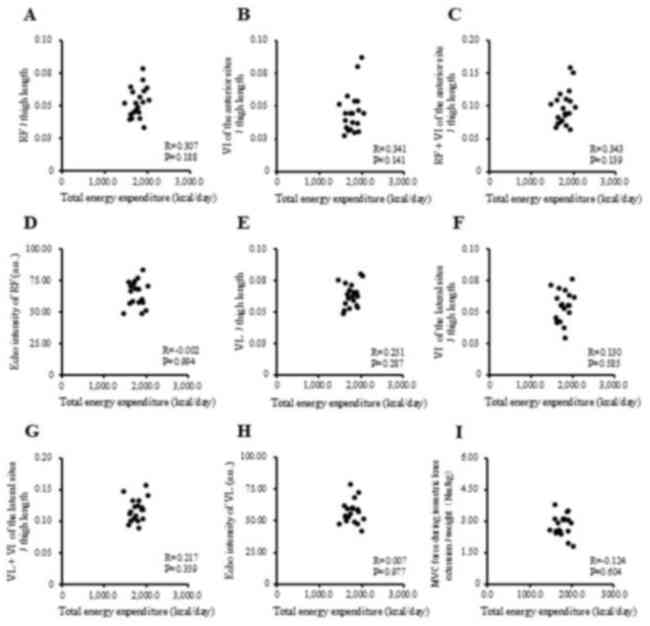
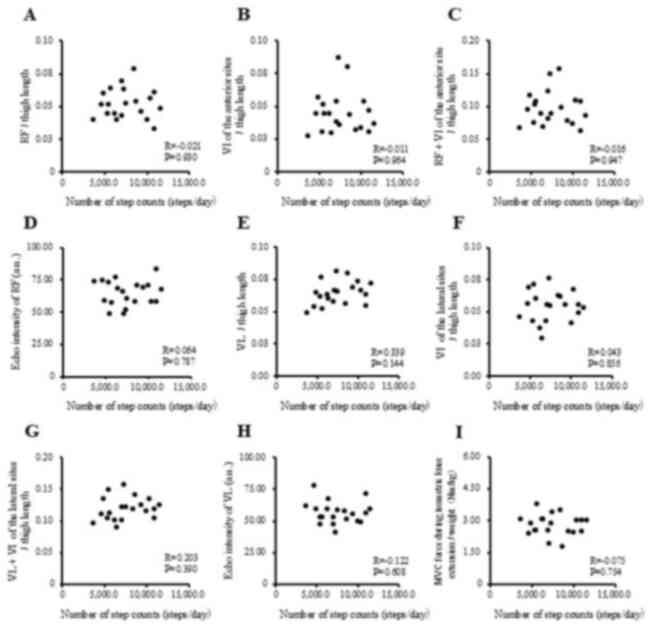
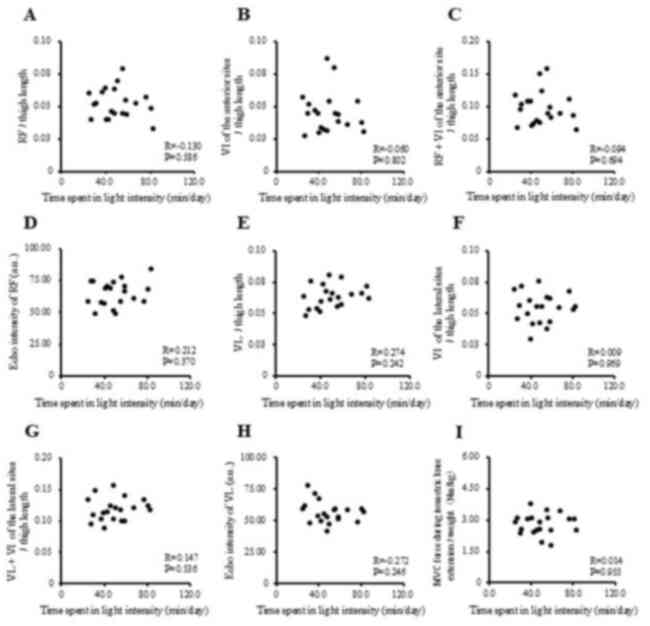
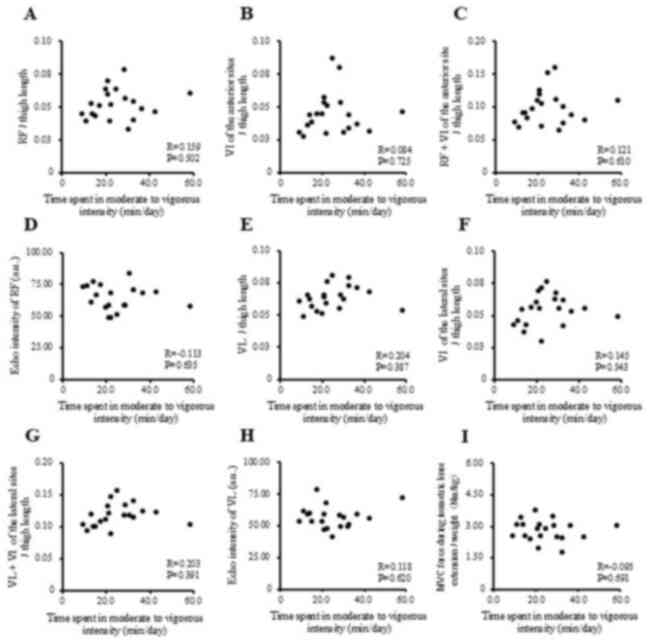
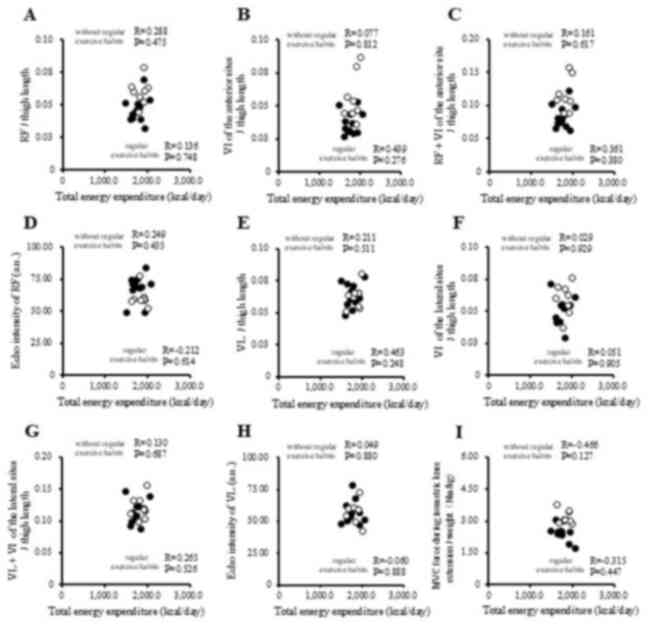
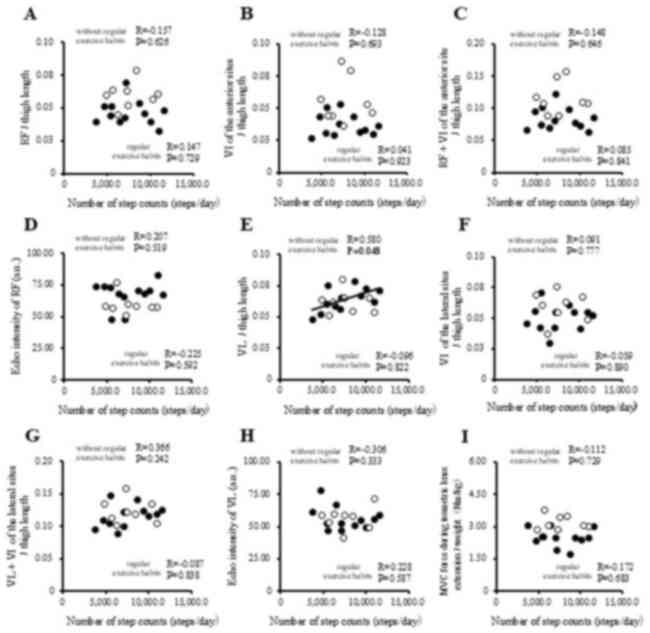
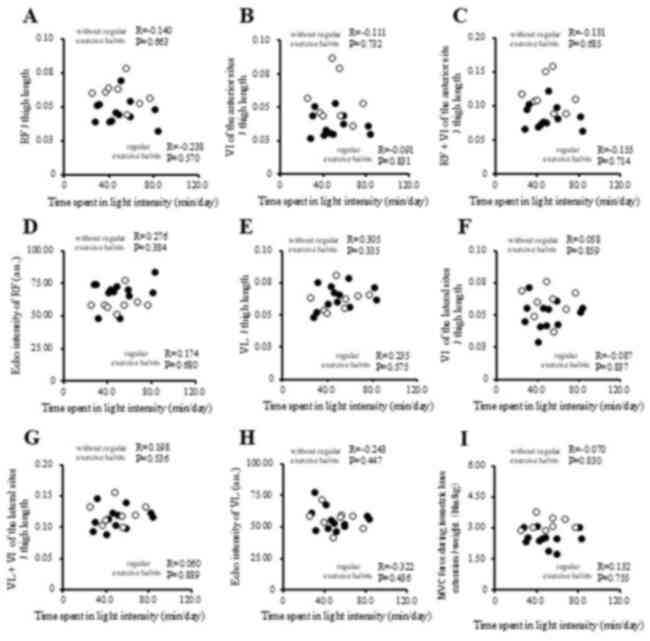
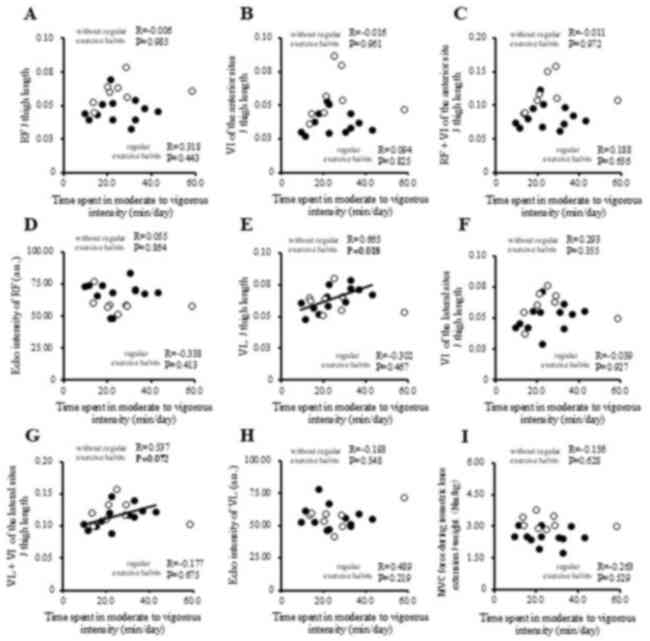
|
1
|
Oshita K and Myotsuzono R: An association
between the physical activity level and skeletal muscle mass index
in female university students with a past exercise habituation.
Osteoporos Sarcopenia. 7:146–152. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brown WJ and Trost SG: Life transitions
and changing physical activity patterns in young women. Am J Prev
Med. 25:140–143. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Engberg E, Alen M, Kukkonen-Harjula K,
Peltonen JE, Tikkanen HO and Pekkarinen H: Life events and change
in leisure time physical activity: A systematic review. Sports Med.
42:433–447. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Guthold R, Stevens GA, Riley LM and Bull
FC: Worldwide trends in insufficient physical activity from 2001 to
2016: A pooled analysis of 358 population-based surveys with 1·9
million participants. Lancet Glob Health. 6:e1077–e1086.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Peng B, Ng JYY and Ha AS: Barriers and
facilitators to physical activity for young adult women: A
systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative literature.
Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 20(23)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Uijtdewilligen L, Peeters GMEE, van
Uffelen JGZ, Twisk JWR, Singh AS and Brown WJ: Determinants of
physical activity in a cohort of young adult women. Who is at risk
of inactive behaviour? J Sci Med Sport. 18:49–55. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Paddon-Jones D, Sheffield-Moore M, Urban
RJ, Sanford AP, Aarsland A, Wolfe RR and Ferrando AA: Essential
amino acid and carbohydrate supplementation ameliorates muscle
protein loss in humans during 28 days bedrest. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 89:4351–4358. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Akima H, Kubo K, Kanehisa H, Suzuki Y,
Gunji A and Fukunaga T: Leg-press resistance training during 20
days of 6˚ head-down-tilt bed rest prevents muscle deconditioning.
Eur J Appl Physiol. 82:30–38. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Landers KA, Hunter GR, Wetzstein CJ,
Bamman MM and Weinsier RL: The interrelationship among muscle mass,
strength, and the ability to perform physical tasks of daily living
in younger and older women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci.
56:B443–B448. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Bahat G, Bauer J, Boirie
Y, Bruyère O, Cederholm T, Cooper C, Landi F, Rolland Y, Sayer AA,
et al: Sarcopenia: Revised European consensus on definition and
diagnosis. Age Ageing. 48:16–31. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kitagawa F, Ogawa M, Yoshiko A, Oshida Y,
Koike T, Akima H and Tanaka NI: Factors related to trunk
intramuscular adipose tissue content-A comparison of younger and
older men. Exp Gerontol. 168(111922)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hioki M, Kanehira N, Koike T, Saito A,
Shimaoka K, Sakakibara H, Oshida Y and Akima H: Relationship
between adiponectin and intramuscular fat content determined by
ultrasonography in older adults. PLoS One.
17(e0262271)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Akima H, Hioki M, Yoshiko A, Koike T,
Sakakibara H, Takahashi H and Oshida Y: Intramuscular adipose
tissue determined by T1-weighted MRI at 3 T primarily reflects
extramyocellular lipids. Magn Reson Imaging. 34:397–403.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kumahara H, Schutz Y, Ayabe M, Yoshioka M,
Yoshitake Y, Shindo M, Ishii K and Tanaka H: The use of uniaxial
accelerometry for the assessment of physical-activity-related
energy expenditure: A validation study against whole-body indirect
calorimetry. Br J Nutr. 91:235–243. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hioki M, Kanehira N, Koike T, Saito A,
Shimaoka K, Sakakibara H, Oshida Y and Akima H: Age-related changes
in muscle volume and intramuscular fat content in quadriceps
femoris and hamstrings. Exp Gerontol. 132(110834)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Young HJ, Jenkins NT, Zhao Q and Mccully
KK: Measurement of intramuscular fat by muscle echo intensity.
Muscle Nerve. 52:963–971. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Akima H, Hioki M and Furukawa T: Effect of
arthroscopic partial meniscectomy on the function of quadriceps
femoris. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 16:1017–1025.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Foong YC, Chherawala N, Aitken D, Scott D,
Winzenberg T and Jones G: Accelerometer-determined physical
activity, muscle mass, and leg strength in community-dwelling older
adults. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 7:275–283. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Rosique-Esteban N, Babio N, Díaz-López A,
Romaguera D, Alfredo Martínez J, Sanchez VM, Schröder H, Estruch R,
Vidal J, Buil-Cosiales P, et al: Leisure-time physical activity at
moderate and high intensity is associated with parameters of body
composition, muscle strength and sarcopenia in aged adults with
obesity and metabolic syndrome from the PREDIMED-Plus study. Clin
Nutr. 38:1324–1331. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu F, Wills K, Laslett LL, Oldenburg B,
Jones G and Winzenberg T: Moderate-to-vigorous physical activity
but not sedentary time is associated with musculoskeletal health
outcomes in a cohort of Australian middle-aged women. J Bone Miner
Res. 32:708–715. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Miyatani M, Kanehisa H, Azuma K, Kuno S
and Fukunaga T: Site-related differences in muscle loss with aging.
Int J Sport Health Sci. 1:34–40. 2003.
|
|
22
|
Yamada Y, Yamada M, Yoshida T, Miyachi M
and Arai H: Validating muscle mass cutoffs of four International
sarcopenia-working groups in Japanese people using DXA and BIA. J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 12:1000–1010. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lexell J, Taylor CC and Sjöström M: What
is the cause of the ageing atrophy? J Neurol Sci. 84:275–294.
1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Abe T, Sakamaki M, Yasuda T, Bemben MG,
Kondo M, Kawakami Y and Fukunaga T: Age-related, site-specific
muscle loss in 1507 Japanese men and women aged 20 to 95 years. J
Sports Sci Med. 10:145–150. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ito J: Morphological analysis of the human
lower extremity based on the relative muscle weight. Okajimas Folia
Anat Jpn. 73:247–251. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Akima H, Foley JM, Prior BM, Dudley GA and
Meyer RA: Vastus lateralis fatigue alters recruitment of musculus
quadriceps femoris in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985). 92:679–684.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Trappe TA, Lindquist DM and Carrithers JA:
Muscle-specific atrophy of the quadriceps femoris with aging. J
Appl Physiol (1985). 90:2070–2074. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jacob I, Johnson MI, Jones G, Jones A and
Francis P: Age-related differences of vastus lateralis muscle
morphology, contractile properties, upper body grip strength and
lower extremity functional capability in healthy adults aged 18 to
70 years. BMC Geriatr. 22(538)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Akima H, Yoshiko A, Hioki M, Kanehira N,
Shimaoka K, Koike T, Sakakibara H and Oshida Y: Skeletal muscle
size is a major predictor of intramuscular fat content regardless
of age. Eur J Appl Physiol. 115:1627–1635. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Otsuka Y, Yamada Y, Maeda A, Izumo T, Rogi
T, Shibata H, Fukuda M, Arimitsu T, Miyamoto N and Hashimoto T:
Effects of resistance training intensity on muscle quantity/quality
in middle-aged and older people: A randomized controlled trial. J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 13:894–908. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ainsworth BE, Haskell WL, Herrmann SD,
Meckes N, Bassett DR Jr, Tudor-Locke C, Greer JL, Vezina J,
Whitt-Glover MC and Leon AS: 2011 compendium of physical
activities: A second update of codes and MET values. Med Sci Sports
Exerc. 43:1575–1581. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liu MQ, Anderson FC, Schwartz MH and Delp
SL: Muscle contributions to support and progression over a range of
walking speeds. J Biomech. 41:3243–3252. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hayashida I, Tanimoto Y, Takahashi Y,
Kusabiraki T and Tamaki J: Correlation between muscle strength and
muscle mass, and their association with walking speed, in
community-dwelling elderly Japanese individuals. PLoS One.
9(e111810)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Uesugi Y, Kanaya S, Nakanishi H and Naito
Y: The relationship between locomotive syndrome risk, gait pattern,
and standing posture in young Japanese women: A cross-sectional
study. Healthcare (Basel). 8(565)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kyröläinen H, Avela J and Komi PV: Changes
in muscle activity with increasing running speed. J Sports Sci.
23:1101–1109. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sjöholm K, Gripeteg L and Larsson I:
Macronutrient and alcohol intake is associated with intermuscular
adipose tissue in a randomly selected group of younger and older
men and women. Clin Nutr ESPEN. 13:e46–e51. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|