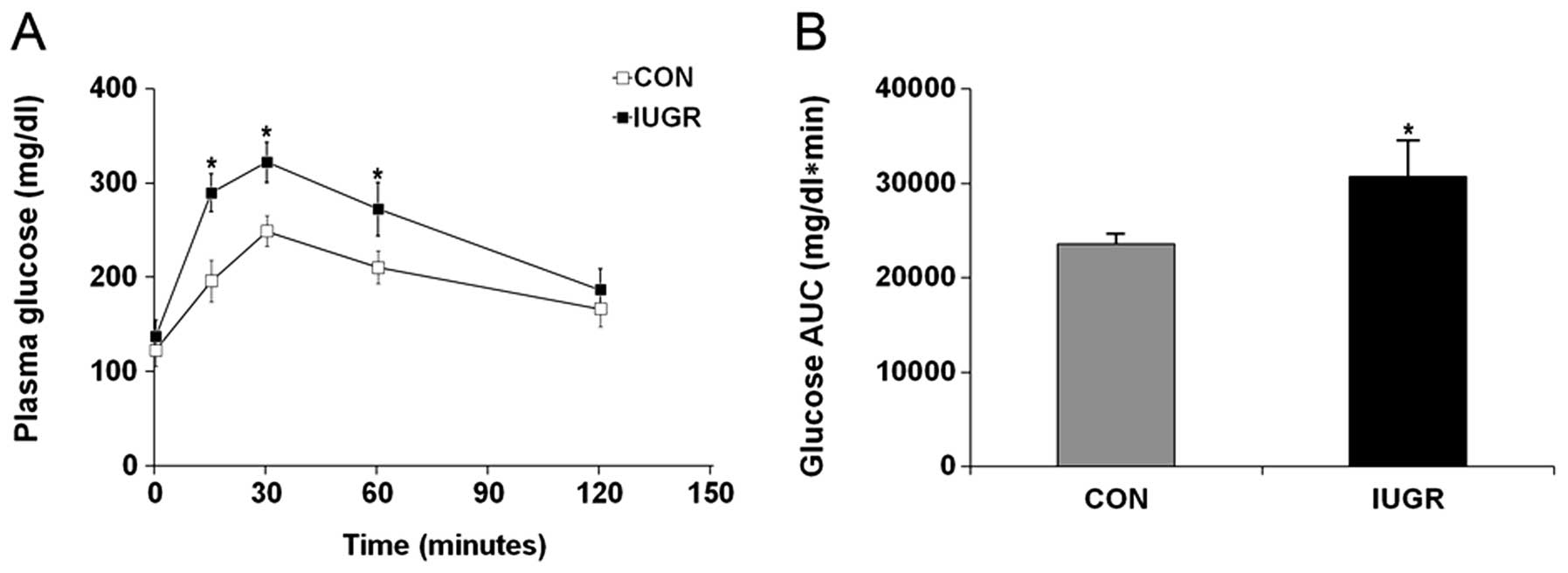
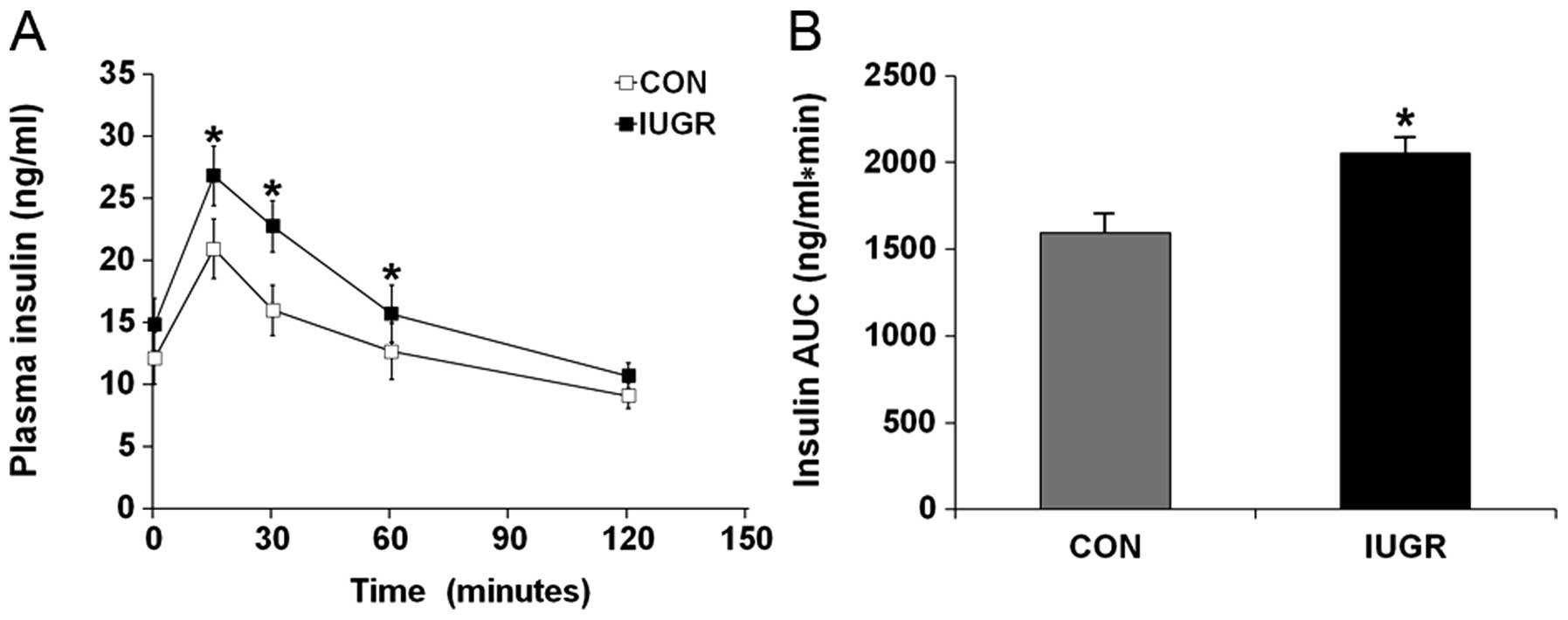
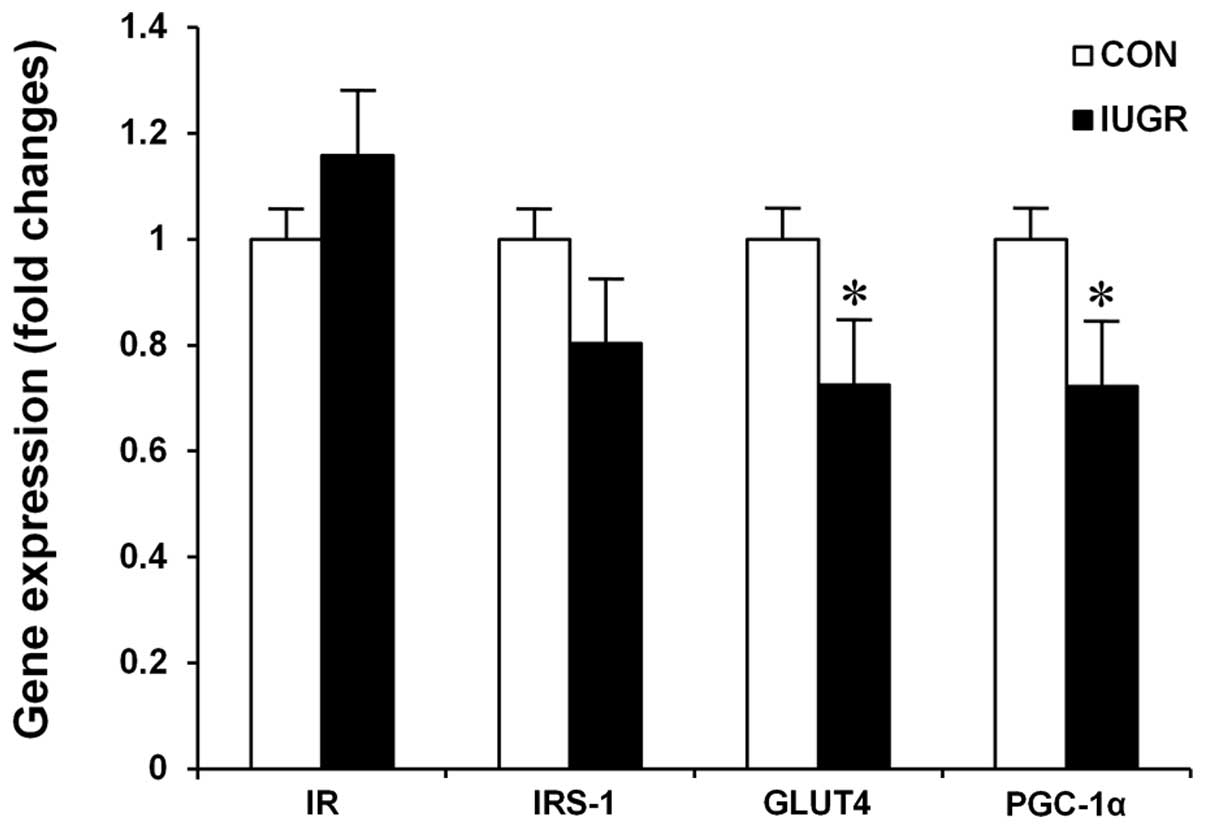
|
1
|
Barker DJ: The fetal and infant origins of
adult disease. BMJ. 301:11111990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kanaka-Gantenbein C: Fetal origins of
adult diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1205:99–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Hales CN and Barker DJ: The thrifty
phenotype hypothesis. Br Med Bull. 60:5–20. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ozanne SE, Martensz ND, Petry CJ, Loizou
CL and Hales CN: Maternal low protein diet in rats programmes fatty
acid desaturase activities in the offspring. Diabetologia.
41:1337–1342. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thamotharan M, Shin BC, Suddirikku DT,
Thamotharan S, Garg M and Devaskar SU: GLUT4 expression and
subcellular localization in the intrauterine growth-restricted
adult rat female offspring. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
288:E935–E947. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lisle SJ, Lewis RM, Petry CJ, Ozanne SE,
Hales CN and Forhead AJ: Effect of maternal iron restriction during
pregnancy on renal morphology in the adult rat offspring. Br J
Nutr. 90:33–39. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
de Grauw TJ, Myers RE and Scott WJ: Fetal
growth retardation in rats from different levels of hypoxia. Biol
Neonate. 49:85–89. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Simmons RA, Templeton LJ and Gertz SJ:
Intrauterine growth retardation leads to the development of type 2
diabetes in the rat. Diabetes. 50:2279–2286. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kahn BB: Facilitative glucose
transporters: regulatory mechanisms and dysregulation in diabetes.
J Clin Invest. 89:1367–1374. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sampaio de Freitas M, Garcia De Souza EP,
Vargas da Silva S, et al: Up-regulation of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase and glucose transporter 4 in muscle of rats subjected to
maternal undernutrition. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1639:8–16.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ozanne SE, Olsen GS, Hansen LL, et al:
Early growth restriction leads to down regulation of protein kinase
C zeta and insulin resistance in skeletal muscle. J Endocrinol.
177:235–241. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Agote M, Goya L, Ramos S, et al: Glucose
uptake and glucose transporter proteins in skeletal muscle from
undernourished rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
281:E1101–E1109. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gavete ML, Martin MA, Alvarez C and
Escriva F: Maternal food restriction enhances insulin-induced
GLUT-4 translocation and insulin signaling pathway in skeletal
muscle from suckling rats. Endocrinology. 146:3368–3378. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Selak MA, Storey BT, Peterside I and
Simmons RA: Impaired oxidative phosphorylation in skeletal muscle
of intrauterine growth-retarded rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 285:E130–E137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lin J, Handschin C and Spiegelman BM:
Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription
coactivators. Cell Metab. 1:361–370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bird A: DNA methylation patterns and
epigenetic memory. Genes Dev. 16:6–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lillycrop KA, Phillips ES, Jackson AA,
Hanson MA and Burdge GC: Dietary protein restriction of pregnant
rats induces and folic acid supplementation prevents epigenetic
modification of hepatic gene expression in the offspring. J Nutr.
135:1382–1386. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bock C, Reither S, Mikeska T, Paulsen M,
Walter J and Lengauer T: BiQ Analyzer: visualization and quality
control for DNA methylation data from bisulfite sequencing.
Bioinformatics. 21:4067–4068. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu XM, Kong J, Song WW and Lu Y: Glucose
metabolic and gluconeogenic pathways disturbance in the
intrauterine growth restricted adult male rats. Chin Med Sci J.
24:208–212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Blondeau B, Avril I, Duchene B and Breant
B: Endocrine pancreas development is altered in foetuses from rats
previously showing intra-uterine growth retardation in response to
malnutrition. Diabetologia. 45:394–401. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Phipps K, Barker DJ, Hales CN, Fall CH,
Osmond C and Clark PM: Fetal growth and impaired glucose tolerance
in men and women. Diabetologia. 36:225–228. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sadiq HF, Das UG, Tracy TF and Devaskar
SU: Intra-uterine growth restriction differentially regulates
perinatal brain and skeletal muscle glucose transporters. Brain
Res. 823:96–103. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Raychaudhuri N, Raychaudhuri S,
Thamotharan M and Devaskar SU: Histone code modifications repress
glucose transporter 4 expression in the intrauterine
growth-restricted offspring. J Biol Chem. 283:13611–13626. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boloker J, Gertz SJ and Simmons RA:
Gestational diabetes leads to the development of diabetes in
adulthood in the rat. Diabetes. 51:1499–1506. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ozanne SE, Jensen CB, Tingey KJ, Storgaard
H, Madsbad S and Vaag AA: Low birthweight is associated with
specific changes in muscle insulin-signalling protein expression.
Diabetologia. 48:547–552. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jaquet D, Vidal H, Hankard R, Czernichow P
and Levy-Marchal C: Impaired regulation of glucose transporter 4
gene expression in insulin resistance associated with in utero
undernutrition. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 86:3266–3271.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ling C, Del Guerra S, Lupi R, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of PPARGC1A in human type 2 diabetic islets
and effect on insulin secretion. Diabetologia. 51:615–622. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mootha VK, Lindgren CM, Eriksson KF, et
al: PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative
phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes.
Nat Genet. 34:267–273. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ling JQ and Hoffman AR: Epigenetics of
long-range chromatin interactions. Pediatr Res. 61:R11–R16. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Thompson JD, Higgins DG and Gibson TJ:
CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple
sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific
gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res.
22:4673–4680. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Gemma C, Sookoian S, Alvarinas J, et al:
Maternal pregestational BMI is associated with methylation of the
PPARGC1A promoter in newborns. Obesity (Silver Spring).
17:1032–1039. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brons C, Jacobsen S, Nilsson E, et al:
Deoxyribonucleic acid methylation and gene expression of PPARGC1A
in human muscle is influenced by high-fat overfeeding in a
birth-weight-dependent manner. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
95:3048–3056. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lillycrop KA, Phillips ES, Torrens C,
Hanson MA, Jackson AA and Burdge GC: Feeding pregnant rats a
protein-restricted diet persistently alters the methylation of
specific cytosines in the hepatic PPAR alpha promoter of the
offspring. Br J Nutr. 100:278–282. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|