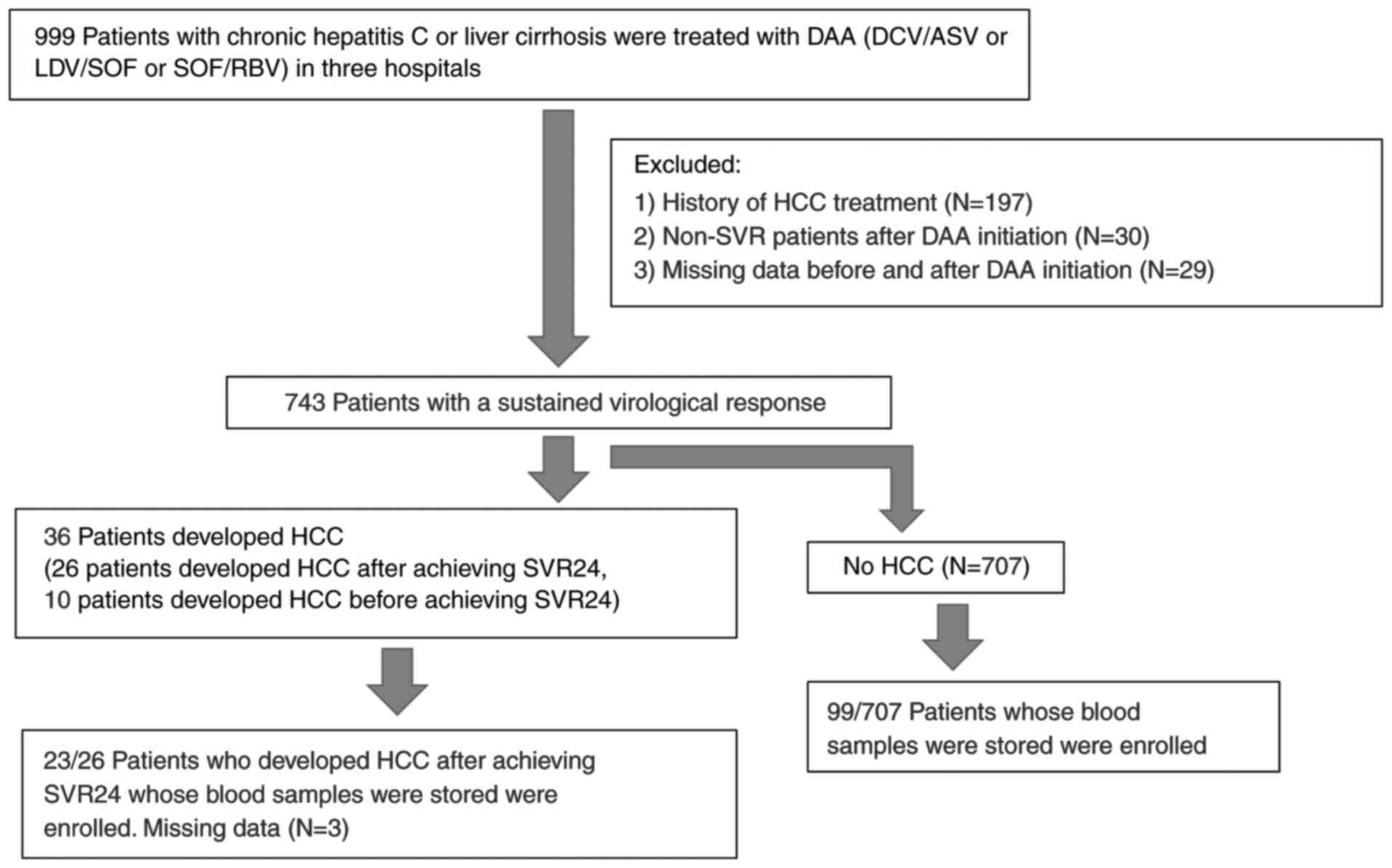
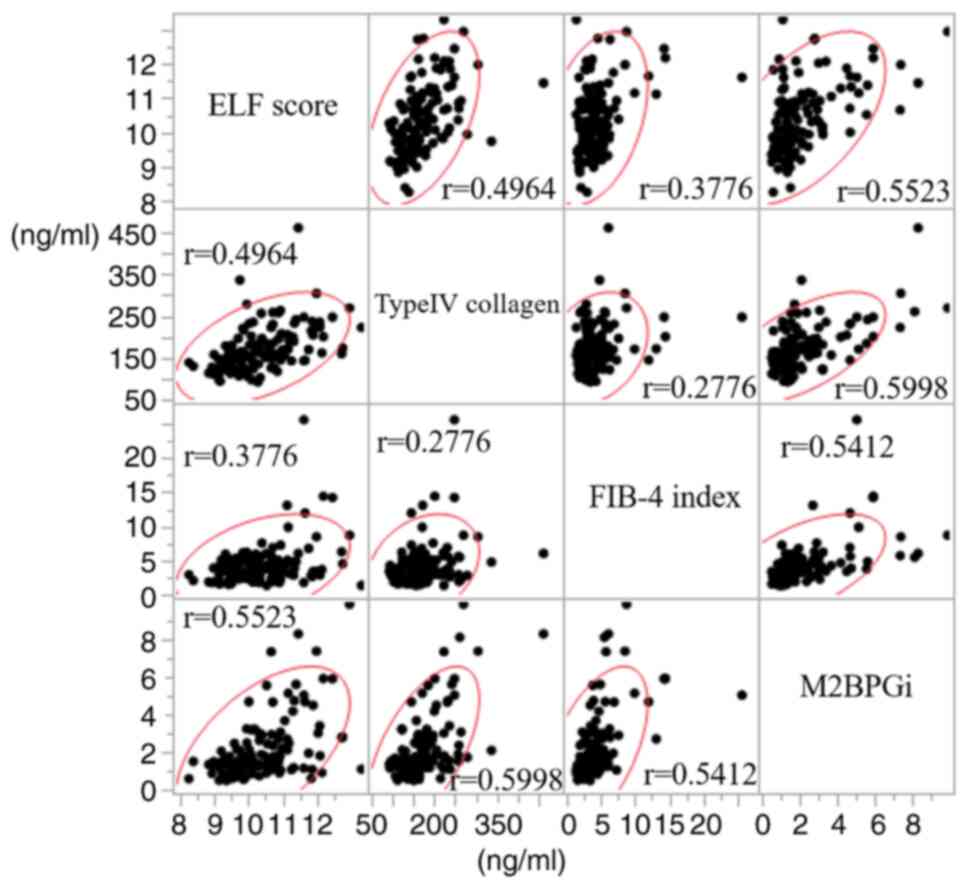
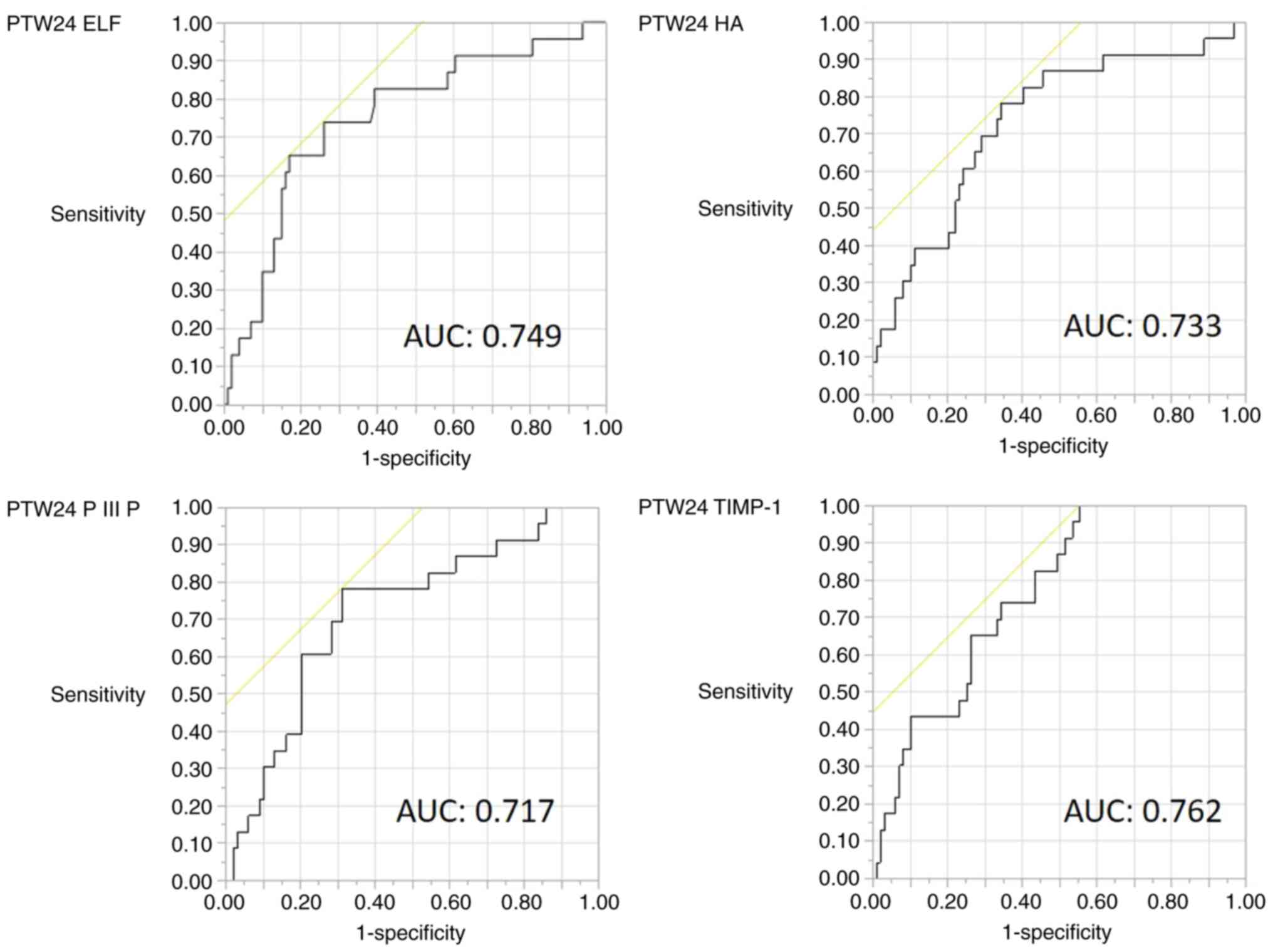
|
1
|
Ji F, Wei B, Yeo YH, Ogawa E, Zou B, Stave
CD, Li Z, Dang S, Furusyo N, Cheung RC and Nguyen MH: Systematic
review with meta-analysis: Effectiveness and tolerability of
interferon-free direct-acting antiviral regimens for chronic
hepatitis C genotype 1 in routine clinical practice in Asia.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 47:550–562. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wei B, Ji F, Yeo YH, Ogawa E, Zou B, Stave
CD, Dang S, Li Z, Furusyo N, Cheung RC and Nguyen MH: Real-world
effectiveness of sofosbuvir plus ribavirin for chronic hepatitis C
genotype 2 in Asia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open
Gastroenterol. 5(e000207)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mizokami M, Liu LJ, Fujiyama N, Littman M,
Yuan J, Sekiya T, Hedskog C and Ng LJ: Real-world safety and
effectiveness of ledipasvir/sofosbuvir for the treatment of chronic
hepatitis C virus genotype 1 in Japan. J Viral Hepat. 28:129–141.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Calvaruso V, Cabibbo G, Cacciola I, Petta
S, Madonia S, Bellia A, Tinè F, Distefano M, Licata A,
Giannitrapani L, et al: Incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in
patients With HCV-associated cirrhosis treated with direct-acting
antiviral agents. Gastroenterology. 155:411–421.e4. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li DK, Ren Y, Fierer DS, Rutledge S,
Shaikh OS, Lo Re V III, Simon T, Abou-Samra AB, Chung RT and Butt
AA: The short-term incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma is not
increased after hepatitis C treatment with direct-acting
antivirals: An ERCHIVES study. Hepatology. 67:2244–2253.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ioannou GN, Green PK and Berry K: HCV
eradication induced by direct-acting antiviral agents reduces the
risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol: Sep 5, 2017 (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
7
|
Kanwal F, Kramer J, Asch SM, Chayanupatkul
M, Cao Y and El-Serag HB: Risk of hepatocellular cancer in HCV
patients treated with direct-acting antiviral agents.
Gastroenterology. 153:996–1005.e1. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yabu K, Kiyosawa K, Mori H, Matsumoto A,
Yoshizawa K, Tanaka E and Furuta S: Serum collagen type IV for the
assessment of fibrosis and resistance to interferon therapy in
chronic hepatitis C. Scand J Gastroenterol. 29:474–479.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yamasaki K, Tateyama M, Abiru S, Komori A,
Nagaoka S, Saeki A, Hashimoto S, Sasaki R, Bekki S, Kugiyama Y, et
al: Elevated serum levels of Wisteria floribunda
agglutinin-positive human Mac-2 binding protein predict the
development of hepatocellular carcinoma in hepatitis C patients.
Hepatology. 60:1563–1570. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vallet-Pichard A, Mallet V, Nalpas B,
Verkarre V, Nalpas A, Dhalluin-Venier V, Fontaine H and Pol S:
FIB-4: An inexpensive and accurate marker of fibrosis in HCV
infection. Comparison with liver biopsy and fibrotest. Hepatology.
46:32–36. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li X, Xu H and Gao P: Fibrosis index based
on 4 factors (FIB-4) predicts liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular
carcinoma in chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) patients. Med Sci
Monit. 25:7243–7250. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rosenberg WM, Voelker M, Thiel R, Becka M,
Burt A, Schuppan D, Hubscher S, Roskams T, Pinzani M and Arthur MJ:
European Liver Fibrosis Group. Serum markers detect the presence of
liver fibrosis: A cohort study. Gastroenterology. 127:1704–1713.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Guha IN, Parkes J, Roderick P,
Chattopadhyay D, Cross R, Harris S, Kaye P, Burt AD, Ryder SD,
Aithal GP, et al: Noninvasive markers of fibrosis in nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease: Validating the European liver fibrosis panel
and exploring simple markers. Hepatology. 47:455–460.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mayo MJ, Parkes J, Adams-Huet B, Combes B,
Mills AS, Markin RS, Rubin R, Wheeler D, Contos M, West AB, et al:
Prediction of clinical outcomes in primary biliary cirrhosis by
serum enhanced liver fibrosis assay. Hepatology. 48:1549–1557.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Parkes J, Guha IN, Roderick P, Harris S,
Cross R, Manos MM, Irving W, Zaitoun A, Wheatley M, Ryder S and
Rosenberg W: Enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) test accurately
identifies liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J
Viral Hepat. 18:23–31. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Omran D, Yosry A, Darweesh SK, Nabeel MM,
El-Beshlawey M, Saif S, Fared A, Hassany M and Zayed RA: Enhanced
liver fibrosis test using ELISA assay accurately discriminates
advanced stage of liver fibrosis as determined by transient
elastography fibroscan in treatment naïve chronic HCV patients.
Clin Exp Med. 18:45–50. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Loo WM, Goh GB, Wang Y, Yuan JM, Ong L,
Dan YY and Koh WP: Enhanced liver fibrosis score as a predictor of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Chem. 64:1404–1405. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nagata H, Nakagawa M, Asahina Y, Sato A,
Asano Y, Tsunoda T, Miyoshi M, Kaneko S, Otani S, Kawai-Kitahata F,
et al: Effect of interferon-based and -free therapy on early
occurrence and recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic
hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 67:933–939. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ioannou GN, Beste LA, Green PK, Singal AG,
Tapper EB, Waljee AK, Sterling RK, Feld JJ, Kaplan DE, Taddei TH
and Berry K: Increased risk for hepatocellular carcinoma persists
up to 10 years after HCV eradication in patients with baseline
cirrhosis or high FIB-4 scores. Gastroenterology. 157:1264–1278.e4.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Asahina Y, Tsuchiya K, Nishimura T,
Muraoka M, Suzuki Y, Tamaki N, Yasui Y, Hosokawa T, Ueda K,
Nakanishi H, et al: α-fetoprotein levels after interferon therapy
and risk of hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis C.
Hepatology. 58:1253–1262. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yasui Y, Kurosaki M, Komiyama Y, Takada H,
Tamaki N, Watakabe K, Okada M, Wang W, Shimizu T, Kubota Y, et al:
Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-positive Mac-2 binding
protein predicts early occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after
sustained virologic response by direct-acting antivirals for
hepatitis C virus. Hepatol Res. 48:1131–1139. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Dvorak K, Stritesky J, Petrtyl J, Vitek L,
Sroubkova R, Lenicek M, Smid V, Haluzik M and Bruha R: Use of
non-invasive parameters of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and liver
fibrosis in daily practice-an exploratory case-control study. PLoS
One. 9(e111551)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tanwar S, Trembling PM, Guha IN, Parkes J,
Kaye P, Burt AD, Ryder SD, Aithal GP, Day CP and Rosenberg WM:
Validation of terminal peptide of procollagen III for the detection
and assessment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 57:103–111.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yilmaz Y and Eren F: Serum biomarkers of
fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodeling in patients with
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Association with liver histology.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 31:43–46. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
McHutchison JG, Blatt LM, de Medina M,
Craig JR, Conrad A, Schiff ER and Tong MJ: Measurement of serum
hyaluronic acid in patients with chronic hepatitis C and its
relationship to liver histology. Consensus interferon study group.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15:945–951. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Leroy V, Monier F, Bottari S, Trocme C,
Sturm N, Hilleret MN, Morel F and Zarski JP: Circulating matrix
metalloproteinases 1, 2, 9 and their inhibitors TIMP-1 and TIMP-2
as serum markers of liver fibrosis in patients with chronic
hepatitis C: Comparison with PIIINP and hyaluronic acid. Am J
Gastroenterol. 99:271–279. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Boeker KH, Haberkorn CI, Michels D,
Flemming P, Manns MP and Lichtinghagen R: Diagnostic potential of
circulating TIMP-1 and MMP-2 as markers of liver fibrosis in
patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin Chim Acta. 316:71–81.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Miyaki E, Imamura M, Hiraga N, Murakami E,
Kawaoka T, Tsuge M, Hiramatsu A, Kawakami Y, Aikata H, Hayes CN and
Chayama K: Daclatasvir and asunaprevir treatment improves liver
function parameters and reduces liver fibrosis markers in chronic
hepatitis C patients. Hepatol Res. 46:758–764. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bernuth S, Yagmur E, Schuppan D, Sprinzl
MF, Zimmermann A, Schad A, Kittner JM, Weyer V, Knapstein J,
Schattenberg JM, et al: Early changes in dynamic biomarkers of
liver fibrosis in hepatitis C virus-infected patients treated with
sofosbuvir. Dig Liver Dis. 48:291–297. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yamazaki T, Joshita S, Umemura T, Usami Y,
Sugiura A, Fujimori N, Kimura T, Matsumoto A, Igarashi K, Ota M and
Tanaka E: Changes in serum levels of autotaxin with direct-acting
antiviral therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis C. PLoS One.
13(e0195632)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hsu WF, Lai HC, Su WP, Lin CH, Chuang PH,
Chen SH, Chen HY, Wang HW, Huang GT and Peng CY: Rapid decline of
noninvasive fibrosis index values in patients with hepatitis C
receiving treatment with direct-acting antiviral agents. BMC
Gastroenterol. 19(63)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bachofner JA, Valli PV, Kröger A, Bergamin
I, Künzler P, Baserga A, Braun D, Seifert B, Moncsek A, Fehr J, et
al: Direct antiviral agent treatment of chronic hepatitis C results
in rapid regression of transient elastography and fibrosis markers
fibrosis-4 score and aspartate aminotransferase-platelet ratio
index. Liver Int. 37:369–376. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Shiratori Y, Imazeki F, Moriyama M, Yano
M, Arakawa Y, Yokosuka O, Kuroki T, Nishiguchi S, Sata M, Yamada G,
et al: Histologic improvement of fibrosis in patients with
hepatitis C who have sustained response to interferon therapy. Ann
Intern Med. 132:517–524. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Fujita K, Kuroda N, Morishita A, Oura K,
Tadokoro T, Nomura T, Yoneyama H, Arai T, Himoto T, Watanabe S and
Masaki T: Fibrosis staging using direct serum biomarkers is
influenced by hepatitis activity grading in hepatitis C virus
infection. J Clin Med. 7(267)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hiramatsu N, Oze T and Takehara T:
Suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma development in hepatitis C
patients given interferon-based antiviral therapy. Hepatol Res.
45:152–161. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Motoyama H, Tamori A, Kubo S,
Uchida-Kobayashi S, Takemura S, Tanaka S, Ohfuji S, Teranishi Y,
Kozuka R, Kawamura E, et al: Stagnation of histopathological
improvement is a predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma development
after hepatitis C virus eradication. PLoS One.
13(e0194163)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yamaguchi T, Matsuzaki K, Inokuchi R,
Kawamura R, Yoshida K, Murata M, Fujisawa J, Fukushima N, Sata M,
Kage M, et al: Phosphorylated Smad2 and Smad3 signaling: Shifting
between tumor suppression and fibro-carcinogenesis in chronic
hepatitis C. Hepatol Res. 43:1327–1342. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|