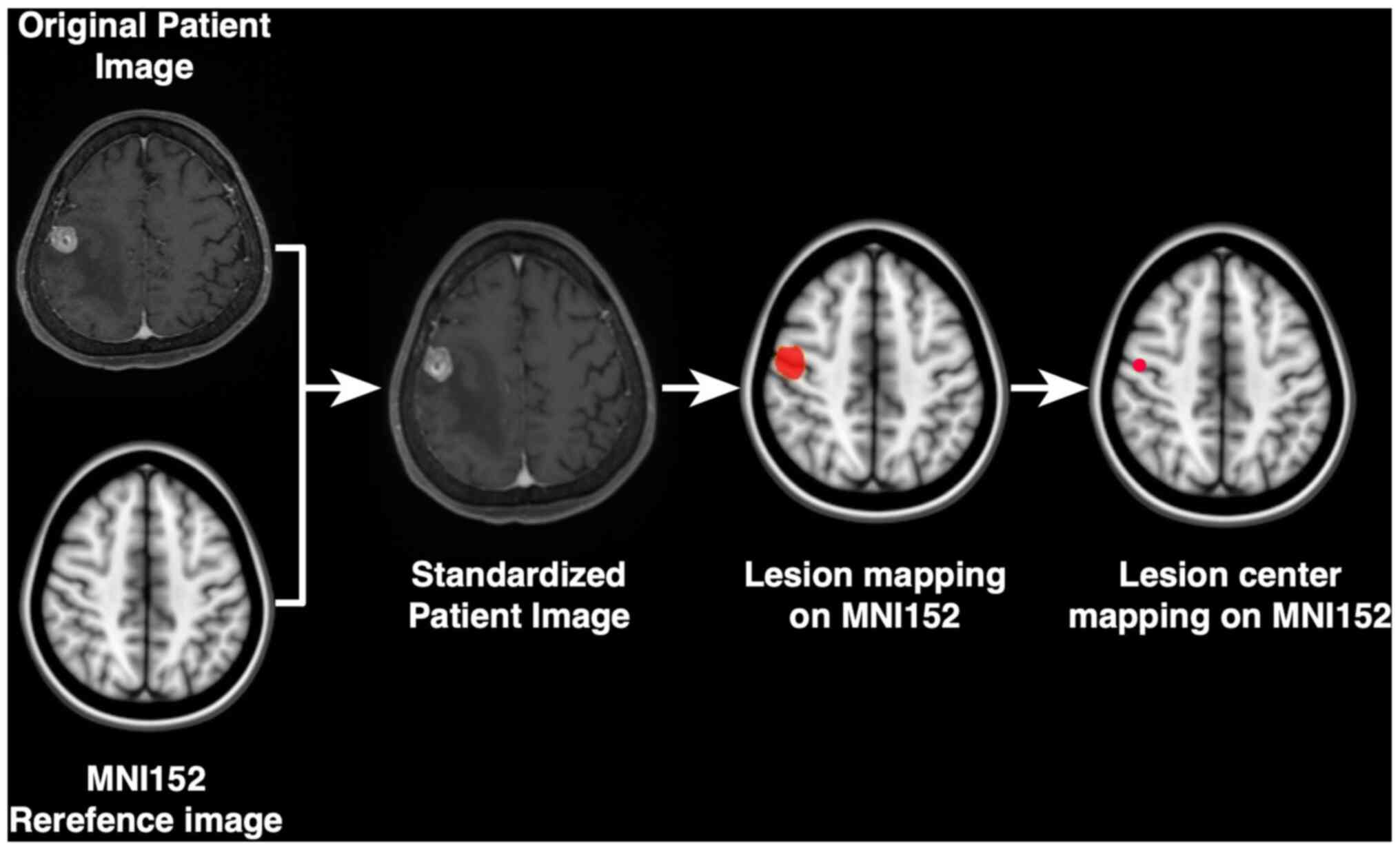
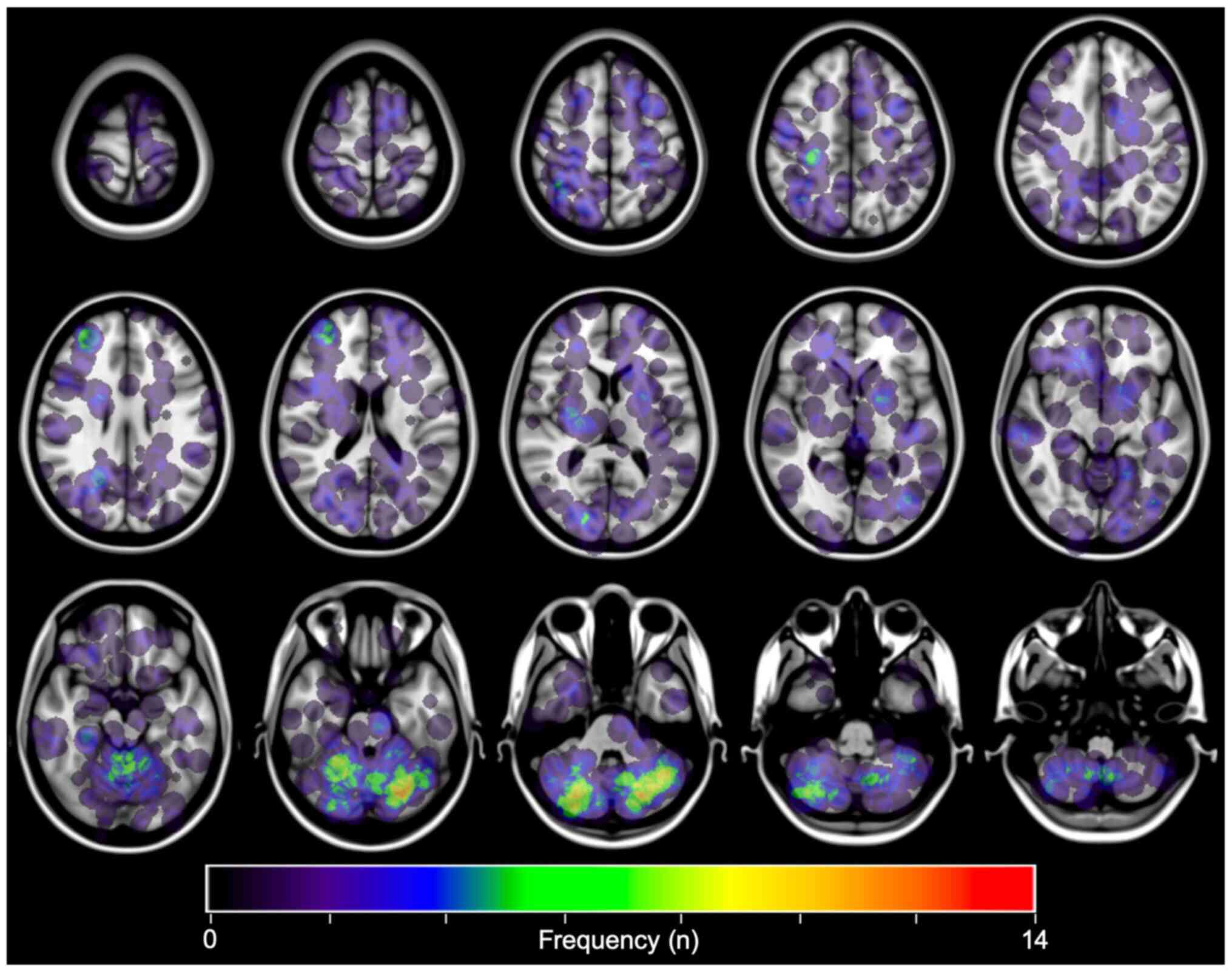
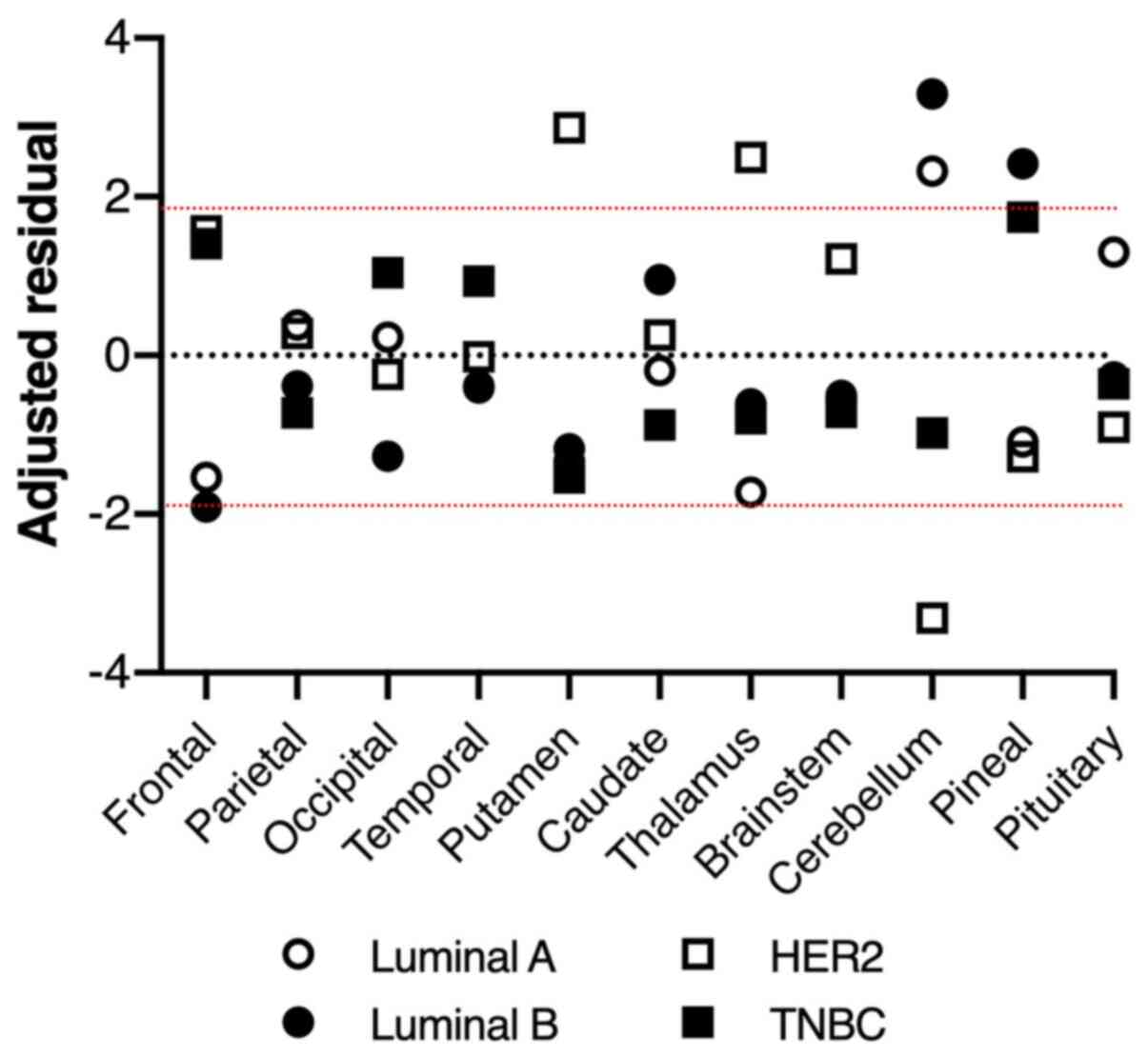
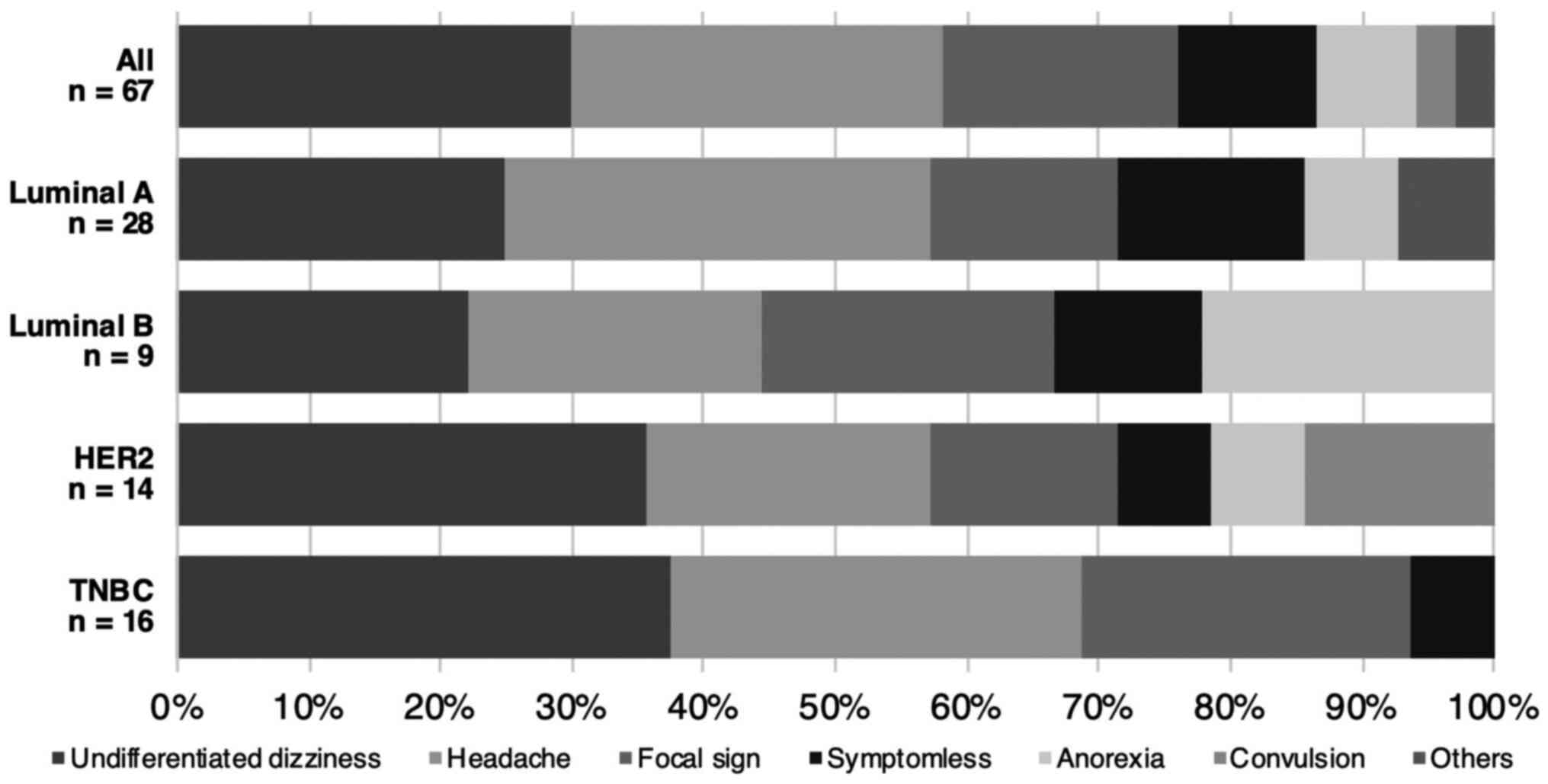
|
1
|
Maher EA, Mietz J, Arteaga CL, DePinho RA
and Mohla S: Brain metastasis: Opportunities in basic and
translational research. Cancer Res. 69:6015–6020. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Darlix A, Louvel G, Fraisse J, Jacot W,
Brain E, Debled M, Mouret-Reynier MA, Goncalves A, Dalenc F,
Delaloge S, et al: Impact of breast cancer molecular subtypes on
the incidence, kinetics and prognosis of central nervous system
metastases in a large multicentre real-life cohort. Br J Cancer.
121:991–1000. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kim YJ, Kim JS and Kim IA: Molecular
subtype predicts incidence and prognosis of brain metastasis from
breast cancer in SEER database. J Cancer Res Clin. 144:1803–1816.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Nagao E, Yoshiura T, Hiwatashi A, Obara M,
Yamashita K, Kamano H, Takayama Y, Kobayashi K and Honda H: 3D
turbo spin-echo sequence with motion-sensitized driven-equilibrium
preparation for detection of brain metastases on 3T MR imaging.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 32:664–670. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Lin NU and Winer EP: Brain metastases: The
HER2 paradigm. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1648–1655. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chason JL, Walker FB and Landers JW:
Metastatic carcinoma in the central nervous system and dorsal root
ganglia. A prospective autopsy study. Cancer. 16:781–787.
1963.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Delattre JY, Krol G, Thaler HT and Posner
JB: Distribution of brain metastases. Arch Neurol. 45:741–744.
1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Takano K, Kinoshita M, Takagaki M, Sakai
M, Tateishi S, Achiha T, Hirayama R, Nishio K, Uchida J, Kumagai T,
et al: Different spatial distributions of brain metastases from
lung cancer by histological subtype and mutation status of
epidermal growth factor receptor. Neuro Oncol. 18:716–724.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Meyer PC and Reah TG: Secondary Neoplasms
of the central nervous system and meninges. Br J Cancer. 7:438–448.
1953.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ellingson BM, Cloughesy TF, Pope WB, Zaw
TM, Phillips H, Lalezari S, Nghiemphu PL, Ibranim H, Naeini KM,
Harris RJ and Lai A: Anatomic localization of O6-methylguanine DNA
methyltransferase (MGMT) promoter methylated and unmethylated
tumors: A radiographic study in 358 de novo human glioblastomas.
Neuroimage. 59:908–916. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kinoshita M, Sasayama T, Narita Y,
Yamashita F, Kawaguchi A, Chiba Y, Kagawa N, Tanaka K, Kohmura E,
Arita H, et al: Different spatial distribution between germinal
center B and non-germinal center B primary central nervous system
lymphoma revealed by magnetic resonance group analysis. Neuro
Oncol. 16:728–734. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mazziotta J, Toga A, Evans A, Fow P,
Lancaster J, Zilles K, Woods R, Paus T, Simpson G, Pike B, et al: A
probabilistic atlas and reference system for the human brain:
International Consortium for Brain Mapping (ICBM). Philos Trans R
Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 356:1293–1322. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bender ET and Tomé WA: Distribution of
brain metastases: Implications for non-uniform dose prescriptions.
Br J Radiol. 84:649–658. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Quattrocchi CC, Errante Y, Gaudino C,
Mallio CA, Giona A, Santini D, Tonini G and Zobel BB: Spatial brain
distribution of intra-axial metastatic lesions in breast and lung
cancer patients. J Neurooncol. 110:79–87. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Blows FM, Driver KE, Schmidt MK, Broeks A,
van Leeuwen FE, Wesseling J, Cheang MC, Gelmon K, Nielsen TO,
Blomqvist C, et al: Subtyping of breast cancer by
immunohistochemistry to investigate a relationship between subtype
and short and long term survival: A collaborative analysis of data
for 10,159 cases from 12 studies. PLoS Med.
7(e1000279)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Weigelt B, Baehner FL and Reis-Filho JS:
The contribution of gene expression profiling to breast cancer
classification, prognostication and prediction: A retrospective of
the last decade. J Pathol. 220:263–280. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gabos Z, Sinha R, Hanson J, Chauhan N,
Hugh J, Mackey JR and Abdulkarim B: Prognostic significance of
human epidermal growth factor receptor positivity for the
development of brain metastasis after newly diagnosed breast
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:5658–5663. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nam BH, Kim SY, Han HS, Kwon Y, Lee KS,
Kim TH and Ro J: Breast cancer subtypes and survival in patients
with brain metastases. Breast Cancer Res. 10(R20)2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tham YL, Sexton K, Kramer R, Hilsenbeck S
and Elledge R: Primary breast cancer phenotypes associated with
propensity for central nervous system metastases. Cancer.
107:696–704. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pakneshan S, Safarpour D, Tavassoli F and
Jabbari B: Brain metastasis from ovarian cancer: A systematic
review. J Neurooncol. 119:1–6. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kyeong S, Cha YJ, Ahn SG, Suh SH, Son EJ
and Ahn SJ: Subtypes of breast cancer show different spatial
distributions of brain metastases. PLoS One.
12(e0188542)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B,
Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B and
Joliot M: Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using
a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject
brain. Neuroimage. 15:273–289. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Guo Y, Arciero CA, Jiang R, Behera M, Peng
L and Li X: Different breast cancer subtypes show different
metastatic patterns: A study from a large public database. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 21:3587–3593. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Schroeder T, Bittrich P, Kuhne JF, Noebel
C, Leischner H, Fiehler J, Schroeder J, Schoen G and Gellißen S:
Mapping distribution of brain metastases: Does the primary tumor
matter? J Neurooncol. 147:229–235. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Paget S: The distribution of secondary
growths in cancer of the breast 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
8:98–101. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Morgan AJ, Giannoudis A and Palmieri C:
The genomic landscape of breast cancer brain metastases: A
systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 22:e7–e17. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Smid M, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Sieuwerts AM, Yu
J, Klijn JG, Foekens JA and Martens JW: Subtypes of breast cancer
show preferential site of relapse. Cancer Res. 68:3108–3114.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Komorowski AS, Warner E, MacKay HJ, Sahgal
A, Pritchard KI and Jerzak KJ: Incidence of brain metastases in
non-metastatic and metastatic breast cancer: Is there a role for
screening? Clin Breast Cancer. 20:e54–e64. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gil-Gil MJ, Martinez-Garcia M, Sierra A,
Conesa G, Del Barco S, González-Jimenez S and Villà S: Breast
cancer brain metastases: A review of the literature and a current
multidisciplinary management guideline. Clin Transl Oncol.
16:436–446. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Takahashi H and Isogawa M: Management of
breast cancer brain metastases. Chin Clin Oncol.
7(30)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gandhi AK, Sharma DN and Rath GK:
Prophylactic cranial irradiation in breast cancer: A new way
forward. Indian J Medical Paediatr Oncol. 36:77–78. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Hashem T, Eldin KK, Metwaly H and Elkholy
E: Prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) in high-risk breast
cancer patients: Preliminary data. J Clin Oncol. 26(11501)2008.
|