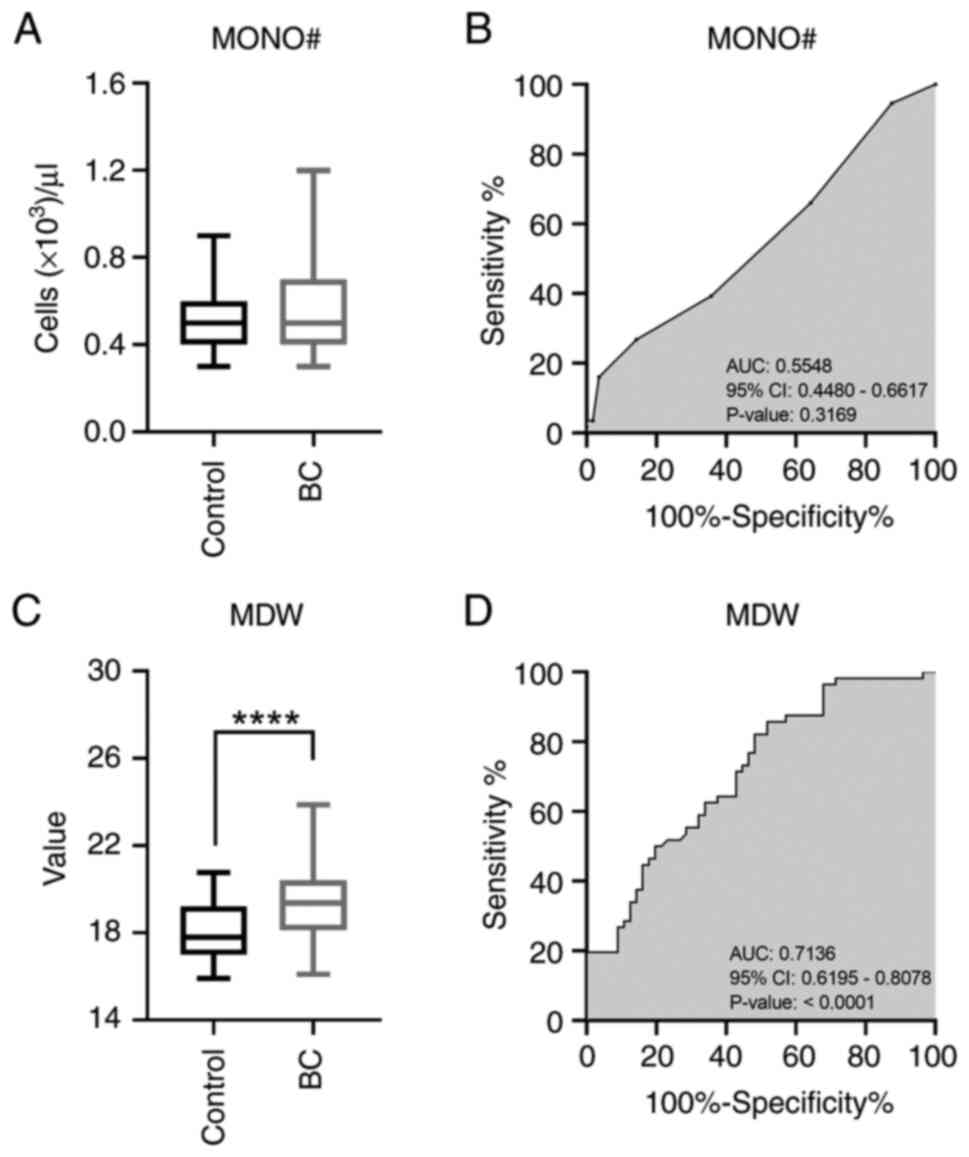
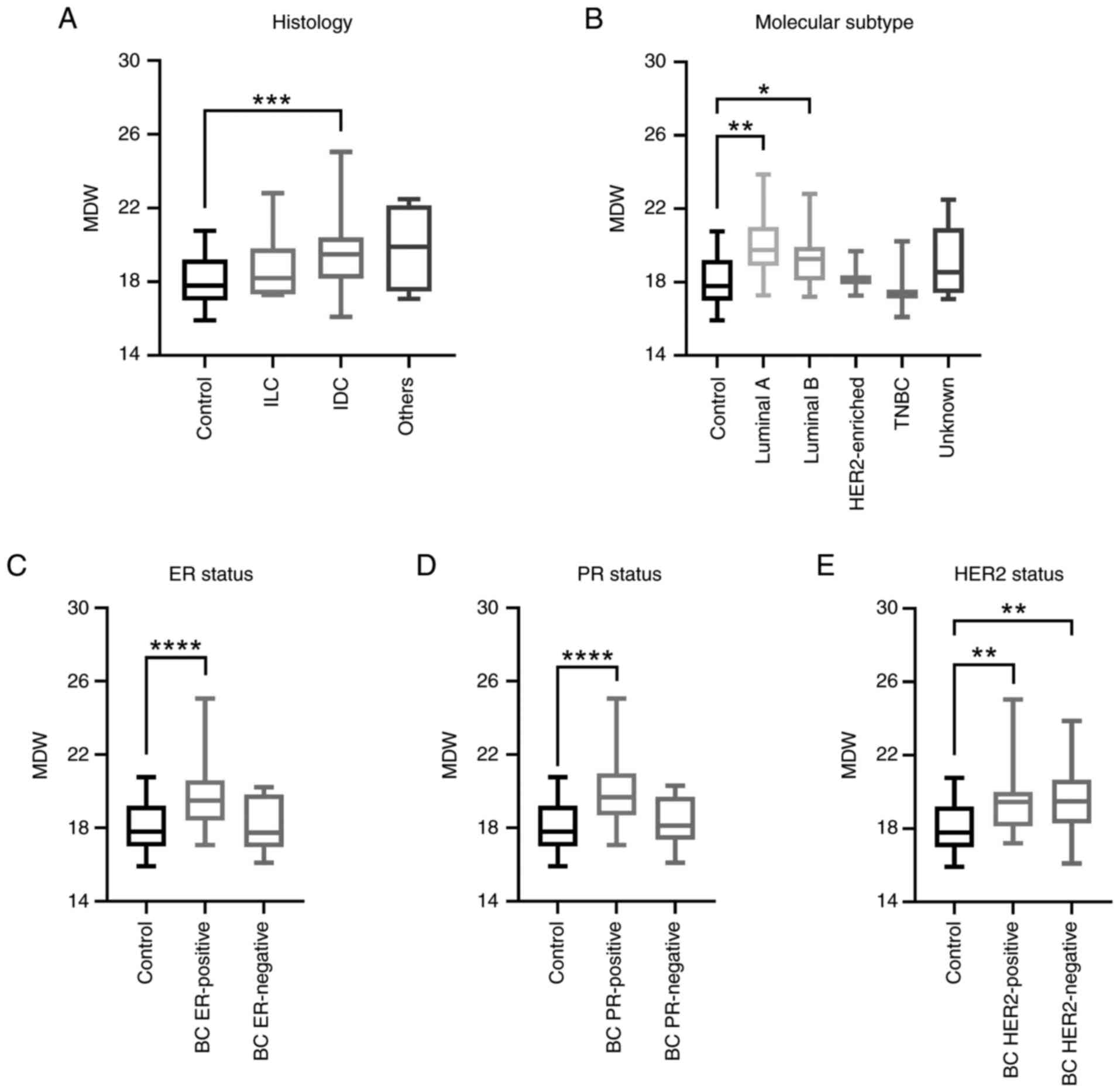
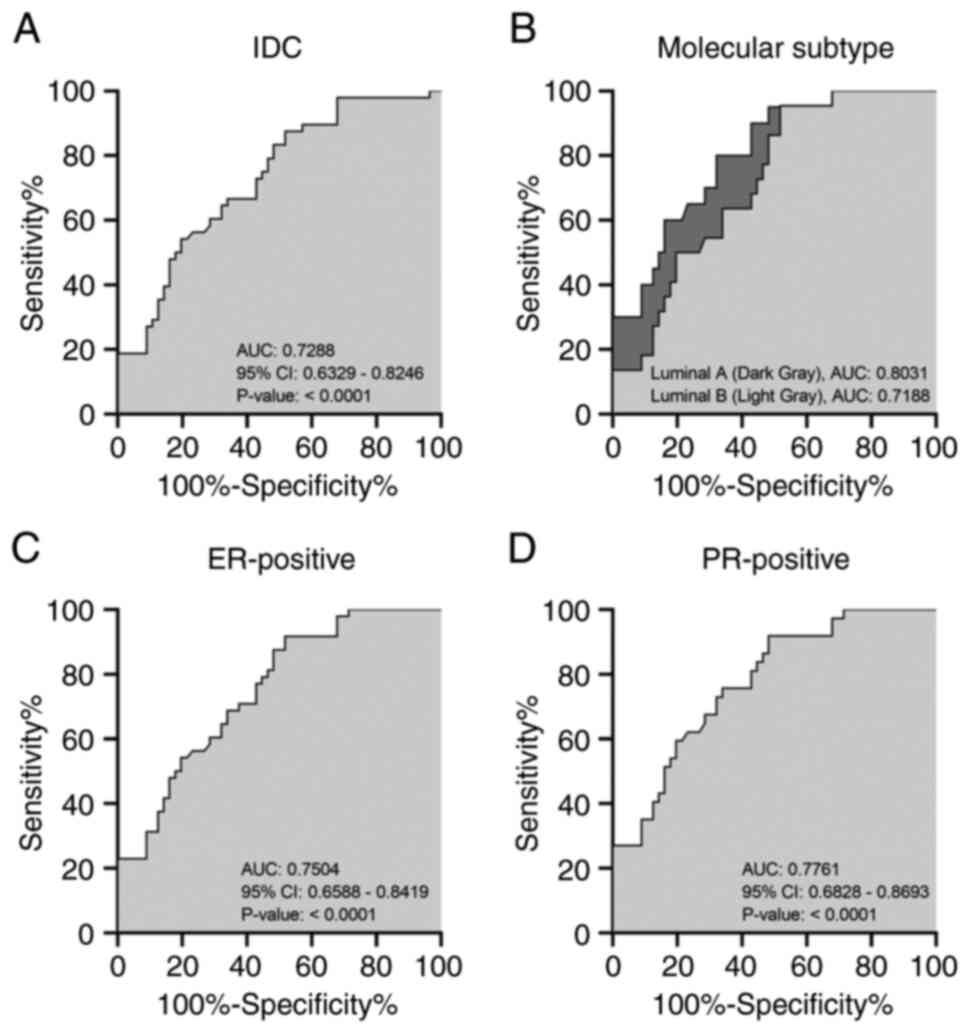
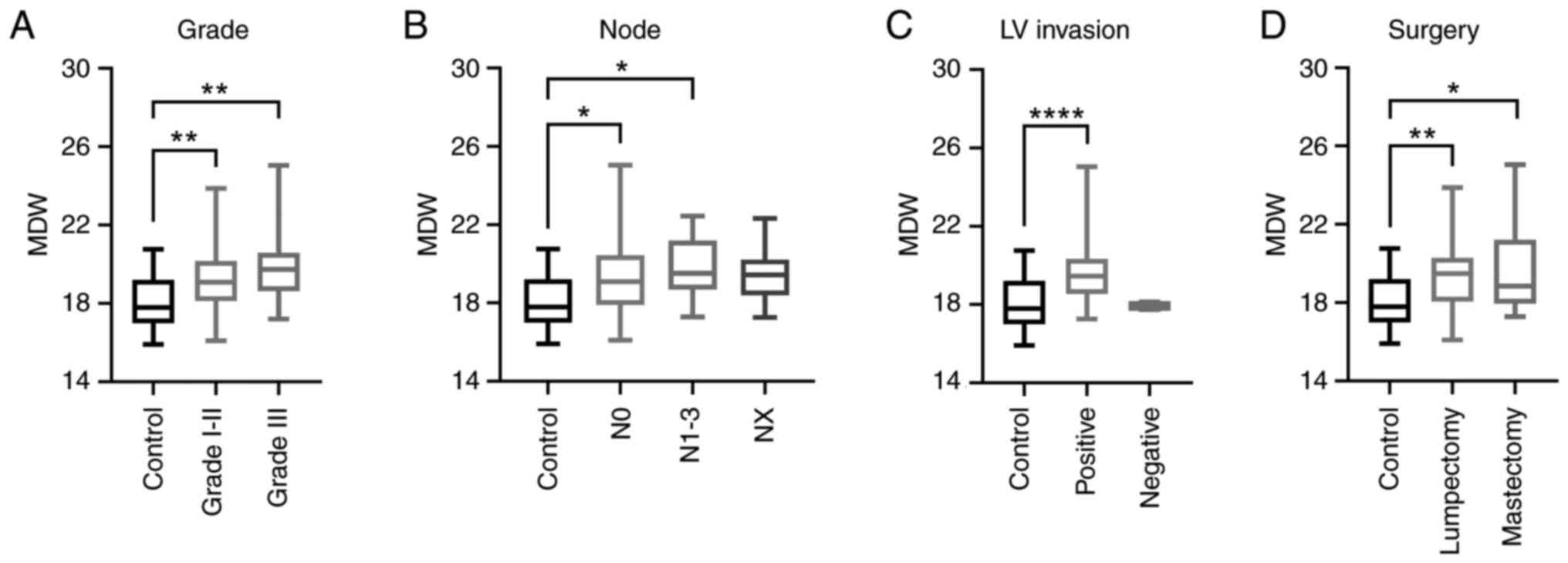
|
1
|
Dizon DS and Kamal AH: Cancer statistics
2024: All hands on deck. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:8–9. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Arnold M, Morgan E, Rumgay H, Mafra A,
Singh D, Laversanne M, Vignat J, Gralow JR, Cardoso F, Siesling S
and Soerjomataram I: Current and future burden of breast cancer:
Global statistics for 2020 and 2040. Breast. 66:15–23.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
The Lancet Oncology: Curbing the climb in
cancer incidence. Lancet Oncol. 25(529)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xiong X, Zheng LW, Ding Y, Chen YF, Cai
YW, Wang LP, Huang L, Liu CC, Shao ZM and Yu KD: Breast cancer:
Pathogenesis and treatments. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
10(49)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang J and Wu SG: Breast cancer: An
overview of current therapeutic strategies, challenge, and
perspectives. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 15:721–730.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shin J, Kim JY, Oh JM, Lee JE, Kim SW, Nam
SJ, Park W, Park YH, Ahn JS and Im YH: Comprehensive clinical
characterization of decade-long survivors of metastatic breast
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15(4720)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Seale KN and Tkaczuk KHR: Circulating
biomarkers in breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 22:e319–e331.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhou Y, Tao L, Qiu J, Xu J, Yang X, Zhang
Y, Tian X, Guan X, Cen X and Zhao Y: Tumor biomarkers for
diagnosis, prognosis and targeted therapy. Signal Transduct Target
Ther. 9(132)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Moar K, Pant A, Saini V, Pandey M and
Maurya PK: Potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for
breast cancer: A compiled review. Pathol Res Pract.
251(154893)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Varzaru VB, Eftenoiu AE, Vlad DC, Vlad CS,
Moatar AE, Popescu R and Cobec IM: The influence of tumor-specific
markers in breast cancer on other blood parameters. Life (Basel).
14(458)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lopez-Gonzalez L, Sanchez Cendra A,
Sanchez Cendra C, Roberts Cervantes ED, Espinosa JC, Pekarek T,
Fraile-Martinez O, García-Montero C, Rodriguez-Slocker AM,
Jiménez-Álvarez L, et al: Exploring biomarkers in breast cancer:
Hallmarks of diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up in clinical
practice. Medicina (Kaunas). 60(168)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Agnello L, Ciaccio AM, Vidali M,
Cortegiani A, Biundo G, Gambino CM, Scazzone C, Lo Sasso B and
Ciaccio M: Monocyte distribution width (MDW) in sepsis. Clin Chim
Acta. 548(117511)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ligi D, Lo Sasso B, Henry BM, Ciaccio M,
Lippi G, Plebani M and Mannello F: Deciphering the role of monocyte
and monocyte distribution width (MDW) in COVID-19: An updated
systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Chem Lab Med. 61:960–973.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Malinovska A, Hernried B, Lin AD,
Badaki-Makun O, Fenstermacher K, Ervin AM, Ehrhardt S, Levin S and
Hinson JS: Monocyte distribution width as a diagnostic marker for
infection a systematic review and meta-analysis. Chest.
164:101–113. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu J, Li L and Luo J: Diagnostic and
prognostic value of monocyte distribution width in sepsis. J
Inflamm Res. 15:4107–4117. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cusinato M, Sivayoham N and Planche T:
Sensitivity and specificity of monocyte distribution width (MDW) in
detecting patients with infection and sepsis in patients on sepsis
pathway in the emergency department. Infection. 51:715–727.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Agnello L, Ciaccio AM, Ben FD, Gambino CM,
Scazzone C, Giglia A, Biundo G, Cortegiani A, Sasso BL and Ciaccio
M: Clinical usefulness of presepsin and monocyte distribution width
(MDW) kinetic for predicting mortality in critically ill patients
in intensive care unit. Front Med (Lausanne).
11(1393843)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Agnello L, Ciaccio AM, Del Ben F, Lo Sasso
B, Biundo G, Giglia A, Giglio RV, Cortegiani A, Gambino CM and
Ciaccio M: Monocyte distribution width (MDW) kinetic for monitoring
sepsis in intensive care unit. Diagnosis (Berl). 11:422–429.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Lin S, Yang X, Yang X, Tang M, Yao X, Ye
Y, Huang Q, Huang J, Li J, Yi Q, et al: Monocyte distribution width
as a promising biomarker for differential diagnosis of chronic
hepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Immunol.
15(1406671)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Jaroensri R, Wulczyn E, Hegde N, Brown T,
Flament-Auvigne I, Tan F, Cai Y, Nagpal K, Rakha EA, Dabbs DJ, et
al: Deep learning models for histologic grading of breast cancer
and association with disease prognosis. NPJ Breast Cancer.
8(113)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Brierley J, O'Sullivan B, Asamura H, Byrd
D, Huang SH, Lee A, Piñeros M, Mason M, Moraes FY, Rösler W, et al:
Global consultation on cancer staging: Promoting consistent
understanding and use. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 16:763–771.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Houvenaeghel G, Cohen M, Classe JM, Reyal
F, Mazouni C, Chopin N, Martinez A, Daraï E, Coutant C, Colombo PE,
et al: Lymphovascular invasion has a significant prognostic impact
in patients with early breast cancer, results from a large,
national, multicenter, retrospective cohort study. ESMO Open.
6(100316)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nishimura R, Osako T, Okumura Y, Nakano M,
Ohtsuka H, Fujisue M and Arima N: An evaluation of lymphovascular
invasion in relation to biology and prognosis according to subtypes
in invasive breast cancer. Oncol Lett. 24(245)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Emanuelle Pereira Santos V, Luiz de Franca
Neto P, Eda de Oliveira Isidio B, Henrique Bezerra Fontes P,
Andrêssa de Moura I, Isabel Santos Cruz B, Máyra Gois de Sousa M,
Luana Dos Santos D, de França São Marcos B, Sousa de Pinho S, et
al: An overview about biomarkers in breast cancer: Insights into
the diagnostic and prognostic significance. Clin Chim Acta.
567(120030)2025.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang H, Hussin H, Hoh CC, Cheong SH, Lee
WK and Yahaya BH: Big data in breast cancer: Towards precision
treatment. Digit Health. 10(20552076241293695)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kinnel B, Singh SK, Oprea-Ilies G and
Singh R: Targeted therapy and mechanisms of drug resistance in
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 15(1320)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pedersen RN, Esen BO, Mellemkjaer L,
Christiansen P, Ejlertsen B, Lash TL, Nørgaard M and Cronin-Fenton
D: The incidence of breast cancer recurrence 10-32 years after
primary diagnosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 114:391–399. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Adrada BE, Moseley TW, Kapoor MM, Scoggins
ME, Patel MM, Perez F, Nia ES, Khazai L, Arribas E, Rauch GM and
Guirguis MS: Triple-negative breast cancer: Histopathologic
features, genomics, and treatment. Radiographics.
43(e230034)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Manjunath M and Choudhary B:
Triple-negative breast cancer: A run-through of features,
classification and current therapies (Review). Oncol Lett.
22(512)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Wang R, Zhong S, Qian L and Wang D:
Monocyte distribution width as an early predictor of short-term
outcome in adult patients with sepsis. Clin Chem Lab Med.
62:562–571. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
de Hond AAH, Steyerberg EW and van Calster
B: Interpreting area under the receiver operating characteristic
curve. Lancet Digit Health. 4:e853–e855. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li D, Ju F, Wang H, Fan C, Jacob JC, Gul
S, Zaliani A, Wartmann T, Polidori MC, Bruns CJ and Zhao Y:
Combination of the biomarkers for aging and cancer?-Challenges and
current status. Transl Oncol. 38(101783)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang Y, Zhong F and Liu L: Single-cell
transcriptional atlas of tumor-associated macrophages in breast
cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 26(129)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Huang XQ, Cao JS and Zu XY:
Tumor-associated macrophages: An important player in breast cancer
progression. Thorac Cancer. 13:269–276. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Arwert EN, Harney AS, Entenberg D, Wang Y,
Sahai E, Pollard JW and Condeelis JS: A unidirectional transition
from migratory to perivascular macrophage is required for tumor
cell intravasation. Cell Rep. 23:1239–1248. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Munir MT, Kay MK, Kang MH, Rahman MM,
Al-Harrasi A, Choudhury M, Moustaid-Moussa N, Hussain F and Rahman
SM: Tumor-Associated macrophages as multifaceted regulators of
breast tumor growth. Int J Mol Sci. 22(6526)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pan Y, Yu Y, Wang X and Zhang T:
Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immunity. Front Immunol.
11(583084)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Komohara Y, Kurotaki D, Tsukamoto H,
Miyasato Y, Yano H, Pan C, Yamamoto Y and Fujiwara Y: Involvement
of protumor macrophages in breast cancer progression and
characterization of macrophage phenotypes. Cancer Sci.
114:2220–2229. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
In J: Introduction of a pilot study.
Korean J Anesthesiol. 70:601–605. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kunselman AR: A brief overview of pilot
studies and their sample size justification. Fertil Steril.
121:899–901. 2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Totton N, Lin J, Julious S, Chowdhury M
and Brand A: A review of sample sizes for UK pilot and feasibility
studies on the ISRCTN registry from 2013 to 2020. Pilot Feasibility
Stud. 9(188)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Teresi JA, Yu X, Stewart AL and Hays RD:
Guidelines for designing and evaluating feasibility pilot studies.
Med Care. 60:95–103. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cocks K and Torgerson DJ: Sample size
calculations for pilot randomized trials: A confidence interval
approach. J Clin Epidemiol. 66:197–201. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Italian National Statistics Institute
(ISTAT). ISTAT, Rome, 2025. Accessed on July 3, 2025. https://www.istat.it/en/.
|
|
45
|
Italian Association of Medical Oncology
(AIOM). AIOM, Mila, 2025. Accessed on July 3, 2025. https://www.aiom.it/en/.
|
|
46
|
Naing L, Nordin RB, Abdul Rahman H and
Naing YT: Sample size calculation for prevalence studies using
Scalex and ScalaR calculators. BMC Med Res Methodol.
22(209)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kralovcova M, Müller J, Hajsmanova Z,
Sigutova P, Bultasova L, Palatova J and Matejovic M: Understanding
the value of monocyte distribution width (MDW) in acutely ill
medical patients presenting to the emergency department: A
prospective single center evaluation. Sci Rep.
14(152555)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
García-Álvarez A, Posada Franco Y,
Martinez-Novillo González M, Hernández Álvarez E, Serrano García I
and Sanz-Casla MT: Monocyte distribution width (MDW): Study of
reference values in blood donors. Clin Chem Lab Med. 62:1133–1137.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|