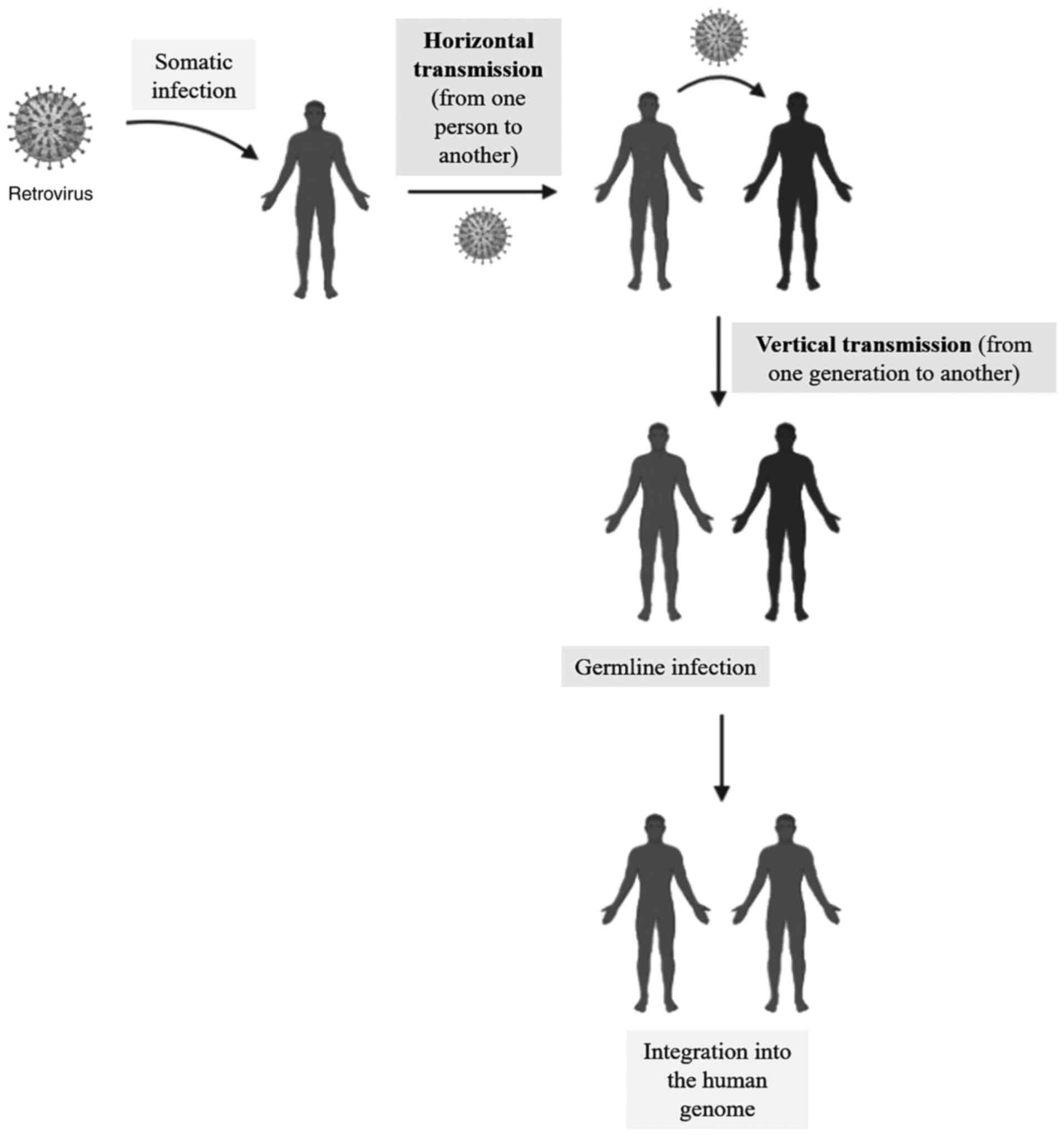
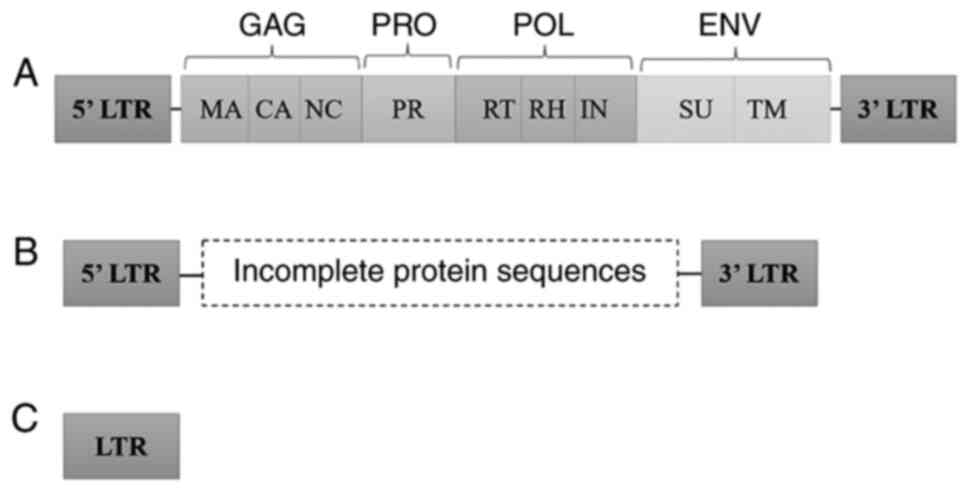
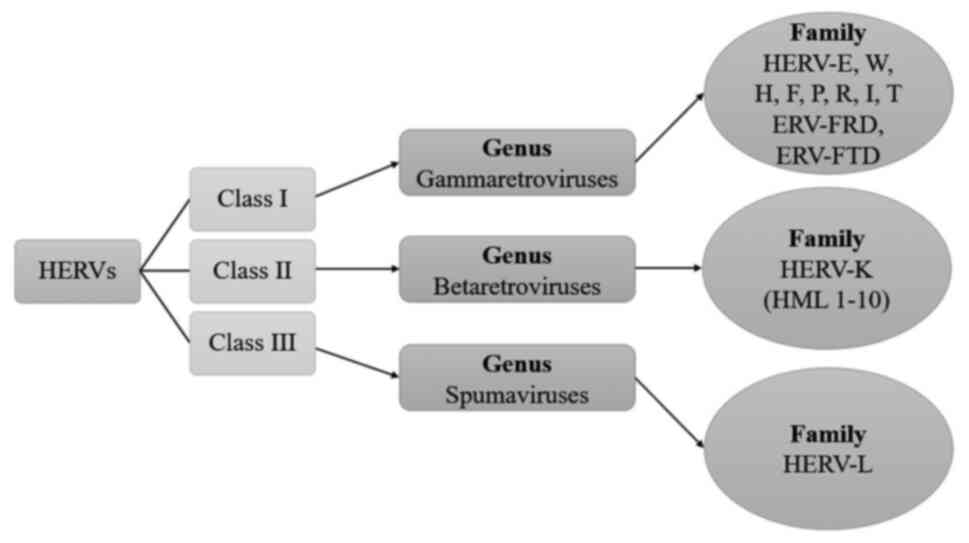
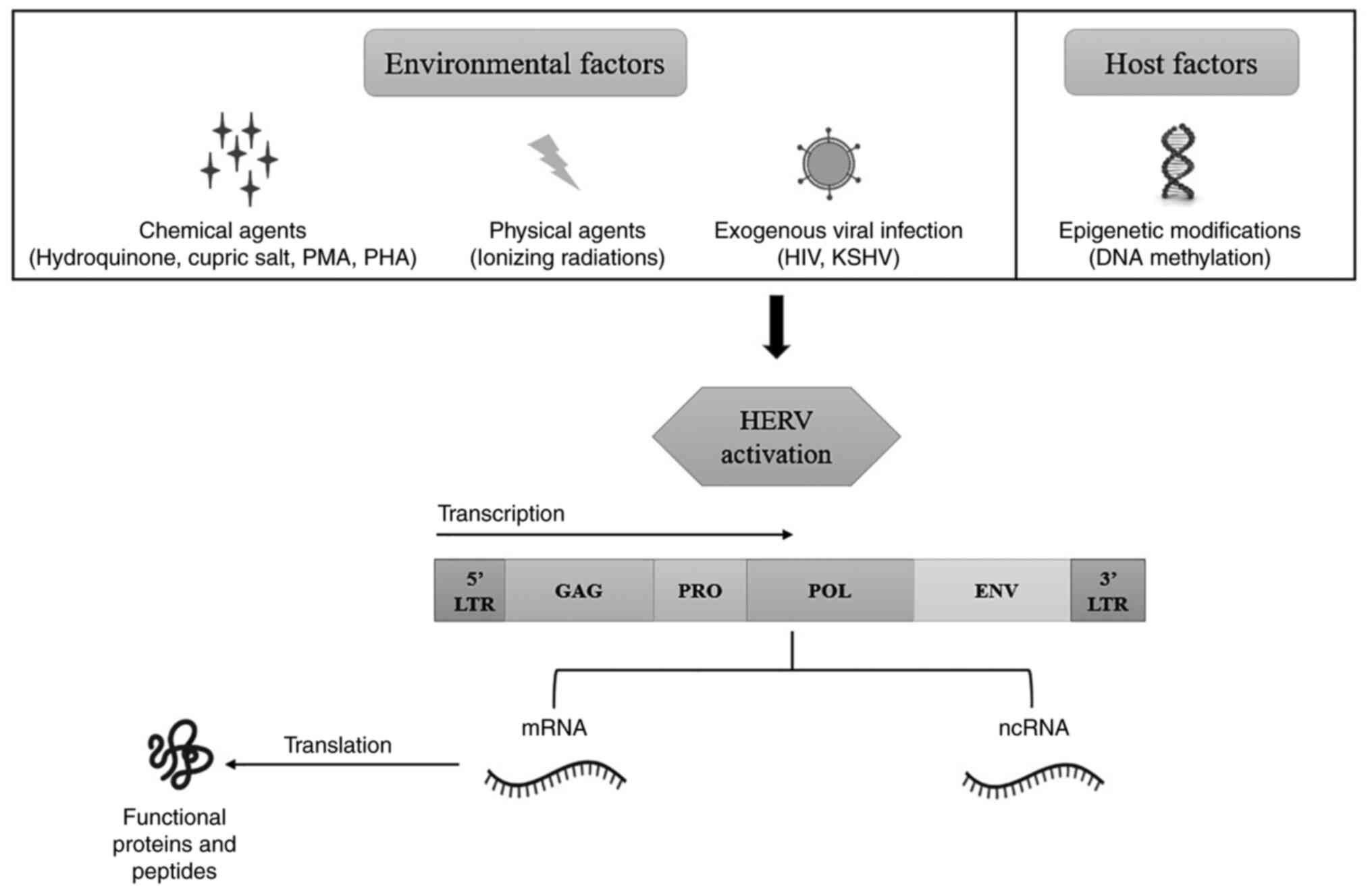
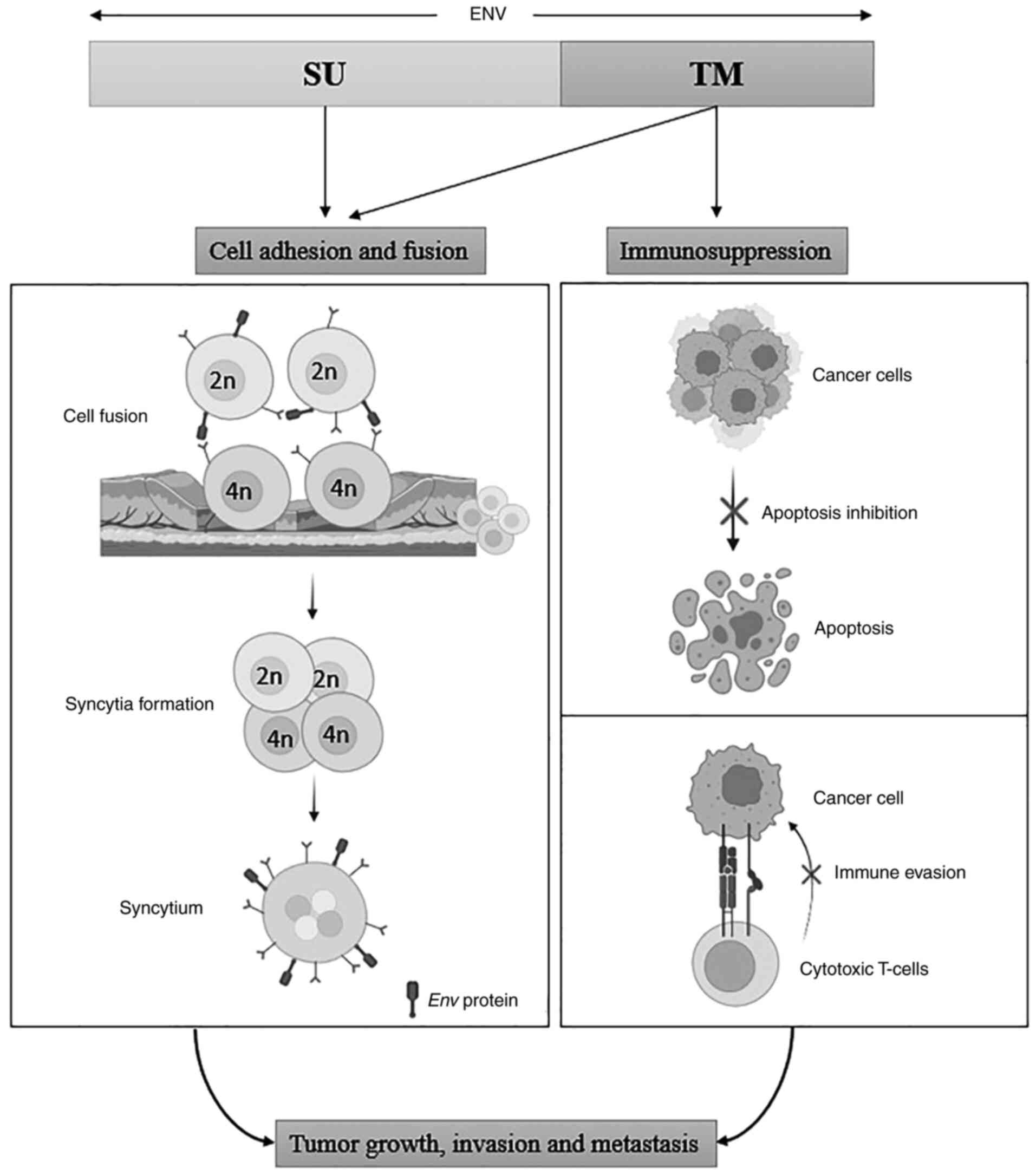
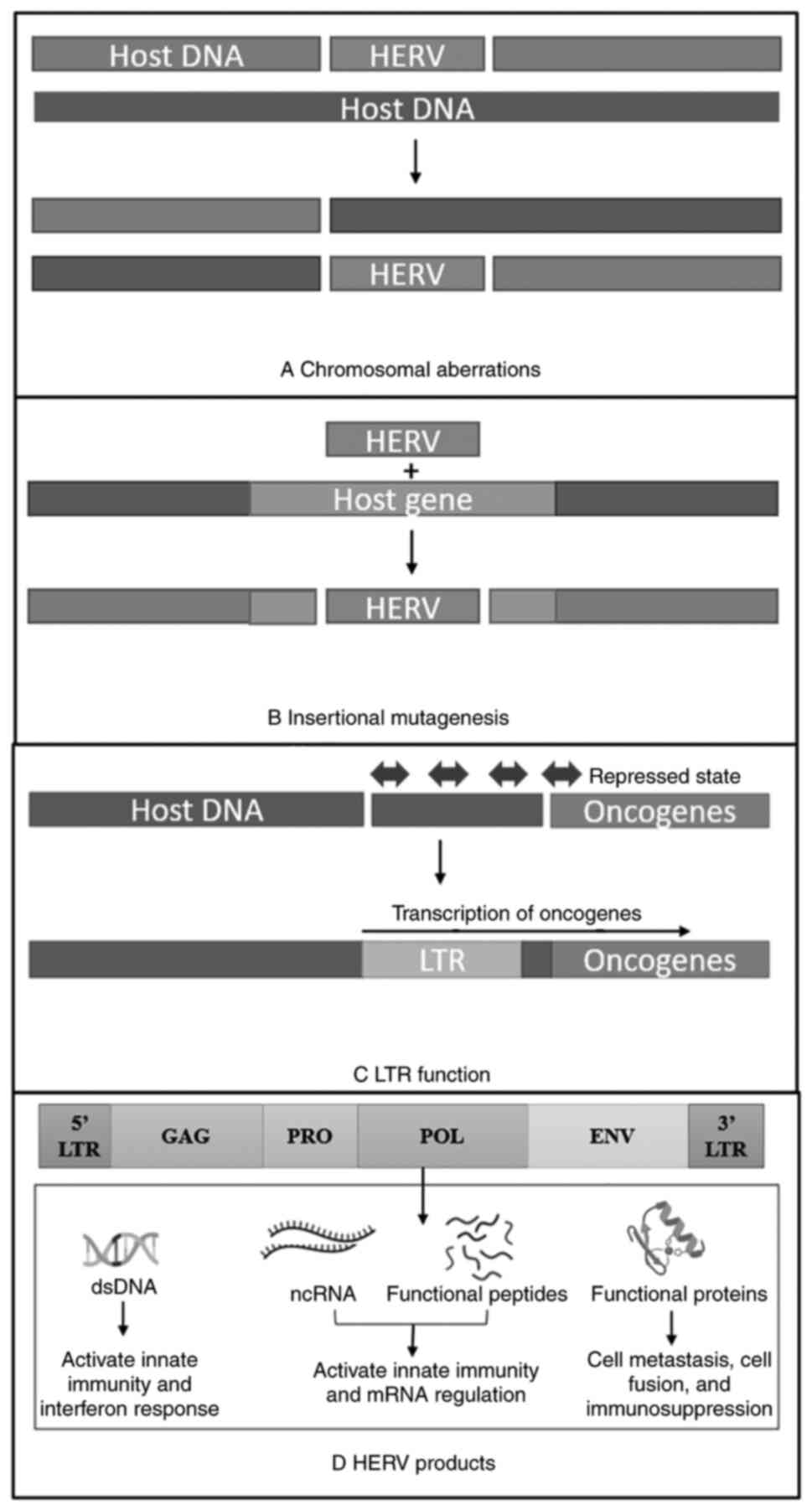
|
1
|
Wang X, Huang J and Zhu F: Human
endogenous retroviral envelope protein syncytin-1 and inflammatory
abnormalities in neuropsychological diseases. Front Psychiatry.
9(422)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gao Y, Yu XF and Chen T: Human endogenous
retroviruses in cancer: Expression, regulation and function. Oncol
Lett. 21(121)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Grandi N and Tramontano E: HERV envelope
proteins: physiological role and pathogenic potential in cancer and
autoimmunity. Front Microbiol. 9(462)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Durnaoglu S, Lee SK and Ahnn J: Syncytin,
envelope protein of human endogenous retrovirus (HERV): No longer
‘fossil’in human genome. Anim Cells Syst (Seoul). 25:358–368.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Salavatiha Z, Soleimani-Jelodar R and
Jalilvand S: The role of endogenous retroviruses-K in human cancer.
Rev Med Virol. 30:1–13. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Santoni FA, Guerra J and Luban J: HERV-H
RNA is abundant in human embryonic stem cells and a precise marker
for pluripotency. Retrovirology. 9(111)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mi S, Lee X, Li X, Veldman GM, Finnerty H,
Racie L, LaVallie E, Tang XY, Edouard P, Howes S, et al: Syncytin
is a captive retroviral envelope protein involved in human
placental morphogenesis. Nature. 403:785–789. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Alcazer V, Bonaventura P and Depil S:
Human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs): Shaping the innate immune
response in cancers. Cancers (Basel). 12(610)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kim HS: Genomic impact, chromosomal
distribution and transcriptional regulation of HERV elements. Mol
Cells. 33:539–544. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kremer D, Gruchot J, Weyers V, Oldemeier
L, Göttle P, Healy L, Ho Jang J, Kang T, Xu Y, Volsko C, et al:
pHERV-W envelope protein fuels microglial cell-dependent damage of
myelinated axons in multiple sclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:15216–15225. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dervan E, Bhattacharyya DD, McAuliffe JD,
Khan FH and Glynn SA: Ancient adversary-HERV-K (HML-2) in cancer.
Front Oncol. 11(658489)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Huang WJ, Liu ZC, Wei W, Wang GH, Wu JG
and Zhu F: Human endogenous retroviral pol RNA and protein detected
and identified in the blood of individuals with schizophrenia.
Schizophr Res. 83:193–199. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Monde K, Terasawa H, Nakano Y, Soheilian
F, Nagashima K, Maeda Y and Ono A: Molecular mechanisms by which
HERV-K Gag interferes with HIV-1 Gag assembly and particle
infectivity. Retrovirology. 14(27)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu X, Liu Z, Sun L, Ren J, Wu Z, Jiang X,
Ji Q, Wang Q, Fan Y, Cai Y, et al: Resurrection of human endogenous
retroviruses during aging reinforces senescence. bioRxiv:
2021.02.22.432260, 2021.
|
|
15
|
Levet S, Charvet B, Bertin A, Deschaumes
A, Perron H and Hober D: Human endogenous retroviruses and type 1
diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 19(141)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hurst TP and Magiorkinis G: Activation of
the innate immune response by endogenous retroviruses. J Gen Virol.
96:1207–1218. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Smith CC, Beckermann KE, Bortone DS, De
Cubas AA, Bixby LM, Lee SJ, Panda A, Ganesan S, Bhanot G, Wallen
EM, et al: Endogenous retroviral signatures predict immunotherapy
response in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Invest.
128:4804–4820. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mangeney M, Pothlichet J, Renard M, Ducos
B and Heidmann T: Endogenous retrovirus expression is required for
murine melanoma tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res. 65:2588–2591.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Díaz-Carballo D, Acikelli AH, Klein J,
Jastrow H, Dammann P, Wyganowski T, Guemues C, Gustmann S,
Bardenheuer W, Malak S, et al: Therapeutic potential of antiviral
drugs targeting chemorefractory colorectal adenocarcinoma cells
overexpressing endogenous retroviral elements. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 34(81)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Müller MD, Holst PJ and Nielsen KN: A
systematic review of expression and immunogenicity of human
endogenous retroviral proteins in cancer and discussion of
therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci. 23(1330)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu CH, Grandi N, Palanivelu L, Tramontano
E and Lin LT: Contribution of human retroviruses to disease
development-A focus on the HIV- and HERV-cancer relationships and
treatment strategies. Viruses. 12(852)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kassiotis G: Endogenous retroviruses and
the development of cancer. J Immunol. 192:1343–1349.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Subramanian RP, Wildschutte JH, Russo C
and Coffin JM: Identification, characterization, and comparative
genomic distribution of the HERV-K (HML-2) group of human
endogenous retroviruses. Retrovirology. 8(90)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Curty G, Marston JL, de Mulder Rougvie M,
Leal FE, Nixon DF and Soares MA: Human endogenous retrovirus K in
cancer: A potential biomarker and immunotherapeutic target.
Viruses. 12(726)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lavie L, Kitova M, Maldener E, Meese E and
Mayer J: CpG methylation directly regulates transcriptional
activity of the human endogenous retrovirus family HERV-K(HML-2). J
Virol. 79:876–883. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Contreras-Galindo R, López P, Vélez R and
Yamamura Y: HIV-1 infection increases the expression of human
endogenous retroviruses type K (HERV-K) in vitro. AIDS Res Hum
Retroviruses. 23:116–122. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dai L, Del Valle L, Miley W, Whitby D,
Ochoa AC, Flemington EK and Qin Z: Transactivation of human
endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) by KSHV promotes Kaposi's sarcoma
development. Oncogene. 37:4534–4545. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sutkowski N, Conrad B, Thorley-Lawson DA
and Huber BT: Epstein-Barr virus transactivates the human
endogenous retrovirus HERV-K18 that encodes a superantigen.
Immunity. 15:579–589. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Toufaily C, Landry S, Leib-Mosch C,
Rassart E and Barbeau B: Activation of LTRs from different human
endogenous retrovirus (HERV) families by the HTLV-1 tax protein and
T-cell activators. Viruses. 3:2146–2159. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Romanish MT, Cohen CJ and Mager DL:
Potential mechanisms of endogenous retroviral-mediated genomic
instability in human cancer. In: Seminars in cancer biology.
Elsevier, pp246-253, 2010.
|
|
31
|
Conti A, Rota F, Ragni E, Favero C, Motta
V, Lazzari L, Bollati V, Fustinoni S and Dieci G: Hydroquinone
induces DNA hypomethylation-independent overexpression of
retroelements in human leukemia and hematopoietic stem cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 474:691–695. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Johnston JB, Silva C, Holden J, Warren KG,
Clark AW and Power C: Monocyte activation and differentiation
augment human endogenous retrovirus expression: Implications for
inflammatory brain diseases. Ann Neurol. 50:434–442.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kelleher CA, Wilkinson DA, Freeman JD,
Mager DL and Gelfand EW: Expression of novel transposon-containing
mRNAs in human T cells. J Gen Virol. 77:1101–1110. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Karimi A, Sheervalilou R and Kahroba H: A
new insight on activation of human endogenous retroviruses (HERVs)
in malignant melanoma upon exposure to CuSO4. Biol Trace Elem Res.
191:70–74. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lee JR, Ahn K, Kim YJ, Jung YD and Kim HS:
Radiation-induced human endogenous retrovirus (HERV)-R env gene
expression by epigenetic control. Radiat Res. 178:379–384.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Reiche J, Pauli G and Ellerbrok H:
Differential expression of human endogenous retrovirus K
transcripts in primary human melanocytes and melanoma cell lines
after UV irradiation. Melanoma Res. 20:435–440. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Katsumata K, Ikeda H, Sato M, Ishizu A,
Kawarada Y, Kato H, Wakisaka A, Koike T and Yoshiki T: Cytokine
regulation of env gene expression of human endogenous retrovirus-R
in human vascular endothelial cells. Clin Immunol. 93:75–80.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Montesion M, Bhardwaj N, Williams ZH,
Kuperwasser C and Coffin JM: Mechanisms of HERV-K (HML-2)
transcription during human mammary epithelial cell transformation.
J Virol. 92:e01258–17. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Barth M, Gröger V, Cynis H and Staege MS:
Identification of human endogenous retrovirus transcripts in
Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Mol Biol Rep. 46:1885–1893. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Liang Q, Xu Z, Xu R, Wu L and Zheng S:
Expression patterns of non-coding spliced transcripts from human
endogenous retrovirus HERV-H elements in colon cancer. PLoS One.
7(e29950)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhou F, Li M, Wei Y, Lin K, Lu Y, Shen J,
Johanning GL and Wang-Johanning F: Activation of HERV-K Env protein
is essential for tumorigenesis and metastasis of breast cancer
cells. Oncotarget. 7:84093–84117. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chan SM, Sapir T, Park SS, Rual JF,
Contreras-Galindo R, Reiner O and Markovitz DM: The HERV-K
accessory protein Np9 controls viability and migration of
teratocarcinoma cells. PLoS One. 14(e0212970)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sauter M, Roemer K, Best B, Afting M,
Schommer S, Seitz G, Hartmann M and Mueller-Lantzsch N: Specificity
of antibodies directed against Env protein of human endogenous
retroviruses in patients with germ cell tumors. Cancer Res.
56:4362–4365. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ibba G, Piu C, Uleri E, Serra C and Dolei
A: Disruption by SaCas9 endonuclease of HERV-Kenv, a retroviral
gene with oncogenic and neuropathogenic potential, inhibits
molecules involved in cancer and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Viruses. 10(412)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Rycaj K, Plummer JB, Yin B, Li M, Garza J,
Radvanyi L, Ramondetta LM, Lin K, Johanning GL, Tang DG and
Wang-Johanning F: Cytotoxicity of human endogenous retrovirus
K-specific T cells toward autologous ovarian cancer cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 21:471–483. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zare M, Mostafaei S, Ahmadi A, Azimzadeh
Jamalkandi S, Abedini A, Esfahani-Monfared Z, Dorostkar R and
Saadati M: Human endogenous retrovirus env genes: Potential blood
biomarkers in lung cancer. Microb Pathog. 115:189–193.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Krishnamurthy J, Rabinovich BA, Mi T,
Switzer KC, Olivares S, Maiti SN, Plummer JB, Singh H, Kumaresan
PR, Huls HM, et al: Genetic engineering of T cells to target
HERV-K, an ancient retrovirus on melanoma. Clin Cancer Res.
21:3241–3251. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Kreimer U, Schulz WA, Koch A, Niegisch G
and Goering W: HERV-K and LINE-1 DNA methylation and reexpression
in urothelial carcinoma. Front Oncol. 3(255)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Grabski DF, Hu Y, Sharma M and Rasmussen
SK: Close to the bedside: A systematic review of endogenous
retroviruses and their impact in oncology. J Surg Res. 240:145–155.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Giebler M, Staege MS, Blauschmidt S, Ohm
LI, Kraus M, Würl P, Taubert H and Greither T: Elevated HERV-K
expression in soft tissue sarcoma is associated with worsened
relapse-free survival. Front Microbiol. 9(211)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Galli UM, Sauter M, Lecher B, Maurer S,
Herbst H, Roemer K and Mueller-Lantzsch N: Human endogenous
retrovirus rec interferes with germ cell development in mice and
may cause carcinoma in situ, the predecessor lesion of germ cell
tumors. Oncogene. 24:3223–3228. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Aagaard L, Bjerregaard B, Kjeldbjerg AL,
Pedersen FS, Larsson LI and Rossi JJ: Silencing of endogenous
envelope genes in human choriocarcinoma cells shows that envPb1 is
involved in heterotypic cell fusions. J Gen Virol.
93(1696)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Bergallo M, Montanari P, Mareschi K,
Merlino C, Berger M, Bini I, Daprà V, Galliano I and Fagioli F:
Expression of the pol gene of human endogenous retroviruses HERV-K
and -W in leukemia patients. Arch Virol. 162:3639–3644.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Mangeney M, Renard M, Schlecht-Louf G,
Bouallaga I, Heidmann O, Letzelter C, Richaud A, Ducos B and
Heidmann T: Placental syncytins: Genetic disjunction between the
fusogenic and immunosuppressive activity of retroviral envelope
proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:20534–20539. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Cianciolo GJ, Copeland TD, Oroszlan S and
Snyderman R: Inhibition of lymphocyte proliferation by a synthetic
peptide homologous to retroviral envelope proteins. Science.
230:453–455. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Lemaître C, Tsang J, Bireau C, Heidmann T
and Dewannieux M: A human endogenous retrovirus-derived gene that
can contribute to oncogenesis by activating the ERK pathway and
inducing migration and invasion. PLoS Pathog.
13(e1006451)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Bjerregaard B, Holck S, Christensen I and
Larsson LI: Syncytin is involved in breast cancer-endothelial cell
fusions. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:1906–1911. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Argaw-Denboba A, Balestrieri E, Serafino
A, Cipriani C, Bucci I, Sorrentino R, Sciamanna I, Gambacurta A,
Sinibaldi-Vallebona P and Matteucci C: HERV-K activation is
strictly required to sustain CD133+ melanoma cells with stemness
features. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36(20)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Chen T, Meng Z, Gan Y, Wang X, Xu F, Gu Y,
Xu X, Tang J, Zhou H, Zhang X, et al: The viral oncogene Np9 acts
as a critical molecular switch for co-activating β-catenin, ERK,
Akt and Notch1 and promoting the growth of human leukemia
stem/progenitor cells. Leukemia. 27:1469–1478. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Li M, Radvanyi L, Yin B, Rycaj K, Li J,
Chivukula R, Lin K, Lu Y, Shen J, Chang DZ, et al: Downregulation
of human endogenous retrovirus type K (HERV-K) viral env RNA in
pancreatic cancer cells decreases cell proliferation and tumor
growth. Clin Cancer Res. 23:5892–5911. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang M, Liang JQ and Zheng S:
Expressional activation and functional roles of human endogenous
retroviruses in cancers. Rev Med Virol. 29(e2025)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Cherkasova E, Malinzak E, Rao S, Takahashi
Y, Senchenko VN, Kudryavtseva AV, Nickerson ML, Merino M, Hong JA,
Schrump DS, et al: Inactivation of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor
suppressor leads to selective expression of a human endogenous
retrovirus in kidney cancer. Oncogene. 30:4697–4706.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Rai AK, Singh A, Saxena A, Seth T, Raina V
and Mitra DK: Exonal switch down-regulates the expression of CD5 on
blasts of acute T cell leukaemia. Clin Exp Immunol. 190:340–350.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Denne M, Sauter M, Armbruester V, Licht
JD, Roemer K and Mueller-Lantzsch N: Physical and functional
interactions of human endogenous retrovirus proteins Np9 and rec
with the promyelocytic leukemia zinc finger protein. J Virol.
81:5607–5616. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Strissel PL, Ruebner M, Thiel F, Wachter
D, Ekici AB, Wolf F, Thieme F, Ruprecht K, Beckmann MW and Strick
R: Reactivation of codogenic endogenous retroviral (ERV) envelope
genes in human endometrial carcinoma and prestages: Emergence of
new molecular targets. Oncotarget. 3:1204–1219. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Yu H, Liu T, Zhao Z, Chen Y, Zeng J, Liu S
and Zhu F: Mutations in 3'-long terminal repeat of HERV-W family in
chromosome 7 upregulate syncytin-1 expression in urothelial cell
carcinoma of the bladder through interacting with c-Myb. Oncogene.
33:3947–3958. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Li S, Liu ZC, Yin SJ, Chen YT, Yu HL, Zeng
J, Zhang Q and Zhu F: Human endogenous retrovirus W family envelope
gene activates the small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channel in
human neuroblastoma cells through CREB. Neuroscience. 247:164–174.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Barbalat R, Ewald SE, Mouchess ML and
Barton GM: Nucleic acid recognition by the innate immune system.
Annu Rev Immunol. 29:185–214. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Bannert N, Hofmann H, Block A and Hohn O:
HERVs new role in cancer: From accused perpetrators to cheerful
protectors. Front Microbiol. 9(178)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Panda A, de Cubas AA, Stein M, Riedlinger
G, Kra J, Mayer T, Smith CC, Vincent BG, Serody JS, Beckermann KE,
et al: Endogenous retrovirus expression is associated with response
to immune checkpoint blockade in clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
JCI Insight. 3(e121522)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Cao W, Kang R, Xiang Y and Hong J: Human
endogenous retroviruses in clear cell renal cell carcinoma:
Biological functions and clinical values. Onco Targets Ther.
13:7877–7885. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Rolland A, Jouvin-Marche E, Viret C, Faure
M, Perron H and Marche PN: The envelope protein of a human
endogenous retrovirus-W family activates innate immunity through
CD14/TLR4 and promotes Th1-like responses. J Immunol.
176:7636–7644. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Wang-Johanning F, Li M, Esteva FJ, Hess
KR, Yin B, Rycaj K, Plummer JB, Garza JG, Ambs S and Johanning GL:
Human endogenous retrovirus type K antibodies and mRNA as serum
biomarkers of early-stage breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 134:587–595.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Mueller T, Hantsch C, Volkmer I and Staege
MS: Differentiation-dependent regulation of human endogenous
retrovirus K sequences and neighboring genes in germ cell tumor
cells. Front Microbiol. 9(1253)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Kleiman A, Senyuta N, Tryakin A, Sauter M,
Karseladze A, Tjulandin S, Gurtsevitch V and Mueller-Lantzsch N:
HERV-K(HML-2) GAG/ENV antibodies as indicator for therapy effect in
patients with germ cell tumors. Int J Cancer. 110:459–461.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Götzinger N, Sauter M, Roemer K and
Mueller-Lantzsch N: Regulation of human endogenous retrovirus-K Gag
expression in teratocarcinoma cell lines and human tumours. J Gen
Virol. 77:2983–2990. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Wang Z, Zheng Y, Park HJ, Li J, Carr JR,
Chen YJ, Kiefer MM, Kopanja D, Bagchi S, Tyner AL and Raychaudhuri
P: Targeting FoxM1 effectively retards p53-null lymphoma and
sarcoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:759–767. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
von Lintig FC, Dreilinger AD, Varki NM,
Wallace AM, Casteel DE and Boss GR: Ras activation in human breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 62:51–62. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Golan M, Hizi A, Resau JH, Yaal-Hahoshen
N, Reichman H, Keydar I and Tsarfaty I: Human endogenous retrovirus
(HERV-K) reverse transcriptase as a breast cancer prognostic
marker. Neoplasia. 10:521–533. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Johanning GL, Malouf GG, Zheng X, Esteva
FJ, Weinstein JN, Wang-Johanning F and Su X: Expression of human
endogenous retrovirus-K is strongly associated with the basal-like
breast cancer phenotype. Sci Rep. 7(41960)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Kim HJ, Moon BI, Lee JW, Kim SC and Kim
HJ: Age-related reduction of antibody response against the human
endogenous retrovirus K envelope in women. Oncotarget.
7:17327–17337. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Zhou F, Krishnamurthy J, Wei Y, Li M, Hunt
K, Johanning GL, Cooper LJ and Wang-Johanning F: Chimeric antigen
receptor T cells targeting HERV-K inhibit breast cancer and its
metastasis through downregulation of Ras. Oncoimmunology.
4(e1047582)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Jin X, Xu XE, Jiang YZ, Liu YR, Sun W, Guo
YJ, Ren YX, Zuo WJ, Hu X, Huang SL, et al: The endogenous
retrovirus-derived long noncoding RNA TROJAN promotes
triple-negative breast cancer progression via ZMYND8 degradation.
Sci Adv. 5(eaat9820)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Li N, Li Y, Lv J, Zheng X, Wen H, Shen H,
Zhu G, Chen TY, Dhar SS, Kan PY, et al: ZMYND8 reads the dual
histone mark H3K4me1-H3K14ac to antagonize the expression of
metastasis-linked genes. Mol Cell. 63:470–484. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Büscher K, Hahn S, Hofmann M, Trefzer U,
Ozel M, Sterry W, Löwer J, Löwer R, Kurth R and Denner J:
Expression of the human endogenous retrovirus-K transmembrane
envelope, Rec and Np9 proteins in melanomas and melanoma cell
lines. Melanoma Res. 16:223–234. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Hahn S, Ugurel S, Hanschmann KM, Strobel
H, Tondera C, Schadendorf D, Löwer J and Löwer R: Serological
response to human endogenous retrovirus K in melanoma patients
correlates with survival probability. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses.
24:717–723. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Kudo-Saito C, Yura M, Yamamoto R and
Kawakami Y: Induction of immunoregulatory CD271+ cells by
metastatic tumor cells that express human endogenous retrovirus H.
Cancer Res. 74:1361–1370. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Maliniemi P, Vincendeau M, Mayer J, Frank
O, Hahtola S, Karenko L, Carlsson E, Mallet F, Seifarth W,
Leib-Mösch C and Ranki A: Expression of human endogenous
retrovirus-w including syncytin-1 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
PLoS One. 8(e76281)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Blond JL, Lavillette D, Cheynet V, Bouton
O, Oriol G, Chapel-Fernandes S, Mandrand B, Mallet F and Cosset FL:
An envelope glycoprotein of the human endogenous retrovirus HERV-W
is expressed in the human placenta and fuses cells expressing the
type D mammalian retrovirus receptor. J Virol. 74:3321–3329.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Wallace TA, Downey RF, Seufert CJ,
Schetter A, Dorsey TH, Johnson CA, Goldman R, Loffredo CA, Yan P,
Sullivan FJ, et al: Elevated HERV-K mRNA expression in PBMC is
associated with a prostate cancer diagnosis particularly in older
men and smokers. Carcinogenesis. 35:2074–2083. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Reis BS, Jungbluth AA, Frosina D, Holz M,
Ritter E, Nakayama E, Ishida T, Obata Y, Carver B, Scher H, et al:
Prostate cancer progression correlates with increased humoral
immune response to a human endogenous retrovirus GAG protein. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:6112–6125. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Saini SK, Ørskov AD, Bjerregaard AM,
Unnikrishnan A, Holmberg-Thydén S, Borch A, Jensen KV, Anande G,
Bentzen AK, Marquard AM, et al: Human endogenous retroviruses form
a reservoir of T cell targets in hematological cancers. Nat Commun.
11(5660)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Alqahtani S, Promtong P, Oliver AW, He XT,
Walker TD, Povey A, Hampson L and Hampson IN: Silver nanoparticles
exhibit size-dependent differential toxicity and induce expression
of syncytin-1 in FA-AML1 and MOLT-4 leukaemia cell lines.
Mutagenesis. 31:695–702. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Sun Y, Ouyang DY, Pang W, Tu YQ, Li YY,
Shen XM, Tam SC, Yang HY and Zheng YT: Expression of syncytin in
leukemia and lymphoma cells. Leuk Res. 34:1195–1202.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Contreras-Galindo R, Kaplan MH, Leissner
P, Verjat T, Ferlenghi I, Bagnoli F, Giusti F, Dosik MH, Hayes DF,
Gitlin SD and Markovitz DM: Human endogenous retrovirus K (HML-2)
elements in the plasma of people with lymphoma and breast cancer. J
Virol. 82:9329–9336. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Tatkiewicz W, Dickie J, Bedford F, Jones
A, Atkin M, Kiernan M, Maze EA, Agit B, Farnham G, Kanapin A and
Belshaw R: Characterising a human endogenous retrovirus
(HERV)-derived tumour-associated antigen: Enriched RNA-Seq analysis
of HERV-K(HML-2) in mantle cell lymphoma cell lines. Mob DNA.
11(9)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Morgan D and Brodsky I: Human endogenous
retrovirus (HERV-K) particles in megakaryocytes cultured from
essential thrombocythemia peripheral blood stem cells. Exp Hematol.
32:520–525. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Takahashi Y, Harashima N, Kajigaya S,
Yokoyama H, Cherkasova E, McCoy JP, Hanada K, Mena O, Kurlander R,
Tawab A, et al: Regression of human kidney cancer following
allogeneic stem cell transplantation is associated with recognition
of an HERV-E antigen by T cells. J Clin Invest. 118:1099–1109.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Rao S, Abdul T, Kurlander R, Harashima N,
Lundqvist A, Hong J, Malinzak E, Smith A, Cherkasova E, McCoy P, et
al: The human endogenous retrovirus (HERV) derived kidney cancer
antigen CT-RCC1 induces proliferation of CD8+ antigen-specific
T-cells in vitro that kill renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and is
up-regulated by inhibiting histone deacetylase. Cancer Res. 68 (9
Suppl)(S1033)2008.
|
|
100
|
Haruta M, Gray WM and Sussman MR:
Regulation of the plasma membrane proton pump (H(+)-ATPase) by
phosphorylation. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 28:68–75. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Weyerer V, Strissel PL, Stöhr C, Eckstein
M, Wach S, Taubert H, Brandl L, Geppert CI, Wullich B, Cynis H, et
al: Endogenous retroviral-K envelope is a novel tumor antigen and
prognostic indicator of renal cell carcinoma. Front Oncol.
11(657187)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Gabaev I, Williamson JC, Crozier TWM,
Schulz TF and Lehner PJ: Quantitative proteomics analysis of lytic
KSHV infection in human endothelial cells reveals targets of viral
immune modulation. Cell Rep. 33(108249)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Chiappinelli KB, Strissel PL, Desrichard
A, Li H, Henke C, Akman B, Hein A, Rote NS, Cope LM, Snyder A, et
al: Inhibiting DNA methylation causes an interferon response in
cancer via dsRNA including endogenous retroviruses. Cell.
162:974–986. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Larsen JM, Christensen IJ, Nielsen HJ,
Hansen U, Bjerregaard B, Talts JF and Larsson LI: Syncytin
immunoreactivity in colorectal cancer: Potential prognostic impact.
Cancer Lett. 280:44–49. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Golkaram M, Salmans ML, Kaplan S,
Vijayaraghavan R, Martins M, Khan N, Garbutt C, Wise A, Yao J,
Casimiro S, et al: HERVs establish a distinct molecular subtype in
stage II/III colorectal cancer with poor outcome. NPJ Genom Med.
6(13)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|