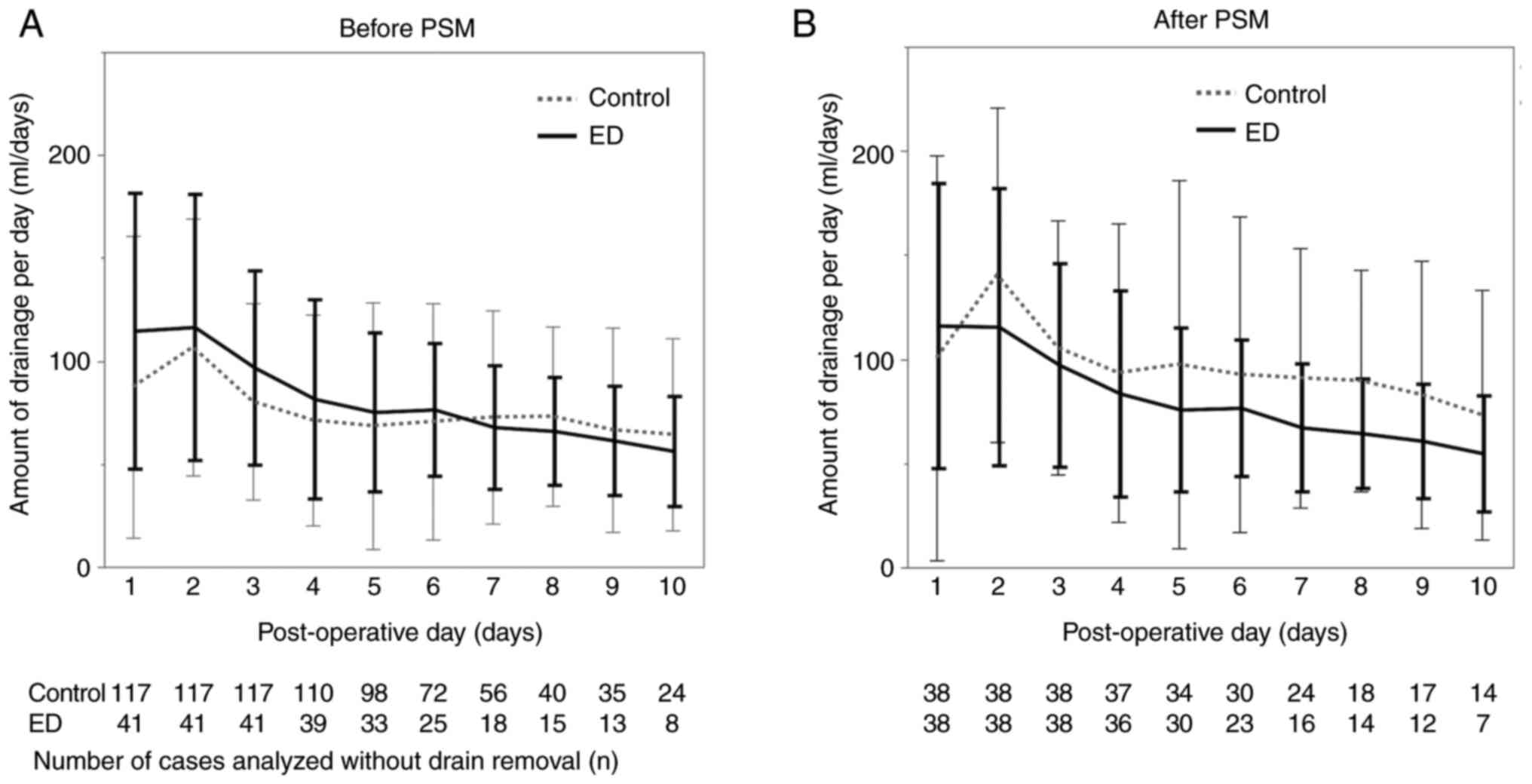
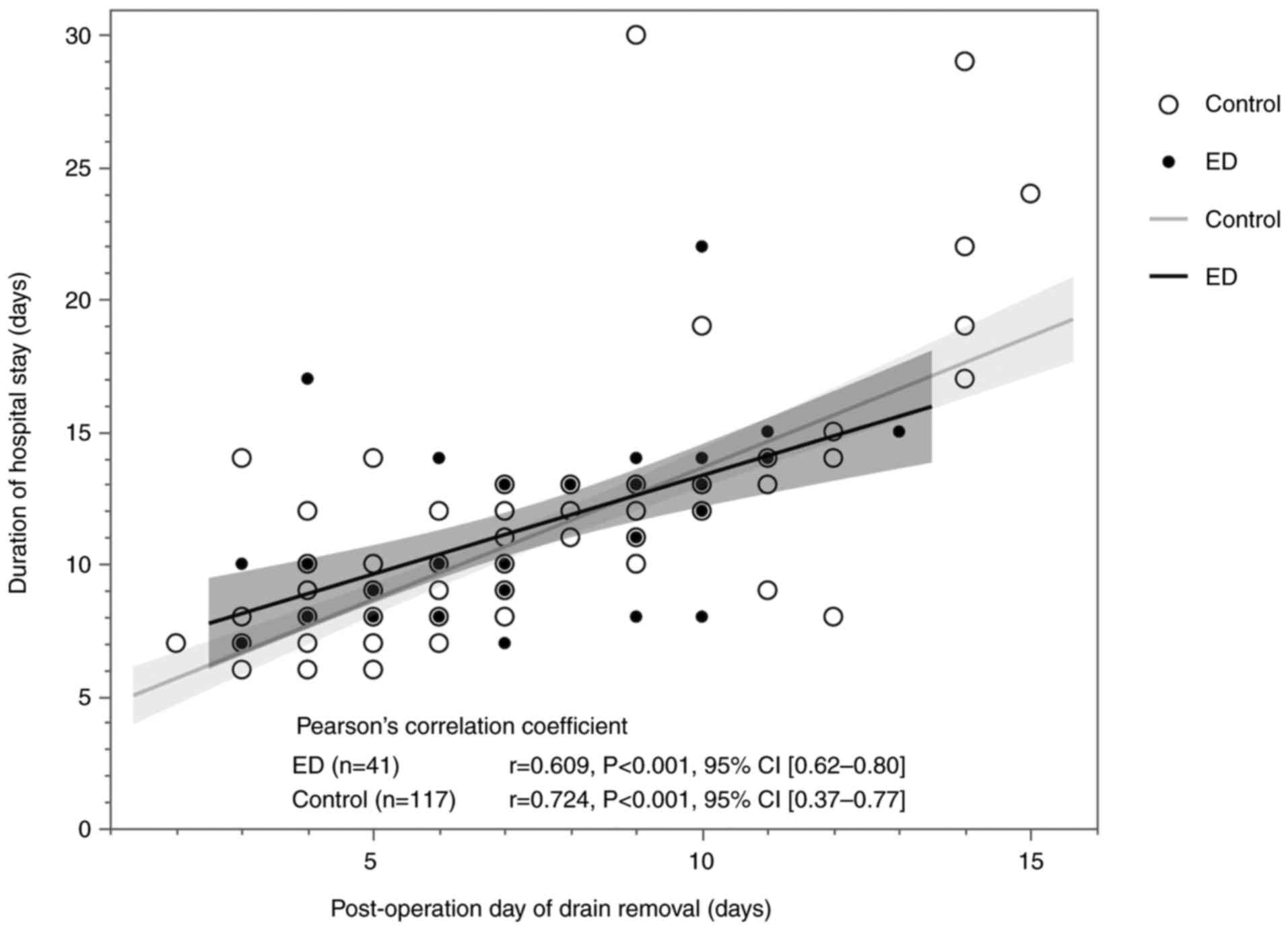
|
1
|
Zhang-Petersen C, Sowden M, Chen J, Burns
J and Sprague BL: Changes to the US preventive services task force
screening guidelines and incidence of breast cancer. JAMA Netw
Open. 7(e2452688)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shima H, Kutomi G, Sato K, Kuga Y, Wada A,
Satomi F, Uno S, Nisikawa N, Kameshima H, Ohmura T, et al: An
optimal timing for removing a drain after breast surgery: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Surg Res. 267:267–273.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dalberg K, Johansson H, Signomklao T,
Rutqvist LE, Bergkvist L, Frisell J, Liljegren G, Ambre T and
Sandelin K: A randomized study of axillary drainage and pectoral
fascia preservation after mastectomy for breast cancer. Eur J Surg
Oncol. 30:602–609. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ackroyd R and Reed MWR: A prospective
randomized trial of the management of suction drains following
breast cancer surgery with axillary clearance. The Breast.
6:271–274. 1997.
|
|
5
|
Gupta R, Pate K, Varshney S, Goddard J and
Royle GT: A comparison of 5-day and 8-day drainage following
mastectomy and axillary clearance. Eur J Surg Oncol. 27:26–30.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Peeters MJ, Kluit AB, Merkus JW and
Breslau PJ: Short versus long-term postoperative drainage of the
axilla after axillary lymph node dissection. A prospective
randomized study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 93:271–275.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Seenivasagam RK, Gupta V and Singh G:
Prevention of seroma formation after axillary dissection-a
comparative randomized clinical trial of three methods. Breast J.
19:478–484. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Seki T, Hayashida T, Takahashi M, Jinno H
and Kitagawa Y: A randomized controlled study comparing a vessel
sealing system with the conventional technique in axillary lymph
node dissection for primary breast cancer. Springerplus.
5(1004)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Cheng H, Clymer JW, Ferko NC, Patel L,
Soleas IM, Cameron CG and Hinoul P: A systematic review and
meta-analysis of Harmonic technology compared with conventional
techniques in mastectomy and breast-conserving surgery with
lymphadenectomy for breast cancer. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press).
8:125–140. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Alharran AM, Alenezi YY, Hammoud SM,
Alshammari B, Alrashidi M, Alyaqout FB, Almarri A, Alharran YM,
Alazemi MH, Allafi F and Al*Sadder KA: Efficacy of ligasure versus
harmonic devices in laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Cureus. 16(e57478)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gruber RP, Kahn RA, Lash H, Maser MR,
Apfelberg DB and Laub DR: Breast reconstruction following
mastectomy: A comparison of submuscular and subcutaneous
techniques. Plast Reconstr Surg. 67:312–317. 1981.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Baek WY, Byun IH, Kim YS, Jung BK, Yun IS
and Roh TS: Variance of the pectoralis major in relation to the
inframammary fold and the pectoralis minor and its application to
breast surgery. Clin Anat. 30:357–361. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Cieśla1 S, Wichtowski M, Poźniak-Balicka R
and Murawa D: The surgical anatomy of the mammary gland:
Vascularization, innervation, lymphatic drainage, the structure of
the axillary fossa (part 2.). J Oncol. 71:62–69. 2021.
|
|
14
|
He XD, Guo ZH, Tian JH, Yang KH and Xie
XD: Whether drainage should be used after surgery for breast
cancer? A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Med
Oncol. 28 (Suppl 1):S22–S30. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Droeser RA, Frey DM, Oertli D, Kopelman D,
Peeters MJ, Giuliano AE, Dalberg K, Kallam R and Nordmann A:
Volume-controlled vs no/short-term drainage after axillary lymph
node dissection in breast cancer surgery: A meta-analysis. Breast.
18:109–114. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Kennedy JS, Stranahan PL, Taylor KD and
Chandler JG: High-burst-strength, feedback-controlled bipolar
vessel sealing. Surg Endosc. 12:876–878. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Timm RW, Asher RM, Tellio KR, Welling AL,
Clymer JW and Amaral JF: Sealing vessels up to 7 mm in diameter
solely with ultrasonic technology. Med Devices (Auckl). 7:263–271.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Parikh HK, Badwe RA, Ash CM, Hamed H,
Freitas R Jr, Chaudary MA and Fentiman IS: Early drain removal
following modified radical mastectomy: a randomized trial. J Surg
Oncol. 51:266–269. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kopelman D, Klemm O, Bahous H, Klein R,
Krausz M and Hashmonai M: Postoperative suction drainage of the
axilla: For how long? Prospective randomised trial. Eur J Surg.
165:117–120. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Clegg-Lamptey JN, Dakubo JC and Hodasi WM:
Comparison of four-day and ten-day post-mastectomy passive drainage
in Accra, Ghana. East Afr Med J. 84:561–565. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|