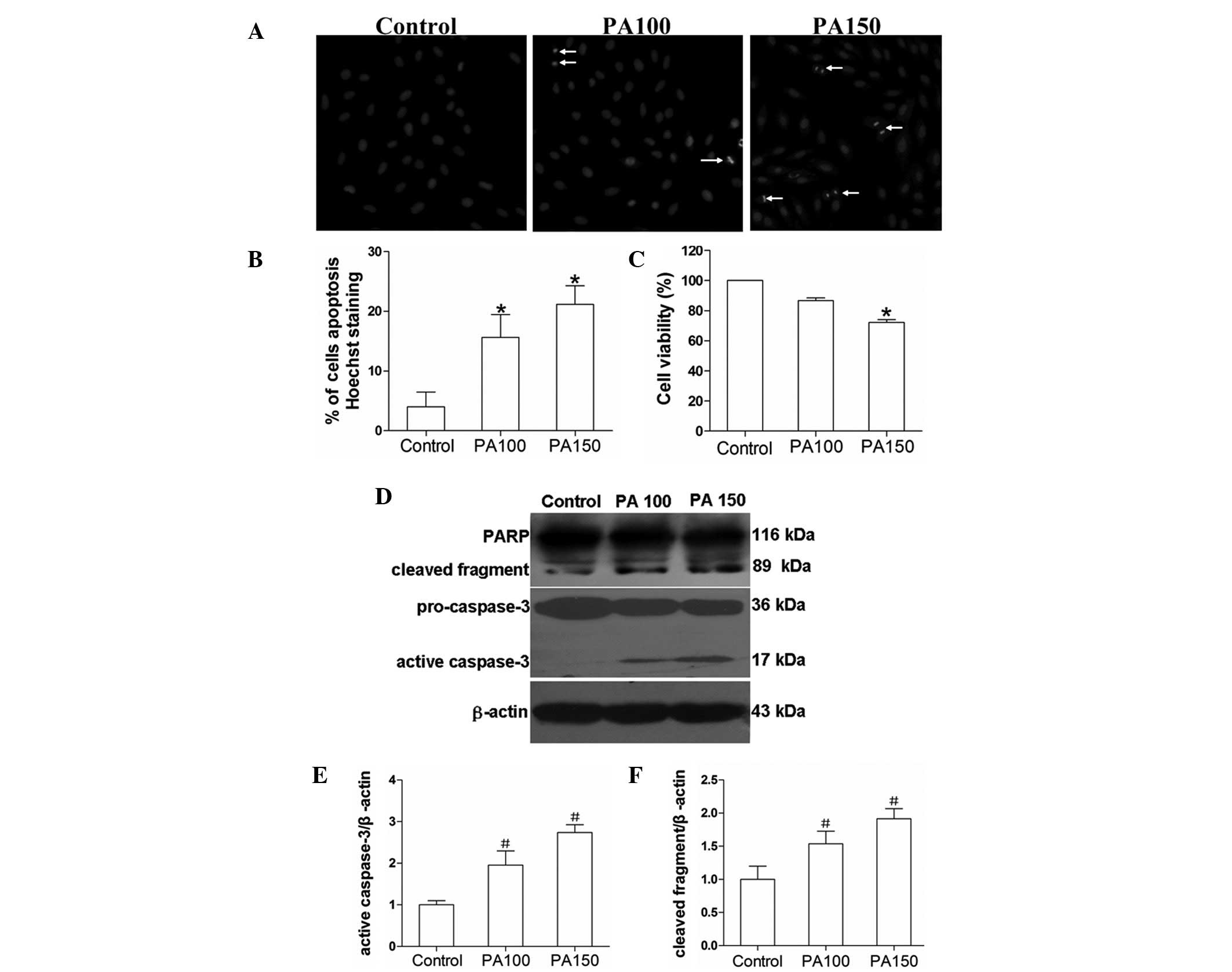
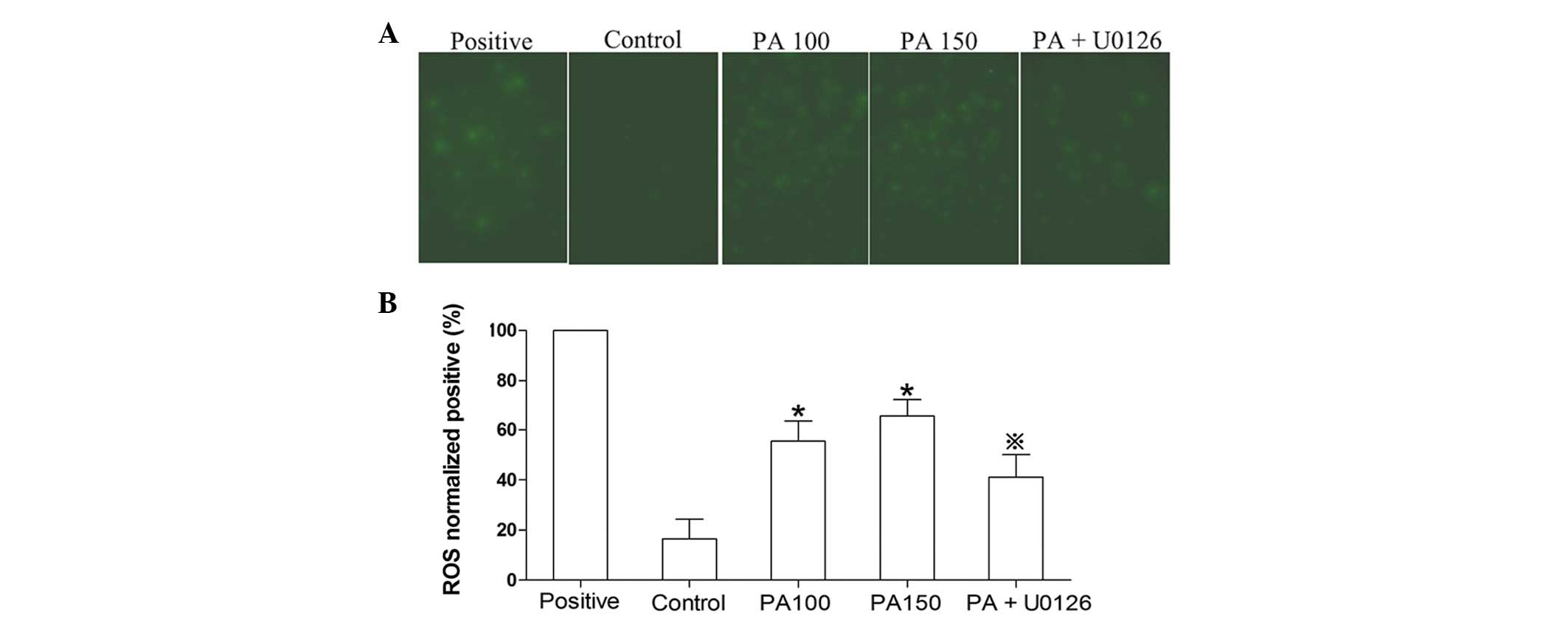
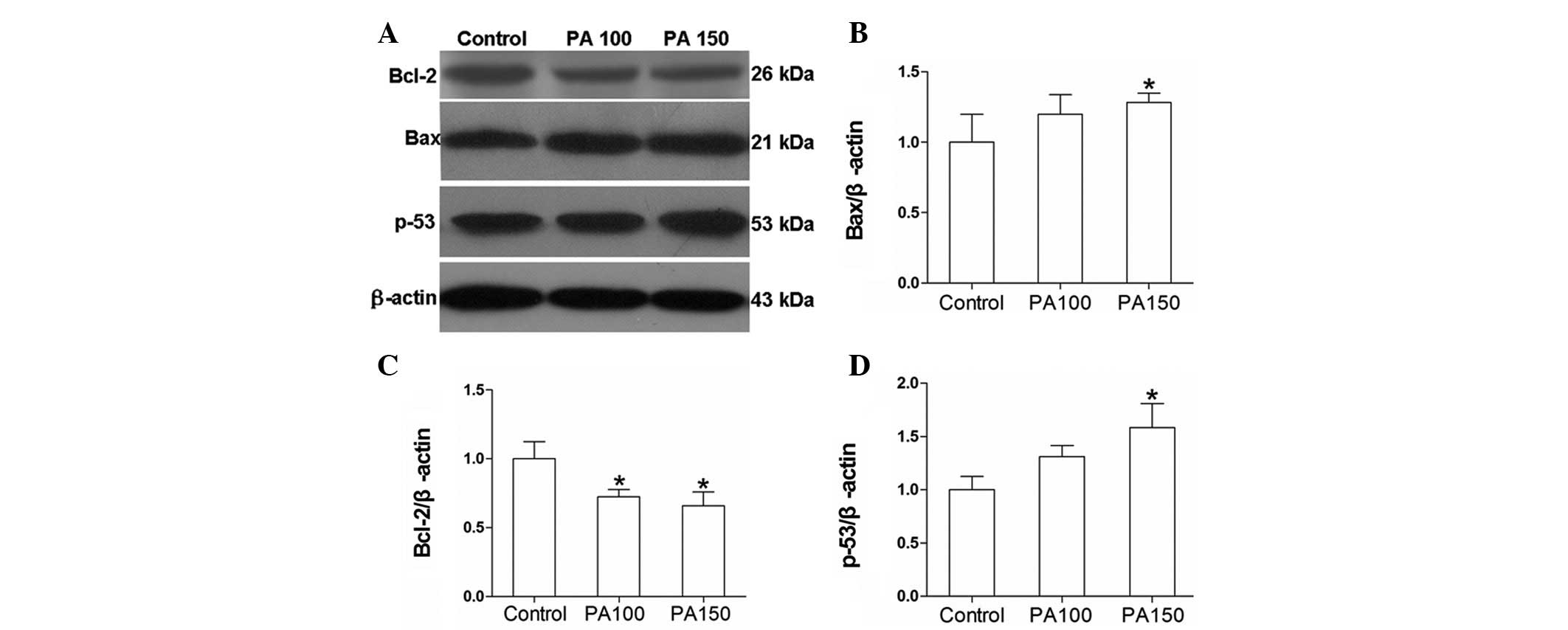
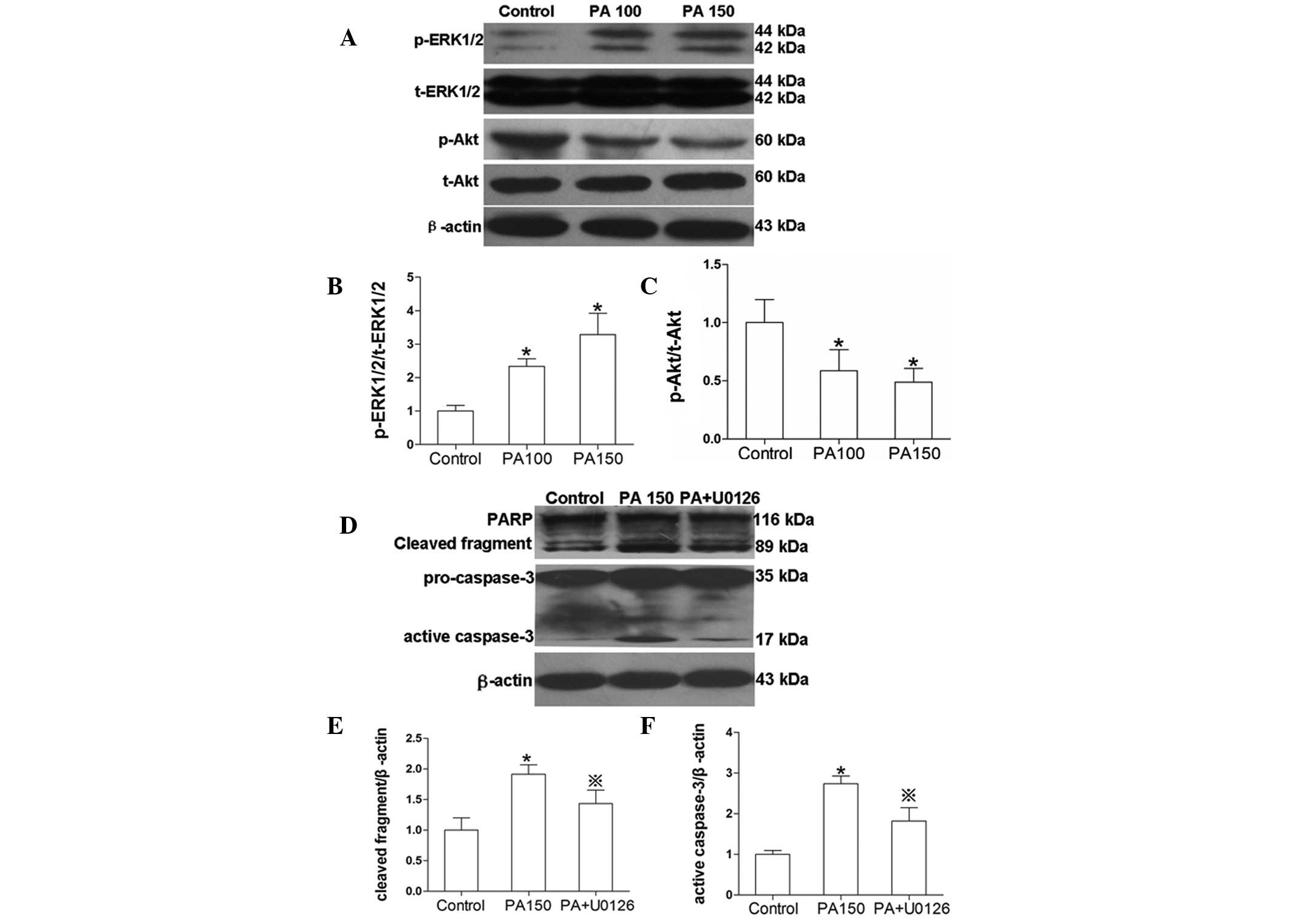
|
1
|
de Vries JE, Vork MM, Roemen TH, et al:
Saturated but not mono-unsaturated fatty acids induce apoptotic
cell death in neonatal rat ventricular myocytes. J Lipid Res.
38:1384–1394. 1997.
|
|
2
|
Miller TA, LeBrasseur NK, Cote GM, et al:
Oleate prevents palmitate-induced cytotoxic stress in cardiac
myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 336:309–315. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hickson-Bick DL, Buja LM and McMillin JB:
Palmitate-mediated alterations in the fatty acid metabolism of rat
neonatal cardiac myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 32:511–519. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haunstetter A and Izumo S: Apoptosis:
basic mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease. Circ
Res. 82:1111–1129. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Opie LH: Metabolism of free fatty acids,
glucose and catecholamines in acute myocardial infarction. Relation
to myocardial ischemia and infarct size. Am J Cardiol. 36:938–953.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Oliver MF, Kurien VA and Greenwood TW:
Relation between serum-free-fatty acids and arrhythmias and death
after acute myocardial infarction. Lancet. 1:710–714. 1968.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vik-Mo H and Mjos OD: Influence of free
fatty acids on myocardial oxygen consumption and ischemic injury.
Am J Cardiol. 48:361–365. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Listenberger LL, Ory DS and Schaffer JE:
Palmitate-induced apoptosis can occur through a
ceramide-independent pathway. J Biol Chem. 276:14890–14895. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sparagna GC, Hickson-Bick DL, Buja LM and
McMillin JB: A metabolic role for mitochondria in palmitate-induced
cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
279:H2124–H2132. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cave AC, Brewer AC, Narayanapanicker A, et
al: NADPH oxidases in cardiovascular health and disease. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 8:691–728. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Selvaraju V, Joshi M, Suresh S, Sanchez
JA, Maulik N and Maulik G: Diabetes, oxidative stress, molecular
mechanism and cardiovascular disease - an overview. Toxicol Mech
Methods. 22:330–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Polyak K, Xia Y, Zweier JL, Kinzler KW and
Vogelstein B: A model for p53-induced apoptosis. Nature.
389:300–305. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Agarwal ML, Taylor WR, Chernov MV,
Chernova OB and Stark GR: The p53 network. J Biol Chem. 273:1–4.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hemann MT and Lowe SW: The p53-Bcl-2
connection. Cell Death Differ. 13:1256–1259. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Haupt S, Berger M, Goldberg Z and Haupt Y:
Apoptosis - the p53 network. J Cell Sci. 116:4077–4085. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
von Harsdorf R, Li PF and Dietz R:
Signaling pathways in reactive oxygen species-induced cardiomyocyte
apoptosis. Circulation. 99:2934–2941. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Circu ML and Aw TY: Reactive oxygen
species, cellular redox systems and apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
48:749–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lu Z and Xu S: ERK1/2 MAP kinases in cell
survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life. 58:621–631. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tantini B, Pignatti C, Fattori M, et al:
Polyamine depletion inhibits etoposide-induced NF-kappaB activation
in transformed mouse fibroblasts. Amino Acids. 27:207–214. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Mao W, Ding B and Liang CS:
ERKs/p53 signal transduction pathway is involved in
doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in H9c2 cells and cardiomyocytes. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1956–H1965. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong XB, Yang CT, Zheng DD, et al:
Inhibition of ROS-activated ERK1/2 pathway contributes to the
protection of H2S against chemical hypoxia-induced injury in H9c2
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 362:149–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dyntar D, Eppenberger-Eberhardt M, Maedler
K, et al: Glucose and palmitic acid induce degeneration of
myofibrils and modulate apoptosis in rat adult cardiomyocytes.
Diabetes. 50:2105–2113. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fiordaliso F, Leri A, Cesselli D, et al:
Hyperglycemia activates p53 and p53-regulated genes leading to
myocyte cell death. Diabetes. 50:2363–2375. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cousin SP, Hugl SR, Wrede CE, Kajio H,
Myers MG Jr and Rhodes CJ: Free fatty acid-induced inhibition of
glucose and insulin-like growth factor I-induced deoxyribonucleic
acid synthesis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1.
Endocrinology. 142:229–240. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nicholson DW and Thornberry NA: Caspases:
killer proteases. Trends Biochem Sci. 22:299–306. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Herceg Z and Wang ZQ: Failure of
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage by caspases leads to induction
of necrosis and enhanced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 19:5124–5133.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Diffley JM, Wu M, Sohn M, Song W, Hammad
SM and Lyons TJ: Apoptosis induction by oxidized glycated LDL in
human retinal capillary pericytes is independent of activation of
MAPK signaling pathways. Mol Vis. 15:135–145. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takano H, Zou Y, Hasegawa H, Akazawa H,
Nagai T and Komuro I: Oxidative stress-induced signal transduction
pathways in cardiac myocytes: involvement of ROS in heart diseases.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 5:789–794. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yao Y, Li R, Ma Y, et al: α-Lipoic acid
increases tolerance of cardiomyoblasts to glucose/glucose
oxidase-induced injury via ROS-dependent ERK1/2 activation. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1823:920–929. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Tsai KH, Wang WJ, Lin CW, et al: NADPH
oxidase-derived superoxide anion-induced apoptosis is mediated via
the JNK-dependent activation of NF-κB in cardiomyocytes exposed to
high glucose. J Cell Physiol. 227:1347–1357. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun B, Sun GB, Xiao J, et al: Isorhamnetin
inhibits HO-induced activation of the intrinsic apoptotic pathway
in H9c2 cardiomyocytes through scavenging reactive oxygen species
and ERK inactivation. J Cell Biochem. 113:473–485. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhu H, Yang Y, Wang Y, Li J, Schiller PW
and Peng T: MicroRNA-195 promotes palmitate-induced apoptosis in
cardiomyocytes by down-regulating Sirt1. Cardiovasc Res. 92:75–84.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakamura S, Takamura T, Matsuzawa-Nagata
N, et al: Palmitate induces insulin resistance in H4IIEC3
hepatocytes through reactive oxygen species produced by
mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 284:14809–14818. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maloney E, Sweet IR, Hockenbery DM, et al:
Activation of NF-kappaB by palmitate in endothelial cells: a key
role for NADPH oxidase-derived superoxide in response to TLR4
activation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:1370–1375. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin N, Chen H, Zhang H, Wan X and Su Q:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species (ROS) inhibition ameliorates
palmitate-induced INS-1 beta cell death. Endocrine. 42:107–117.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yeop Han C, Kargi AY, Omer M, et al:
Differential effect of saturated and unsaturated free fatty acids
on the generation of monocyte adhesion and chemotactic factors by
adipocytes: dissociation of adipocyte hypertrophy from
inflammation. Diabetes. 59:386–396. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hickson-Bick DL, Sparagna GC, Buja LM and
McMillin JB: Palmitate-induced apoptosis in neonatal cardiomyocytes
is not dependent on the generation of ROS. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 282:H656–H664. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shimabukuro M, Wang MY, Zhou YT, Newgard
CB and Unger RH: Protection against lipoapoptosis of beta cells
through leptin-dependent maintenance of Bcl-2 expression. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 95:9558–9561. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Peterson JM, Wang Y, Bryner RW, Williamson
DL and Alway SE: Bax signaling regulates palmitate-mediated
apoptosis in C(2)C(12) myotubes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
295:E1307–E1314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cheng M, Sexl V, Sherr CJ and Roussel MF:
Assembly of cyclin D-dependent kinase and titration of p27Kip1
regulated by mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK1). Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:1091–1096. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tran SE, Holmstrom TH, Ahonen M, Kahari VM
and Eriksson JE: MAPK/ERK overrides the apoptotic signaling from
Fas, TNF and TRAIL receptors. J Biol Chem. 276:16484–16490. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Martelli AM, Faenza I, Billi AM, et al:
Intranuclear 3′-phosphoinositide metabolism and Akt signaling: new
mechanisms for tumorigenesis and protection against apoptosis? Cell
Signal. 18:1101–1107. 2006.
|
|
43
|
Matsui T and Rosenzweig A: Convergent
signal transduction pathways controlling cardiomyocyte survival and
function: the role of PI 3-kinase and Akt. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
38:63–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|