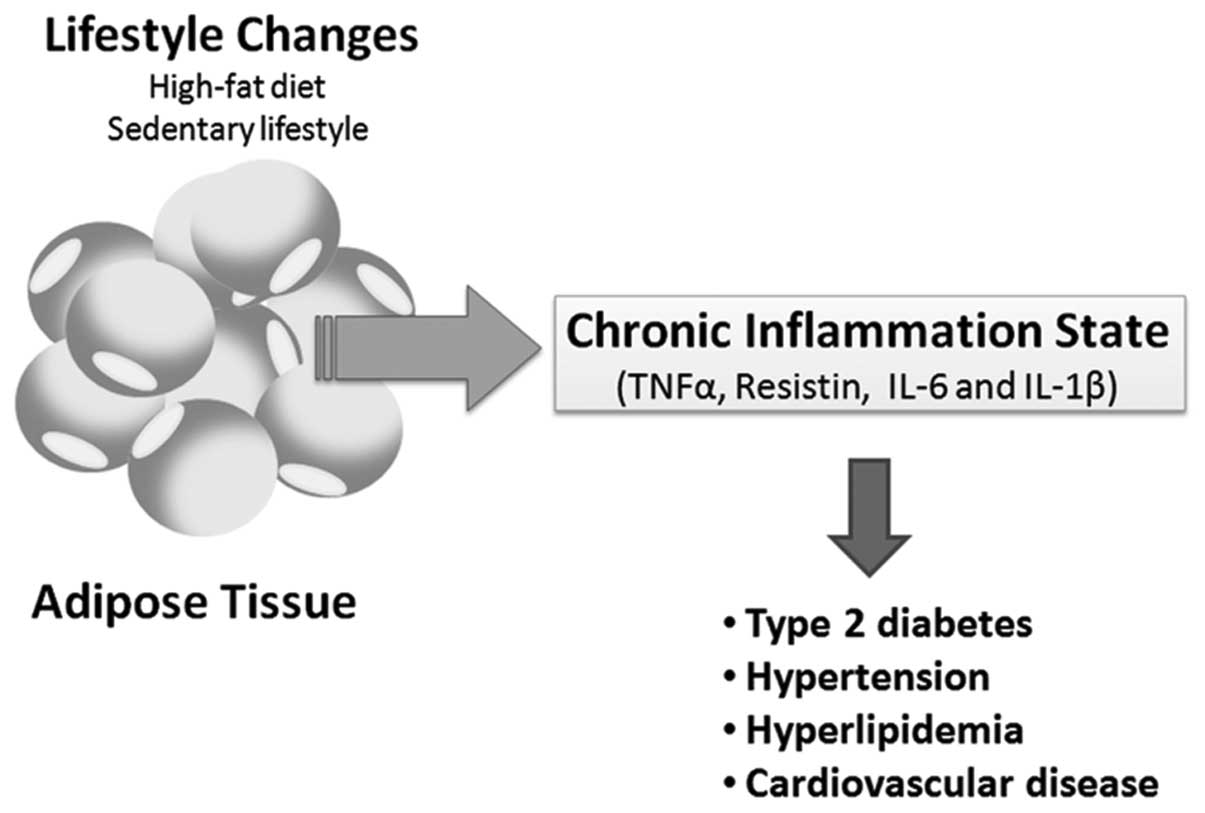
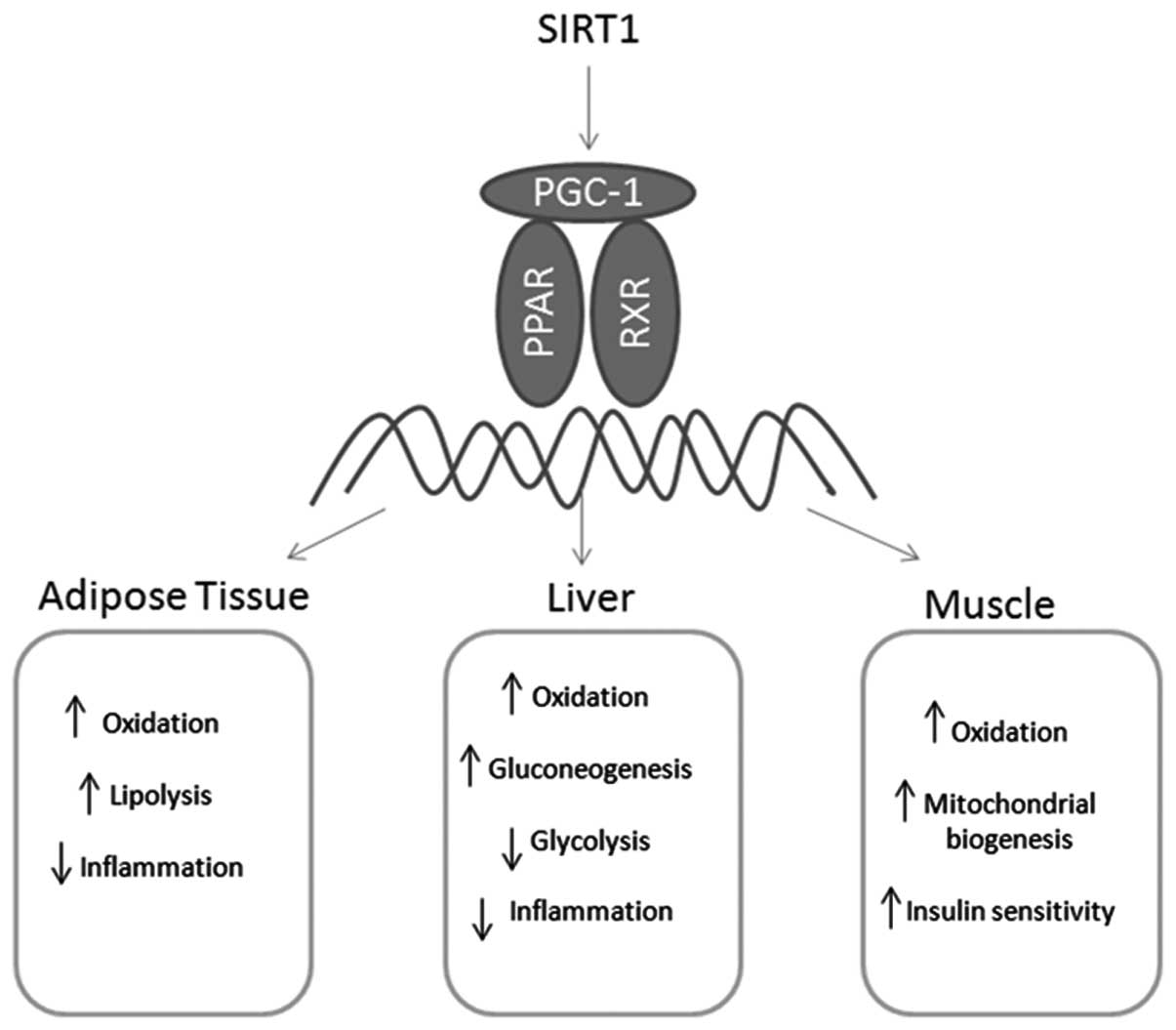
|
1
|
Bastard JP, Maachi M, Lagathu C, et al:
Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation,
and insulin resistance. Eur Cytokine Netw. 17:4–12. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cnop M, Havel PJ, Utzschneider KM, et al:
Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin
sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: evidence for independent roles
of age and sex. Diabetologia. 46:459–469. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kersten S, Desvergne B and Wahli W: Roles
of PPARs in health and disease. Nature. 405:421–424. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, et al:
The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease
mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA. 288:2709–2716. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sattar N, Gaw A, Scherbakova O, et al:
Metabolic syndrome with and without C-reactive protein as a
predictor of coronary heart disease and diabetes in the West of
Scotland Coronary Prevention Study. Circulation. 108:414–419. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Grundy SM, Brewer HB Jr, Cleeman JI, et
al: Definition of metabolic syndrome. Report of the National Heart,
Lung, and Blood Institute/American Heart Association conference on
scientific issues related to definition. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 24:e13–e18. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Greenberg AS and Obin MS: Obesity and the
role of adipose tissue in inflammation and metabolism. Am J Clin
Nutr. 83:461S–465S. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hotamisligil GS, Shargill NS and
Spiegelman BM: Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha:
direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science.
259:87–91. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Orio F Jr, Palomba S, Cascella T,
Savastano S, Lombardi G and Colao A: Cardiovascular complications
of obesity in adolescents. J Endocrinol Invest. 30:70–80. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Grundy SM: Obesity, metabolic syndrome,
and cardiovascular disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 89:2595–2600.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shoelson SE and Goldfine AB: Getting away
from glucose: fanning the flames of obesity-induced inflammation.
Nat Med. 15:373–374. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Leone TC, Weinheimer CJ and Kelly DP: A
critical role for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
alpha (PPARalpha) in the cellular fasting response: the
PPARalpha-null mouse as a model of fatty acid oxidation disorders.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:7473–7478. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Iizuka K and Horikawa Y: ChREBP: a
glucose-activated transcription factor involved in the development
of metabolic syndrome. Endocr J. 55:617–624. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Berger J and Moller DE: The mechanisms of
action of PPARs. Annu Rev Med. 53:409–435. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Viana Abranches M, Esteves de Oliveira FC
and Bressan J: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor: effects
on nutritional homeostasis, obesity and diabetes mellitus. Nutr
Hosp. 26:271–279. 2011.
|
|
16
|
Adeghate E, Adem A, Hasan MY, Tekes K and
Kalasz H: Medicinal chemistry and actions of dual and pan PPAR
modulators. Open Med Chem J. 5:93–98. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Israelian-Konaraki Z and Reaven PD:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha and
atherosclerosis: from basic mechanisms to clinical implications.
Cardiology. 103:1–9. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nicholls SJ and Uno K: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR alpha/gamma) agonists as a
potential target to reduce cardiovascular risk in diabetes. Diab
Vasc Dis Res. 9:89–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Salmenniemi U, Ruotsalainen E, Pihlajamäki
J, et al: Multiple abnormalities in glucose and energy metabolism
and coordinated changes in levels of adiponectin, cytokines, and
adhesion molecules in subjects with metabolic syndrome.
Circulation. 110:3842–3848. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Mujica V, Leiva E, Icaza G, et al:
Evaluation of metabolic syndrome in adults of Talca city, Chile.
Nutr J. 7:142008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Palomo I, Contreras A, Alarcon LM, et al:
Elevated concentration of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in
individuals with metabolic syndrome. Nitric Oxide. 24:224–228.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Palomo I, Moore-Carrasco R, Alarcon M, et
al: Pathophysiology of the proatherothrombotic state in the
metabolic syndrome. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2:194–208. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Palomo I, Alarcón M, Moore-Carrasco R and
Argilés JM: Hemostasis alterations in metabolic syndrome (review).
Int J Mol Med. 18:969–974. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Salmenniemi U, Ruotsalainen E, Vänttinen
M, et al: High amount of visceral fat mass is associated with
multiple metabolic changes in offspring of type 2 diabetic
patients. Int J Obes (Lond). 29:1464–1470. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Flier JS: Obesity wars: molecular progress
confronts an expanding epidemic. Cell. 116:337–350. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ahima RS: Adipose tissue as an endocrine
organ. Obesity (Silver Spring). 14:242S–249S. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Barreda R and Ros PR: Diagnostic imaging
of liver abscess. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging. 33:29–58. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pittas AG, Joseph NA and Greenberg AS:
Adipocytokines and insulin resistance. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
89:447–452. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Satoh M, Andoh Y, Clingan CS, et al: Type
II NKT cells stimulate diet-induced obesity by mediating adipose
tissue inflammation, steatohepatitis and insulin resistance. PLoS
One. 7:e305682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lumeng CN and Saltiel AR: Inflammatory
links between obesity and metabolic disease. J Clin Invest.
121:2111–2117. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, et al: Chronic
inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of
obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 112:1821–1830.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kern PA, Ranganathan S, Li C, Wood L and
Ranganathan G: Adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor and
interleukin-6 expression in human obesity and insulin resistance.
Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 280:E745–751. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shimomura I, Funahashi T, Takahashi M, et
al: Enhanced expression of PAI-1 in visceral fat: possible
contributor to vascular disease in obesity. Nat Med. 2:800–803.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bruce CR and Dyck DJ: Cytokine regulation
of skeletal muscle fatty acid metabolism: effect of interleukin-6
and tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
287:E616–E621. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dyck DJ: Adipokines as regulators of
muscle metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab.
34:396–402. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kriketos AD, Greenfield JR, Peake PW, et
al: Inflammation, insulin resistance, and adiposity: a study of
first-degree relatives of type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes Care.
27:2033–2040. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kaidashev IP: NF-kB activation as a
molecular basis of pathological process by metabolic syndrome.
Fiziol Zh. 58:93–101. 2012.(In Ukranian).
|
|
38
|
Ahn J, Lee H, Kim S and Ha T: Resveratrol
inhibits TNF-alpha-induced changes of adipokines in 3T3-L1
adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 364:972–977. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF,
Atkinson RL and Spiegelman BM: Increased adipose tissue expression
of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in human obesity and insulin
resistance. J Clin Invest. 95:2409–2415. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Araki K, Kawauchi K and Tanaka N:
IKK/NF-kappaB signaling pathway inhibits cell-cycle progression by
a novel Rb-independent suppression system for E2F transcription
factors. Oncogene. 27:5696–5705. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gupta S and Gupta BM: Metabolic syndrome:
diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Indian Heart J. 58:149–152.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Mujica V, Urzua A, Leiva E, et al:
Intervention with education and exercise reverses the metabolic
syndrome in adults. J Am Soc Hypertens. 4:148–153. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Klimcakova E, Roussel B, Kovacova Z, et
al: Macrophage gene expression is related to obesity and the
metabolic syndrome in human subcutaneous fat as well as in visceral
fat. Diabetologia. 54:876–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kallio P, Kolehmainen M, Laaksonen DE, et
al: Dietary carbohydrate modification induces alterations in gene
expression in abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue in persons with
the metabolic syndrome: the FUNGENUT Study. Am J Clin Nutr.
85:1417–1427. 2007.
|
|
45
|
Vernochet C, Peres SB, Davis KE, et al:
C/EBPalpha and the corepressors CtBP1 and CtBP2 regulate repression
of select visceral white adipose genes during induction of the
brown phenotype in white adipocytes by peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonists. Mol Cell Biol.
29:4714–4728. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xue B, Sukumaran S, Nie J, Jusko WJ,
Dubois DC and Almon RR: Adipose tissue deficiency and chronic
inflammation in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. PLoS One.
6:e173862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wahli W, Braissant O and Desvergne B:
Peroxisome proliferator activated receptors: transcriptional
regulators of adipogenesis, lipid metabolism and more. Chem Biol.
2:261–266. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Motojima K: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR): structure, mechanisms of
activation and diverse functions. Cell Struct Funct. 18:267–277.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jay MA and Ren J: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) in metabolic syndrome and
type 2 diabetes mellitus. Curr Diabetes Rev. 3:33–39. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Keller H, Mahfoudi A, Dreyer C, et al:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and lipid metabolism.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 684:157–173. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lowell BB: PPARgamma: an essential
regulator of adipogenesis and modulator of fat cell function. Cell.
99:239–242. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sugii S and Evans RM: Epigenetic codes of
PPARgamma in metabolic disease. FEBS Lett. 585:2121–2128. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Heikkinen S, Auwerx J and Argmann CA:
PPARgamma in human and mouse physiology. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1771:999–1013. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fujiki K, Kano F, Shiota K and Murata M:
Expression of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma
gene is repressed by DNA methylation in visceral adipose tissue of
mouse models of diabetes. BMC Biol. 7:382009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Luconi M, Cantini G and Serio M:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma): Is
the genomic activity the only answer? Steroids. 75:585–594. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bouhlel MA, Derudas B, Rigamonti E, et al:
PPARgamma activation primes human monocytes into alternative M2
macrophages with anti-inflammatory properties. Cell Metab.
6:137–143. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Red
Eagle A, et al: Alternative M2 activation of Kupffer cells by
PPARdelta ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance. Cell
Metab. 7:496–507. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Ketsawatsomkron P, Pelham CJ, Groh S, Keen
HL, Faraci FM and Sigmund CD: Does peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR gamma) protect from
hypertension directly through effects in the vasculature? J Biol
Chem. 285:9311–9316. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Halabi CM, Beyer AM, de Lange WJ, et al:
Interference with PPAR gamma function in smooth muscle causes
vascular dysfunction and hypertension. Cell Metab. 7:215–226. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Guri AJ, Hontecillas R, Ferrer G, et al:
Loss of PPAR gamma in immune cells impairs the ability of abscisic
acid to improve insulin sensitivity by suppressing monocyte
chemoattractant protein-1 expression and macrophage infiltration
into white adipose tissue. J Nutr Biochem. 19:216–228. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Tsuchida A, Yamauchi T, Takekawa S, et al:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)alpha activation
increases adiponectin receptors and reduces obesity-related
inflammation in adipose tissue: comparison of activation of
PPARalpha, PPARgamma, and their combination. Diabetes.
54:3358–3370. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Li Y, Cheng L, Qin Q, et al: High-fat
feeding in cardiomyocyte-restricted PPARdelta knockout mice leads
to cardiac overexpression of lipid metabolic genes but fails to
rescue cardiac phenotypes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 47:536–543. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Juge-Aubry C, Pernin A, Favez T, et al:
DNA binding properties of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor subtypes on various natural peroxisome proliferator
response elements. Importance of the 5′-flanking region. J Biol
Chem. 272:25252–25259. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Delerive P, De Bosscher K, Vanden Berghe
W, Fruchart JC, Haegeman G and Staels B: DNA binding-independent
induction of IkappaBalpha gene transcription by PPARalpha. Mol
Endocrinol. 16:1029–1039. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Tontonoz P and Spiegelman BM: Fat and
beyond: the diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem.
77:289–312. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Cortez M, Carmo LS, Rogero MM, Borelli P
and Fock RA: A high-fat diet increases IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-alpha
production by increasing NF-kappaB and attenuating PPAR-gamma
expression in bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Inflammation.
36:379–386. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chinetti G, Fruchart JC and Staels B:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and inflammation: from
basic science to clinical applications. Int J Obes Relat Metab
Disord. 27:S41–S45. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Skelhorne-Gross G and Nicol CJ: The key to
unlocking the chemotherapeutic potential of PPARgamma ligands:
Having the right combination. PPAR Res. 2012:9469432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Moore-Carrasco R, Figueras M, Ametller E,
López-Soriano FJ, Argilés JM and Busquets S: Effects of the
PPARgamma agonist GW1929 on muscle wasting in tumour-bearing mice.
Oncol Rep. 19:253–256. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Scheen AJ: Combined
thiazolidinedione-insulin therapy: should we be concerned about
safety? Drug Saf. 27:841–586. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Jiang C, Ting AT and Seed B: PPAR-gamma
agonists inhibit production of monocyte inflammatory cytokines.
Nature. 391:82–86. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Hong G, Davis B, Khatoon N, Baker SF and
Brown J: PPAR gamma-dependent anti-inflammatory action of
rosiglitazone in human monocytes: suppression of TNF alpha
secretion is not mediated by PTEN regulation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 303:782–787. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kusminski CM and Scherer PE: The road from
discovery to clinic: adiponectin as a biomarker of metabolic
status. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 86:592–595. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Furukawa H, Mawatari K, Koyama K, et al:
Telmisartan increases localization of glucose transporter 4 to the
plasma membrane and increases glucose uptake via peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gamma in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Eur J
Pharmacol. 660:485–491. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Charbonnel B: PPAR-alpha and PPAR-gamma
agonists for type 2 diabetes. Lancet. 374:96–98. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Clockaerts S, Bastiaansen-Jenniskens YM,
Feijt C, et al: Cytokine production by infrapatellar fat pad can be
stimulated by interleukin 1beta and inhibited by peroxisome
proliferator activated receptor alpha agonist. Ann Rheum Dis.
71:1012–1018. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Delerive P, De Bosscher K, Besnard S, et
al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha negatively
regulates the vascular inflammatory gene response by negative
cross-talk with transcription factors NF-kappaB and AP-1. J Biol
Chem. 274:32048–32054. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Guerre-Millo M, Rouault C, Poulain P, et
al: PPAR-alpha-null mice are protected from high-fat diet-induced
insulin resistance. Diabetes. 50:2809–2814. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Tordjman K, Bernal-Mizrachi C, Zemany L,
et al: PPARalpha deficiency reduces insulin resistance and
atherosclerosis in apoE-null mice. J Clin Invest. 107:1025–1034.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Holst JJ and McGill MA: Potential new
approaches to modifying intestinal GLP-1 secretion in patients with
type 2 diabetes mellitus: focus on bile acid sequestrants. Clin
Drug Investig. 32:1–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Maida A, Lamont BJ, Cao X and Drucker DJ:
Metformin regulates the incretin receptor axis via a pathway
dependent on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha in
mice. Diabetologia. 54:339–349. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Vu-Dac N, Schoonjans K, Laine B, Fruchart
JC, Auwerx J and Staels B: Negative regulation of the human
apolipoprotein A-I promoter by fibrates can be attenuated by the
interaction of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor with
its response element. J Biol Chem. 269:31012–31018. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Vu-Dac N, Schoonjans K, Kosykh V, et al:
Fibrates increase human apolipoprotein A-II expression through
activation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. J
Clin Invest. 96:741–750. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Coleman JD, Prabhu KS, Thompson JT, et al:
The oxidative stress mediator 4-hydroxynonenal is an intracellular
agonist of the nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-beta/delta (PPARbeta/delta). Free Radic Biol Med.
42:1155–1164. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Barish GD, Atkins AR, Downes M, et al:
PPARdelta regulates multiple proinflammatory pathways to suppress
atherosclerosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:4271–4276. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Schnegg CI, Kooshki M, Hsu FC, Sui G and
Robbins ME: PPARdelta prevents radiation-induced proinflammatory
responses in microglia via transrepression of NF-kappaB and
inhibition of the PKCalpha/MEK1/2/ERK1/2/AP-1 pathway. Free Radic
Biol Med. 52:1734–1743. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Matsushita Y, Ogawa D, Wada J, et al:
Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta
inhibits streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy through
anti-inflammatory mechanisms in mice. Diabetes. 60:960–968. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Ye JM, Tid-Ang J, Turner N, et al:
PPARdelta agonists have opposing effects on insulin resistance in
high fat-fed rats and mice due to different metabolic responses in
muscle. Br J Pharmacol. 163:556–566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Moore-Carrasco R, Poblete Bustamante M,
González Guerra O, et al: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptors: Targets for the treatment of metabolic illnesses
(Review). Mol Med Report. 1:317–324. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Puigserver P, Wu Z, Park CW, Graves R,
Wright M and Spiegelman BM: A cold-inducible coactivator of nuclear
receptors linked to adaptive thermogenesis. Cell. 92:829–839. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wu Z, Puigserver P, Andersson U, et al:
Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration
through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell. 98:115–124. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Canto C and Auwerx J: PGC-1alpha, SIRT1
and AMPK, an energy sensing network that controls energy
expenditure. Curr Opin Lipidol. 20:98–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Girnun GD: The diverse role of the
PPARgamma coactivator 1 family of transcriptional coactivators in
cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 23:381–388. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Buechler C and Schäffler A: Does global
gene expression analysis in type 2 diabetes provide an opportunity
to identify highly promising drug targets? Endocr Metab Immune
Disord Drug Targets. 7:250–258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Schilling J and Kelly DP: The PGC-1
cascade as a therapeutic target for heart failure. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 51:578–583. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Eisele PS, Salatino S, Sobek J, Hottiger
MO and Handschin C: The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
gamma coactivator 1alpha/beta (PGC-1) coactivators repress the
transcriptional activity of NF-kappaB in skeletal muscle cells. J
Biol Chem. 288:2246–2260. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Wang Y, Xu C, Liang Y and Vanhoutte PM:
SIRT1 in metabolic syndrome: where to target matters. Pharmacol
Ther. 136:305–318. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Porcu M and Chiarugi A: The emerging
therapeutic potential of sirtuin-interacting drugs: from cell death
to lifespan extension. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 26:94–103. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Canto C and Auwerx J: Targeting sirtuin 1
to improve metabolism: all you need is NAD(+)? Pharmacol Rev.
64:166–187. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hallows WC, Lee S and Denu JM: Sirtuins
deacetylate and activate mammalian acetyl-CoA synthetases. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:10230–10235. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Rodgers JT, Lerin C, Haas W, Gygi SP,
Spiegelman BM and Puigserver P: Nutrient control of glucose
homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1alpha and SIRT1. Nature.
434:113–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|