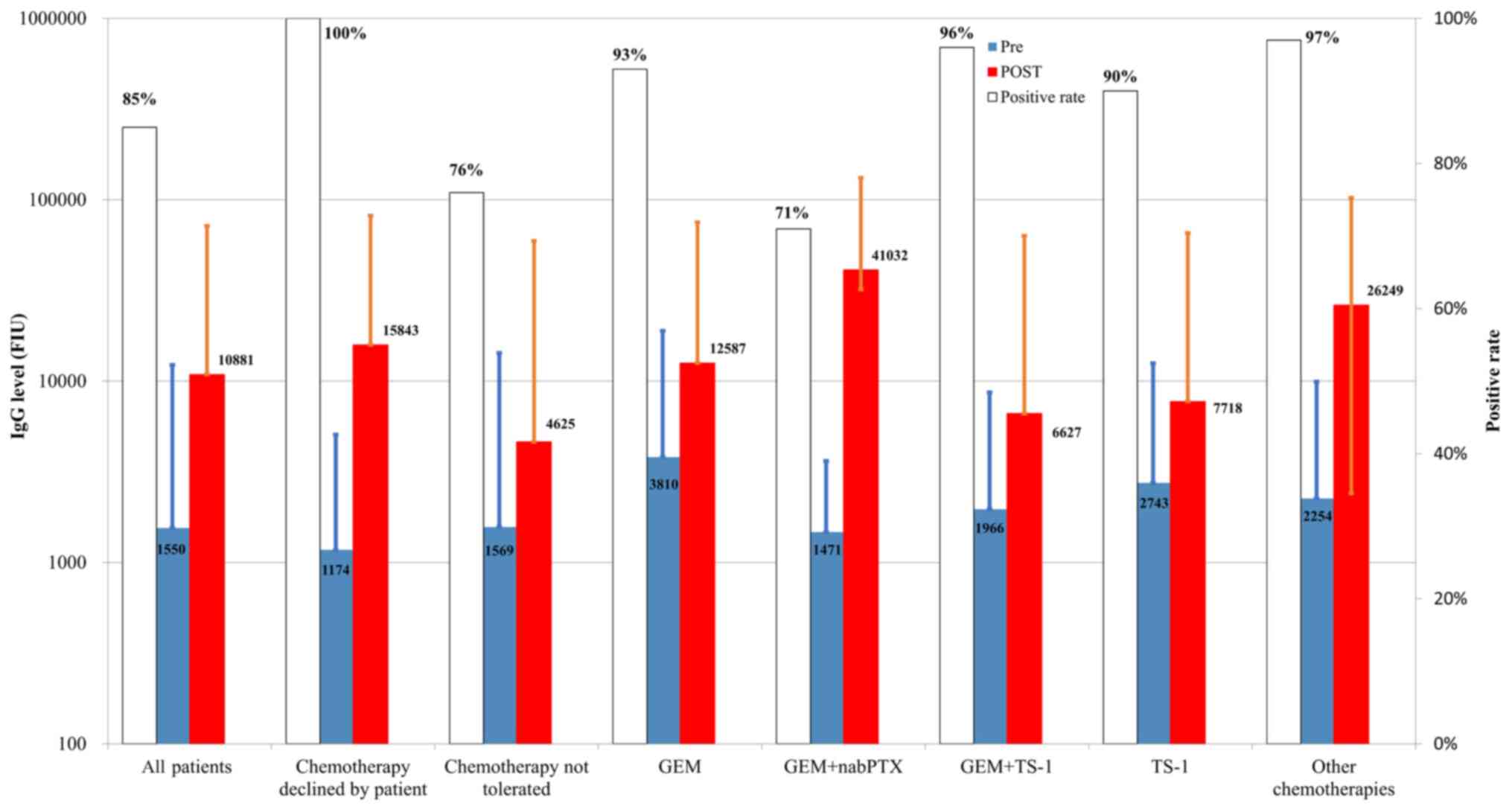
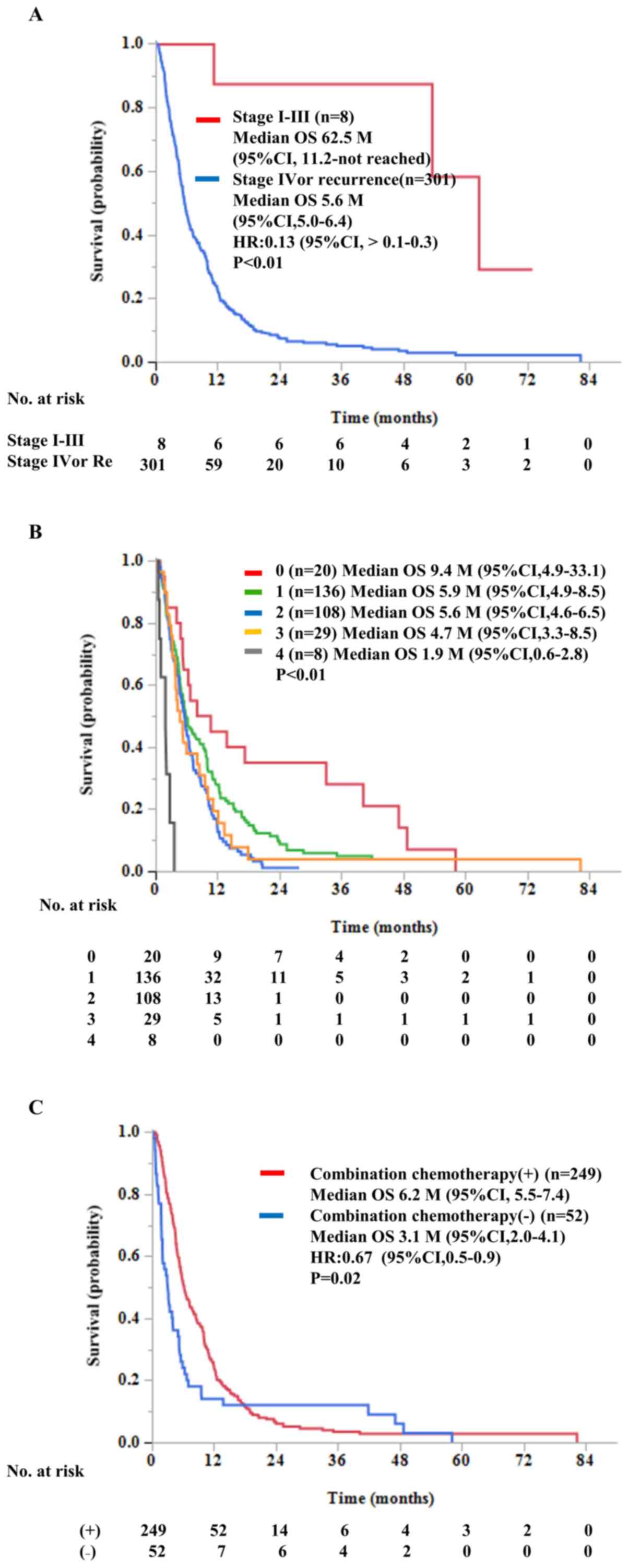
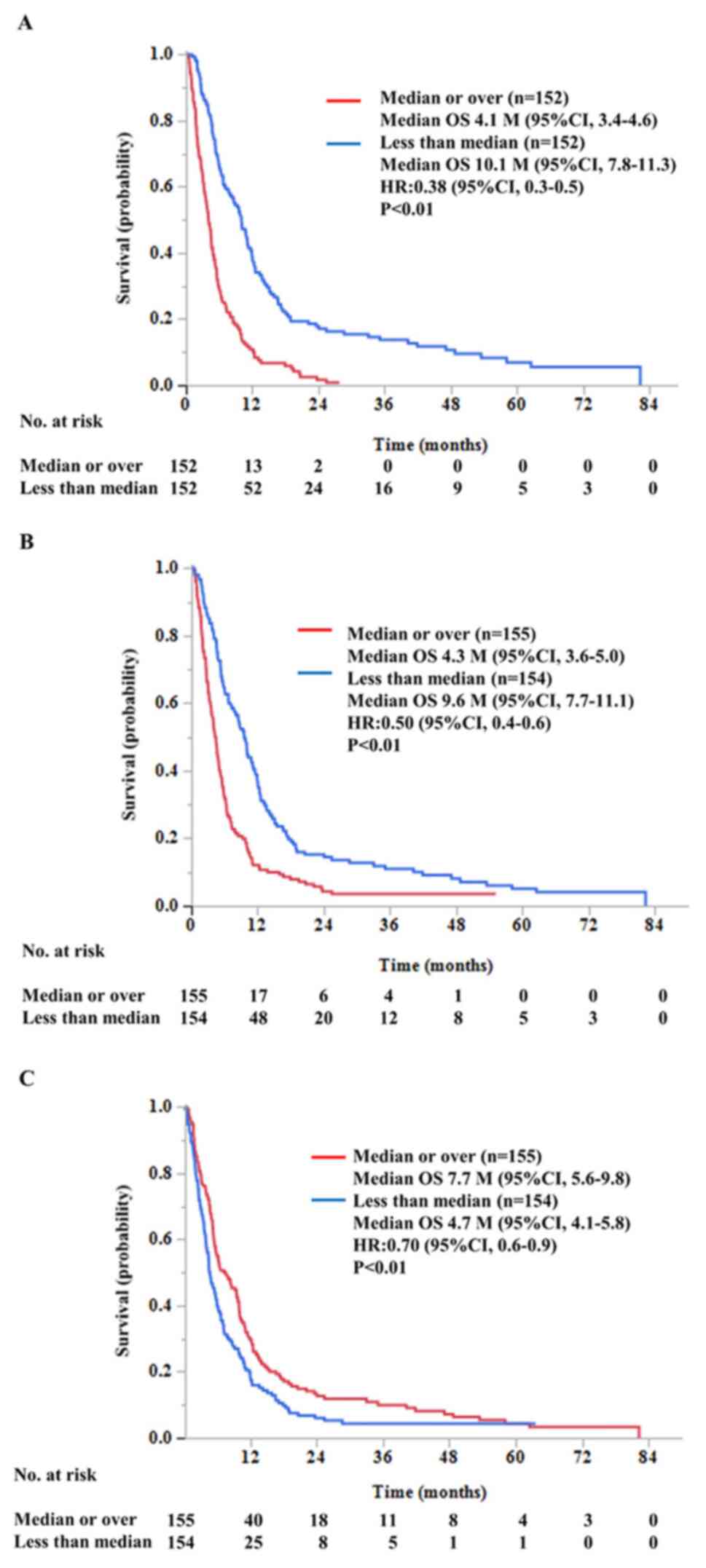
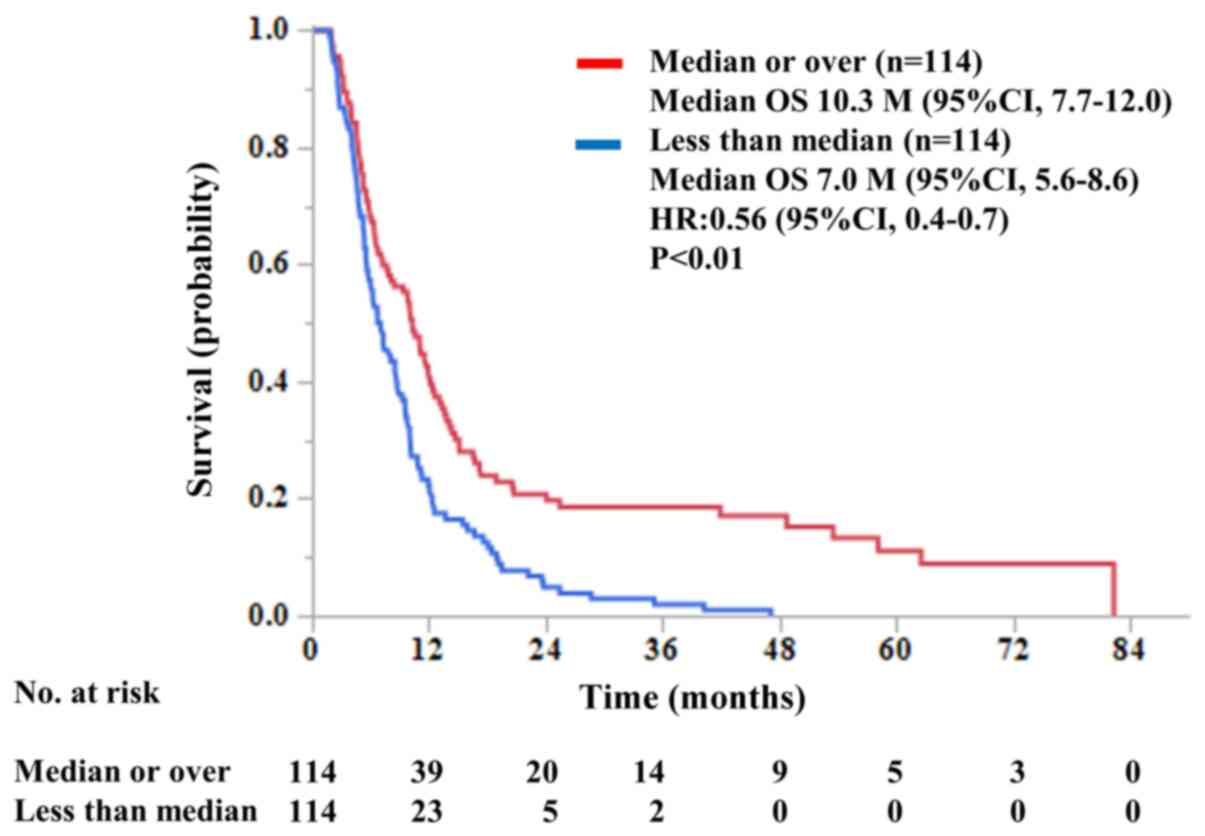
|
1
|
Kleeff J, Korc M, Apte M, La vecchia C,
Jhonson CD, Biankin AV, Neale RE, Tempero M, Tuveson DA, Hruban RH
and Neoptolemos JP: Pancreatic cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
2(16022)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hingorani SR, Zheng L, Bullock AJ, Seery
TE, Harris WP, Sigal DS, Braiteh F, Ritch PS, Zalupski MM, Bahary
N, Oberstein PE, et al: Randomized Phase II Study of PEGPH20 plus
nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine versus nab-paclitaxel/gemcitabine in
patients with untreated, metastatic pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 36:359–366. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 67:7–30. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Johansson H, Andersson R, Bauden M, Hammes
S, Holdenrieder S and Ansari D: Immune checkpoint therapy for
pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 22:9457–9476.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Morrison AH, Byrne KT and Vonderheide RH:
Immunotherapy and prevention of pancreatic cancers. Trends Cancers.
4:418–428. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bezu J, Kepp O, Cerrato G, Pol J, Fucikova
J, Spisek R, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Trial watch:
Peptide-based cancer vaccines in anticancer therapy.
Oncoimmunology. 7(e1511506)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yamaue H, Tsunoda T, Tani M, Miyazawa M,
Yamao K, Mizuno N, Okusaka T, Ueno H, Boku N, Fukutomi A, et al:
Randomized phase II/III clinical trial of elpamotide for patients
with advanced pancreatic cancer: PEGASUS-PC study. Cancer Sci.
106:883–890. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sasada T, Yamada A, Noguchi M and Itoh K:
Personalized peptide vaccine for treatment of advanced cancer. Curr
Med Chem. 21:2332–2345. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Noguchi M, Sasada T and Itoh K:
Personalized peptide vaccination: A new approach for advanced
cancer as therapeutic cancer vaccine. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
62:919–929. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yoshimura K, Minami T, Nozawa M, Kimura T,
Egawa S, Fujimoto H, Yamada A, Itoh K and Uemura H: A Phase 2
randomized controlled trial of personalized peptide vaccine
immunotherapy with low-dose dexamethasone versus dexamethasone
alone in chemotherapy-naive castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Eur Urol. 70:35–41. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Noguchi M, Matsumoto K, Uemura H, Arai G,
Eto M, Naito S, Ohyama C, Nasu Y, Tanaka M, Moriya F, et al: An
open-label, randomized phase ii trial of personalized peptide
vaccination in patients with bladder cancer that progressed after
platinum-based chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 22:54–60.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Narita Y, Arakawa Y, Yamasaki F, Nishikawa
R, Aoki T, Kanamori M, Nagane M, Kumabe T, Hirose Y, Ichikawa T, et
al: A randomized, double-blind, phase III trial of personalized
peptide vaccination for recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol.
21:348–359. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yanagimoto H, Mine T, Yamamoto K, Satoi S,
Terakawa N, Takahashi K, Nakamura K, Honma S, Tanaka M, Mizoguchi
J, et al: Immunological evaluation of personalized peptide
vaccination with gemcitabine for pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci.
98:605–611. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yanagimoto H, Shiomi H, Satoi S, Mine T,
Toyokawa H, Yamamoto T, Tani T, Yamada A, Kwon A, Komatsu N, et al:
A phase II study of personalized peptide vaccination combined with
gemcitabine for non-resectable pancreatic cancer patients. Oncol
Rep. 24:795–801. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yutani S, Komatsu N, Yoshitomi M, Matsueda
S, Yonemoto K, Mine T, Noguchi M, Ishihara M, Yamada A, Itoh K and
Sasada T: A phase II study of a personalized peptide vaccination
for chemotherapy-resistant advanced pancreatic cancer patients.
Oncol Rep. 30:1094–1100. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yutani S, Komatsu N, Matsueda S, Yoshitomi
M, Shirahama T, Yamada A, Itoh K and Sasada T: Juzentaihoto failed
to augment antigen-specific immunity but prevented deterioration of
patients' conditions in advanced pancreatic cancer under
personalized peptide vaccine. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2013(981717)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sato Y, Fujiwara T, Mine T, Shomura H,
Homma S, Maeda Y, Tokunaga N, Ikeda Y, Ishihara Y, Yamada A, et al:
Immunological evaluation of personalized peptide vaccination in
combination with a 5-fluorouracil derivative (TS-1) for advanced
gastric or colorectal carcinoma patients. Cancer Sci. 98:1113–1119.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Takahashi R, Toh U, Iwakuma N, Takenaka M,
Otsuka H, Furukawa M, Fujii T, Seki N, Kawahara A, Kage M, et al:
Feasibility study of personalized peptide vaccination for
metastatic recurrent triple-negative breast cancer patients. Breast
Cancer Rese. 16(R70)2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kawano K, Tsuda N, Matsueda S, Sasada T,
Watanabe N, Ushijima K, Yamaguchi T, Yokomine M, Itoh K, Yamada A
and Kamura T: Feasibility study of personalized peptide vaccination
for recurrent ovarian cancer patients. Immunopharmacol
Immunotoxicol. 36:224–236. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kibe S, Yutani S, Motoyama S, Nomura T,
Tanaka N, Kawahara A, Yamaguchi T, Matsueda S, Komatsu N, Miura M,
et al: phase ii study of personalized peptide vaccination for
previously treated advanced colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Res.
2:1154–1162. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Takayama K, Sugawara S, Saijo Y, Maemondo
M, Sato A, Takamori S, Harada T, Sasada T, Kakuma T, Kishimoto J,
et al: Randomized phase II study of docetaxel plus personalized
peptide vaccination versus docetaxel plus placebo for patients with
previously treated advanced wild type EGFR non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Immunol Res. 2116(1745108)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Vansteenkiste JF, Cho BC, Vanakesa T, De
Pas T, Zielinski M, Kim MS, Jassem J, Yoshimura M, Dahabreh J,
Nakayama H, et al: Effect of the MAGE3-cancer immunotherapeutic as
adjuvant therapy in patients with MAGE-A3-positive non-small-cell
lung cancer (MAGRIT): A randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 17:822–835.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Satoi S, Yamamoto T, Motoi F, Matsumoto I,
Yoshitomi H, Amano R, Tahara M, Murakami Y, Arimitsu H, Hirono S,
et al: Clinical impact of developing better practices at the
institutional level on surgical outcomes after distal
pancreatectomy in 1515 patients: Domestic audit of the Japanese
Society of Pancreatic Surgery. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 2:212–219.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hajatdoost L, Sedaghat K, Walker EJ,
Thomas J and Kosari S: Chemotherapy in pancreatic cancer: A
systematic review. Medicina (Kaunas). 54(48)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Neoptolemos JP, Kleeff J, Michl P,
Costello E, Greenhalf W and Palmer DH: Therapeutic developments in
pancreatic cancer: Current and future perspectives. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepato. 15:333–348. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|