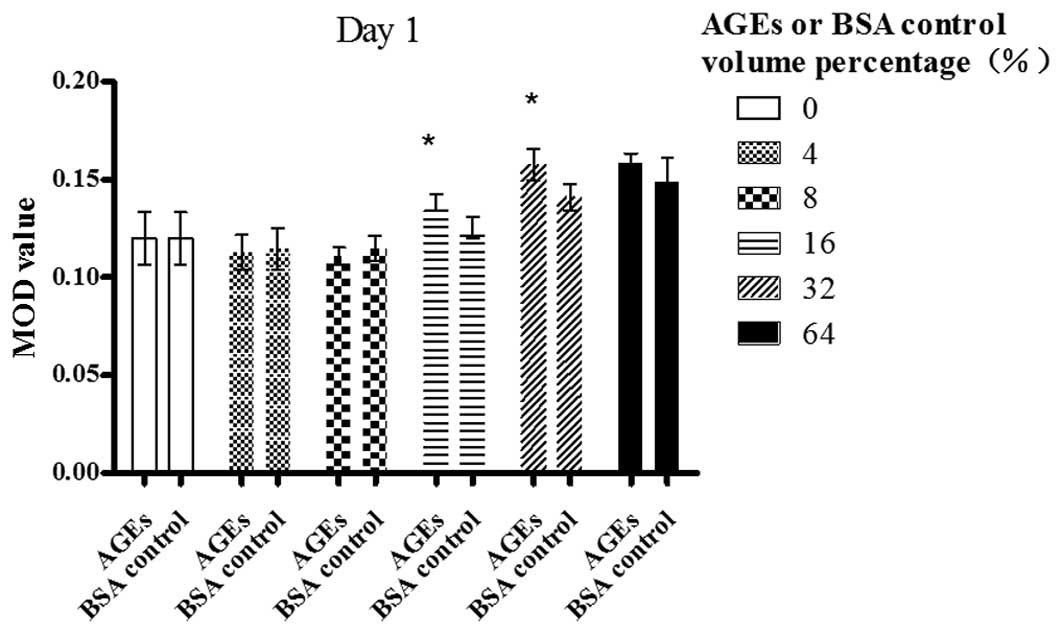
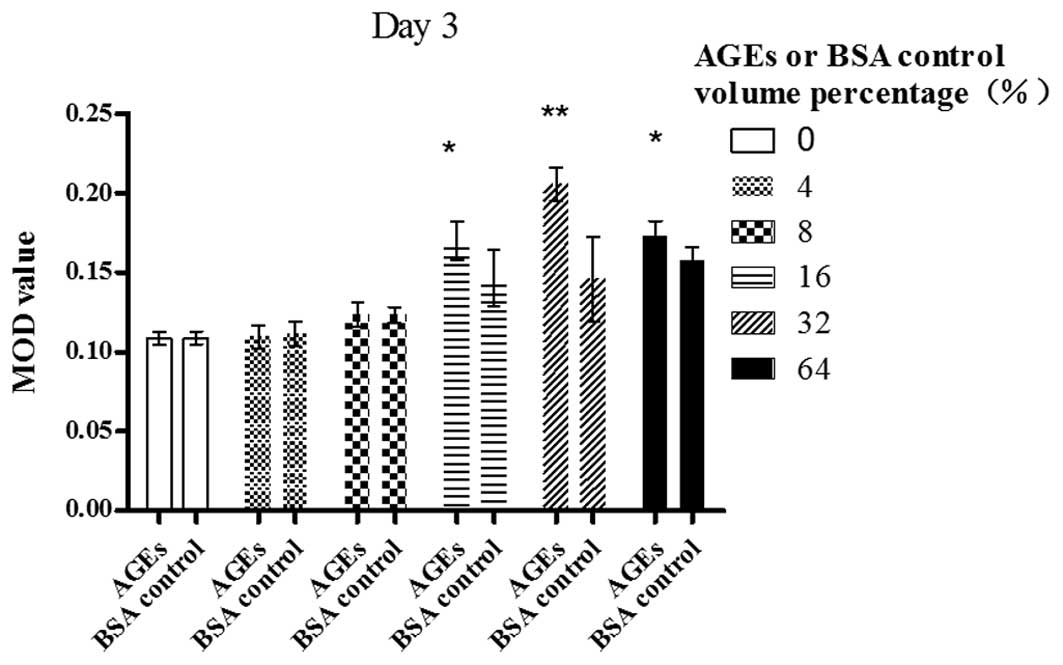
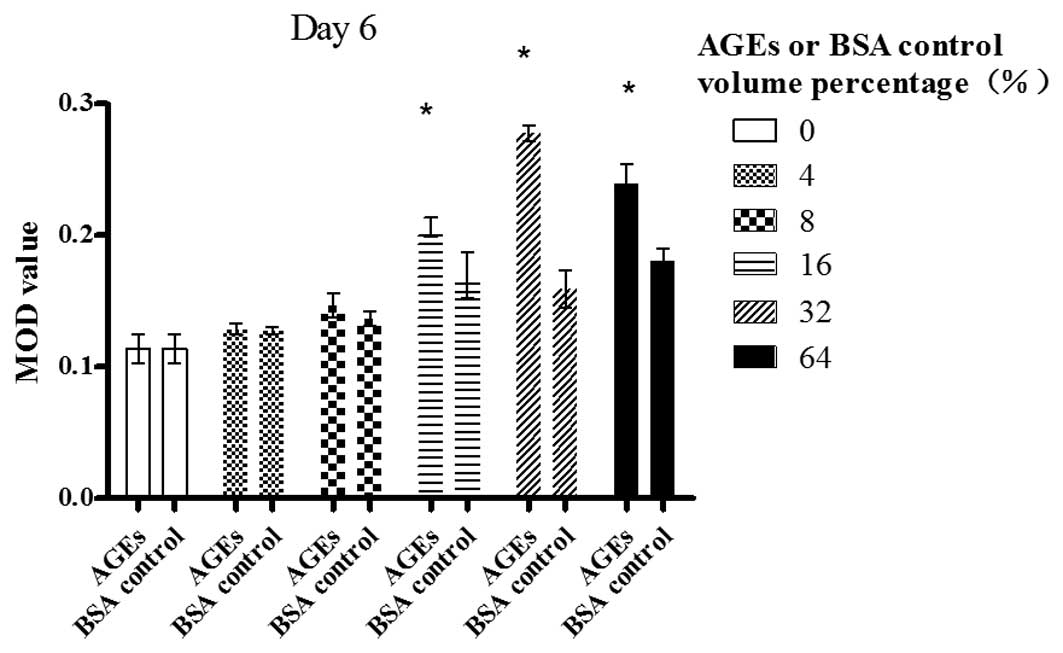
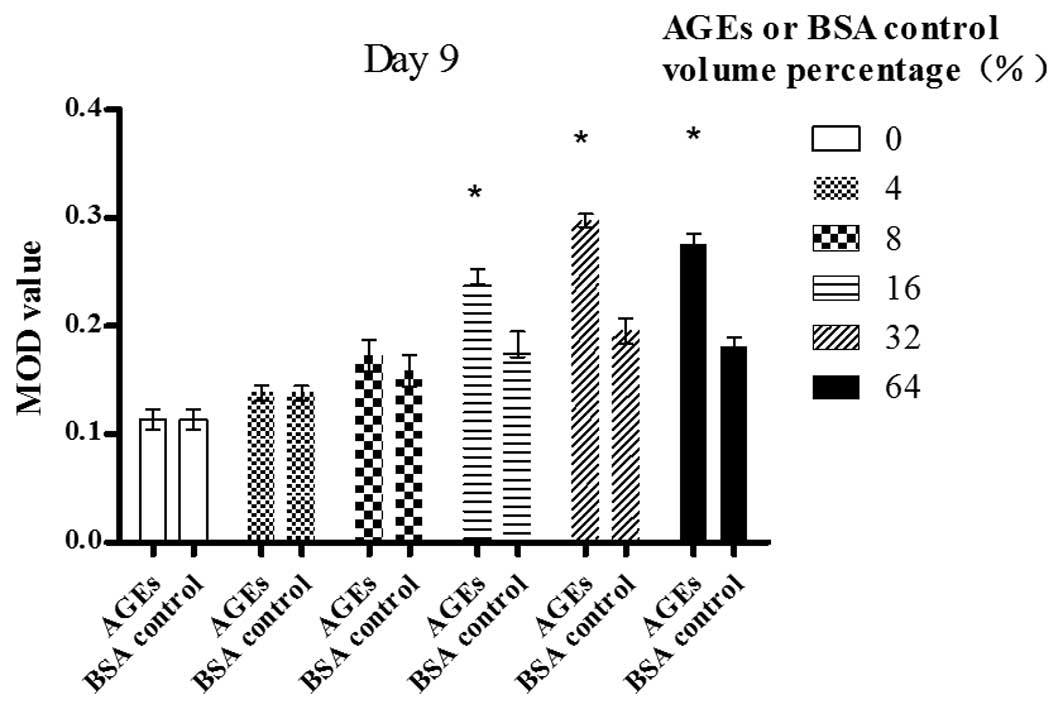
|
1
|
Daroux M, Prévost G, Maillard-Lefebvre H,
Gaxatte C, D’Agati VD, Schmidt AM and Boulanger E: Advanced
glycation end-products: implications for diabetic and non-diabetic
nephropathies. Diabetes Metab. 36:1–10. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Berrou J, Tostivint I, Verrecchia F,
Berthier C, Boulanger E, Mauviel A, Marti HP, Wautier MP, Wautier
JL, Rondeau E and Hertig A: Advanced glycation end products
regulate extracellular matrix protein and protease expression by
human glomerular mesangial cells. Int J Mol Med. 23:513–520.
2009.
|
|
3
|
Wolffenbuttel BH, Giordano D, Founds HW
and Bucala R: Long-term assessment of glucose control by
haemoglobin-AGE measurement. Lancet. 347:513–515. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Meerwaldt R, Links T, Zeebregts C, Tio R,
Hillebrands JL and Smit A: The clinical relevance of assessing
advanced glycation endproducts accumulation in diabetes. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 7:292008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamagishi S: Role of advanced glycation
end products (AGEs) and receptor for AGEs (RAGE) in vascular damage
in diabetes. Exp Gerontol. 46:217–224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bringmann A and Wiedemann P: Involvement
of Müller glial cells in epiretinal membrane formation. Graefes
Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 247:865–883. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Simó R, Carrasco E, García-Ramírez M and
Hernández C: Angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors in proliferative
diabetic retinopathy. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2:71–98. 2006.
|
|
8
|
Aiello LP, Avery RL, Arrigg PG, Keyt BA,
Jampel HD, Shah ST, Pasquale LR, Thieme H, Iwamoto MA, Park JE, et
al: Vascular endothelial growth factor in ocular fluid of patients
with diabetic retinopathy and other retinal disorders. N Engl J
Med. 331:1480–1487. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kakehashi A, Inoda S, Mameuda C, Kuroki M,
Jono T, Nagai R, Horiuchi S, Kawakami M and Kanazawa Y:
Relationship among VEGF, VEGF receptor, AGEs and macrophages in
proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
79:438–445. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Payne JF, Tangpricha V, Cleveland J, Lynn
MJ, Ray R and Srivastava SK: Serum insulin-like growth factor-I in
diabetic retinopathy. Mol Vis. 17:2318–2324. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shimizu F, Sano Y, Haruki H and Kanda T:
Advanced glycation end-products induce basement membrane
hypertrophy in endoneurial microvessels and disrupt the blood-nerve
barrier by stimulating the release of TGF-β and vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by pericytes. Diabetologia.
54:1517–1526. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Simó R, Vidal MT, García-Arumí J, Carrasco
E, García-Ramírez M, Segura RM and Hernández C: Intravitreous
hepatocyte growth factor in patients with proliferative diabetic
retinopathy: a case-control study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.
71:36–44. 2006.
|
|
13
|
Yang XM, Yafai Y, Wiedemann P, Kuhrt H,
Wang YS, Reichenbach A and Eichler W: Hypoxia-induced upregulation
of pigment epithelium-derived factor by retinal glial (Müller)
cells. J Neurosci Res. 90:257–266. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He S, Jin ML, Worpel V and Hinton DR: A
role for connective tissue growth factor in the pathogenesis of
choroidal neovascularization. Arch Ophthalmol. 121:1283–1288. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Watanabe D, Suzuma K, Suzuma I, Ohashi H,
Ojima T, Kurimoto M, Murakami T, Kimura T and Takagi H: Vitreous
levels of angiopoietin 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor in
patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Am J Ophthalmol.
139:476–481. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cao R, Eriksson A, Kubo H, Alitalo K, Cao
Y and Thyberg J: Comparative evaluation of FGF-2-, VEGF-A- and
VEGF-C-induced angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis, vascular
fenestrations and permeability. Circ Res. 94:664–670. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tokuda H, Adachi S, Matsushima-Nishiwaki
R, Kato K, Natsume H, Otsuka T and Kozawa O: Enhancement of basic
fibroblast growth factor-stimulated VEGF synthesis by Wnt3a in
osteoblasts. Int J Mol Med. 27:859–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lee JJ, Hsiao CC, Yang IH, Chou MH, Wu CL,
Wei YC, Chen CH and Chuang JH: High-mobility group box 1 protein is
implicated in advanced glycation end products-induced vascular
endothelial growth factor A production in the rat retinal ganglion
cell line RGC-5. Mol Vis. 18:838–850. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wakakura M and Foulds WS:
Immunocytochemical characteristics of Müller cells cultured from
adult rabbit retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 29:892–900.
1988.
|
|
20
|
Liu Y and Wakakura M: P1-/P2-purinergic
receptors on cultured rabbit retinal Müller cells. Jpn J
Ophthalmol. 42:33–40. 1998.
|
|
21
|
Neumann A, Schinzel R, Palm D, Riederer P
and Münch G: High molecular weight hyaluronic acid inhibits
advanced glycation endproduct-induced NF-kappaB activation and
cytokine expression. FEBS Lett. 453:283–287. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vlassara H, Brownlee M, Manogue KR,
Dinarello CA and Pasagian A: Cachectin/TNF and IL-1 induced by
glucose-modified proteins: role in normal tissue remodeling.
Science. 240:1546–1548. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Walcher D and Marx N: Advanced glycation
end products and C-peptide-modulators in diabetic vasculopathy and
atherogenesis. Semin Immunopathol. 31:103–111. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamagishi S, Maeda S, Matsui T, Ueda S,
Fukami K and Okuda S: Role of advanced glycation end products
(AGEs) and oxidative stress in vascular complications in diabetes.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1820:663–671. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nam MH, Lee HS, Seomun Y, Lee Y and Lee
KW: Monocyte-endothelium-smooth muscle cell interaction in
co-culture: proliferation and cytokine productions in response to
advanced glycation end products. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1810:907–912. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Curtis TM, Hamilton R, Yong PH, McVicar
CM, Berner A, Pringle R, Uchida K, Nagai R, Brockbank S and Stitt
AW: Müller glial dysfunction during diabetic retinopathy in rats is
linked to accumulation of advanced glycation end-products and
advanced lipoxidation end-products. Diabetologia. 54:690–698.
2011.
|
|
27
|
Bhatia B, Jayaram H, Singhal S, Jones MF
and Limb GA: Differences between the neurogenic and proliferative
abilities of Müller glia with stem cell characteristics and the
ciliary epithelium from the adult human eye. Exp Eye Res.
93:852–861. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guidry C, King JL and Mason JO III:
Fibrocontractive Müller cell phenotypes in proliferative diabetic
retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:1929–1939.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
King JL, Mason JO III, Cartner SC and
Guidry C: The influence of alloxan-induced diabetes on Müller cell
contraction-promoting activities in vitreous. Invest Ophthalmol Vis
Sci. 52:7485–7491. 2011.
|
|
30
|
Crawford TN, Alfaro DV III, Kerrison JB
and Jablon EP: Diabetic retinopathy and angiogenesis. Curr Diabetes
Rev. 5:8–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu W, Xu J, Wang M, Wang Q, Bi Y and Han
M: Tumor-derived vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-a
facilitates tumor metastasis through the VEGF-VEGFR1 signaling
pathway. Int J Oncol. 39:1213–1220. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dieudonné SC, La Heij EC, Diederen RM,
Kessels AG, Liem AT, Kijlstra A and Hendrikse F: Balance of
vascular endothelial growth factor and pigment epithelial growth
factor prior to development of proliferative vitreoretinopathy.
Ophthalmic Res. 39:148–154. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Funatsu H, Noma H, Mimura T, Eguchi S and
Hori S: Association of vitreous inflammatory factors with diabetic
macular edema. Ophthalmology. 116:73–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Baharivand N, Zarghami N, Panahi F, Dokht
Ghafari MY, Mahdavi Fard A and Mohajeri A: Relationship between
vitreous and serum vascular endothelial growth factor levels,
control of diabetes and microalbuminuria in proliferative diabetic
retinopathy. Clin Ophthalmol. 6:185–191. 2012.
|
|
35
|
Kanda S, Naba A and Miyata Y: Inhibition
of endothelial cell chemotaxis toward FGF-2 by gefitinib associates
with downregulation of Fes activity. Int J Oncol. 35:1305–1312.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hollborn M, Jahn K, Limb GA, Kohen L,
Wiedemann P and Bringmann A: Characterization of the basic
fibroblast growth factor-evoked proliferation of the human Müller
cell line, MIO-M1. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 242:414–422.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zakareia FA, Alderees AA, Al Regaiy KA and
Alrouq FA: Correlation of electroretinography b-wave absolute
latency, plasma levels of human basic fibroblast growth factor,
vascular endothelial growth factor, soluble fatty acid synthase and
adrenomedullin in diabetic retinopathy. J Diabetes Complications.
24:179–185. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Matsui M and Tabata Y: Enhanced
angiogenesis by multiple release of platelet-rich plasma contents
and basic fibroblast growth factor from gelatin hydrogels. Acta
Biomater. 8:1792–1801. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gündüz K and Bakri SJ: Management of
proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Compr Ophthalmol Update.
8:245–256. 2007.
|