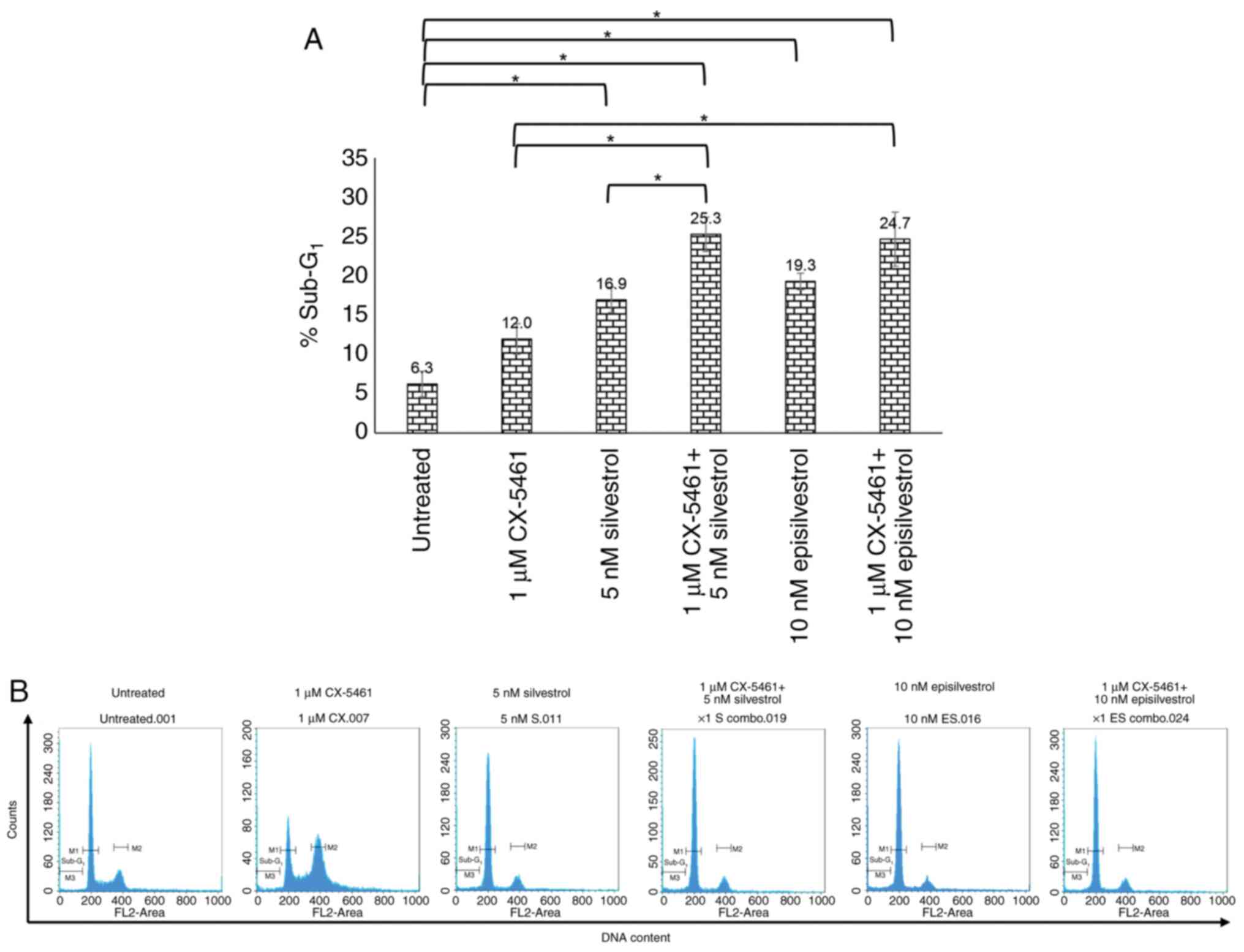
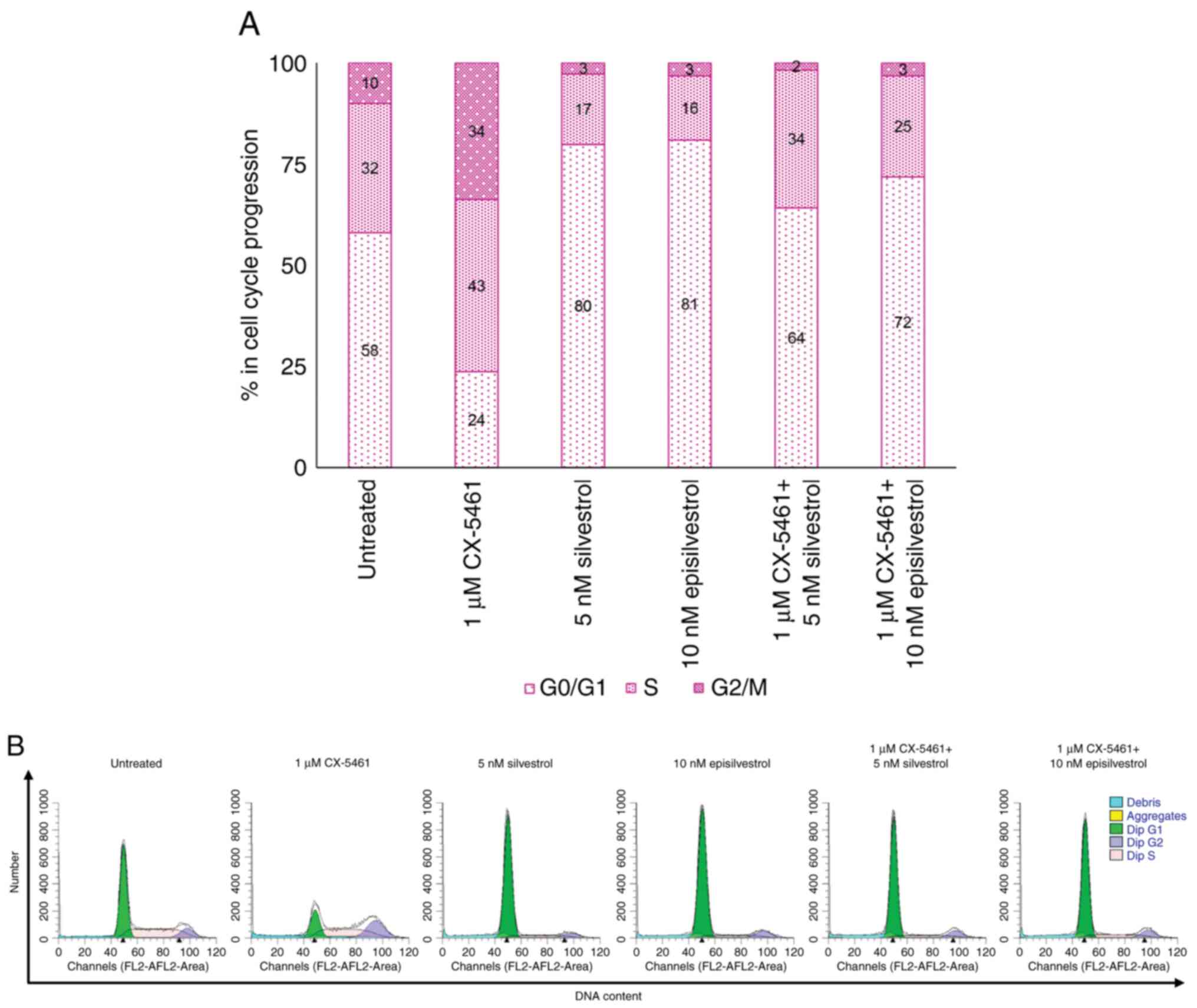
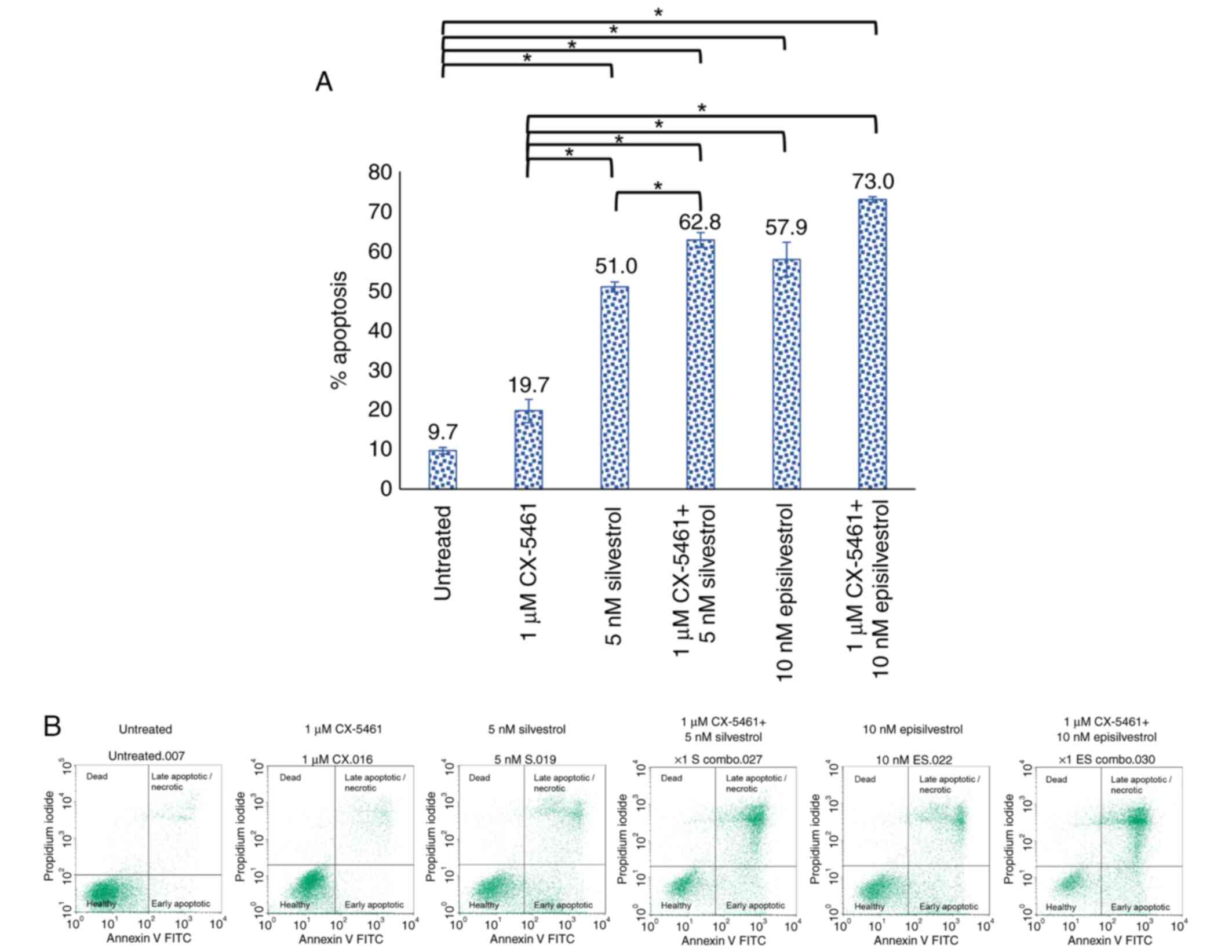
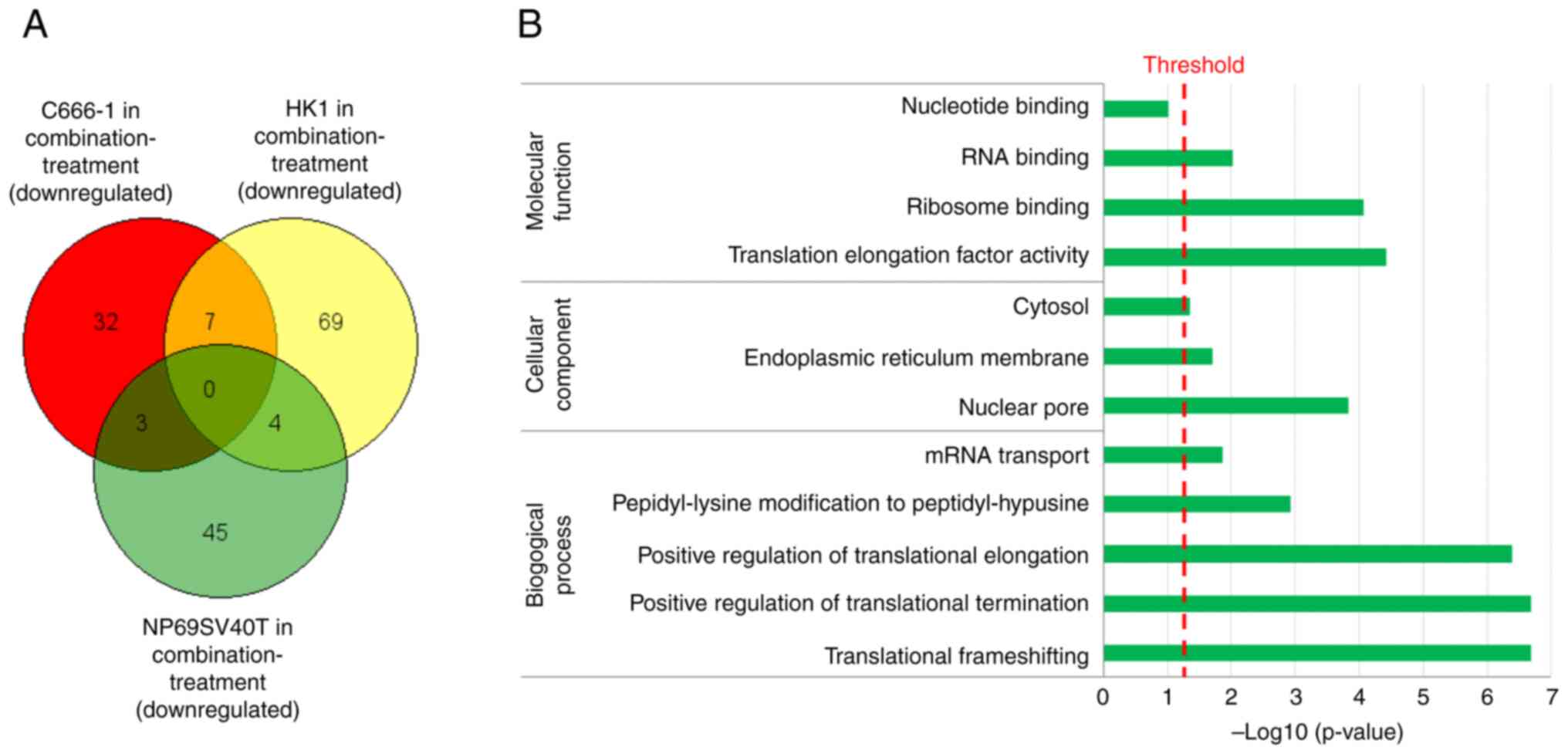
|
1
|
Malaysia National Cancer Registry Report
2012-2016. National Cancer Institute, Ministry of Health Malaysia,
Malaysia, 2019.
|
|
2
|
Epidemiology of Cancer in Sarawak
2007-2011. Sarawak Cancer Registry, Malaysia, 2017.
|
|
3
|
Lung ML: Unlocking the Rosetta Stone
enigma for nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Genetics, viral infection, and
epidemiological factors. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:77–78.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tan LP, Tan GW, Sivanesan VM, Goh SL, Ng
XJ, Lim CS, Kim WR, Mohidin TBBM, Mohd Dali NS, Ong SH, et al:
Systematic comparison of plasma EBV DNA, anti-EBV antibodies and
miRNA levels for early detection and prognosis of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 146:2336–2347. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Linton RE, Daker M, Khoo ASB, Choo DCY,
Viljoen M and Neilsen PM: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma among the
Bidayuh of Sarawak, Malaysia: History and risk factors. Oncol Lett.
22(514)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Clinical Practice Guidelines Management of
Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Malaysia Health Technology Assessment
Section (MaHTAS), Ministry of Health Malaysia, Malaysia, 2016.
|
|
8
|
Lee AWM, Ma BBY, Ng WT and Chan ATC:
Management of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Current practice and future
perspective. J Clin Oncol. 33:3356–3364. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Malaysian Study on Cancer Survival
(MySCan). National Cancer Registry, National Cancer Institute,
Ministry of Health Malaysia, Malaysia, 2018.
|
|
10
|
Pannell CM: Aglaia. In: Soepadmo E,
Saw LG, Chung RCK and Kiew R (eds). Tree Flora of Sabah and Sarawak
Volume Six. Vol. 6. Sabah Forestry Department, Forest Research
Institute Malaysia (FRIM), Sarawak Forestry Department, Malaysia,
pp24-99, 2007.
|
|
11
|
Henkin JM, Ren Y, Soejarto DD and Kinghorn
AD: The search for anticancer agents from tropical plants. Prog
Chem Org Nat Prod. 107:1–94. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Robert F, Carrier M, Rawe S, Chen S, Lowe
S and Pelletier J: Altering chemosensitivity by modulating
translation elongation. PLoS One. 4(e5428)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Patton JT, Lustberg ME, Lozanski G, Garman
SL, Towns WH, Drohan CM, Lehman A, Zhang X, Bolon B, Pan L, et al:
The translation inhibitor silvestrol exhibits direct anti-tumor
activity while preserving innate and adaptive immunity against
EBV-driven lymphoproliferative disease. Oncotarget. 6:2693–2708.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lucas DM, Edwards RB, Lozanski G, West DA,
Shin JD, Vargo MA, Davis ME, Rozewski DM, Johnson AJ, Su BN, et al:
The novel plant-derived agent silvestrol has B-cell selective
activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and acute lymphoblastic
leukemia in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 113:4656–4666.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kogure T, Kinghorn AD, Yan I, Bolon B,
Lucas DM, Grever MR and Patel T: Therapeutic potential of the
translation inhibitor silvestrol in hepatocellular cancer. PLoS
One. 8(e76136)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cencic R, Carrier M, Trnkus A, Porco JA,
Minden M and Pelletier J: Synergistic effect of inhibiting
translation initiation in combination with cytotoxic agents in
acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leuk Res. 34:535–541.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cencic R, Carrier M, Galicia-Vázquez G,
Bordeleau ME, Sukarieh R, Bourdeau A, Brem B, Teodoro JG, Greger H,
Tremblay ML, et al: Antitumor activity and mechanism of action of
the cyclopenta[b]benzofuran, silvestrol. PLoS One.
4(e5223)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bordeleau ME, Robert F, Gerard B,
Lindqvist L, Chen SM, Wendel HG, Brem B, Greger H, Lowe SW, Porco
JA Jr and Pelletier J: Therapeutic suppression of translation
initiation modulates chemosensitivity in a mouse lymphoma model. J
Clin Invest. 118:2651–2660. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Alinari L, Prince CJ, Edwards RB, Towns
WH, Mani R, Lehman A, Zhang X, Jarjoura D, Pan L, Kinghorn AD, et
al: Dual targeting of the cyclin/Rb/E2F and mitochondrial pathways
in mantle cell lymphoma with the translation inhibitor silvestrol.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:4600–4611. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Pan L, Woodard JL, Lucas DM, Fuchs JR and
Kinghorn AD: Rocaglamide, silvestrol and structurally related
bioactive compounds from Aglaia species. Nat Prod Rep.
31:924–939. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Haddach M, Schwaebe MK, Michaux J,
Nagasawa J, O'Brien SE, Whitten JP, Pierre F, Kerdoncuff P,
Darjania L, Stansfield R, et al: Discovery of CX-5461, the first
direct and selective inhibitor of RNA polymerase I, for cancer
therapeutics. ACS Med Chem Lett. 3:602–606. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bywater MJ, Poortinga G, Sanij E, Hein N,
Peck A, Cullinane C, Wall M, Cluse L, Drygin D, Anderes K, et al:
Inhibition of RNA polymerase i as a therapeutic strategy to promote
cancer-specific activation of p53. Cancer Cell. 22:51–65.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Drygin D, Lin A, Bliesath J, Ho CB,
O'Brien SE, Proffitt C, Omori M, Haddach M, Schwaebe MK,
Siddiqui-Jain A, et al: Targeting RNA polymerase I with an oral
small molecule CX-5461 inhibits ribosomal RNA synthesis and solid
tumor growth. Cancer Res. 71:1418–1430. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Khot A, Brajanovski N, Cameron DP, Hein N,
Maclachlan KH, Sanij E, Lim J, Soong J, Link E, Blombery P, et al:
First-in-human RNA polymerase I transcription inhibitor CX-5461 in
patients with advanced hematologic cancers: Results of a phase I
dose-escalation study. Cancer Discov. 9:1036–1049. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Daker M, Yeo JT, Bakar N, Abdul Rahman AS,
Ahmad M, Yeo TC and Khoo AS: Inhibition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cell proliferation and synergism of cisplatin with silvestrol and
episilvestrol isolated from Aglaia stellatopilosa. Exp Ther
Med. 11:2117–2126. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cheung ST, Huang DP, Hui AB, Lo KW, Ko CW,
Tsang YS, Wong N, Whitney BM and Lee JC: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cell line (C666-1) consistently harbouring Epstein-Barr virus. Int
J Cancer. 83:121–126. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Huang DP, Ho JH, Poon YF, Chew EC, Saw D,
Lui M, Li CL, Mak LS, Lai SH and Lau WH: Establishment of a cell
line (NPC/HK1) from a differentiated squamous carcinoma of the
nasopharynx. Int J Cancer. 26:127–132. 1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tsao SW, Wang X, Liu Y, Cheung YC, Feng H,
Zheng Z, Wong N, Yuen PW, Lo AK, Wong YC and Huang DP:
Establishment of two immortalized nasopharyngeal epithelial cell
lines using SV40 large T and HPV16E6/E7 viral oncogenes. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1590:150–158. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li HM, Man C, Jin Y, Deng W, Yip YL, Feng
HC, Cheung YC, Lo KW, Meltzer PS, Wu ZG, et al: Molecular and
cytogenetic changes involved in the immortalization of
nasopharyngeal epithelial cells by telomerase. Int J Cancer.
119:1567–1576. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chan SYY, Choy KW, Tsao SW, Tao Q, Tang T,
Chung GT and Lo KW: Authentication of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
tumor lines. Int J Cancer. 122:2169–2171. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Daker M, Jayaweera U, Marzuki M,
Gunasegaran G, Chew YL, Ahmad M and Akowuah G: Content of luteolin
and luteolin-7-О-glucoside from the leaves of Vernonia amygdalina
Del., and synergistic inhibitory effect with cisplatin on
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Chem Data Collect.
45(101039)2023.
|
|
32
|
Chou TC: Theoretical basis, experimental
design, and computerized simulation of synergism and antagonism in
drug combination studies. Pharmacol Rev. 58:621–681.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Teow SY, Liew K, Che Mat MF, Marzuki M,
Abdul Aziz N, Chu TL, Ahmad M and Khoo AS: Development of a
luciferase/luciferin cell proliferation (XenoLuc) assay for
real-time measurements of Gfp-Luc2-modified cells in a co-culture
system. BMC Biotechnol. 19(34)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sherman BT, Hao M, Qiu J, Jiao X, Baseler
MW, Lane HC, Imamichi T and Chang W: DAVID: A web server for
functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene
lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (W1):W216–W221.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Pirooznia M, Nagarajan V and Deng Y:
GeneVenn-A web application for comparing gene lists using Venn
diagrams. Bioinformation. 1:420–422. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Northcott PA: Cancer: Keeping it real to
kill glioblastoma. Nature. 547:291–292. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Willyard C: The mice with human tumours:
Growing pains for a popular cancer model. Nature. 560:156–157.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pompili L, Porru M, Caruso C, Biroccio A
and Leonetti C: Patient-derived xenografts: A relevant preclinical
model for drug development. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
35(189)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Pucci B, Kasten M and Giordano A: Cell
cycle and apoptosis. Neoplasia. 2:291–299. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Giacinti C and Giordano A: RB and cell
cycle progression. Oncogene. 25:5220–5227. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hui ABY, Or YYY, Takano H, Tsang RKY, To
KF, Guan XY, Sham JST, Hung KWK, Lam CN, van Hasselt CA, et al:
Array-based comparative genomic hybridization analysis identified
cyclin D1 as a target oncogene at 11q13.3 in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Cancer Res. 65:8125–8133. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Baloche V, Ferrand FR, Makowska A, Even C,
Kontny U and Busson P: Emerging therapeutic targets for
nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin
Ther Targets. 24:545–558. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Tsang CM, Yip YL, Lo KW, Deng W, To KF,
Hau PM, Lau VM, Takada K, Lui VW, Lung ML, et al: Cyclin D1
overexpression supports stable EBV infection in nasopharyngeal
epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:E3473–E3482.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Obaya AJ, Mateyak MK and Sedivy JM:
Mysterious liaisons: The relationship between c-Myc and the cell
cycle. Oncogene. 18:2934–2941. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Whitfield JR, Beaulieu ME and Soucek L:
Strategies to inhibit Myc and their clinical applicability. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 5(10)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wiegering A, Uthe FW, Jamieson T, Ruoss Y,
Hüttenrauch M, Küspert M, Pfann C, Nixon C, Herold S, Walz S, et
al: Targeting translation initiation bypasses signaling crosstalk
mechanisms that maintain high MYC levels in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Discov. 5:768–781. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Coller HA, Grandori C, Tamayo P, Colbert
T, Lander ES, Eisenman RN and Golub TR: Expression analysis with
oligonucleotide microarrays reveals that MYC regulates genes
involved in growth, cell cycle, signaling, and adhesion. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 97:3260–3265. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Levine AJ: p53, the cellular gatekeeper
for growth and division. Cell. 88:323–331. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Carvalho-Silva D, Pierleoni A, Pignatelli
M, Ong C, Fumis L, Karamanis N, Carmona M, Faulconbridge A,
Hercules A, McAuley E, et al: Open targets platform: New
developments and updates two years on. Nucleic Acids Res. 47
(D1):D1056–D1065. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Mathews MB and Hershey JWB: The
translation factor eIF5A and human cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1849:836–844. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Li AL, Li HY, Jin BF, Ye QN, Zhou T, Yu
XD, Pan X, Man JH, He K, Yu M, et al: A novel eIF5A complex
functions as a regulator of p53 and p53-dependent apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 279:49251–49258. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Mandal A, Mandal S and Park MH: Global
quantitative proteomics reveal up-regulation of endoplasmic
reticulum stress response proteins upon depletion of eIF5A in HeLa
cells. Sci Rep. 6(25795)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Hanauske-Abel HM, Park MH, Hanauske AR,
Popowicz AM, Lalande M and Folk JE: Inhibition of the G1-S
transition of the cell cycle by inhibitors of deoxyhypusine
hydroxylation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1221:115–124. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|