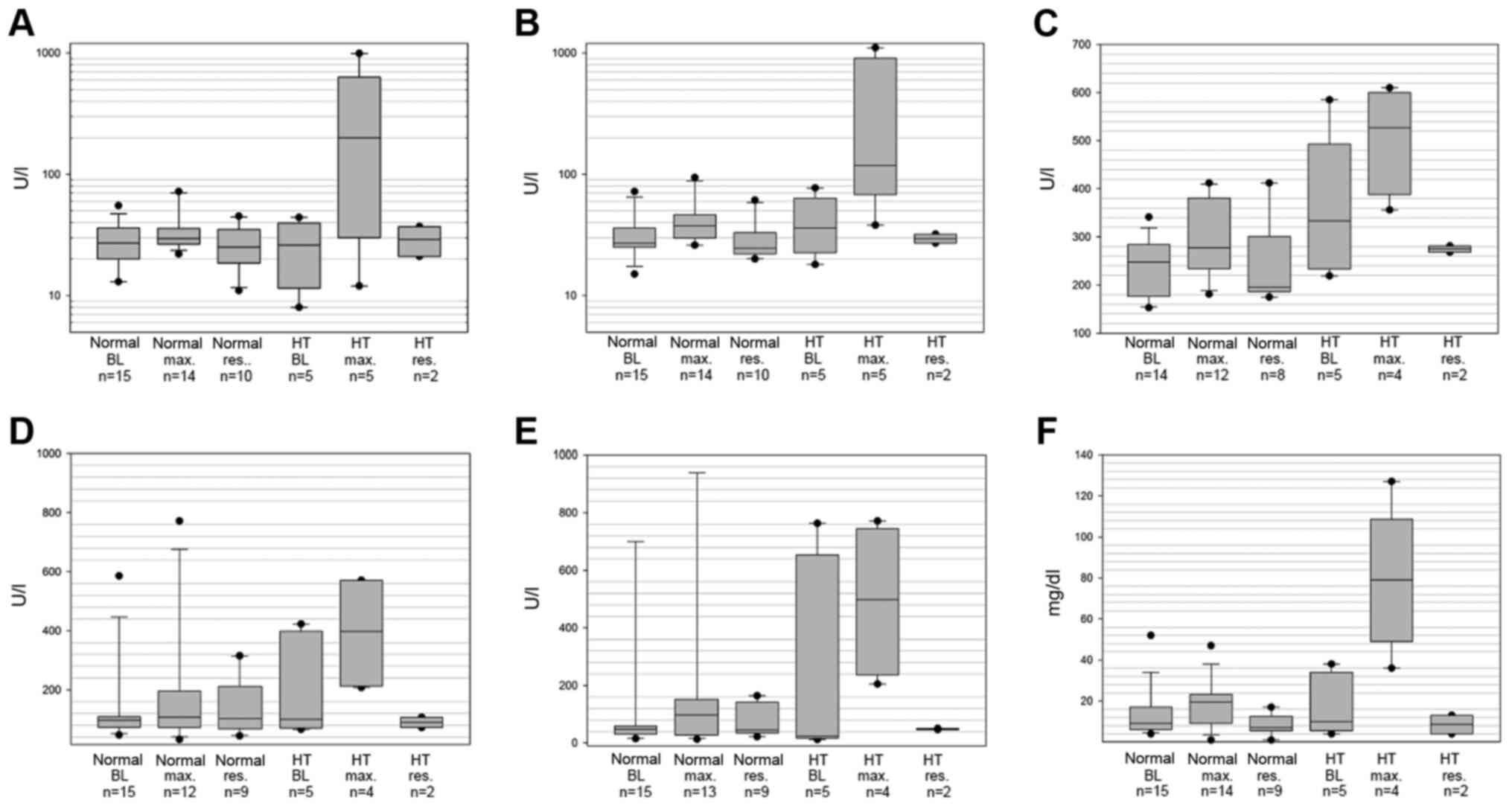
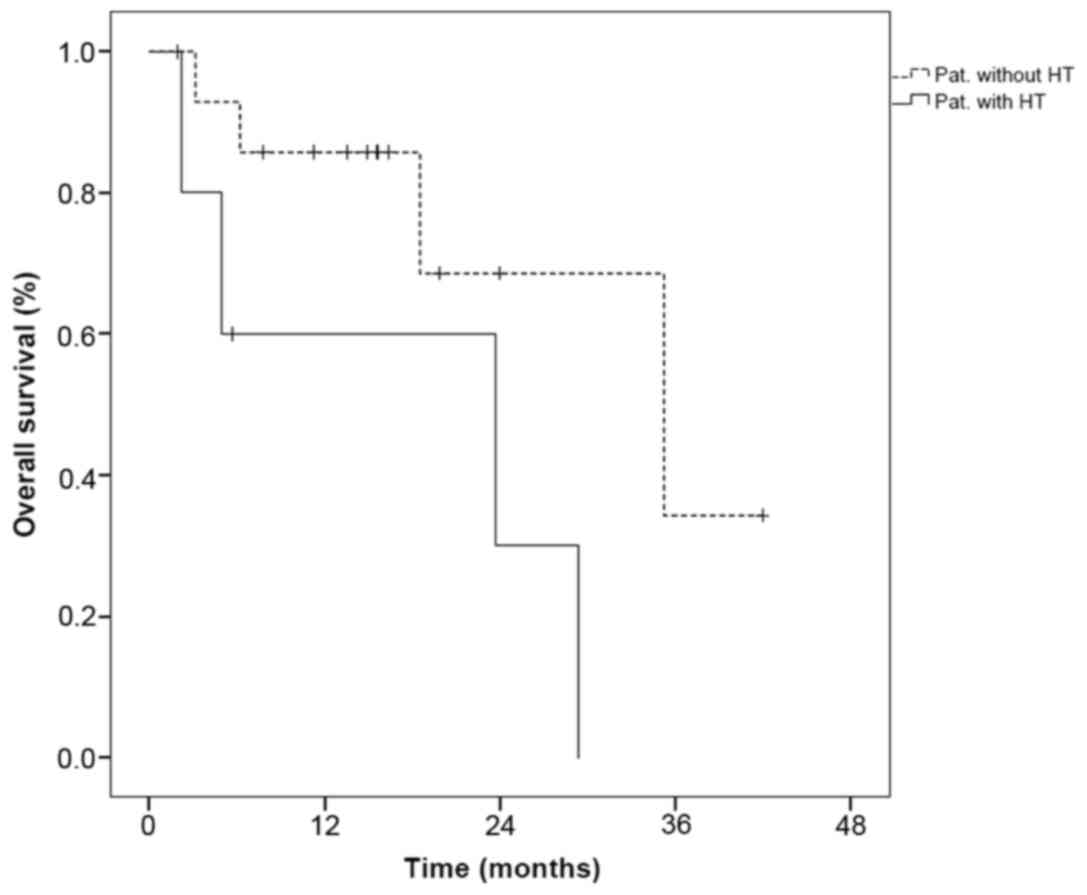
|
1
|
Wilhelm SM, Dumas J, Adnane L, Lynch M,
Carter CA, Schütz G, Thierauch KH and Zopf D: Regorafenib (BAY
73-4506): A new oral multikinase inhibitor of angiogenic, stromal
and oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinases with potent preclinical
antitumor activity. Int J Cancer. 129:245–255. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Demetri GD, Reichardt P, Kang YK, Blay JY,
Rutkowski P, Gelderblom H, Hohenberger P, Leahy M, von Mehren M,
Joensuu H, et al: Efficacy and safety of regorafenib for advanced
gastrointestinal stromal tumours after failure of imatinib and
sunitinib (GRID): An international, multicentre, randomised,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 381:295–302.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Grothey A, Van Cutsem E, Sobrero A, Siena
S, Falcone A, Ychou M, Humblet Y, Bouché O, Mineur L, Barone C, et
al: Regorafenib monotherapy for previously treated metastatic
colorectal cancer (CORRECT): An international, multicentre,
randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 381:303–312.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang
YH, Bodoky G, Pracht M, Yokosuka O, Rosmorduc O, Breder V, et al:
Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who
progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 389:56–66.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Roderburg C, Özdirik B, Wree A, Demir M
and Tacke F: Systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: From
sorafenib to combination therapies. Hepat Oncol.
7(HEP20)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J,
Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, Barrios CH, Salman P, Gladkov OA,
Kavina A, et al: Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal
cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin
Oncol. 28:1061–1068. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kudo M, Imanaka K, Chida N, Nakachi K, Tak
WY, Takayama T, Yoon JH, Hori T, Kumada H, Hayashi N, et al: Phase
III study of sorafenib after transarterial chemoembolisation in
Japanese and Korean patients with unresectable hepatocellular
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 47:2117–2127. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik C, Pili
R, Bjarnason GA, et al: Overall survival and updated results for
sunitinib compared with interferon alfa in patients with metastatic
renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 27:3584–3590. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Iacovelli R, Palazzo A, Procopio G,
Santoni M, Trenta P, De Benedetto A, Mezi S and Cortesi E:
Incidence and relative risk of hepatic toxicity in patients treated
with anti-angiogenic tyrosine kinase inhibitors for malignancy. Br
J Clin Pharmacol. 77:929–938. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
World Medical Association. World medical
association declaration of helsinki: Ethical principles for medical
research involving human subjects. JAMA. 310:2191–2194.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Cancer Therapy Evaluation Programm D NCI,
NIH, DHHS: Common terminology criteria for adverse events v4.0
(CTCAE), 2009.
|
|
12
|
Komatsu Y, Doi T, Sawaki A, Kanda T,
Yamada Y, Kuss I, Demetri GD and Nishida T: Regorafenib for
advanced gastrointestinal stromal tumors following imatinib and
sunitinib treatment: A subgroup analysis evaluating Japanese
patients in the phase III GRID trial. Int J Clin Oncol. 20:905–912.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kollàr A, Maruzzo M, Messiou C, Cartwright
E, Miah A, Martin-Liberal J, Thway K, McGrath E, Dunlop A, Khabra
K, et al: Regorafenib treatment for advanced, refractory
gastrointestinal stromal tumor: A report of the UK managed access
program. Clin Sarcoma Res. 4(17)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chamberlain F, Farag S, Williams-Sharkey
C, Collingwood C, Chen L, Mansukhani S, Engelmann B, Al-Muderis O,
Chauhan D, Thway K, et al: Toxicity management of regorafenib in
patients with gastro-intestinal stromal tumour (GIST) in a tertiary
cancer centre. Clin Sarcoma Res. 10(1)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Schvartsman G, Wagner MJ, Amini B, Zobniw
CM, Trinh VA, Barbo AG, Lin HY, Wang WL, Conley AP, Ravi V, et al:
Treatment patterns, efficacy and toxicity of regorafenib in
gastrointestinal stromal tumour patients. Sci Rep.
7(9519)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Xu CF, Reck BH, Xue Z, Huang L, Baker KL,
Chen M, Chen EP, Ellens HE, Mooser VE, Cardon LR, et al:
Pazopanib-induced hyperbilirubinemia is associated with Gilbert's
syndrome UGT1A1 polymorphism. Br J Cancer. 102:1371–1377.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|