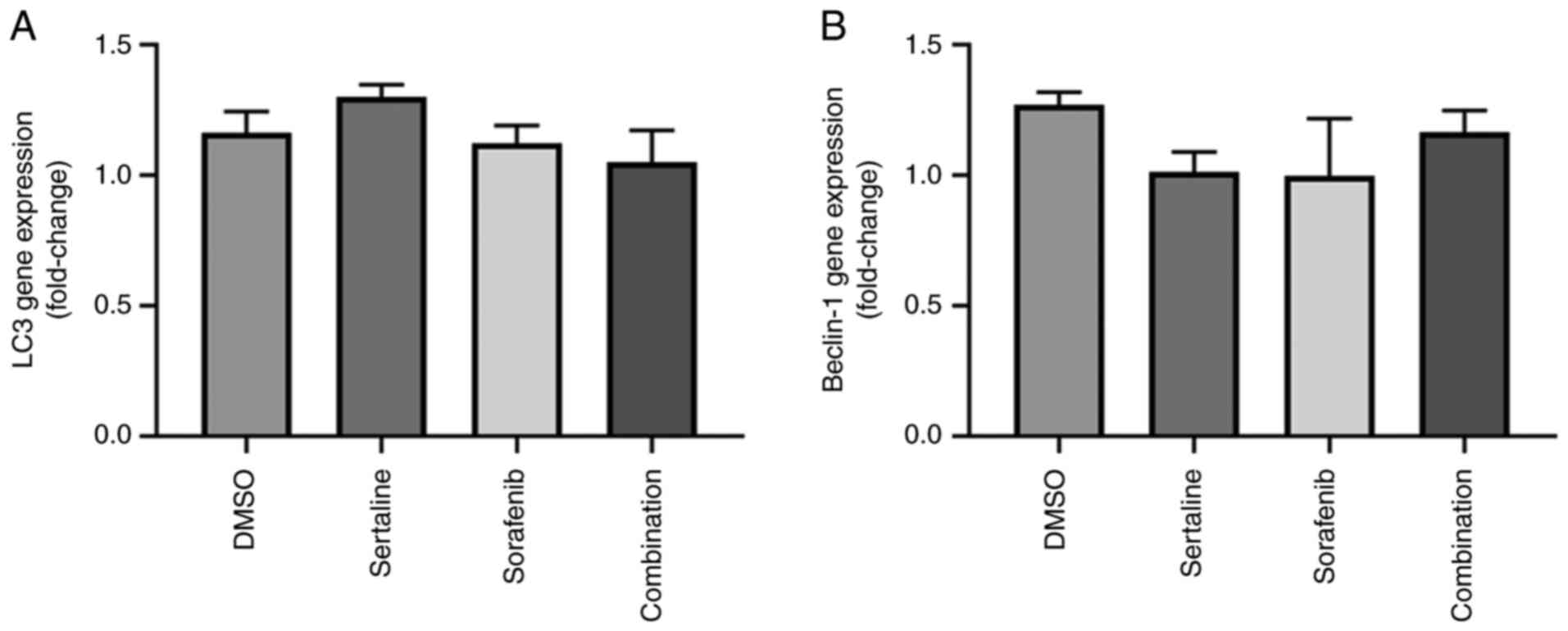
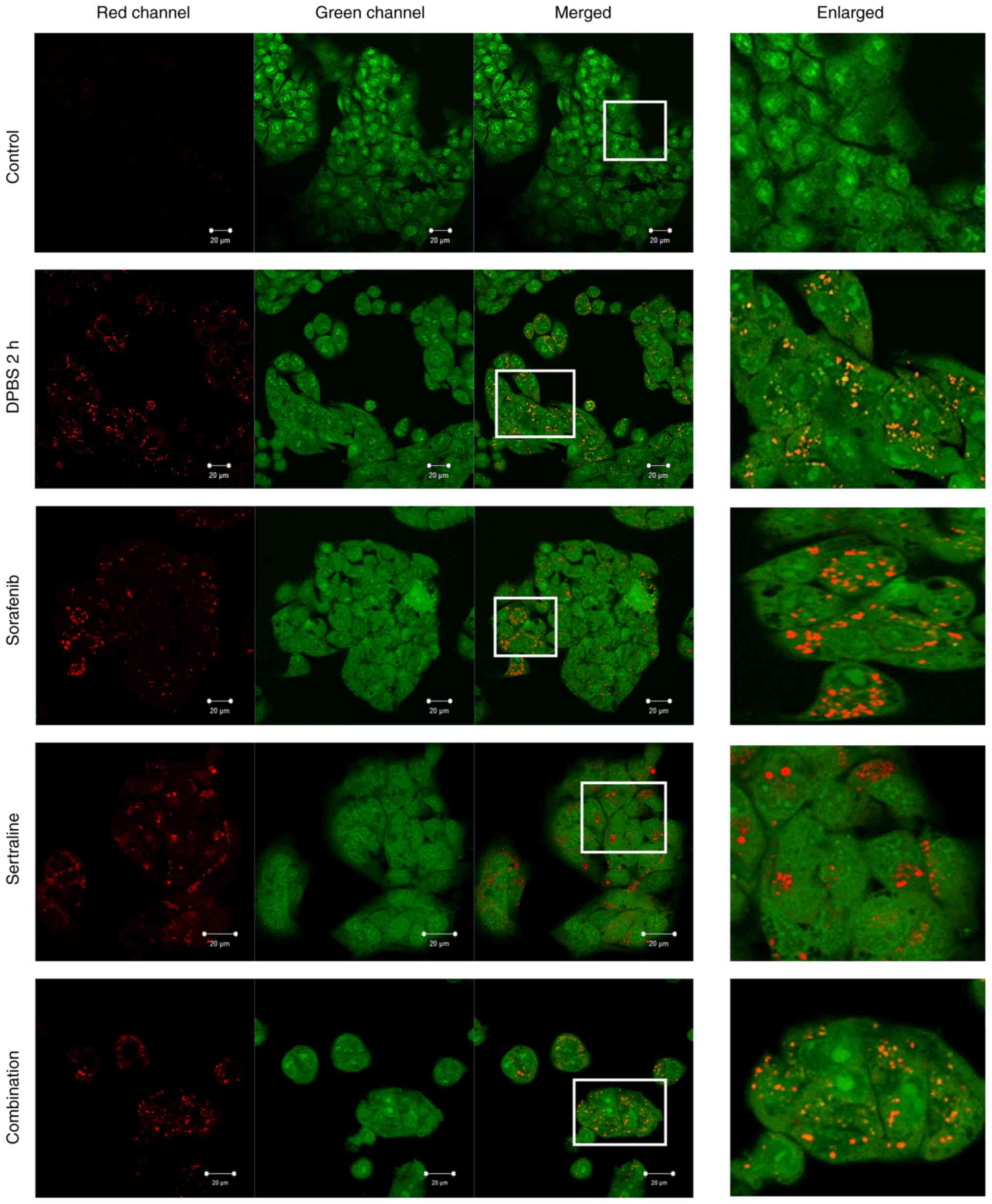
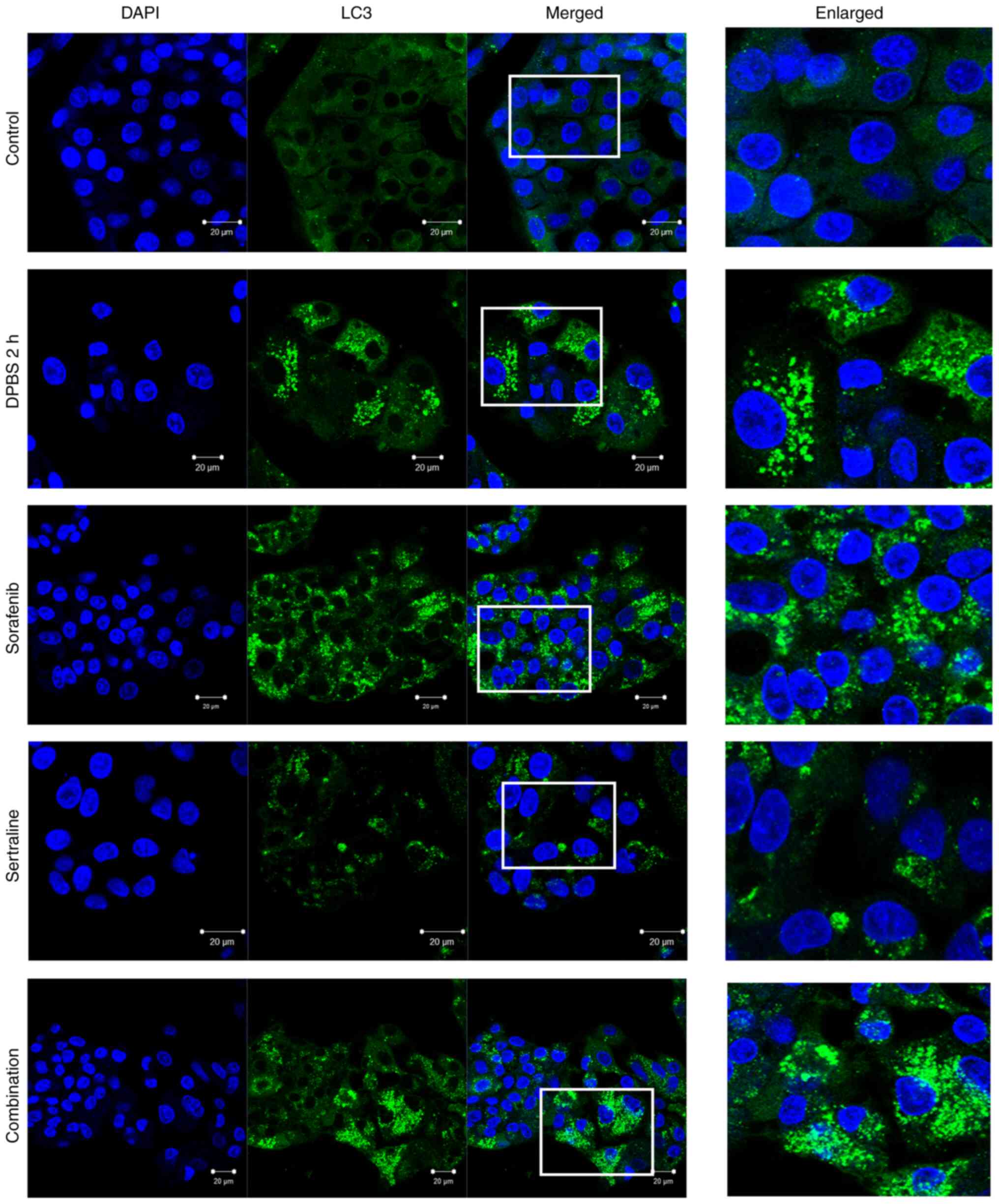
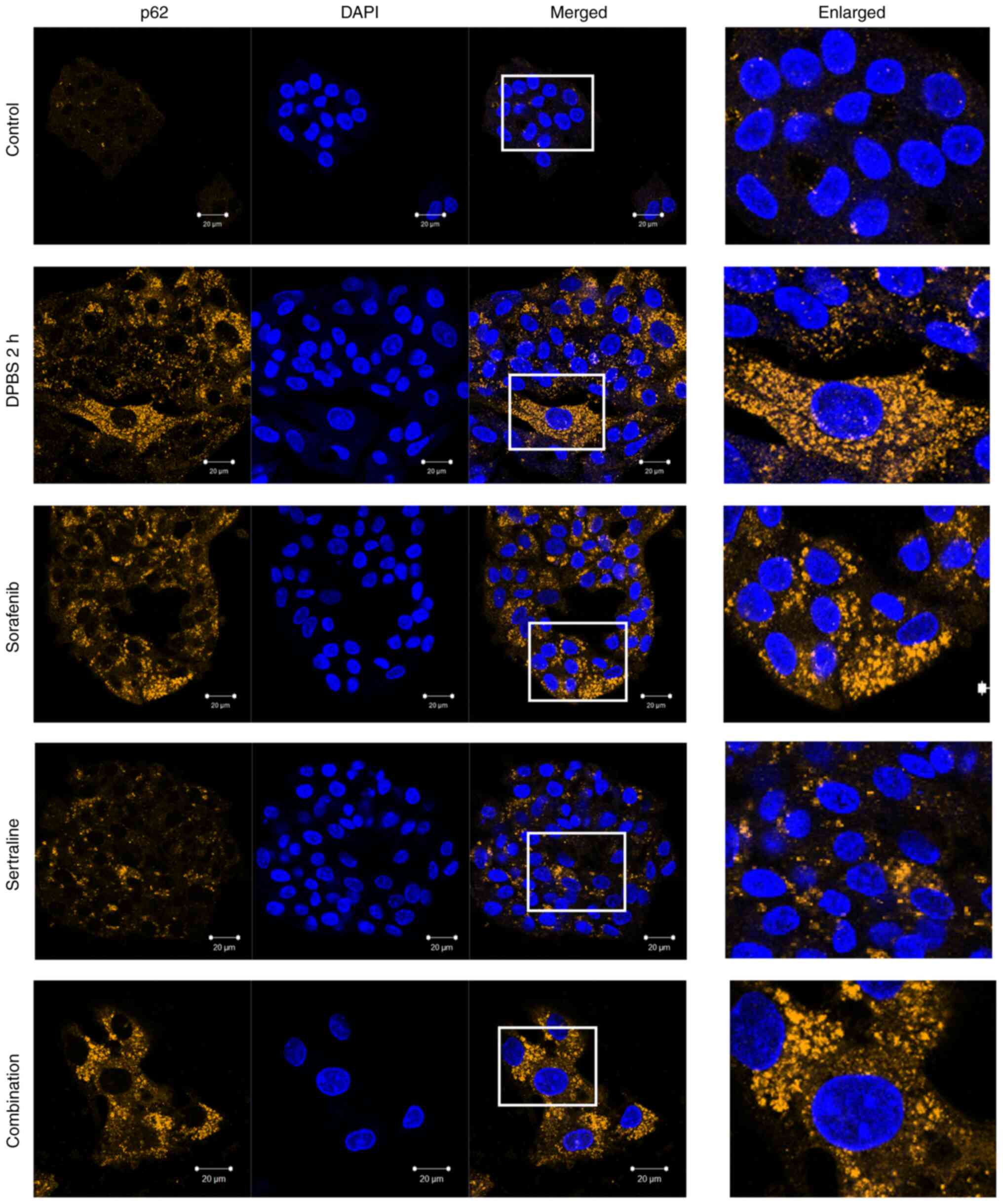
|
1
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tang W, Chen Z, Zhang W, Cheng Y, Zhang B,
Wu F, Wang Q, Wang S, Rong D, Reiter FP, et al: The mechanisms of
sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis
and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
5(87)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Liu J, Xia S, Zhang B, Mohammed DM, Yang
X, Zhu Y and Jiang X: Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors
approved for systemic therapy of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma:
Recent advances and future perspectives. Discov Oncol.
15(259)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zarlashat Y, Abbas S and Ghaffar A:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Beyond the border of advanced stage
therapy. Cancers (Basel). 16(2034)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Baú-Carneiro JL, Akemi Guirao Sumida I,
Gallon M, Zaleski T, Boia-Ferreira M and Bridi Cavassin F:
Sertraline repositioning: An overview of its potential use as a
chemotherapeutic agent after four decades of tumor reversal
studies. Transl Oncol. 16(101303)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jiang X, Lu W, Shen X, Wang Q, Lv J, Liu
M, Cheng F, Zhao Z and Pang X: Repurposing sertraline sensitizes
non-small cell lung cancer cells to erlotinib by inducing
autophagy. JCI Insight. 3(e98921)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xia D, Zhang YT, Xu GP, Yan WW, Pan XR and
Tong JH: Sertraline exerts its antitumor functions through both
apoptosis and autophagy pathways in acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Leuk Lymphoma. 58:1–10. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Telerman A, Tuynder M, Dupressoir T,
Robaye B, Sigaux F, Shaulian E, Oren M, Rommelaere J and Amson R: A
model for tumor suppression using H-1 parvovirus. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 90:8702–8706. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Sun T, Liu H and Ming L: Multiple roles of
autophagy in the sorafenib resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:716–727. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Elleithi Y, El-Gayar A and Amin MN:
Autophagy modulation attenuates sorafenib resistance in HCC induced
in rats. Cell Death Dis. 15(595)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Gómez-Virgilio L, Silva-Lucero MD,
Flores-Morelos DS, Gallardo-Nieto J, Lopez-Toledo G,
Abarca-Fernandez AM, Zacapala-Gómez AE, Luna-Muñoz J, Montiel-Sosa
F, Soto-Rojas LO, et al: Autophagy: A key regulator of homeostasis
and disease: An overview of molecular mechanisms and modulators.
Cells. 11(2262)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang K, Zhang Q, Jia R, Xiang S and Xu L:
A comprehensive review of the relationship between autophagy and
sorafenib-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: Ferroptosis is
noteworthy. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11(1156383)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hwang HY, Shim JS, Kim D and Kwon HJ:
Antidepressant drug sertraline modulates AMPK-MTOR
signaling-mediated autophagy via targeting mitochondrial VDAC1
protein. Autophagy. 17:2783–2799. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zinnah KMA, Seol JW and Park SY:
Inhibition of autophagy flux by sertraline attenuates TRAIL
resistance in lung cancer via death receptor 5 upregulation. Int J
Mol Med. 46:795–805. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ozunal ZG, Cakil YD, Isan H, Saglam E and
Aktas RG: Sertraline in combination with sorafenib: A promising
pharmacotherapy to target both depressive disorders and
hepatocellular cancer. Biol Futur. 70:341–348. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chen R, Zou Y, Mao D, Sun D, Gao G, Shi J,
Liu X, Zhu C, Yang M, Ye W, et al: The general amino acid control
pathway regulates mTOR and autophagy during serum/glutamine
starvation. J Cell Biol. 206:173–182. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ladd AD, Duarte S, Sahin I and Zarrinpar
A: Mechanisms of drug resistance in HCC. Hepatology. 79:926–940.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhu YJ, Zheng B, Wang HY and Chen L: New
knowledge of the mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in liver
cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:614–622. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Duarte D and Vale N: Antidepressant drug
sertraline against human cancer cells. Biomolecules.
12(1513)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Parkhitko AA, Favorova OO and Henske EP:
Autophagy: Mechanisms, regulation, and its role in tumorigenesis.
Biochemistry (Mosc). 78:355–367. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li X, He S and Ma B: Autophagy and
autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer.
19(12)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
White E and DiPaola RS: The double-edged
sword of autophagy modulation in cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:5308–5316. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Runwal G, Stamatakou E, Siddiqi FH, Puri
C, Zhu Y and Rubinsztein DC: LC3-positive structures are prominent
in autophagy-deficient cells. Sci Rep. 9(10147)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cohen-Kaplan V, Ciechanover A and Livneh
I: p62 at the crossroad of the ubiquitin-proteasome system and
autophagy. Oncotarget. 7:83833–83834. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pankiv S, Clausen TH, Lamark T, Brech A,
Bruun JA, Outzen H, Øvervatn A, Bjørkøy G and Johansen T:
p62/SQSTM1 binds directly to Atg8/LC3 to facilitate degradation of
ubiquitinated protein aggregates by autophagy. J Biol Chem.
282:24131–24145. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yoshii SR and Mizushima N: Monitoring and
measuring autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 18(1865)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Pugsley HR: Assessing autophagic flux by
measuring LC3, p62, and LAMP1 Co-localization using multispectral
imaging flow cytometry. J Vis Exp. 21(55637)2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
He L, Fu Y, Tian Y, Wang X, Zhou X, Ding
RB, Qi X and Bao J: Antidepressants as autophagy modulators for
cancer therapy. Molecules. 28(7594)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Thomé MP, Filippi-Chiela EC, Villodre ES,
Migliavaca CB, Onzi GR, Felipe KB and Lenz G: Ratiometric analysis
of acridine orange staining in the study of acidic organelles and
autophagy. J Cell Sci. 129:4622–4632. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chinnapaka S, Bakthavachalam V and
Munirathinam G: Repurposing antidepressant sertraline as a
pharmacological drug to target prostate cancer stem cells: Dual
activation of apoptosis and autophagy signaling by deregulating
redox balance. Am J Cancer Res. 10:2043–2065. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|