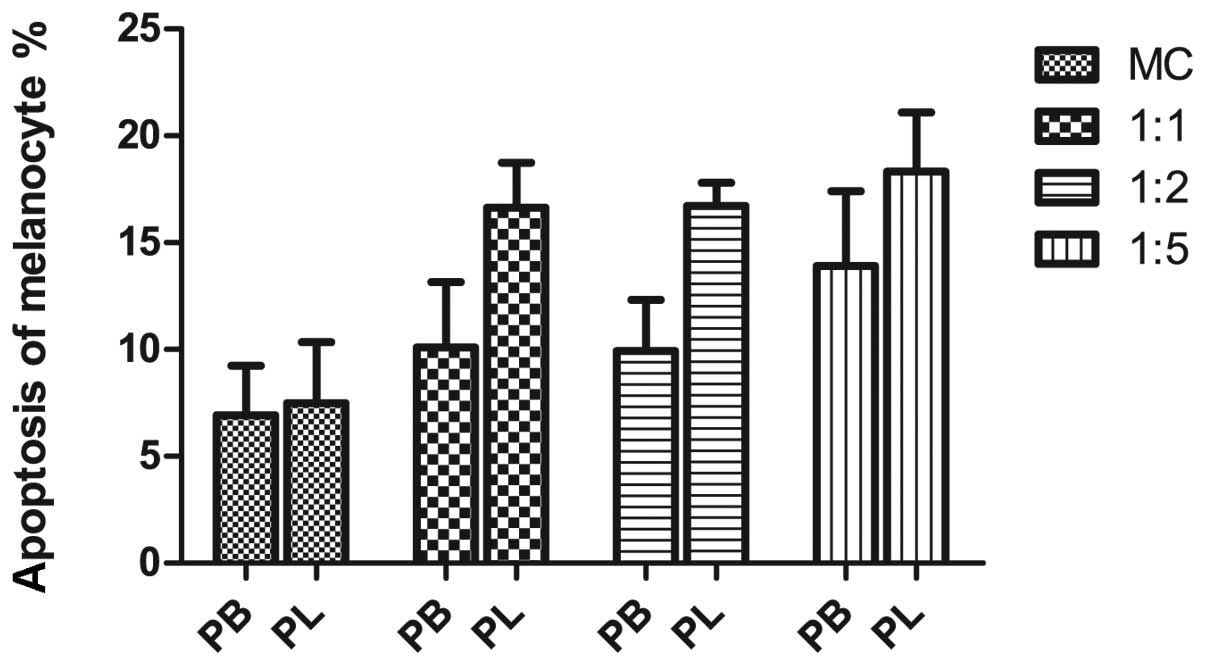
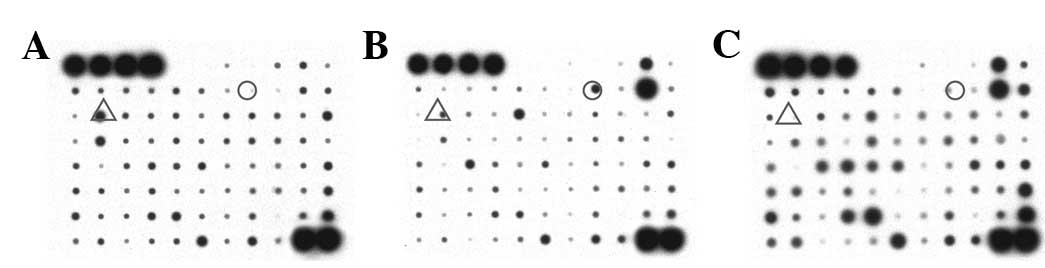
|
1
|
Yee C, Thompson JA, Roche P, et al:
Melanocyte destruction after antigen-specific immunotherapy of
melanoma: direct evidence of T cell-mediated vitiligo. J Exp Med.
192:1637–44. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kemp EH, Waterman EA, Hawes BE, et al: The
melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1, a novel target of
autoantibody responses in vitiligo. J Clin Invest. 109:923–930.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Palermo B, Campanelli R, Garbelli S, et
al: Specific cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses against
Melan-A/MART1, tyrosinase and gp100 in vitiligo by the use of major
histocompatibility complex/peptide tetramers: the role of cellular
immunity in the etiopathogenesis of vitiligo. J Invest Dermatol.
117:326–332. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Glassman SJ: Vitiligo, reactive oxygen
species and T-cells (Review). Clin Sci (Lond). 120:99–120. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Le Poole IC and Luiten RM: Autoimmune
etiology of generalized vitiligo (Review). Curr Dir Autoimmun.
10:227–243. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Le Poole IC, ElMasri WM, Denman CJ, et al:
Langerhans cells and dendritic cells are cytotoxic towards HPV16 E6
and E7 expressing target cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
57:789–797. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ongenae K, Van Geel N and Naeyaert JM:
Evidence for an autoimmune pathogenesis of vitiligo (Review).
Pigment Cell Res. 16:90–100. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Badri AM, Todd PM, Garioch JJ, et al: An
immunohistological study of cutaneous lymphocytes in vitiligo. J
Pathol. 170:149–155. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wankowicz-Kalinska A, van den Wijngaard
RM, Tigges BJ, et al: Immunopolarization of CD4+ and
CD8+ T cells to Type-1-like is associated with
melanocyte loss in human vitiligo. Lab Invest. 83:683–695.
2003.
|
|
10
|
Wankowicz-Kalinska A, Le Poole C, van den
Wijngaard R, et al: Melanocyte-specific immune response in melanoma
and vitiligo: two faces of the same coin? Pigment Cell Res.
16:254–260. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van den Wijngaard RM, Aten J, Scheepmaker
A, et al: Expression and modulation of apoptosis regulatory
molecules in human melanocytes: significance in vitiligo. Br J
Dermatol. 143:573–581. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van den Wijngaard R, Wankowicz-Kalinska A,
Le Poole C, et al: Local immune response in skin of generalized
vitiligo patients. Destruction of melanocytes is associated with
the prominent presence of CLA+ T cells at the
perilesional site. Lab Invest. 80:1299–1309. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bos JD, Zonneveld I, Das PK, et al: The
skin immune system (SIS): distribution and immunophenotype of
lymphocyte subpopulations in normal human skin. J Invest Dermatol.
88:569–573. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gross AJ, Hunt HH, Cantor AB and Clark BC:
Sample size determination in clinical trials with an emphasis on
exponentially distributed responses. Biometrics. 43:875–883. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van den Boorn JG, Konijnenberg D,
Dellemijn TA, et al: Autoimmune destruction of skin melanocytes by
perilesional T cells from vitiligo patients. J Invest Dermatol.
129:2220–2232. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hong WS, Hu DN, Qian GP, et al: Treatment
of vitiligo in children and adolescents by autologous cultured pure
melanocytes transplantation with comparison of efficacy to results
in adults. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 25:538–543. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hong WS, Hu DN, Qian GP, et al: Ratio of
size of recipient and donor areas in treatment of vitiligo by
autologous cultured melanocyte transplantation. Br J Dermatol.
165:520–525. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu HS, Chang KL, Yu CL, et al: Alterations
in IL-6, IL-8, GM-CSF, TNF-alpha, and IFN-gamma release by
peripheral mononuclear cells in patients with active vitiligo. J
Invest Dermatol. 108:527–529. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moretti S, Spallanzani A, Amato L, et al:
New insights into the pathogenesis of vitiligo: imbalance of
epidermal cytokines at sites of lesions. Pigment Cell Res.
15:87–92. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moretti S, Spallanzani A, Amato L, et al:
Vitiligo and epidermal microenvironment: possible involvement of
keratinocyte-derived cytokines. Arch Dermatol. 138:273–274. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tu CX, Gu JS and Lin XR: Increased
interleukin-6 and granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor
levels in the sera of patients with non-segmental vitiligo. J
Dermatol Sci. 31:73–78. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Neurath MF and Finotto S: IL-6 signaling
in autoimmunity, chronic inflammation and inflammation-associated
cancer (Review). Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 22:83–89. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chalaris A, Garbers C, Rabe B, et al: The
soluble Interleukin 6 receptor: generation and role in inflammation
and cancer. Eur J Cell Biol. 90:484–494. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Krasagakis K, Hettmannsperger U, Tebbe B
and Garbe C: Cutaneous metastatic angiosarcoma with a lethal
outcome, following radiotherapy for a cervical carcinoma. Br J
Dermatol. 133:610–614. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Krasagakis K, Garbe C, Zouboulis CC and
Orfanos CE: Growth control of melanoma cells and melanocytes by
cytokines. Recent Results Cancer Res. 139:169–182. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Krasagakis K, Garbe C, Eberle J and
Orfanos CE: Tumour necrosis factors and several interleukins
inhibit the growth and modulate the antigen expression of normal
human melanocytes in vitro. Arch Dermatol Res. 287:259–265. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kotobuki Y, Tanemura A, Yang L, et al:
Dysregulation of melanocyte function by Th17-related cytokines:
significance of Th17 cell infiltration in autoimmune vitiligo
vulgaris. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 25:219–230. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dienz O and Rincon M: The effects of IL-6
on CD4 T cell responses (Review). Clin Immunol. 130:27–33. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dienz O, Eaton SM, Bond JP, et al: The
induction of antibody production by IL-6 is indirectly mediated by
IL-21 produced by CD4+ T cells. J Exp Med. 206:69–78.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoshida H, Hashizume M, Suzuki M and
Mihara M: Anti-IL-6 receptor antibody suppressed T cell activation
by inhibiting IL-2 production and inducing regulatory T cells. Eur
J Pharmacol. 634:178–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoshida H, Hashizume M and Mihara M: IL-6
blockade preferentially inhibits Th17 differentiation in
collagen-induced arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 31:127–131. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Romagnani S, Maggi E, Liotta F, et al:
Properties and origin of human Th17 cells (Review). Mol Immunol.
47:3–7. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Suzuki T, Shoji S, Yamamoto K, et al:
Essential roles of Lyn in fibronectin-mediated filamentous actin
assembly and cell motility in mast cells. J Immunol. 161:3694–3701.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vercelli D: Genetics of IL-13 and
functional relevance of IL-13 variants (Review). Curr Opin Allergy
Clin Immunol. 2:389–393. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mentink-Kane MM and Wynn TA: Opposing
roles for IL-13 and IL-13 receptor alpha 2 in health and disease
(Review). Immunol Rev. 202:191–202. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mentink-Kane MM, Cheever AW, Thompson RW,
et al: IL-13 receptor alpha 2 down-modulates granulomatous
inflammation and prolongs host survival in schistosomiasis. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:586–590. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|