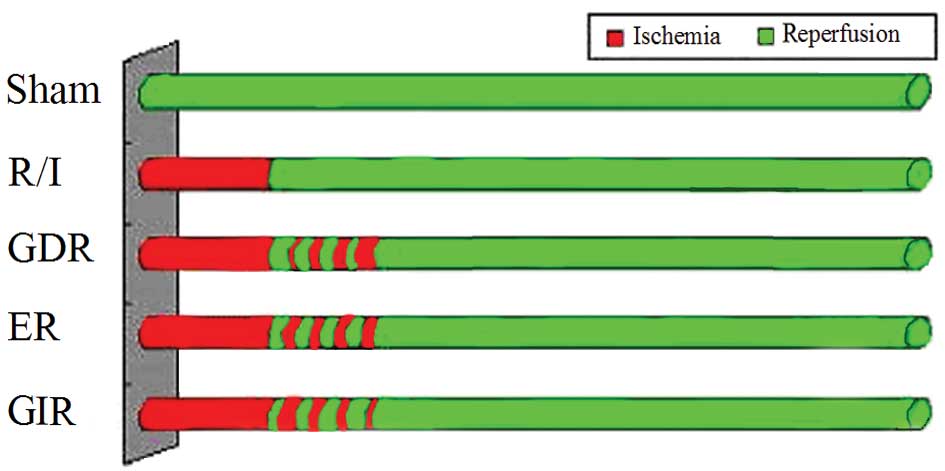
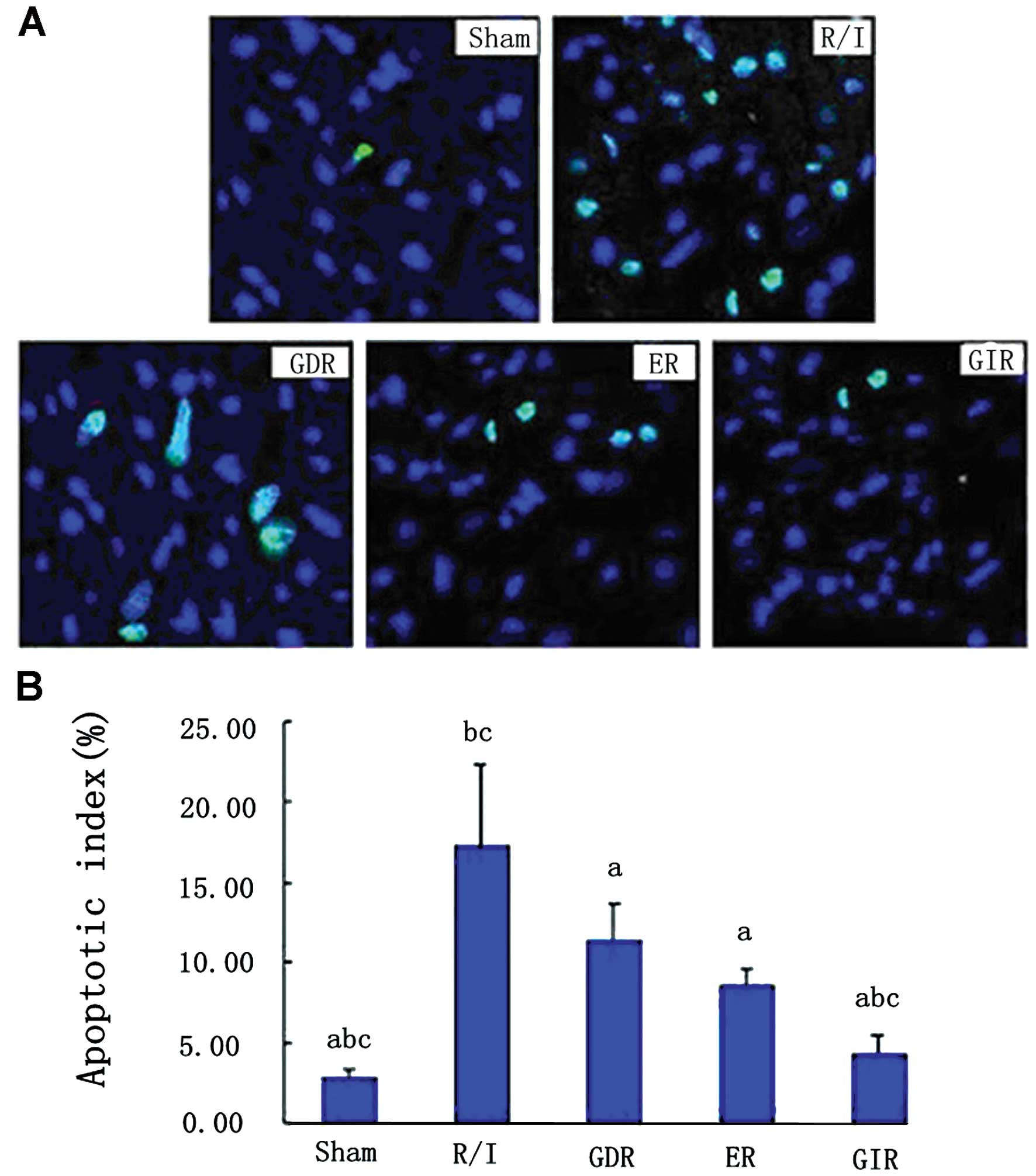
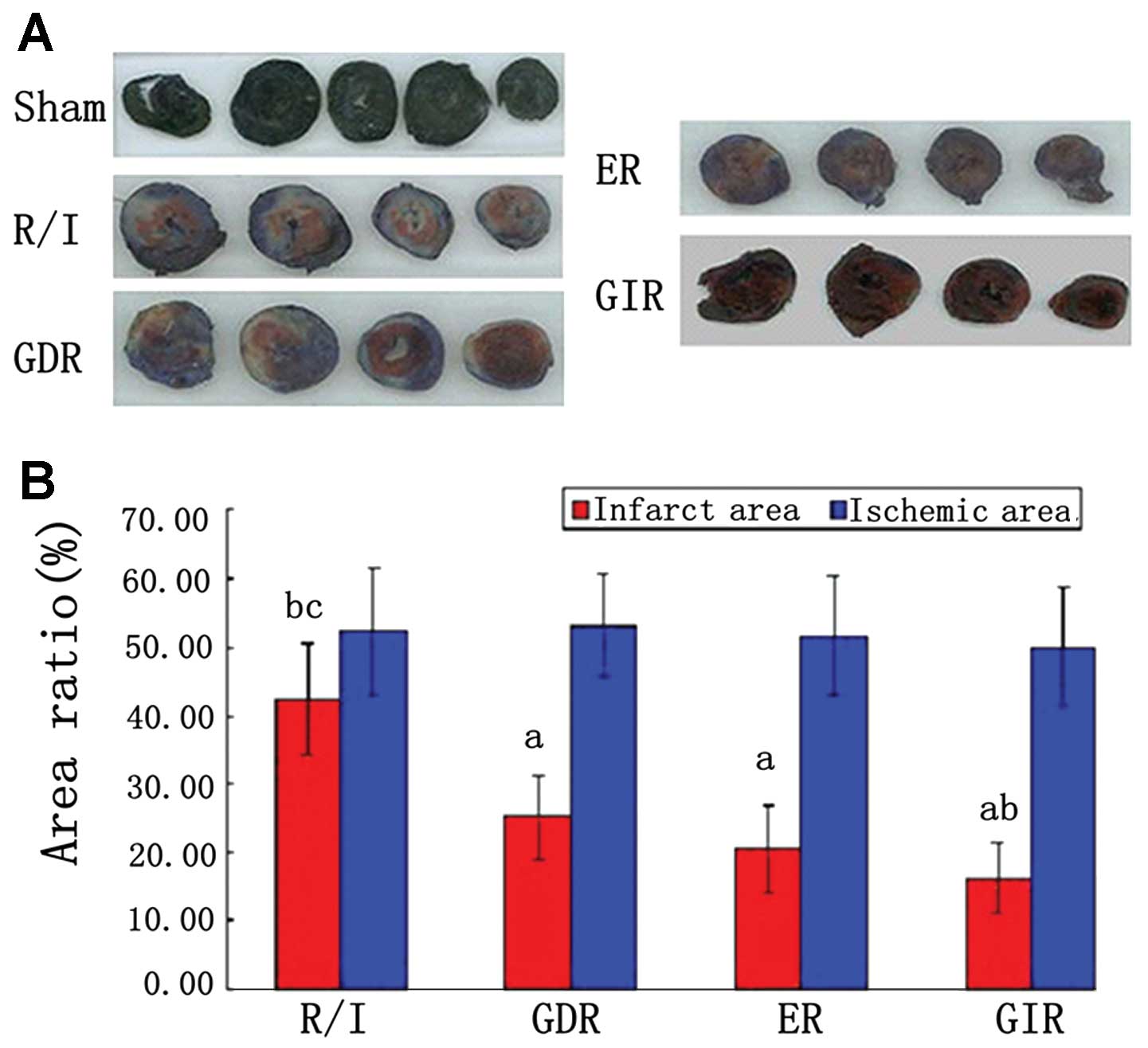
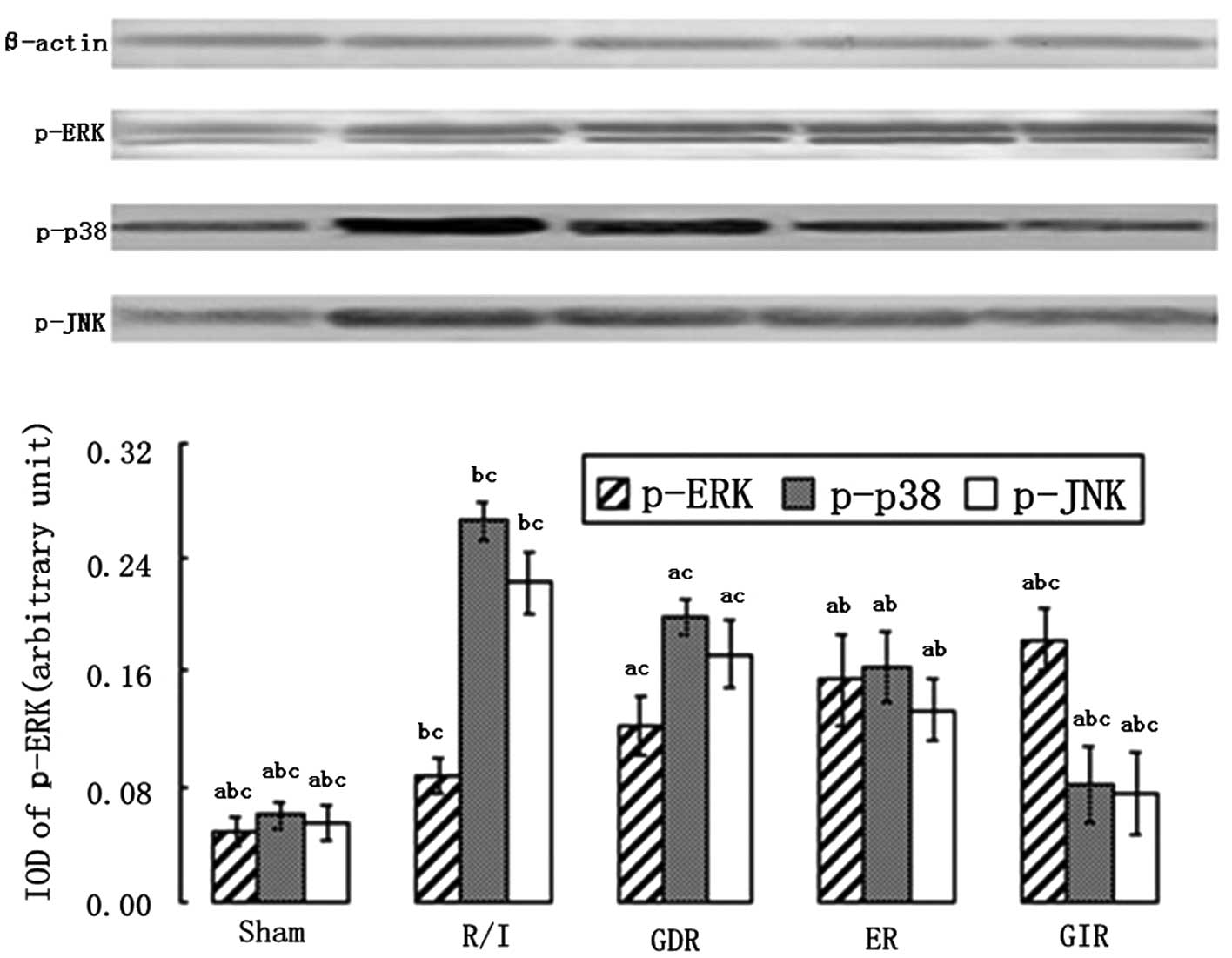
|
1
|
Wu JM, Wang ZR, Hsieh TC, Bruder JL, Zou
JG and Huang YZ: Mechanism of cardioprotection by resveratrol, a
phenolic antioxidant present in red wine (Review). Int J Mol Med.
8:3–17. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Braunwald E and Kloner RA: Myocardial
reperfusion: a double-edged sword? J Clin Invest. 76:1713–1719.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tomatsuri N, Yoshida N, Takagi T, et al:
Edaravone, a newly developed radical scavenger, protects against
ischemia-reperfusion injury of the small intestine in rats. Int J
Mol Med. 13:105–109. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao ZQ, Corvera JS, Halkos ME, et al:
Inhibition of myocardial injury by ischemic postconditioning during
reperfusion: comparison with ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 285:H579–H588. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sanada S, Komuro I and Kitakaze M:
Pathophysiology of myocardial reperfusion injury: preconditioning,
postconditioning, and translational aspects of protective measures.
Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H1723–H1741. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu X, Chen H, Zhan B, et al: Attenuation
of reperfusion injury by renal ischemic postconditioning: the role
of NO. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 359:628–634. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang WH, Lu FH, Zhao YJ, et al:
Post-conditioning protects rat cardiomyocytes via
PKCepsilon-mediated calcium-sensing receptors. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 361:659–664. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thuny F, Lairez O, Roubille F, et al:
Post-conditioning reduces infarct size and edema in patients with
ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Am Coll Cardiol.
59:2175–2181. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Penna C, Mancardi D, Raimondo S, Geuna S
and Pagliaro P: The paradigm of postconditioning to protect the
heart. J Cell Mol Med. 12:435–458. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Skyschally A, van Caster P, Iliodromitis
EK, Schulz R, Kremastinos DT and Heusch G: Ischemic
postconditioning: experimental models and protocol algorithms.
Basic Res Cardiol. 104:469–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iliodromitis EK, Downey JM, Heusch G and
Kremastinos DT: What is the optimal postconditioning algorithm? J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 14:269–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cai M, Li Y, Xu Y, et al: Endothelial NOS
activity and myocardial oxygen metabolism define the salvageable
ischemic time window for ischemic postconditioning. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 300:H1069–H1077. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kin H, Zhao ZQ, Sun HY, et al:
Postconditioning attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
by inhibiting events in the early minutes of reperfusion.
Cardiovasc Res. 62:74–85. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang XM, Proctor JB, Cui L, Krieg T,
Downey JM and Cohen MV: Multiple, brief coronary occlusions during
early reperfusion protect rabbit hearts by targeting cell signaling
pathways. J Am Coll Cardiol. 44:1103–1110. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vinten-Johansen J, Zhao ZQ, Zatta AJ, Kin
H, Halkos ME and Kerendi F: Postconditioning - A new link in
nature’s armor against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury.
Basic Res Cardiol. 100:295–310. 2005.
|
|
16
|
Argaud L, Gateau-Roesch O, Raisky O,
Loufouat J, Robert D and Ovize M: Postconditioning inhibits
mitochondrial permeability transition. Circulation. 111:194–197.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kin H, Zatta AJ, Lofye MT, et al:
Postconditioning reduces infarct size via adenosine receptor
activation by endogenous adenosine. Cardiovasc Res. 67:124–133.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Penna C, Cappello S, Mancardi D, et al:
Post-conditioning reduces infarct size in the isolated rat heart:
role of coronary flow and pressure and the nitric oxide/cGMP
pathway. Basic Res Cardiol. 101:168–179. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang JY, Shen J, Gao Q, et al: Ischemic
postconditioning protects against global cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury in rats. Stroke. 39:983–990.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kerendi F, Kin H, Halkos ME, et al: Remote
postconditioning. Brief renal ischemia and reperfusion applied
before coronary artery reperfusion reduces myocardial infarct size
via endogenous activation of adenosine receptors. Basic Res
Cardiol. 100:404–412. 2005.
|
|
21
|
Li Y, Ge X and Liu X: The cardioprotective
effect of postconditioning is mediated by ARC through inhibiting
mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Apoptosis. 14:164–172. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sumi S, Kobayashi H, Yasuda S, et al:
Postconditioning effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor is
mediated through activation of risk pathway and opening of the
mitochondrial KATP channels. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
299:H1174–H1182. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun HY, Wang NP, Halkos M, et al:
Postconditioning attenuates cardiomyocyte apoptosis via inhibition
of JNK and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways.
Apoptosis. 11:1583–1593. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gomez L, Thibault H, Gharib A, et al:
Inhibition of mitochondrial permeability transition improves
functional recovery and reduces mortality following acute
myocardial infarction in mice. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
293:H1654–H1661. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cao J, Zhu T, Lu L, et al: Estrogen
induces cardioprotection in male C57BL/6J mice after acute
myocardial infarction via decreased activity of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 and increased Akt-Bcl-2 anti-apoptotic
signaling. Int J Mol Med. 28:231–237. 2011.
|
|
26
|
Mao H, Gu H, Qu X, et al: Involvement of
the mitochondrial pathway and Bim/Bcl-2 balance in
dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer in
vitro. Int J Mol Med. 31:213–218. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hausenloy DJ, Ong SB and Yellon DM: The
mitochondrial permeability transition pore as a target for
preconditioning and postconditioning. Basic Res Cardiol.
104:189–202. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Paillard M, Gomez L, Augeul L, Loufouat J,
Lesnefsky EJ and Ovize M: Postconditioning inhibits mPTP opening
independent of oxidative phosphorylation and membrane potential. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 46:902–909. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Weiss JN, Korge P, Honda HM and Ping P:
Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in myocardial
disease. Circ Res. 93:292–301. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park SS, Zhao H, Mueller RA and Xu Z:
Bradykinin prevents reperfusion injury by targeting mitochondrial
permeability transition pore through glycogen synthase kinase
3beta. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 40:708–716. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sato H, Jordan JE, Zhao ZQ, Sarvotham SS
and Vinten-Johansen J: Gradual reperfusion reduces infarct size and
endothelial injury but augments neutrophil accumulation. Ann Thorac
Surg. 64:1099–1107. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Unal S, Ozmen S, DemIr Y, et al: The
effect of gradually increased blood flow on ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Ann Plast Surg. 47:412–416. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shi E, Jiang X, Kazui T, et al: Controlled
low-pressure perfusion at the beginning of reperfusion attenuates
neurologic injury after spinal cord ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 133:942–948. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|