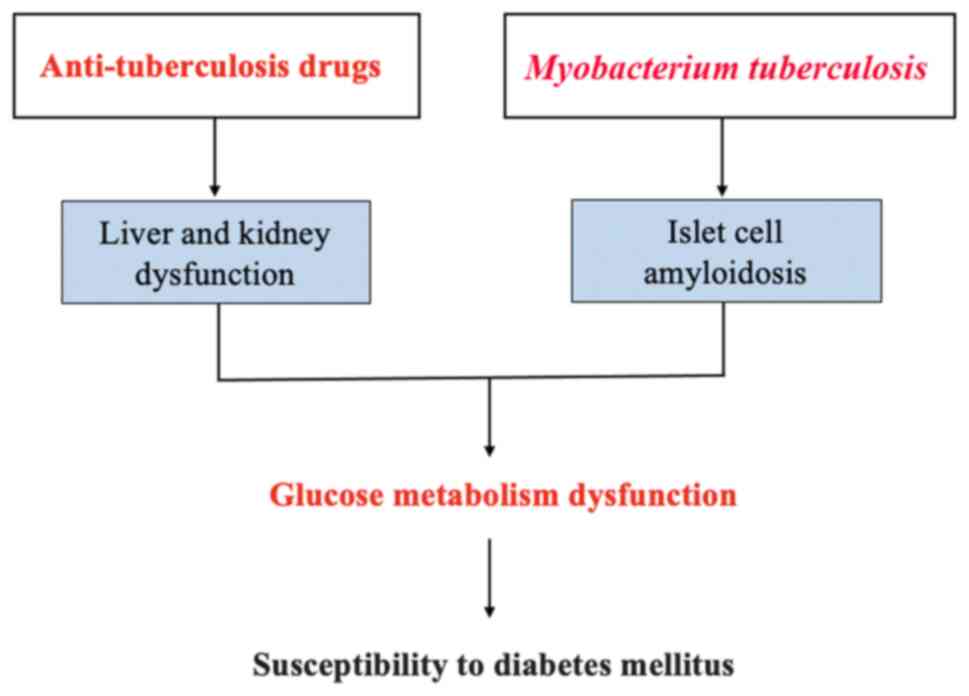
|
1
|
International Diabetes Federation. IDF
Diabetes Atlas, 10th edition. International Diabetes Federation,
Brussels, 2021.
|
|
2
|
Zheng Y, Ley SH and Hu FB: Global
aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:88–98. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kaparianos A, Argyropoulou E, Sampsonas F,
Karkoulias K, Tsiamita M and Spiropoulos K: Pulmonary complications
in diabetes mellitus. Chron Respir Dis. 5:101–108. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ali MO: Pulmonary complications in
diabetes mellitus. Mymensingh Med J. 23:603–605. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Natarajan A, Beena PM, Devnikar AV and
Mali S: A systemic review on tuberculosis. Indian J Tuberc.
67:295–311. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zheng C, Hu M and Gao F: Diabetes and
pulmonary tuberculosis: A global overview with special focus on the
situation in Asian countries with high TB-DM burden. Glob Health
Action. 10:1–11. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li M, Chen T, Hua Z, Yan H, Wang D, Li Z,
Kang Y, Zhu N and Li C: Global, regional, and national prevalence
of diabetes mellitus in patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr.
13(127)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mugusi F, Swai AB, Alberti KG and McLarty
DG: Increased prevalence of diabetes mellitus in patients with
pulmonary tuberculosis in Tanzania. Tubercle. 71:271–276.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wu Q, Wang M, Zhang Y, Wang W, Ye TF, Liu
K and Chen SH: Epidemiological characteristics and their
influencing factors among pulmonary tuberculosis patients with and
without diabetes mellitus: A survey study from drug resistance
surveillance in east china. Front Public Health.
9(777000)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Lee EH, Lee JM, Kang YA, Leem AY, Kim EY,
Jung JY, Park MS, Kim YS, Kim SK, Chang J and Kim SY: Prevalence
and impact of diabetes mellitus among patients with active
pulmonary tuberculosis in South Korea. Lung. 195:209–215.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Rahim Z, Momi MS, Saha SK, Zaman K, Uddin
KN, Jamil SN, Nahar N, Khan AK, Cooreman EA, Ahmed M, et al:
Pulmonary tuberculosis in patients with diabetes mellitus in
Bangladesh. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 16:1132–1133. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Delgado-Sánchez G, García-García L,
Castellanos-Joya M, Cruz-Hervert P, Ferreyra-Reyes L,
Ferreira-Guerrero E, Hernández A, Ortega-Baeza VM, Montero-Campos
R, Sulca JA, et al: Association of pulmonary tuberculosis and
diabetes in Mexico: Analysis of the national tuberculosis registry
2000-2012. PLoS One. 10(e0129312)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Guo S, Lei S, Li J, Li L, Chen H and
Chongsuvivatwong V: Gradient association between pulmonary
tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus among households with a
tuberculosis case: A contact tracing-based study. Sci Rep.
12(1854)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Stevenson CR, Forouhi NG, Roglic G,
Williams BG, Lauer JA, Dye C and Unwin N: Diabetes and
tuberculosis: The impact of the diabetes epidemic on tuberculosis
incidence. BMC Public Health. 7(234)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mave V, Meshram S, Lokhande R, Kadam D,
Dharmshale S, Bharadwaj R, Kagal A, Pradhan N, Deshmukh S, Atre S,
et al: Prevalence of dysglycemia and clinical presentation of
pulmonary tuberculosis in Western India. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis.
21:1280–1287. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang Q, Ma A, Han X, Zhao S, Cai J, Ma Y,
Zhao J, Wang Y, Dong H, Zhao Z, et al: Prevalence of type 2
diabetes among newly detected pulmonary tuberculosis patients in
China: A community based cohort study. PLoS One.
8(e82660)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Vallerskog T, Martens GW and Kornfeld H:
Diabetic mice display a delayed adaptive immune response to
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Immunol. 184:6275–6282.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Panda S, Seelan DM, Faisal S, Arora A,
Luthra K, Palanichamy JK, Mohan A, Vikram NK, Gupta NK,
Ramakrishnan L and Singh A: Chronic hyperglycemia drives
alterations in macrophage effector function in pulmonary
tuberculosis. Eur J Immunol. 52:1595–1609. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Vance J, Santos A, Sadofsky L, Morice A
and Cervantes J: Effect of high glucose on human alveolar
macrophage phenotype and phagocytosis of mycobacteria. Lung.
197:89–94. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alim MA, Sikder S, Sathkumara H, Kupz A,
Rush CM, Govan BL and Ketheesan N: Dysregulation of key cytokines
may contribute to increased susceptibility of diabetic mice to
Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. Tuberculosis (Edinb).
115:113–120. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Martinez N, Ketheesan N, West K,
Vallerskog T and Kornfeld H: Impaired recognition of mycobacterium
tuberculosis by alveolar macrophages from diabetic mice. J Infect
Dis. 214:1629–1637. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Alim MA, Sikder S, Bridson TL, Rush CM,
Govan BL and Ketheesan N: Anti-mycobacterial function of
macrophages is impaired in a diet induced model of type 2 diabetes.
Tuberculosis (Edinb). 102:47–54. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sertl K, Takemura T, Tschachler E, Ferrans
VJ, Kaliner MA and Shevach EM: Dendritic cells with
antigen-presenting capability reside in airway epithelium, lung
parenchyma, and visceral pleura. J Exp Med. 163:436–451.
1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
McWilliam AS, Marsh AM and Holt PG:
Inflammatory infiltration of the upper airway epithelium during
Sendai virus infection: Involvement of epithelial dendritic cells.
J Virol. 71:226–236. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Holt PG, Stumbles PA and McWilliam AS:
Functional studies on dendritic cells in the respiratory tract and
related mucosal tissues. J Leukoc Biol. 66:272–275. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kumar NP, Moideen K, Sivakumar S, Menon
PA, Viswanathan V, Kornfeld H and Babu S: Modulation of dendritic
cell and monocyte subsets in tuberculosis-diabetes co-morbidity
upon standard tuberculosis treatment. Tuberculosis (Edinb).
101:191–200. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kumar NP, Moideen K, Dhakshinraj SD,
Banurekha VV, Nair D, Dolla C, Kumaran P and Babu S: Profiling
leucocyte subsets in tuberculosis-diabetes co-morbidity.
Immunology. 146:243–250. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Andrade BB, Kumar NP, Sridhar R, Banurekha
VV, Jawahar MS, Nutman TB, Sher A and Babu S: Heightened plasma
levels of heme oxygenase-1 and tissue inhibitor of
metalloproteinase-4 as well as elevated peripheral neutrophil
counts are associated with TB-diabetes comorbidity. Chest.
145:1244–1254. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Raposo-García S, Guerra-Laso JM,
García-García S, Juan-García J, López-Fidalgo E, Diez-Tascón C,
Nebreda-Mayoral T, López-Medrano R and Rivero-Lezcano OM:
Immunological response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in
blood from type 2 diabetes patients. Immunol Lett. 186:41–45.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Eruslanov EB, Lyadova IV, Kondratieva TK,
Majorov KB, Scheglov IV, Orlova MO and Apt AS: Neutrophil responses
to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection in genetically susceptible
and resistant mice. Infect Immun. 73:1744–1753. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Vankayalapati R and Barnes PF: Innate and
adaptive immune responses to human Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection. Tuberculosis. 89 (Suppl 1):S77–S80. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zahran WA, Ghonaim MM, Koura BA, El-Banna
H, Ali SM and El-Sheikh N: Human natural killer T cells (NKT), NK
and T cells in pulmonary tuberculosis: Potential indicators for
disease activity and prognosis. Egypt J Immunol. 13:67–78.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Q, Xiao HP, Cui HY and Sugawara I:
Significant increase in natural-killer T cells in patients with
tuberculosis complicated by type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Int Med
Res. 39:105–111. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kumar NP, Sridhar R, Nair D, Banurekha VV,
Nutman TB and Babu S: Type 2 diabetes mellitus is associated with
altered CD8(+) T and natural killer cell function in pulmonary
tuberculosis. Immunology. 144:677–686. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cheekatla SS, Tripathi D,
Venkatasubramanian S, Nathella PK, Paidipally P, Ishibashi M, Welch
E, Tvinnereim AR, Ikebe M, Valluri VL, et al: NK-CD11c+ cell
crosstalk in diabetes enhances IL-6-mediated inflammation during
mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. PLoS Pathog.
12(e1005972)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Prezzemolo T, Guggino G, La Manna MP, Di
Liberto D, Dieli F and Caccamo N: Functional signatures of human
CD4 and CD8 T cell responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis. Front
Immunol. 5(180)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
St Paul M and Ohashi PS: The roles of
CD8+ T cell subsets in antitumor immunity. Trends Cell
Biol. 30:695–704. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mayer-Barber KD and Barber DL: Innate and
adaptive cellular immune responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 5(a018424)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ponnana M, Pydi S and Gaddam S:
Enumeration of lymphocyte subsets during follow-up in the pulmonary
tuberculosis patients with co morbid diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim
Acta. 510:566–572. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Kumar NP, Sridhar R, Banurekha VV, Jawahar
MS, Nutman TB and Babu S: Expansion of pathogen-specific T-helper 1
and T-helper 17 cells in pulmonary tuberculosis with coincident
type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Infect Dis. 208:739–7348.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Stalenhoef JE, Alisjahbana B, Nelwan EJ,
van der Ven-Jongekrijg J, Ottenhoff TH, van der Meer JW, Nelwan RH,
Netea MG and van Crevel R: The role of interferon-gamma in the
increased tuberculosis risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur J Clin
Microbiol Infect Dis. 27:97–103. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Fernández RDV, Díaz A, Bongiovanni B,
Gallucci G, Bértola D, Gardeñez W, Lioi S, Bertolin Y, Galliano R,
Bay ML, et al: Evidence for a more disrupted immune-endocrine
relation and cortisol immunologic influences in the context of
tuberculosis and type 2 diabetes comorbidity. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 11(126)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Sun Q, Zhang Q, Xiao H, Cui H and Su B:
Significance of the frequency of CD4+CD25+CD127- T-cells in
patients with pulmonary tuberculosis and diabetes mellitus.
Respirology. 17:876–882. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kathamuthu GR, Kumar NP, Moideen K, Dolla
C, Kumaran P and Babu S: Multi-dimensionality immunophenotyping
analyses of MAIT cells expressing Th1/Th17 cytokines and cytotoxic
markers in latent tuberculosis diabetes comorbidity. Pathogens.
11(87)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kathamuthu GR, Kumar NP, Moideen K, Menon
PA and Babu S: Decreased frequencies of Gamma/Delta T cells
expressing Th1/Th17 cytokine, cytotoxic, and immune markers in
latent tuberculosis-diabetes/pre-diabetes comorbidity. Front Cell
Infect Microbiol. 11(756854)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wei R, Li P, Xue Y, Liu Y, Gong W and Zhao
W: Impact of diabetes mellitus on the immunity of tuberculosis
patients: A retrospective, cross-sectional study. Risk Manag
Healthc Policy. 15:611–627. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kumar NP, Moideen K, George PJ, Dolla C,
Kumaran P and Babu S: Impaired cytokine but enhanced cytotoxic
marker expression in mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced CD8+ T
cells in individuals with type 2 diabetes and latent mycobacterium
tuberculosis infection. J Infect Dis. 213:866–870. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wang X, Ma A, Han X, Chan L, Liang H,
Litifu A and Xue F: T cell profile was altered in pulmonary
tuberculosis patients with type 2 diabetes. Med Sci Monit.
24:636–642. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kumar NP, Moideen K, Viswanathan V,
Kornfeld H and Babu S: Effect of standard tuberculosis treatment on
naive, memory and regulatory T-cell homeostasis in
tuberculosis-diabetes co-morbidity. Immunology. 149:87–97.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kumar S, Lakhiwal R, Singh CP, Bhandiwad
C, Sharma N, Singhal V and Chakranarayan A: Study of correlation of
CD4, CD8 count with tuberculous pneumonia and non tuberculous
bacterial pneumonia in type 2 diabetes mellitu. J Assoc Physicians
India. 70:11–12. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Kumar NP, Moideen K, Dolla C, Kumaran P
and Babu S: Prediabetes is associated with the modulation of
antigen-specific Th1/Tc1 and Th17/Tc17 responses in latent
Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. PLoS One.
12(e0178000)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Mily A, Sarker P, Taznin I, Hossain D, Haq
MA, Kamal SMM, Agerberth B, Brighenti S and Raqib R: Slow
radiological improvement and persistent low-grade inflammation
after chemotherapy in tuberculosis patients with type 2 diabetes.
BMC Infect Dis. 20(933)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Guo Q, Zhang J, Li G, Liu S, Xiao G, Bi J,
Li F, Zhang S, Ou M, He X, et al: Elevated antigen-specific IFN-γ
responses in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid impervious to clinical
comorbidities improve the pulmonary tuberculosis diagnosis.
Tuberculosis (Edinb). 122(101942)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yamashiro S, Kawakami K, Uezu K, Kinjo T,
Miyagi K, Nakamura K and Saito A: Lower expression of Th1-related
cytokines and inducible nitric oxide synthase in mice with
streptozotocin-induced diabetes mellitus infected with
Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin Exp Immunol. 139:57–64.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Meenakshi P, Ramya S, Lavanya J,
Vijayalakshmi V and Sumanlatha G: Effect of IFN-γ, IL-12 and IL-10
cytokine production and mRNA expression in tuberculosis patients
with diabetes mellitus and their household contacts. Cytokine.
81:127–136. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Gan SH, KhinMar KW, Barkham TM, Koh CK,
Shen L, Wang YT and Chee CB: Interferon-γ responses to
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-specific antigens in diabetes mellitus.
Eur Respir J. 44:805–808. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Karachunskiĭ MA, Balabolkin MI and
Beglarian NR: Changes in carbohydrate metabolism in patients with
tuberculosis. Vestn Ross Akad Med Nauk. 7:18–21. 1995.PubMed/NCBI(In Russian).
|
|
58
|
Chen H, Su L, Bao J, Zhang K, Li Y and Mao
E: The impact of pulmonary tuberculosis on immunological and
metabolic features of diabetic patients. Front Immunol.
13(973991)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Segura-Cerda CA, Marquina-Castillo B,
Lozano-Ordaz V, Mata-Espinosa D, Barrios-Payán JA, López-Torres MO,
Aceves-Sánchez MJ, Bielefeldt-Ohmann H, Hernández-Pando R and
Flores-Valdez MA: BCG and BCGΔBCG1419c protect type 2 diabetic mice
against tuberculosis via different participation of T and B
lymphocytes, dendritic cells and pro-inflammatory cytokines. NPJ
Vaccines. 5(21)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Adeva-Andany MM, Pérez-Felpete N,
Fernández-Fernández C, Donapetry-García C and Pazos-García C: Liver
glucose metabolism in humans. Biosci Rep. 36(e00416)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Legouis D, Faivre A, Cippà PE and de
Seigneux S: Renal gluconeogenesis: An underestimated role of the
kidney in systemic glucose metabolism. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
37:1417–1425. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Gray EL and Goldberg HF: Baseline abnormal
liver function tests are more important than age in the development
of isoniazid-induced hepatoxicity for patients receiving preventive
therapy for latent tuberculosis infection. Intern Med J.
46:281–287. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Becker MW, Schwambach KH, Lunardelli M and
Blatt CR: Overview of drug induced liver injury in Brazil: What is
the role of public health policy on the evidence? World J
Gastrointest Pharmacol Ther. 12:40–55. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Covic A, Golea O, Segall L, Meadipudi S,
Munteanu L, Nicolicioiu M, Tudorache V, Covic M and Goldsmith DJ: A
clinical description of rifampicin-induced acute renal failure in
170 consecutive cases. J Indian Med Assoc. 102:22–25.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Broxmeyer L: Diabetes mellitus,
tuberculosis and the mycobacteria: Two millenia of enigma. Med
Hypotheses. 65:433–439. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Sahakyan S, Petrosyan V and Abrahamyan L:
Diabetes mellitus and treatment outcomes of pulmonary tuberculosis:
A cohort study. Int J Public Health. 65:37–43. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Ahmed M, Omer I, Osman SM and Ahmed-Abakur
EH: Association between pulmonary tuberculosis and Type 2 diabetes
in Sudanese patients. Int J Mycobacteriol. 6:97–101.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Wang Y, Dou M, Kou T, Liu Y, Lv W, Han L,
Wang N, Ma A, Kok FJ, Schouten EG and Wang Q: Risk of having
pulmonary tuberculosis in type 2 diabetes: A hospital-based matched
case-control study. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr. 30:303–310.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Gil-Santana L, Almeida-Junior JL, Oliveira
CA, Hickson LS, Daltro C, Castro S, Kornfeld H, Netto EM and
Andrade BB: Diabetes is associated with worse clinical presentation
in tuberculosis patients from Brazil: A retrospective cohort study.
PLoS One. 11(e0146876)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Ren Y, Ren H, Tian Q, Li X and Liu Y: The
relationship between computed tomography appearance of pulmonary
tuberculosis and blood glucose levels in 763 diabetes mellitus
patients with pulmonary tuberculosis: A comparative study.
Endocrine. 76:584–592. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Buasroung P, Petnak T, Liwtanakitpipat P
and Kiertiburanakul S: Prevalence of diabetes mellitus in patients
with tuberculosis: A prospective cohort study. Int J Infect Dis.
116:374–379. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Chiang CY, Bai KJ, Lin HH, Chien ST, Lee
JJ, Enarson DA, Lee TI and Yu MC: The influence of diabetes,
glycemic control, and diabetes-related comorbidities on pulmonary
tuberculosis. PLoS One. 10(e0121698)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Huangfu P, Ugarte-Gil C, Golub J, Pearson
F and Critchley J: The effects of diabetes on tuberculosis
treatment outcomes: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis.
Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 23:783–796. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Ma Y, Huang ML, Li T, DU J, Shu W, Xie SH,
Wang HH, Zhu GF, Tan SY, Fu YY, et al: Role of diabetes mellitus on
treatment effects in drug-susceptible initial pulmonary
tuberculosis patients in China. Biomed Environ Sci. 30:671–675.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Brunton L, Chapner B and Knollmann B: In:
The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics-Goodman and Gillman.
Brunton L and Chapner B (eds). 12th edition. Mc Graw Hill Medical,
San Diego, CA, 2011.
|
|
76
|
Katzung BG, Mastres SB and Trevor AJ:
Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. 14th edition. Mc Graw Hill
Education, Singapore, 2018.
|
|
77
|
Parida SK, Axelsson-Robertson R, Rao MV,
Singh N, Master I, Lutckii A, Keshavjee S, Andersson J, Zumla A and
Maeurer M: Totally drug- resistant tuberculosis and adjunct
therapies. J Intern Med. 277:388–405. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Novita BD: Metformin: A review of its
potential as enhancer for anti tuberculosis efficacy in diabetes
mellitus-tuberculosis coinfection patients. Indian J Tuberc.
66:294–298. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Alfarisi O, Mave V, Gaikwad S,
Sahasrabudhe T, Ramachandran G, Kumar H, Gupte N, Kulkarni V,
Deshmukh S, Atre S, et al: Effect of diabetes mellitus on the
pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of tuberculosis treatment.
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 62:e01383–e01318. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Babalik A, Ulus IH, Bakirci N, Kuyucu T,
Arpag H, Dagyildizi L and Capaner E: Plasma concentrations of
isoniazid and rifampin are decreased in adult pulmonary
tuberculosis patients with diabetes mellitus. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 57:5740–5742. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Hsu AH, Lee JJ, Chiang CY, Li YH, Chen LK
and Lin CB: Diabetes is associated with drug-resistant tuberculosis
in Eastern Taiwan. Int J Tuberc Lung Dis. 17:354–356.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Lee YJ, Han SK, Park JH, Lee JK, Kim DK,
Chung HS and Heo EY: The effect of metformin on culture conversion
in tuberculosis patients with diabetes mellitus. Korean J Intern
Med. 33:933–940. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Degner NR, Wang JY, Golub JE and
Karakousis PC: Metformin use reverses the increased mortality
associated with diabetes mellitus during tuberculosis treatment.
Clin Infect Dis. 66:198–205. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|