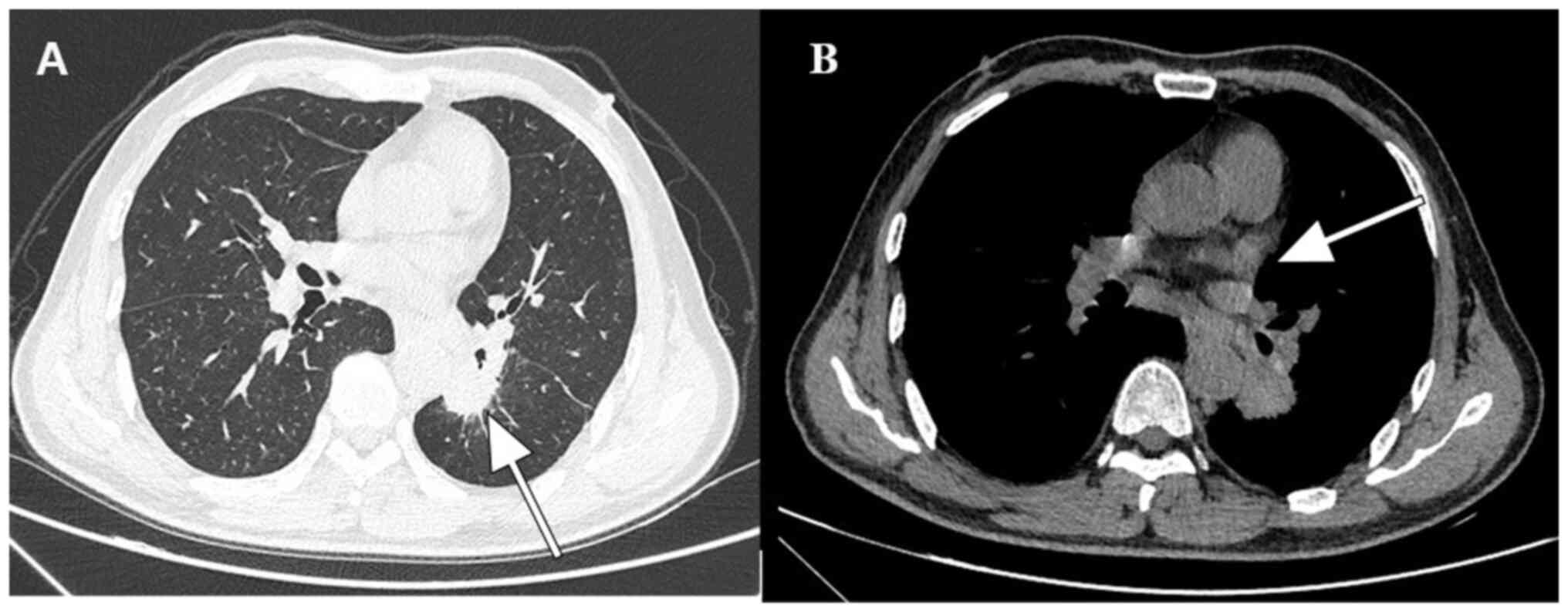
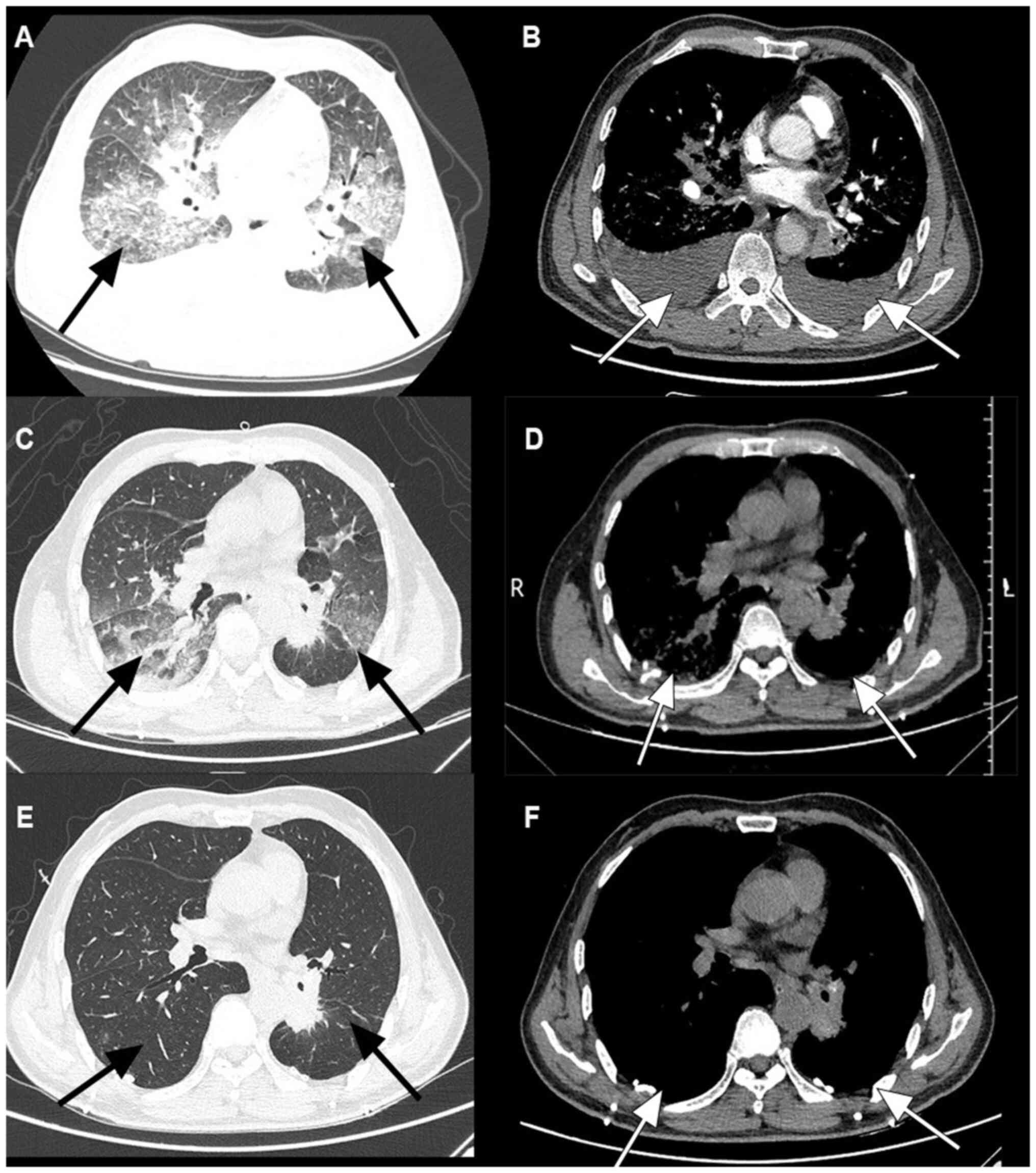
|
1
|
Balata H, Fong KM, Hendriks LE, Lam S,
Ostroff JS, Peled N, Wu N and Aggarwal C: Prevention and early
detection for NSCLC: Advances in thoracic oncology 2018. J Thorac
Oncol. 14:1513–1527. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hendriks LEL, Remon J, Faivre-Finn C,
Garassino MC, Heymach JV, Kerr KM, Tan DSW, Veronesi G and Reck M:
Non-small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
10(71)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Shan L, Qiao Y, Ma L, Zhang X, Chen C, Xu
X, Li D, Qiu S, Xue X, Yu Y, et al: AuNPs/CNC nanocomposite with A
‘Dual Dispersion’ Effect for LDI-TOF MS analysis of intact proteins
in NSCLC serum exosomes. Adv Sci (Weinh).
11(e2307360)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Herbst RS, Morgensztern D and Boshoff C:
The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature.
553:446–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shi Y, Wu L, Ji Y, Chen G, Li B, Bi M,
Yang R, Miao L, Zhang G, Gao H, et al: Efficacy and safety of
limertinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for locally
advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer with
EGFR-sensitising mutation: A randomised, double-blind,
double-dummy, phase 3 trial. Lancet Respir Med. 13:677–686.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gibson AJW, D'Silva A, Elegbede AA, Tudor
RA, Dean ML, Bebb DG and Hao D: Impact of Asian ethnicity on
outcome in metastatic EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer. Asia
Pac J Clin Oncol. 15:343–352. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Velimirovic M, Brignola M, Chheng E, Smith
M and Hassan KA: Management of pulmonary toxicities associated with
systemic therapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Curr Treat Options
Oncol. 25:1297–1311. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Conte P, Ascierto PA, Patelli G, Danesi R,
Vanzulli A, Sandomenico F, Tarsia P, Cattelan A, Comes A, De
Laurentiis M, et al: Drug-induced interstitial lung disease during
cancer therapies: Expert opinion on diagnosis and treatment. ESMO
Open. 7(100404)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hotta K, Kiura K, Takigawa N, Yoshioka H,
Harita S, Kuyama S, Yonei T, Fujiwara K, Maeda T, Aoe K, et al:
Comparison of the incidence and pattern of interstitial lung
disease during erlotinib and gefitinib treatment in Japanese
Patients with non-small cell lung cancer: The Okayama lung cancer
study group experience. J Thorac Oncol. 5:179–184. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Riely GJ, Wood DE, Ettinger DS, Aisner DL,
Akerley W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, et
al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 4.2024, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
22:249–274. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Beom SH, Kim DW, Sim SH, Keam B, Park JH,
Lee JO, Kim TM, Lee SH and Heo DS: Gefitinib-induced interstitial
lung disease in Korean lung cancer patients. Cancer Res Treat.
48:88–97. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Matsuno O: Drug-induced interstitial lung
disease: Mechanisms and best diagnostic approaches. Respir Res.
13(39)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ohmori T, Yamaoka T, Ando K, Kusumoto S,
Kishino Y, Manabe R and Sagara H: Molecular and clinical features
of EGFR-TKI-associated lung injury. Int J Mol Sci.
22(792)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Park SC, Tan J, Wang X, Lederman D, Leader
JK, Kim SH and Zheng B: Computer-aided detection of early
interstitial lung diseases using low-dose CT images. Phys Med Biol.
56:1139–1153. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Miyagahara T, Fujimori N, Ueda K,
Takamatsu Y, Matsumoto K, Teramatsu K, Takaoka T, Suehiro Y,
Shimokawa Y, Omori K, et al: Incidence and appropriate management
of drug-induced interstitial lung disease in Japanese patients with
unresectable pancreatic cancer: A multicenter retrospective study.
Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 19:533–541. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Le T and Gerber DE: Newer-generation EGFR
inhibitors in lung cancer: How are they best used? Cancers (Basel).
11(336)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kawata T, Higashimori M, Itoh Y, Tomkinson
H, Johnson MG, Tang W, Nyberg F, Jiang H and Tanigawara Y:
Gefitinib exposure and occurrence of interstitial lung disease in
Japanese patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 83:849–858. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Taronna G, Leonetti A, Gustavo Dall'Olio
F, Rizzo A, Parisi C, Buti S, Bordi P, Brocchi S, Golfieri R,
Ardizzoni A, et al: Transient asymptomatic pulmonary opacities and
interstitial lung disease in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung
cancer treated with osimertinib. Tumori. 108:592–599.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gemma A, Kudoh S, Ando M, Ohe Y, Nakagawa
K, Johkoh T, Yamazaki N, Arakawa H, Inoue Y, Ebina M, et al: Final
safety and efficacy of erlotinib in the phase 4 POLARSTAR
surveillance study of 10708 Japanese patients with non-small-cell
lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 105:1584–1590. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Zhang X, Huang W and Ge X: The
role of heat shock proteins in the regulation of fibrotic diseases.
Biomed Pharmacother. 135(111067)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Namba T, Tanaka K, Hoshino T, Azuma A and
Mizushima T: Suppression of expression of heat shock protein 70 by
gefitinib and its contribution to pulmonary fibrosis. PLoS One.
6(e27296)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tanguy J, Pommerolle L, Garrido C, Kolb M,
Bonniaud P, Goirand F and Bellaye PS: Extracellular heat shock
proteins as therapeutic targets and biomarkers in fibrosing
interstitial lung diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 22(9316)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ishiguro Y, Ishiguro H and Miyamoto H:
Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibition
up-regulates interleukin-6 in cancer cells and induces subsequent
development of interstitial pneumonia. Oncotarget. 4:550–559.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fujita K, Hirose T, Kusumoto S, Sugiyama
T, Shirai T, Nakashima M, Akiyama Y and Sasaki Y: High exposure to
erlotinib and severe drug-induced interstitial lung disease in
patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 86:113–114.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Akamatsu H, Inoue A, Mitsudomi T,
Kobayashi K, Nakagawa K, Mori K, Nukiwa T, Nakanishi Y and Yamamoto
N: Interstitial lung disease associated with gefitinib in Japanese
patients with EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: Combined
analysis of two Phase III trials (NEJ 002 and WJTOG 3405). Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 43:664–668. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fontes ESM, Campainha S, Marques ID, Dinis
R, Inácio JR, Mendes JJ, Luís R, Ferreira AM, Racha-Pacheco R, Rolo
R, et al: Diagnosis and management of drug-induced interstitial
lung disease in the context of anti-cancer therapy: A
multidisciplinary viewpoint by portuguese experts. Clin Drug
Investig. 44:801–810. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kuo LC, Lin PC, Wang KF, Yuan MK and Chang
SC: Successful treatment of gefitinib-induced acute interstitial
pneumonitis with high-dose corticosteroid: A case report and
literature review. Med Oncol. 28:79–82. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lin X, Guo H, Zhao W, Li M, Lin G, Chu Q,
Chen E, Chen L, Chen R, Chu T, et al: Expert consensus on cancer
treatment-related lung injury. J Thorac Dis. 17:1844–1875.
2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zhang X, Li H, Zhu M and Zhang Y:
Re-administration of gefitinib following diffuse interstitial lung
disease in a patient with advanced lung adenocarcinoma: A case
report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 9:2419–2421.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nishioka N, Imai H, Endo M, Notsu A,
Doshita K, Igawa S, Yokouchi H, Ninomiya T, Tokito T, Soda S, et
al: Real-world data on subsequent therapy for first-line
osimertinib-induced pneumonitis: Safety of EGFR-TKI rechallenge
(Osi-risk Study TORG-TG2101). Target Oncol. 19:423–433.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kiriu T, Tamura D, Tachihara M, Sekiya R,
Hazama D, Katsurada M, Nakata K, Nagano T, Yamamoto M, Kamiryo H,
et al: Successful osimertinib rechallenge with steroid therapy
after osimertinib-induced interstitial lung disease. Intern Med.
57:91–95. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shibaki R, Ozawa Y, Noguchi S, Murakami Y,
Takase E, Azuma Y, Maebeya M, Sugimoto T, Hayata A, Hayakawa T, et
al: Impact of pre-existing interstitial lung abnormal shadow on
lung injury development and severity in patients of non-small cell
lung cancer treated with osimertinib. Cancer Med. 11:3743–3750.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Endo M, Johkoh T, Kimura K and Yamamoto N:
Imaging of gefitinib-related interstitial lung disease:
Multi-institutional analysis by the West Japan thoracic oncology
group. Lung Cancer. 52:135–140. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|