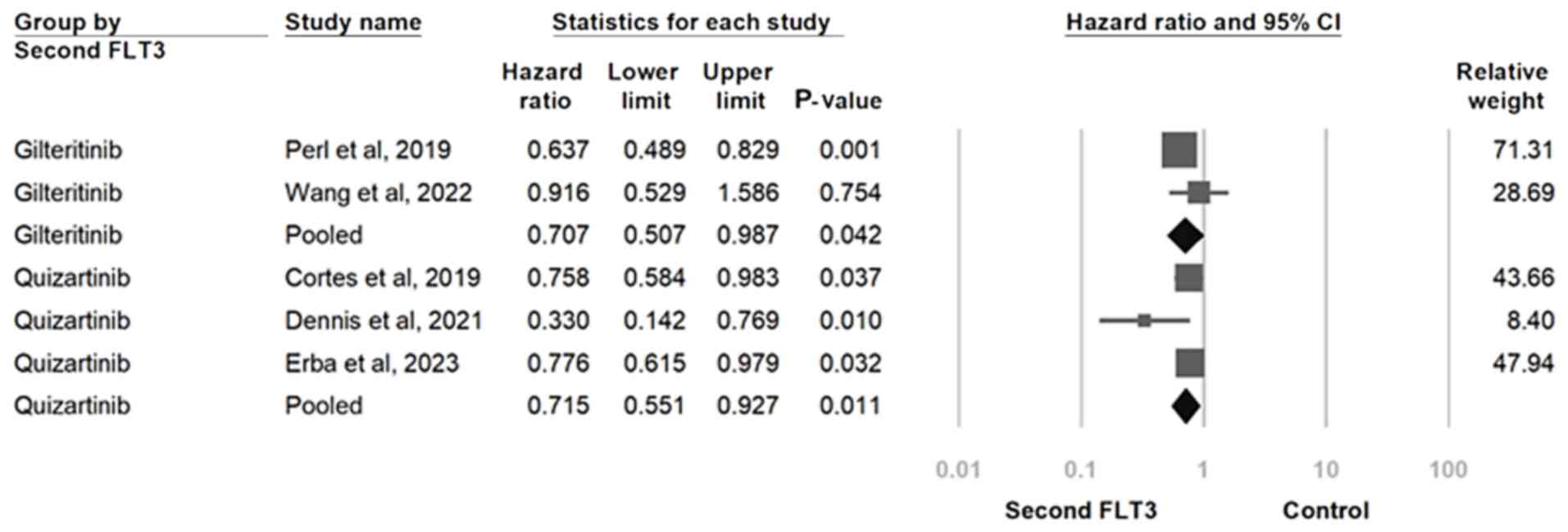
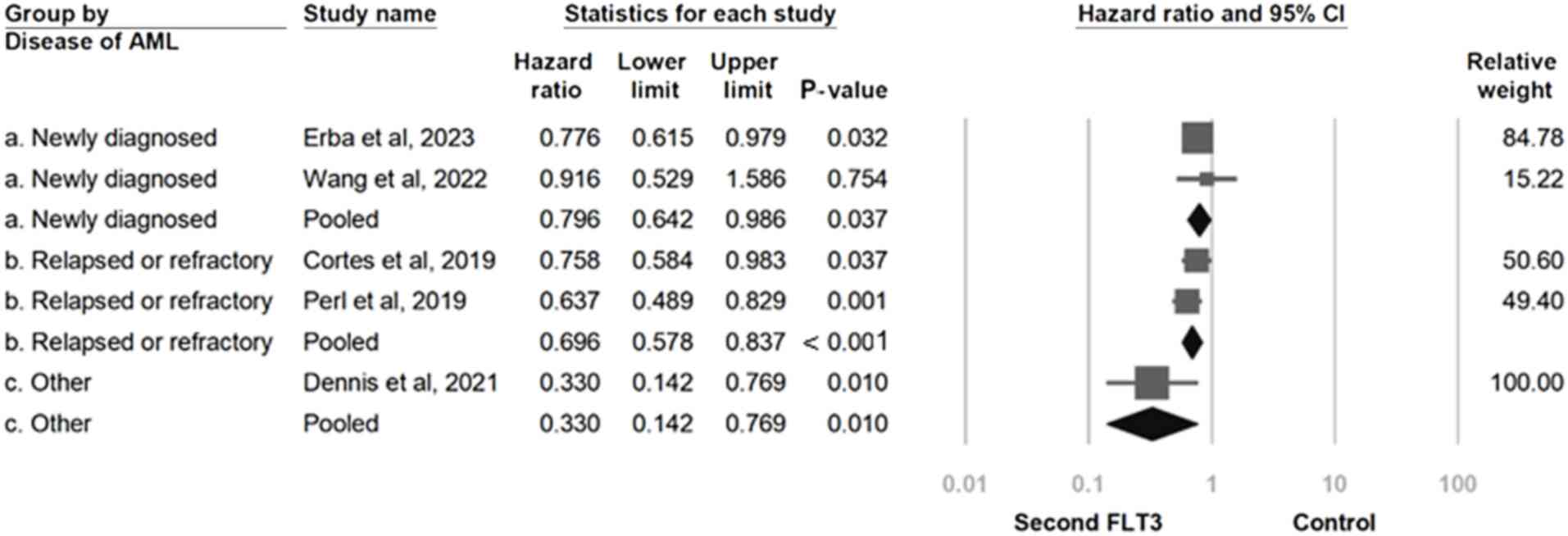
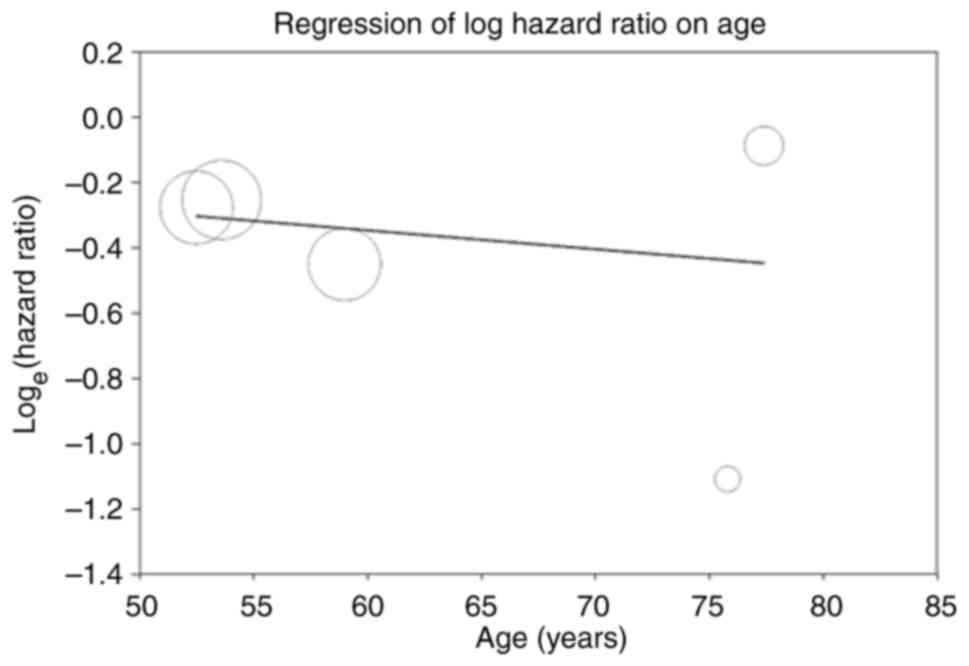
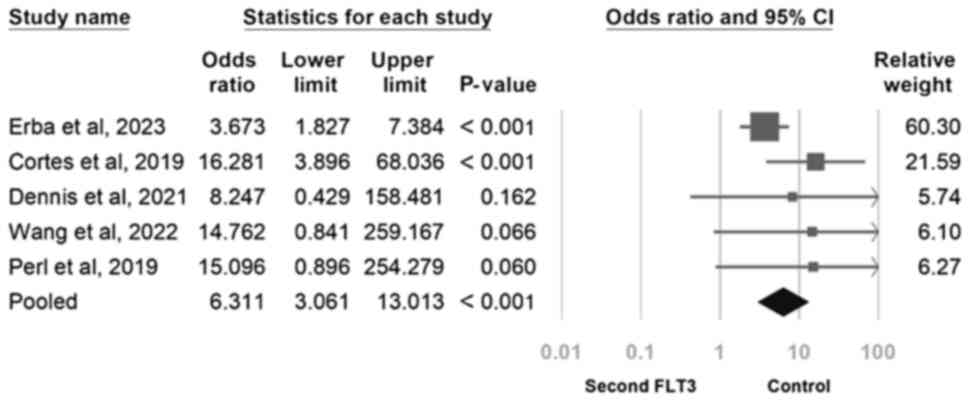
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia-acute myeloid
leukemia (AML). National Cancer Institute. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html.
Accessed on September 1, 2024.
|
|
3
|
DiNardo CD, Jonas BA, Pullarkat V, Thirman
MJ, Garcia JS, Wei AH, Konopleva M, Döhner H, Letai A, Fenaux P, et
al: Azacitidine and venetoclax in previously untreated acute
myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 383:617–629. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Daver N, Schlenk RF, Russell NH and Levis
MJ: Targeting FLT3 mutations in AML: Review of current knowledge
and evidence. Leukemia. 33:299–312. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kottaridis PD, Gale RE, Frew ME, Harrison
G, Langabeer SE, Belton AA, Walker H, Wheatley K, Bowen DT, Burnett
AK, et al: The presence of a FLT3 internal tandem duplication in
patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) adds important
prognostic information to cytogenetic risk group and response to
the first cycle of chemotherapy: Analysis of 854 patients from the
United Kingdom medical research council AML 10 and 12 trials.
Blood. 98:1752–1759. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Thiede C, Steudel C, Mohr B, Schaich M,
Schäkel U, Platzbecker U, Wermke M, Bornhäuser M, Ritter M,
Neubauer A, et al: Analysis of FLT3-activating mutations in 979
patients with acute myelogenous leukemia: Association with FAB
subtypes and identification of subgroups with poor prognosis.
Blood. 99:4326–4335. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Levis M: FLT3 mutations in acute myeloid
leukemia: What is the best approach in 2013? Hematology Am Soc
Hematol Educ Program. 2013:220–226. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wander SA, Levis MJ and Fathi AT: The
evolving role of FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia:
Quizartinib and beyond. Ther Adv Hematol. 5:65–77. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kennedy VE and Smith CC: FLT3 mutations in
acute myeloid leukemia: Key concepts and emerging controversies.
Front Oncol. 10(612880)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Schlenk RF, Döhner K, Krauter J, Fröhling
S, Corbacioglu A, Bullinger L, Habdank M, Späth D, Morgan M, Benner
A, et al: Mutations and treatment outcome in cytogenetically normal
acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 358:1909–1918.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Eguchi M, Minami Y, Kuzume A and Chi S:
Mechanisms underlying resistance to FLT3 inhibitors in acute
myeloid leukemia. Biomedicines. 8(245)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Larrosa-Garcia M and Baer MR: FLT3
inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia: Current status and future
directions. Mol Cancer Ther. 16:991–1001. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kampa-Schittenhelm KM, Heinrich MC, Akmut
F, Döhner H, Döhner K and Schittenhelm MM: Quizartinib (AC220) is a
potent second generation class III tyrosine kinase inhibitor that
displays a distinct inhibition profile against mutant-FLT3, -PDGFRA
and -KIT isoforms. Mol Cancer. 12(19)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tarver TC, Hill JE, Rahmat L, Perl AE,
Bahceci E, Mori K and Smith CC: Gilteritinib is a clinically active
FLT3 inhibitor with broad activity against FLT3 kinase domain
mutations. Blood Adv. 4:514–524. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ge SS, Liu SB and Xue SL: Developments and
challenges of FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia. Front
Oncol. 12(996438)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
The ASCO post: Tale of two FLT3 Inhibitors
in AML:Gilteritinib and quizartinib. https://ascopost.com/issues/april-25-2019/tale-of-two-flt3-inhibitors-in-aml-gilteritinib-and-quizartinib.
Accessed on September 5, 2024.
|
|
17
|
Mohebbi A, Shahriyary F, Farrokhi V,
Bandar B and Saki N: A systematic review of second-generation FLT3
inhibitors for treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory acute
myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 141(107505)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sterne JAC, Savović J, Page MJ, Elbers RG,
Blencowe NS, Boutron I, Cates CJ, Cheng HY, Corbett MS, Eldridge
SM, et al: RoB 2: A revised tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 366(l4898)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Verywell health: Event-free survival (EFS)
after treatment. https://www.verywellhealth.com/event-free-survival-efs-2252150.
Accessed on September 5, 2024.
|
|
20
|
Deeks JJ, Higgins JPT and Altman DG (eds):
Chapter 10: Analysing data and undertaking meta-analyses. In:
Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and
Welch VA (eds). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of
Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane,
2023.
|
|
21
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA,
Hoffmann TC, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline
for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Borenstein M, Hedges LV and Rothstein HR:
Fixed-effect versus random-effects models. In: Introduction to
Meta-Analysis. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ, 2009.
|
|
23
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Page MJ, Higgins JPT and Sterne JAC:
Chapter 13: Assessing risk of bias due to missing results in a
synthesis. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T,
Page MJ and Welch VA (eds). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic
Reviews of Interventions version 6.1 (updated September 2020).
Cochrane, 2020.
|
|
25
|
Sterne JAC, Sutton AJ, Ioannidis JPA,
Terrin N, Jones DR, Lau J, Carpenter J, Rücker G, Harbord RM,
Schmid CH, et al: Recommendations for examining and interpreting
funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomised controlled
trials. BMJ. 343(d4002)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cortes JE, Tallman MS, Schiller GJ, Trone
D, Gammon G, Goldberg SL, Perl AE, Marie JP, Martinelli G,
Kantarjian HM and Levis MJ: Phase 2b study of 2 dosing regimens of
quizartinib monotherapy in FLT3-ITD-mutated, relapsed or refractory
AML. Blood. 132:598–607. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
James AJ, Smith CC, Litzow M, Perl AE,
Altman JK, Shepard D, Kadokura T, Souda K, Patton M, Lu Z, et al:
Pharmacokinetic profile of gilteritinib: A novel FLT-3 tyrosine
kinase inhibitor. Clin Pharmacokinet. 59:1273–1290. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li J, Holmes M, Kankam M, Trone D, Mendell
J and Gammon G: Effect of food on the pharmacokinetics of
quizartinib. Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev. 9:277–286. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li J, Kankam M, Trone D and Gammon G:
Effects of CYP3A inhibitors on the pharmacokinetics of quizartinib,
a potent and selective FLT3 inhibitor, and its active metabolite.
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 85:2108–2117. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Li J, Trone D, Mendell J, O'Donnell P and
Cook N: A drug-drug interaction study to assess the potential
effect of acid-reducing agent, lansoprazole, on quizartinib
pharmacokinetics. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 84:799–807.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
No authors listed. Gilteritinib plus
azacitidine combination shows promise in newly diagnosed
FLT3-mutated AML. Oncologist. 26 (Suppl 1)(S10)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Jaramillo S, Le Cornet L, Kratzmann M,
Krisam J, Görner M, Hänel M, Röllig C, Wass M, Scholl S, Ringhoffer
M, et al: Q-HAM: A multicenter upfront randomized phase II trial of
quizartinib and high-dose Ara-C plus mitoxantrone in
relapsed/refractory AML with FLT3-ITD. Trials.
24(591)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hosono N, Yokoyama H, Aotsuka N, Ando K,
Iida H, Ishikawa T, Usuki K, Onozawa M, Kizaki M, Kubo K, et al:
Gilteritinib versus chemotherapy in Japanese patients with
FLT3-mutated relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Int J Clin
Oncol. 26:2131–2141. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Perl AE, Larson RA, Podoltsev NA,
Strickland S, Wang ES, Atallah E, Schiller GJ, Martinelli G,
Neubauer A, Wang ES, et al: Follow-up of patients with R/R
FLT3-mutation-positive AML treated with gilteritinib in the phase 3
ADMIRAL trial. Blood. 139:3366–3375. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Pulte ED, Norsworthy KJ, Wang Y, Xu Q,
Qosa H, Gudi R, Przepiorka D, Fu W, Okusanya OO, Goldberg KB, et
al: FDA approval summary: Gilteritinib for relapsed or refractory
acute myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. Clin Cancer Res.
27:3515–3521. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
NCT02927262: A Study of ASP2215
(Gilteritinib), administered as maintenance therapy following
induction/consolidation therapy for subjects with FMS-like tyrosine
kinase 3 (FLT3/ITD) acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in first complete
remission. Journal, 2022.
|
|
37
|
Cortes JE, Khaled S, Martinelli G, Perl
AE, Ganguly S, Russell N, Krämer A, Dombret H, Hogge D, Jonas BA,
et al: Quizartinib versus salvage chemotherapy in relapsed or
refractory FLT3-ITD acute myeloid leukaemia (QuANTUM-R): A
multicentre, randomised, controlled, open-label, phase 3 trial.
Lancet Oncol. 20:984–997. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dennis M, Thomas IF, Ariti C, Upton L,
Burnett AK, Gilkes A, Radia R, Hemmaway C, Mehta P, Knapper S, et
al: Randomized evaluation of quizartinib and low-dose ara-C vs
low-dose ara-C in older acute myeloid leukemia patients. Blood Adv.
5:5621–5625. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Erba HP, Montesinos P, Kim HJ, Patkowska
E, Vrhovac R, Žák P, Wang PN, Mitov T, Hanyok J, Kamel YM, et al:
Quizartinib plus chemotherapy in newly diagnosed patients with
FLT3-internal-tandem-duplication-positive acute myeloid leukaemia
(QuANTUM-First): A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
phase 3 trial. Lancet. 401:1571–1583. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Perl AE, Martinelli G, Cortes JE, Neubauer
A, Berman E, Paolini S, Montesinos P, Baer MR, Larson RA, Ustun C,
et al: Gilteritinib or chemotherapy for relapsed or refractory
FLT3-mutated AML. N Engl J Med. 381:1728–1740. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wang ES, Montesinos P, Minden MD, Lee JH,
Heuser M, Naoe T, Chou WC, Laribi K, Esteve J, Altman JK, et al:
Phase 3 trial of gilteritinib plus azacitidine vs azacitidine for
newly diagnosed FLT3mut+ AML ineligible for intensive chemotherapy.
Blood. 140:1845–1857. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hedges LV: Distribution theory for glass's
estimator of effect size and related estimators. J Educ Stat.
6:107–128. 1981.
|
|
43
|
Majothi S, Adams D, Loke J, Stevens SP,
Wheatley K and Wilson JS: FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid
leukaemia: Assessment of clinical effectiveness, adverse events and
future research-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst Rev.
9(285)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Carow CE, Levenstein M, Kaufmann SH, Chen
J, Amin S, Rockwell P, Witte L, Borowitz MJ, Civin CI and Small D:
Expression of the hematopoietic growth factor receptor FLT3
(STK-1/Flk2) in human leukemias. Blood. 87:1089–1096.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Papaemmanuil E, Gerstung M, Bullinger L,
Gaidzik VI, Paschka P, Roberts ND, Potter NE, Heuser M, Thol F,
Bolli N, et al: Genomic classification and prognosis in acute
myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 374:2209–2221. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Nakao M, Yokota S, Iwai T, Kaneko H,
Horiike S, Kashima K, Sonoda Y, Fujimoto T and Misawa S: Internal
tandem duplication of the flt3 gene found in acute myeloid
leukemia. Leukemia. 10:1911–1918. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yamamoto Y, Kiyoi H, Nakano Y, Suzuki R,
Kodera Y, Miyawaki S, Asou N, Kuriyama K, Yagasaki F, Shimazaki C,
et al: Activating mutation of D835 within the activation loop of
FLT3 in human hematologic malignancies. Blood. 97:2434–2439.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Abu-Duhier FM, Goodeve AC, Wilson GA, Care
RS, Peake IR and Reilly JT: Identification of novel FLT-3 Asp835
mutations in adult acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Haematol.
113:983–988. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Inc. AP: Xospata (gilteritinib) tablets
package insert. https://astellas.us/docs/xospata.pdf. Accessed on
October 4, 2024.
|
|
50
|
Lee LY, Hernandez D, Rajkhowa T, Smith SC,
Raman JR, Nguyen B, Small D and Levis M: Preclinical studies of
gilteritinib, a next-generation FLT3 inhibitor. Blood. 129:257–260.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Mori M, Kaneko N, Ueno Y, Yamada M, Tanaka
R, Saito R, Shimada I, Mori K and Kuromitsu S: Gilteritinib, a
FLT3/AXL inhibitor, shows antileukemic activity in mouse models of
FLT3 mutated acute myeloid leukemia. Invest New Drugs. 35:556–565.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Benmimoun B and Spéder P: Breaking down
barriers: Tumors make a leaky brain. Dev Cell. 56:2683–2685.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Slominski RM, Raman C, Chen JY and
Slominski AT: How cancer hijacks the body's homeostasis through the
neuroendocrine system. Trends Neurosci. 46:263–275. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Ruglioni M, Crucitta S, Luculli GI,
Tancredi G, Del Giudice ML, Mechelli S, Galimberti S, Danesi R and
Del Re M: Understanding mechanisms of resistance to FLT3 inhibitors
in adult FLT3-mutated acute myeloid leukemia to guide treatment
strategy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 201(104424)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Takahashi S: Downstream molecular pathways
of FLT3 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia: Biology and
therapeutic implications. J Hematol Oncol. 4(13)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Ballesta-López O, Solana-Altabella A,
Megías-Vericat JE, Martínez-Cuadrón D and Montesinos P:
Gilteritinib use in the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute
myeloid leukemia with a FLT3 mutation. Future Oncol. 17:215–227.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Novatcheva ED, Anouty Y, Saunders I,
Mangan JK and Goodman AM: FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 inhibitors for
the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma
Leuk. 22:e161–e184. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wiśniowska B, Tylutki Z, Wyszogrodzka G
and Polak S: Drug-drug interactions and QT prolongation as a
commonly assessed cardiac effect-comprehensive overview of clinical
trials. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol. 17(12)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kang D, Ludwig E, Jaworowicz D, Huang H,
Fiedler-Kelly J, Cortes J, Ganguly S, Khaled S, Krämer A, Levis M,
et al: Concentration-QTc analysis of quizartinib in patients with
relapsed/refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 87:513–523. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Baracaldo-Santamaría D, Llinás-Caballero
K, Corso-Ramirez JM, Restrepo CM, Dominguez-Dominguez CA,
Fonseca-Mendoza DJ and Calderon-Ospina CA: Genetic and molecular
aspects of drug-induced QT interval prolongation. Int J Mol Sci.
22(8090)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Suknuntha K, Choi YJ, Jung HS, Majumder A,
Shah S, Slukvin I and Ranheim EA: Megakaryocytic expansion in
gilteritinib-treated acute myeloid leukemia patients is associated
with AXL inhibition. Front Oncol. 10(585151)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Higgins JPT, Eldridge S and Li T: Chapter
23: Including variants on randomized trials [last updated October
2019]. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T,
Page MJ and Welch VA (eds). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic
Reviews of Interventions version 6.5. Cochrane, 2024.
|
|
63
|
Higgins JPT, Li T and Deeks JJ (eds):
Chapter 6: Choosing effect measures and computing estimates of
effect [last updated August 2023]. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J,
Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ and Welch VA (ed). Cochrane
Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.5.
Cochrane, 2024.
|