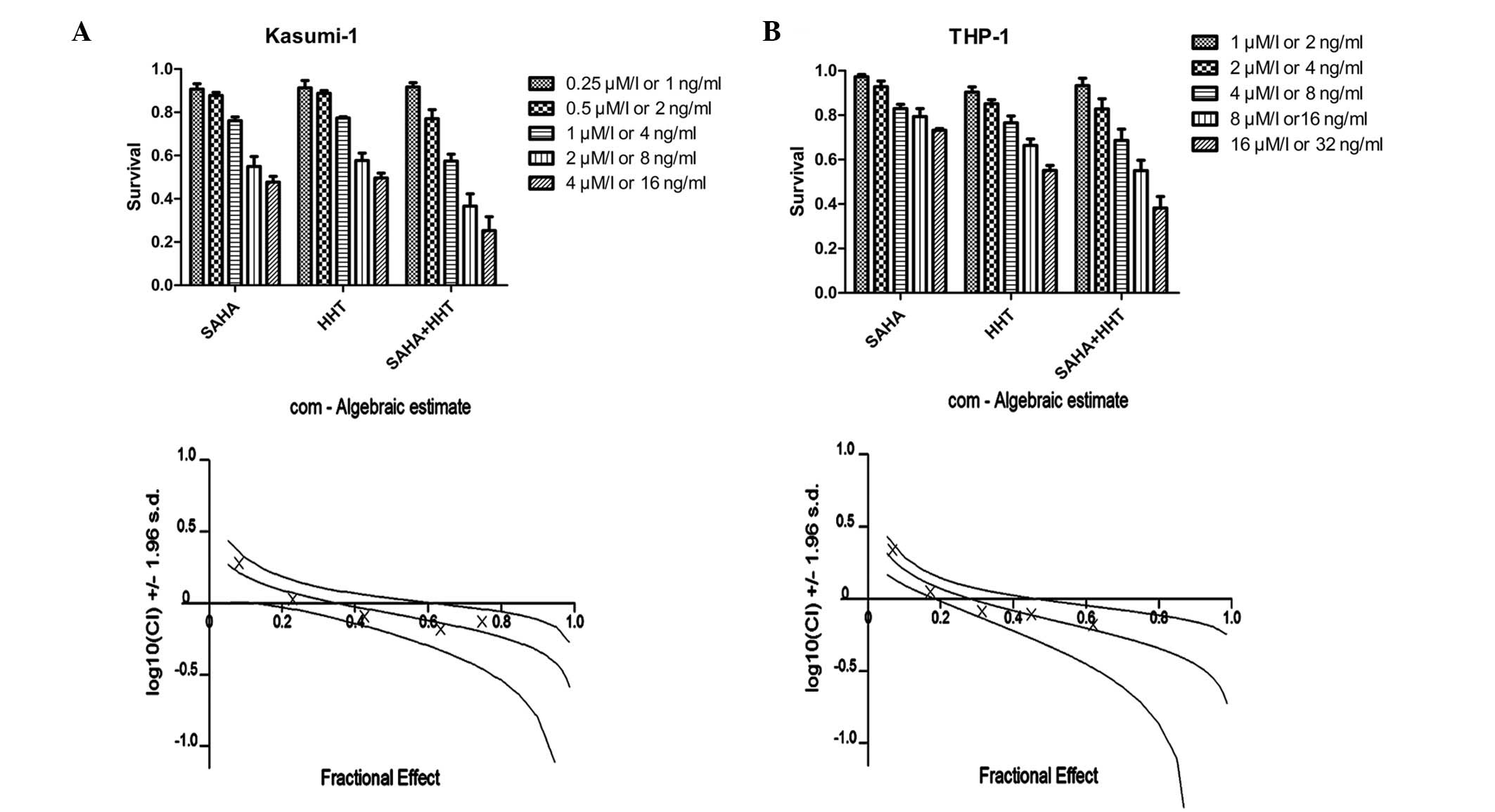
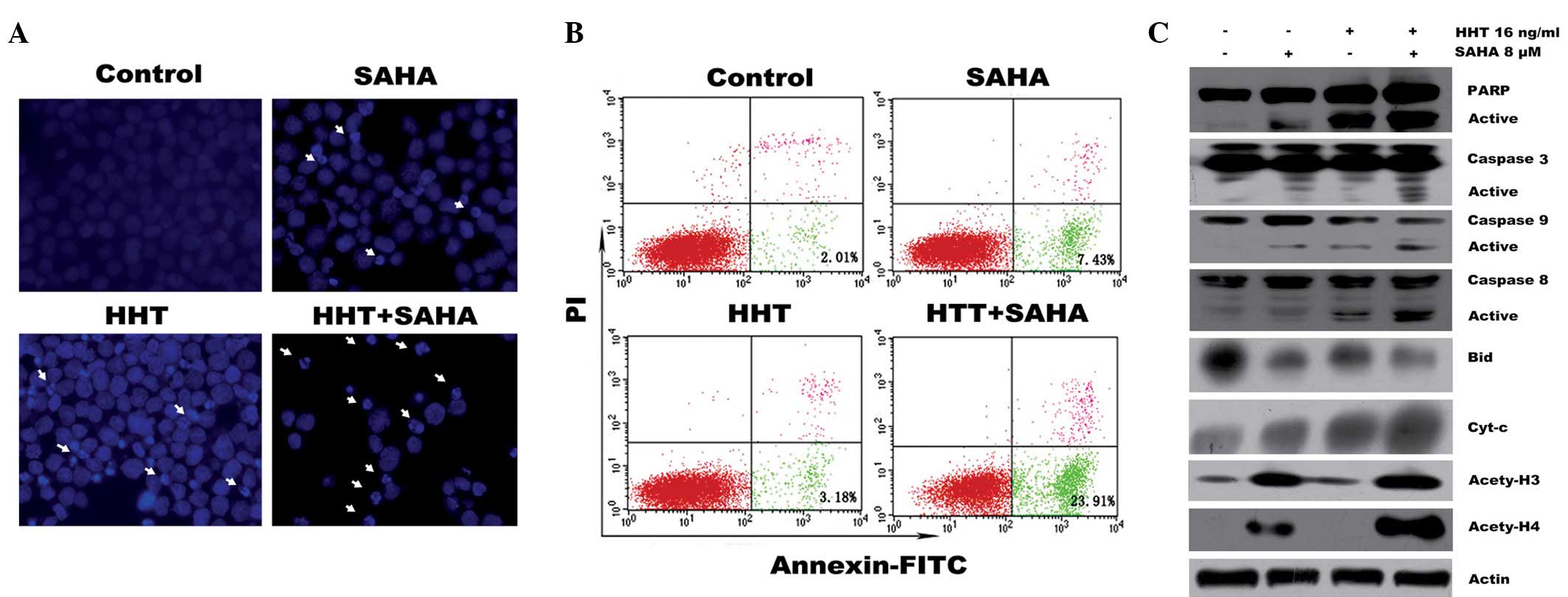
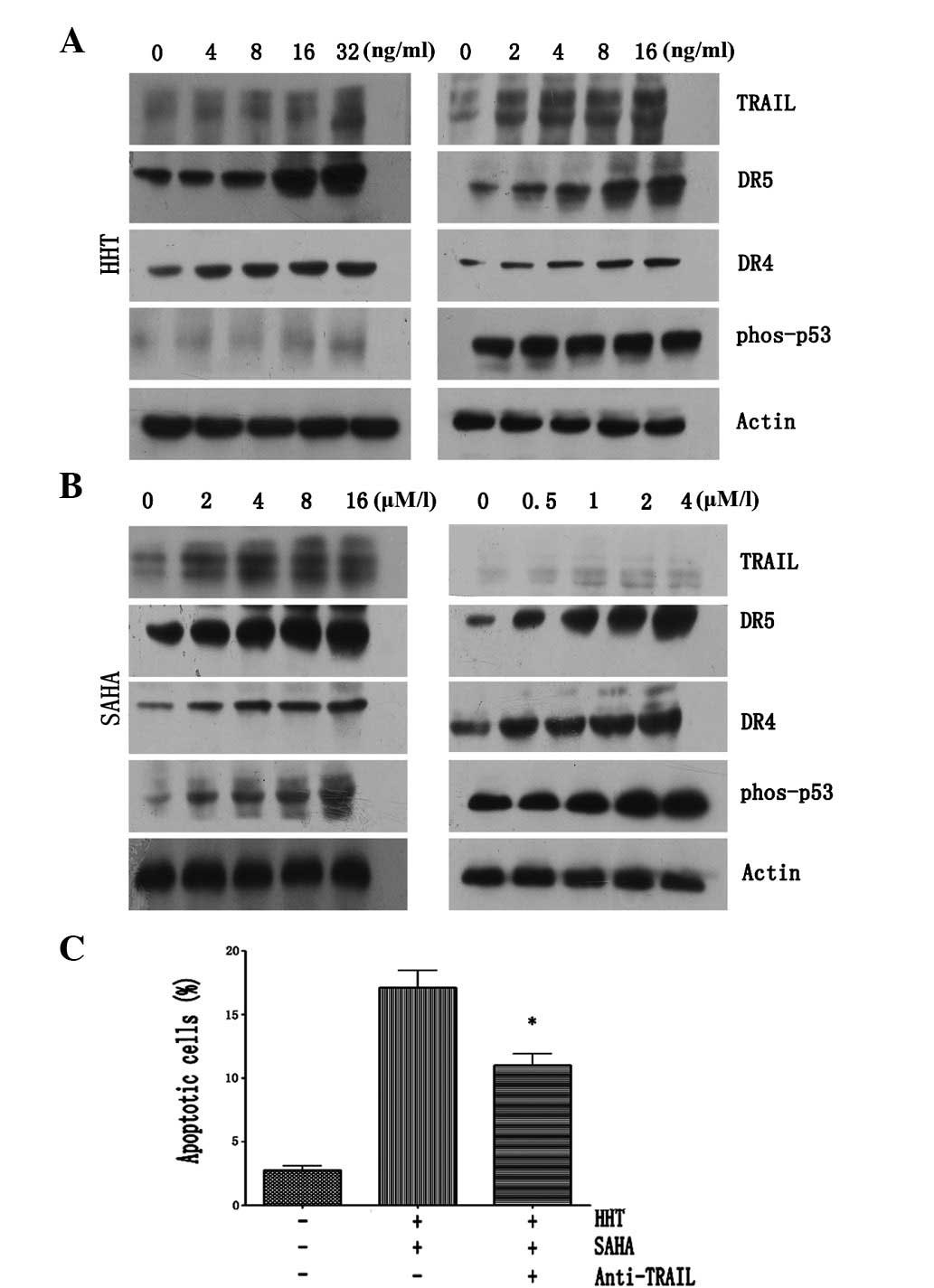
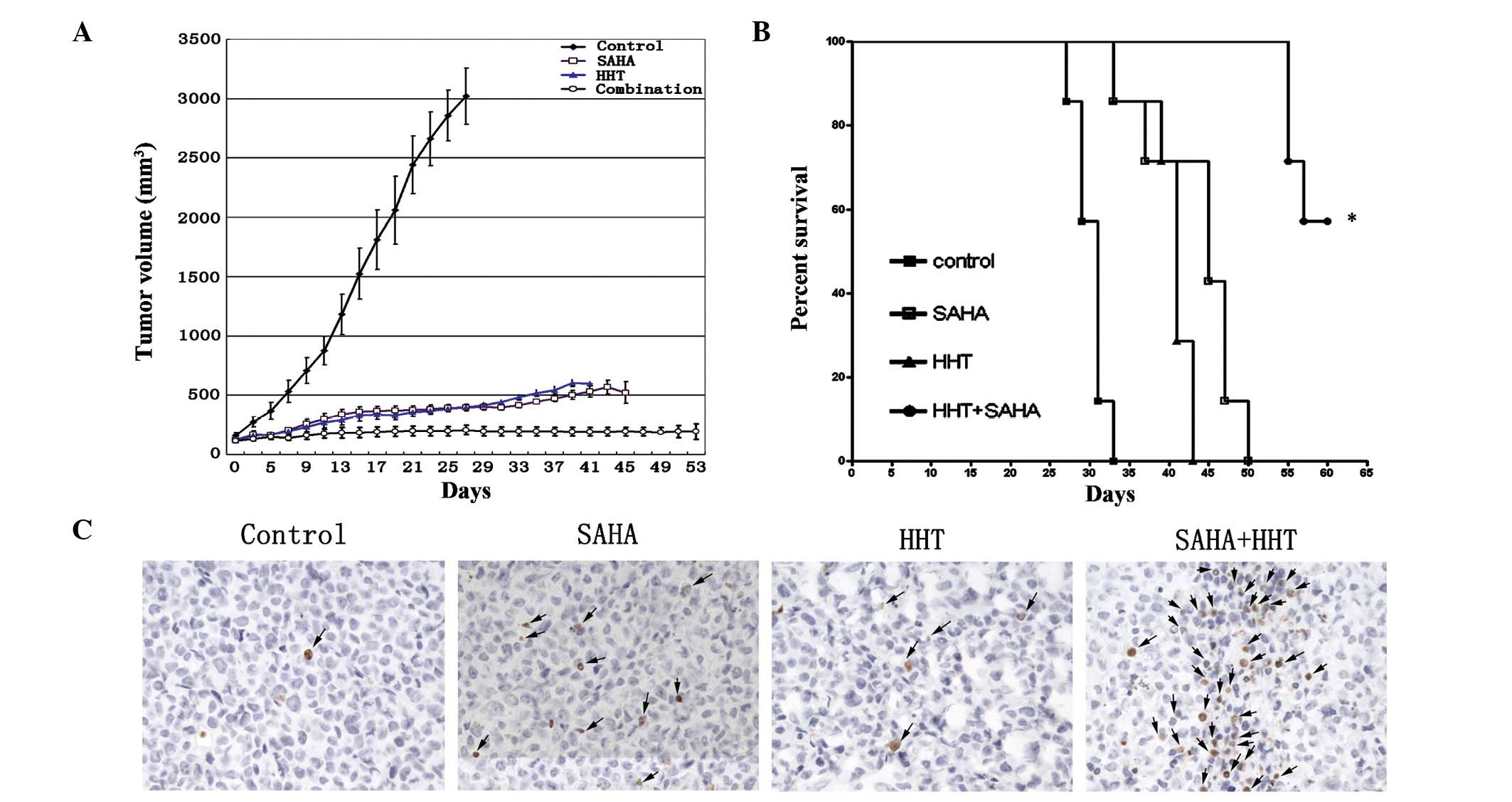
|
1
|
Taby R and Issa JP: Cancer epigenetics. CA
Cancer J Clin. 60:376–392. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shao Y, Gao Z, Marks PA and Jiang X:
Apoptotic and autophagic cell death induced by histone deacetylase
inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:18030–18035. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vrana JA, Decker RH, Johnson CR, et al:
Induction of apoptosis in U937 human leukemia cells by
suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid (SAHA) proceeds through pathways
that are regulated by Bcl-2/Bcl-XL, c-Jun, and p21CIP1, but
independent of p53. Oncogene. 18:7016–7025. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Richon VM, Emiliani S, Verdin E, et al: A
class of hybrid polar inducers of transformed cell differentiation
inhibits histone deacetylases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:3003–3007. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rosato RR, Almenara JA, Maggio SC, et al:
Role of histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced reactive oxygen
species and DNA damage in LAQ-824/fludarabine antileukemic
interactions. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:3285–3297. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Miller CP, Singh MM, Rivera-Del Valle N,
Manton CA and Chandra J: Therapeutic strategies to enhance the
anticancer efficacy of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2011:Jun 28–2011.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
7
|
Bali P, Pranpat M, Bradner J, et al:
Inhibition of histone deacetylase 6 acetylates and disrupts the
chaperone function of heat shock protein 90: a novel basis for
antileukemia activity of histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Biol
Chem. 280:26729–26734. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Redner RL, Wang J and Liu JM: Chromatin
remodeling and leukemia: new therapeutic paradigms. Blood.
94:417–428. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Saunthararajah Y, Redner RL and
Liu JM: Inhibitors of histone deacetylase relieve ETO-mediated
repression and induce differentiation of AML1-ETO leukemia cells.
Cancer Res. 59:2766–2769. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Garcia-Manero G, Yang H, Bueso-Ramos C, et
al: Phase 1 study of the histone deacetylase inhibitor vorinostat
(suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid [SAHA]) in patients with advanced
leukemias and myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood. 111:1060–1066.
2008.
|
|
11
|
Schaefer EW, Loaiza-Bonilla A, Juckett M,
et al: Mayo P2C Phase II Consortium: A phase 2 study of vorinostat
in acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 94:1375–1382. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shiozawa K, Nakanishi T, Tan M, et al:
Preclinical studies of vorinostat (suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid)
combined with cytosine arabinoside and etoposide for treatment of
acute leukemias. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1698–1707. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kuendgen A, Bug G, Ottmann OG, et al:
Treatment of poor-risk myelodysplastic syndromes and acute myeloid
leukemia with a combination of 5-azacytidine and valproic acid.
Clin Epigenetics. 2:389–399. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nie D, Huang K, Yin S, et al:
Synergistic/additive interaction of valproic acid with bortezomib
on proliferation and apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells.
Leuk Lymphoma. 53:2487–2495. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McCormack E, Haaland I, Venås G, et al:
Synergistic induction of p53 mediated apoptosis by valproic acid
and nutlin-3 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 26:910–917. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie C, Edwards H, Xu X, et al: Mechanisms
of synergistic antileukemic interactions between valproic acid and
cytarabine in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res.
16:5499–5510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen R, Guo L, Chen Y, Jiang Y, Wierda WG
and Plunkett W: Homoharringtonine reduced Mcl-1 expression and
induced apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood.
117:156–164. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lou YJ, Qian WB and Jin J:
Homoharringtonine induces apoptosis and growth arrest in human
myeloma cells. Leuk Lymphoma. 48:1400–1406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Legha SS, Keating M, Picket S, Ajani JA,
Ewer M and Bodey GP: Phase I clinical investigation of
homoharringtonine. Cancer Treat Rep. 68:1085–1091. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kantarjian HM, Keating MJ, Walters RS,
Koller CA, McCredie KB and Freireich EJ: Phase II study of low-dose
continuous infusion homoharringtonine in refractory acute
myelogenous leukemia. Cancer. 63:813–817. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kantarjian HM, Talpaz M, Smith TL, et al:
Homoharringtonine and low-dose cytarabine in the management of late
chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia. J Clin Oncol.
18:3513–3521. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang J, Lü S, Yang J, et al: A
homoharringtonine-based induction regimen for the treatment of
elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia: a single center
experience from China. J Hematol Oncol. 2009:Jul 30–2009.(Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
23
|
Jin J, Jiang DZ, Mai WY, et al:
Homoharringtonine in combination with cytarabine and aclarubicin
resulted in high complete remission rate after the first induction
therapy in patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia.
20:1361–1367. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shankar S, Singh TR, Fandy TE, Luetrakul
T, Ross DD and Srivastava RK: Interactive effects of histone
deacetylase inhibitors and TRAIL on apoptosis in human leukemia
cells: involvement of both death receptor and mitochondrial
pathways. Int J Mol Med. 16:1125–1138. 2005.
|
|
25
|
Feldman E, Arlin Z, Ahmed T, et al:
Homoharringtonine is safe and effective for patients with acute
myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia. 6:1185–1188. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kelly WK, O’Connor OA, Krug LM, et al:
Phase I study of an oral histone deacetylase inhibitor,
suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid, in patients with advanced cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 23:3923–3931. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lévy V, Zohar S, Bardin C, et al: A phase
I dose-finding and pharmacokinetic study of subcutaneous
semisynthetic homoharringtonine (ssHHT) in patients with advanced
acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J Cancer. 95:253–259. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Luo CY, Tang JY and Wang YP:
Homoharringtonine: a new treatment option for myeloid leukemia.
Hematology. 9:259–270. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chan YP, Lee FW and Siu TS: Quantitation
of homoharringtonine in plasma by high-performance liquid
chromatography with amperometric detection. J Chromatogr.
496:155–166. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cai Z, Lin M, Wuchter C, et al: Apoptotic
response to homoharringtonine in human wt p53 leukemic cells is
independent of reactive oxygen species generation and implicates
Bax translocation, mitochondrial cytochrome c release and caspase
activation. Leukemia. 15:567–574. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yin S, Wang R, Zhou F, Zhang H and Jing Y:
Bcl-xL is a dominant antiapoptotic protein that inhibits
homoharringtonine-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 79:1072–1083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kaufmann SH and Steensma DP: On the TRAIL
of a new therapy for leukemia. Leukemia. 19:2195–2202. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Riccioni R, Pasquini L, Mariani G, et al:
TRAIL decoy receptors mediate resistance of acute myeloid leukemia
cells to TRAIL. Haematologica. 90:612–624. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jones DT, Ganeshaguru K, Mitchell WA, et
al: Cytotoxic drugs enhance the ex vivo sensitivity of malignant
cells from a subset of acute myeloid leukaemia patients to
apoptosis induction by tumour necrosis factor receptor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand. Br J Haematol. 121:713–720. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Min YJ, Lee JH, Choi SJ, et al: Prognostic
significance of Fas (CD95) and TRAIL receptors (DR4/DR5) expression
in acute myelogenous leukemia. Leuk Res. 28:359–365. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|