
H, Bray F, Jemal A, Yu XQ and He J: Cancer statistics in China,
2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:115–132. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jasperson KW, Tuohy TM, Neklason DW and
Burt RW: Hereditary and familial colon cancer. Gastroenterology.
138:2044–2058. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cappellani A, Zanghì A, D Vita M,
Cavallaro A, Piccolo G, Veroux P, Lo Menzo E, Cavallaro V, de Paoli
P, Veroux M and Berretta M: Strong correlation between diet and
development of colorectal cancer. Front Biosci. 18:190–198.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Abu-Remaileh M, Bender S, Raddatz G,
Ansari I, Cohen D, Gutekunst J, Musch T, Linhart H, Breiling A,
Pikarsky E, et al: Chronic inflammation induces a novel epigenetic
program that is conserved in intestinal adenomas and in colorectal
cancer. Cancer Res. 75:2120–2130. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shussman N and Wexner SD: Colorectal
polyps and polyposis syndromes. Gastroenterol Rep. 2:1–15.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Verdecchia A, Francisci S, Brenner H,
Gatta G, Micheli A, Mangone L and Kunkler I: EUROCARE-4 Working
Group. Recent cancer survival in Europe: A 2000-02 period analysis
of EUROCARE-4 data. Lancet Oncol. 8:784–796. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ciccolallo L, Capocaccia R, Coleman MP,
Berrino F, Coebergh JW, Damhuis RA, Faivre J, Martinez-Garcia C,
Møller H, Ponz de Leon M, et al: Survival differences between
European and US patients with colorectal cancer: Role of stage at
diagnosis and surgery. Gut. 54:268–273. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fearon ER and Vogelstein B: A genetic
model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 61:759–767.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Binefa G, Rodríguez-Moranta F, Teule A and
Medina-Hayas M: Colorectal cancer: From prevention to personalized
medicine. World J Gastroenterol. 20:6786–6808. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ribero D, Viganò L, Amisano M and
Capussotti L: Prognostic factors after resection of colorectal
liver metastases: From morphology to biology. Future Oncol.
9:45–57. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gasparri F, Wang N, Skog S, Galvani A and
Eriksson S: Thymidine kinase 1 expression defines an activated G1
state of the cell cycle as revealed with site-specific antibodies
and arrayscan assays. Eur J Cell Biol. 88:779–785. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhou J, He E and Skog S: The proliferation
marker thymidine kinase 1 in clinical use. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:18–28.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cao X, Zhou J and Chen Z: Standardized
centile curves and reference intervals of serum thymidine kinase 1
levels in a normal Chinese population using the LMS method. Genet
Test Mol Biomarkers. 20:445–450. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen ZH, Huang SQ, Wang Y, Yang AZ, Wen J,
Xu XH, Chen Y, Chen QB, Wang YH, He E, et al: Serological thymidine
kinase 1 is a biomarker for early detection of tumours-a health
screening study on 35,365 people, using a sensitive
chemiluminescent dot blot assay. Sensors (Basel). 11:11064–11080.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
He Q, Zhang P, Zou L, Li H, Wang X, Zhou
S, Fornander T and Skog S: Concentration of thymidine kinase 1 in
serum (S-TK1) is a more sensitive proliferation marker in human
solid tumors than its activity. Oncol Rep. 14:1013–1019.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
He Q, Fornander T, Johansson H, Johansson
U, Hu GZ, Rutqvist LE and Skog S: Thymidine kinase 1 in serum
predicts increased risk of distant or loco-regional recurrence
following surgery in patients with early breast cancer. Anticancer
Res. 26:4753–4759. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar JK, Aronsson AC, Pilko G, Zupan M,
Kumer K, Fabjan T, Osredkar J and Eriksson S: A clinical evaluation
of the TK 210 ELISA in sera from breast cancer patients
demonstrates high sensitivity and specificity in all stages of
disease. Tumour Biol. 37:11937–11945. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu Y, Ling Y, Qi Q, Tang Y, Xu J, Tong Z,
Sheng G, Yang Q and Pan Y: Changes in serum thymidine kinase 1
levels during chemotherapy correlate with objective response in
patients with advanced gastric cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2:1177–1181.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen F, Tang L, Xia T, He E, Hu G, Zhang
M, Li Y, Zhou J, Eriksson S and Skog S: Serum thymidine kinase 1
levels predictcancer-free survival following neoadjuvant, surgical
and adjuvant treatment of patients with locally advanced breast
cancer. Mol Clin Oncol. 1:894–902. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Aufderklamm S, Hennenlotter J, Todenhoefer
T, Gakis G, Schilling D, Vogel U, Kuehs U, Dlugosch J, Knapp J,
Merseburger A, et al: XPA-210: A new proliferation marker
determines locally advanced prostate cancer and is a predictor of
biochemical recurrence. World J Urol. 30:547–552. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Jiang X, Dong S, Shen J, Yu H,
Zhou J, Li J, Ma H, He E and Skog S: Serum TK1 is a more reliable
marker than CEA and AFP for cancer screening survey in a study of
56,286 people. Cancer Biomark. 16:529–536. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lou X, Zhou J, Ma H, Xu S, He E, Skog S
and Wang H: The half-life of serum thymidine kinase 1 concentration
is an important tool for monitoring surgical response in patients
with lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers.
21:471–478. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yurish SY: Serum-biomarker thymidine
kinase 1 for early discovery of tumour process -160,086
participants using a sensitive immune-ECL-dot-blot detection
system. Advances in Sensors: Reviews. 6:529–540. 2018.http://www.sensorsportal.com.
|
|
28
|
Skog S, He E and Haghdoost S: Prevention
and early detection of human tumour. LAP lambert academic
publishing, Schaltungsdienst Lange O.H.G., Berlin. p74, p183-257.
http://www.get-morebook.com.
|
|
29
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fan XJ, Shi ZT and Sun W: Significance of
TuM2-PK, TK1, CEA, CA19-9 and CA72-4 in the diagnosis of colon
cancer patients. Chin J Gerontol. 39:51–53. 2019.
|
|
31
|
Weng YL: Diagnostic value of serum
TuM2-PK, TK1 and HER-2 expression levels in rectal cancer. Henan
Med Res. 1:1795–1797. 2018.
|
|
32
|
Jiang XL, Bo YX and Ye Y: Correlation
between TK1 and tumor markers in diagnosis and pathological
features of digestive tract tumors. J Anhui Med Univ. 53:110–114.
2018.
|
|
33
|
Sun HW, Mei M, Liu YY and Liu XZ: Clinical
value of serum thymidine kinase 1 in the evaluation of chemotherapy
for stage IV colon cancer. Continuing Medical Education. 8:81–83.
2018.
|
|
34
|
Ning S, Wei W, Li J, Hou B, Zhong J, Xie
Y, Liu H, Mo X, Chen J and Zhang L: Clinical significance and
diagnostic capacity of serum TK1, CEA, CA 19-9 and CA 72-4 levels
in gastric and colorectal cancer patients. J Cancer. 3:494–501.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu LP, Li XL, Liu H, Ping YF and Zhang
YN: Expression and clinical significance of thymidine kinase 1 in
rectal cancer. J Xiangnan Univ (Medical Sciences). 19:9–12.
2017.
|
|
36
|
An N, Zhang M, Lan HT and Li HM:
Significance of detecting serum thymidine kinase 1 in metastatic
large intestine carcinoma before and after chemotherapy. Med J West
China. 28:1257–1260. 2016.
|
|
37
|
Zhu YZ, Ma T, Zhang CJ and Sun GP: The
expression and clinical significance of serum thymidine kinase 1 in
cancer patients. Acta Univ Med Anhui. 7:1012–1015. 2015.
|
|
38
|
Zeng QH and Zhang SY: Diagnostic value of
combined detection of CEA, CA199 and TK1 for colorectal cancer. Med
Equipment. 10:2–4. 2015.
|
|
39
|
Xia Y, Liu Y, Qi Q, Zhu M, Zhang Y and
Ling Y: Value of serum thymidine kinase 1 in the chemotherapy
efficacy evaluation for patients with stage IV colon cancer. J
Basic Clin Oncol. 28:6–8. 2015.
|
|
40
|
Liu X, Feng Z, Lai Z, Jiang Y, Xu M and
Zhou X: An analysis on expression difference of serum TK1 between
patients with gastric carcinoma, lung cancer, colon cancer and
healthy person and its clinical significance. J Mathematical Med.
58:913–915. 2015.
|
|
41
|
Huo Y, Yu X and Kong AP: The application
value of TK1 in colon cancer patients. Int J Lab Med. 36:3151–3152.
2015.
|
|
42
|
Zhang Y, Wang J, Xie J, Yang D, Han G and
Zhang Y: The assay and clinical significance of serum thymidine
kinase 1 in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Eur Surg.
47:248–253. 2015.
|
|
43
|
Zhang ZJ, Zheng YP, Lin YH and Mei XQ:
Clinical detecting application of TK1 in the diagnosis of common
malignant tumors. Int J Lab Med. 35:2636–2637. 2014.
|
|
44
|
Lu ZQ, Xie YM, Cheng GH and Li JH:
Clinical diagnostic value of combined detection of serum TK1, CAl99
and CA724 in colorectal cancer. China Practical Medicine. 9:5–7.
2014.
|
|
45
|
Qi QF, Zhu M, Bao YQ and Liu YP: Detection
of serum TK1 in patients with colorectal cancer after operation to
evaluate the effect of value. World Latest Med Information.
13:60–61. 2013.
|
|
46
|
Li QF: Clinical application of serum
thymidine kinase 1 used in colorectal carcinoma patients.
Laboratory Med. 27:1080–1081. 2012.
|
|
47
|
Shen J, Chen W, Xu RH, Zhang JF and Jiang
H: Evaluation of the significance of serum thymidine kinase 1
detection in the diagnosis and curative effect of gastrointestinal
malignant tumors. Exp Lab Med. 29:531–533. 2011.
|
|
48
|
Tian J, Jia Y and Liu H: Serum TK1, EGF,
HGF and CRP and IL-6 levels in patiens with colon cancer using
laparoscopic and open surgery. Shangdong Med. 50:42–43. 2010.
|
|
49
|
Li X and Wang F: Significance of serum
thymidine kinase determination in patients with carcinoma of
rectum. Jiangsu Medical J. 35:1436–1437. 2009.
|
|
50
|
Streiner DL: I have the answer, now what's
the question?: Why meta-analyses do not provide definitive
solutions. Can J Psychiat. 50:829–831. 2005.
|
|
51
|
Chatterji M: Grades of evidence:
Variability in quality of findings in effectiveness studies of
complex field interventions. Am J Eval. 28:239–255. 2007.
|
|
52
|
Baas M, De Dreu CK and Nijstad BA: A
meta-analysis of 25 years of mood-creativity research: Hedonic
tone, activation, or regulatory focus? Psychol Bull. 134:779–806.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zou L, Zhang PG, Zou S, Li Y and He Q: The
half-life of cytosolic thymidine kinase in serum by ECL dot bolt
potential marker for monitoring the response to surgery of patients
with gastric cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 17:135–140.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Zhang J, Jia Q, Zou S, Zhang P, Zhang X,
Skog S, Luo P, Zhang W and He Q: Thymidine kinase 1: A
proliferation marker for determining prognosis and monitoring the
surgical outcome of primary bladder carcinoma patients. Oncol Rep.
15:455–461. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ogino S, Chan AT, Fuchs CS and Giovannucci
E: Molecular pathological epidemiology of colorectal neoplasia: An
emerging transdisciplinary and interdisciplinary field. Gut.
60:397–411. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Dong Y, Liu Y, Shu Y, Chen X, Hu J, Zheng
R, Ma D, Yang C and Guan X: Link between risk of colorectal cancer
and serum vitamin E levels: A meta-analysis of case-control
studies. Medicine (Baltimore). 96(e7470)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Benedix F, Kube R, Meyer F, Schmidt U,
Gastinger I and Lippert H: Colon/Rectum Carcinomas (Primary Tumor)
Study Group. Comparison of 17,641 patients with right- and
left-sided colon cancer: Differences in epidemiology, perioperative
course, histology, and survival. Dis Colon Rectum. 53:57–64.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Lichtenstein P, Holm NV, Verkasalo PK,
Iliadou A, Kaprio J, Koskenvuo M, Pukkala E, Skytthe A and Hemminki
K: Environmental and heritable factors in the causation of
cancer-analyses of cohorts of twins from Sweden, Denmark, and
Finland. N Engl J Med. 343:78–85. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hemminki K and Chen B: Familial risk for
colorectal cancers are mainly due to heritable causes. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 13:1253–1256. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Moritani K, Hasegawa H, Okabayashi K,
Ishii Y, Endo T and Kitagawa Y: Difference in the recurrence rate
between right- and left-sided colon cancer: A 17 year experience at
a single institution. Surg Today. 44:1685–1691. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Qin Q, Yang L, Sun YK, Ying JM, Song Y,
Zhang W, Wang JW and Zhou AP: Comparison of 627 patients with
right- and left-sided colon cancer in China: Differences in
clinicopathology, recurrence, and survival. Chronic Dis Transl Med.
13:51–59. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zou L, Zhang PG, Zou S, Li Y..He Q: The
half-life of cytosolic thymidine kinase in serum by ECL dot blot
potential marker for monitoring the response to surgery of patients
with gastric cancer. International Journal of Biological Markers.
17:135–140. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhang J, Jia Q, Zou S, Zhang P, Zhang X,
Skog S, Luo P, Zhang W and He Q: Thymidine kinase 1: a
proliferation marker for determining prognosis and monitoring the
surgical outcome of primary bladder carcinoma patients. Oncology
Reports. 15:455–461. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Paschke S, Jafarov S, Staib L, Kreuser ED,
Maulbecker-Armstrong C, Roitman M, Holm T, Harris CC, Link KH and
Kornmann M: Are colon and rectal cancer two different tumor
entities? A proposal to abandon the term colorectal cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 19(E2577)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|