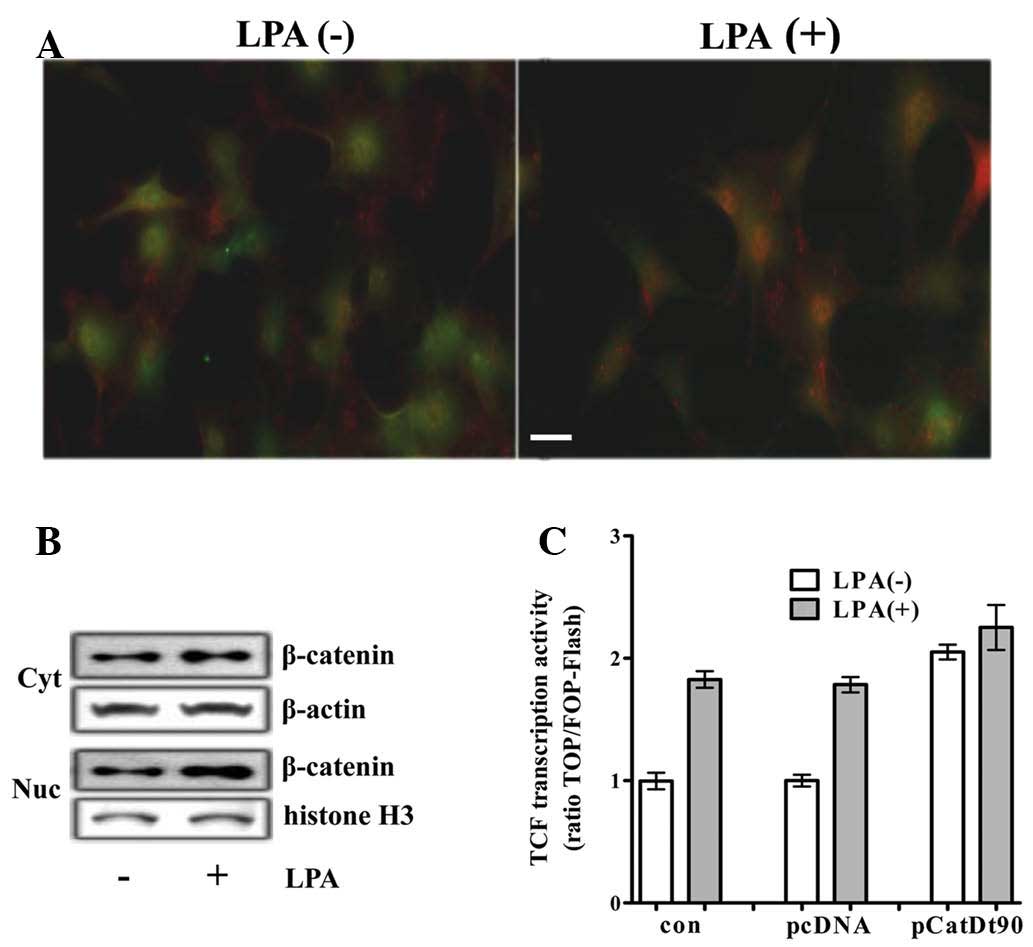
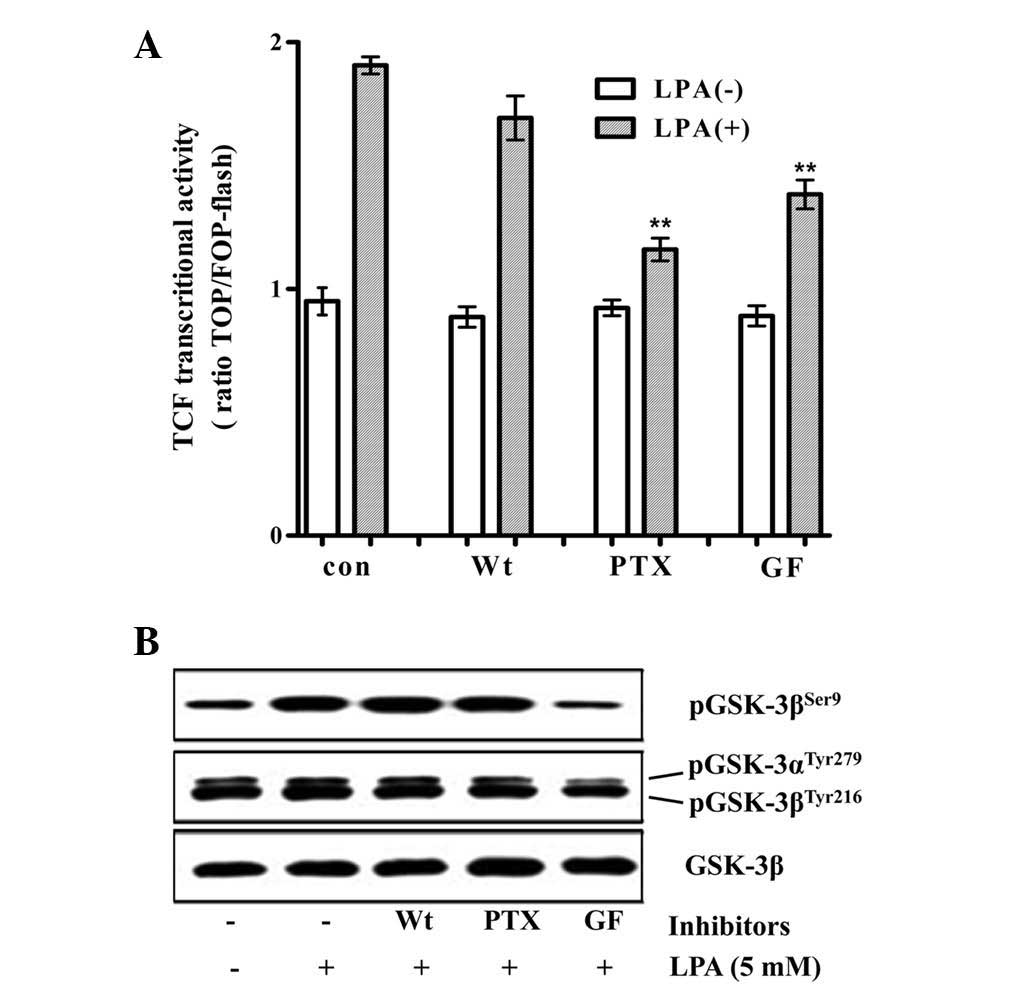
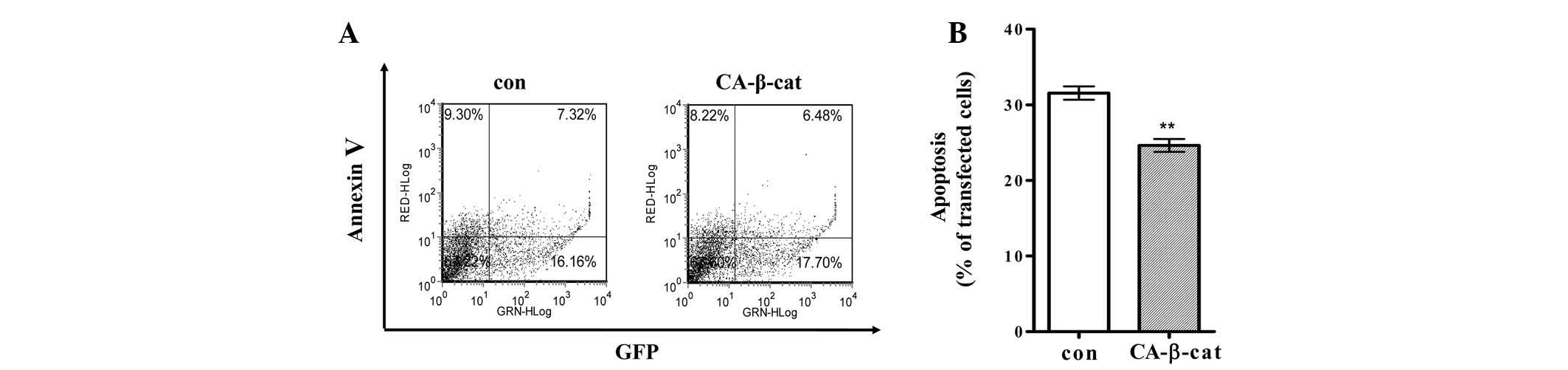
|
1
|
Anliker B and Chun J: Lysophospholipid G
protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 279:20555–20558. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun Y, Nam JS, Han DH, et al:
Lysophosphatidic acid induces upregulation of Mcl-1 and protects
apoptosis in a PTX-dependent manner in H19-7 cells. Cell Signal.
22:484–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhang L, Yang X, Yang S and Zhang J: The
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in the adult neurogenesis. Eur J
Neurosci. 33:1–8. 2011.
|
|
4
|
Ille F, Atanasoski S, Falk S, et al:
Wnt/BMP signal integration regulates the balance between
proliferation and differentiation of neuroepithelial cells in the
dorsal spinal cord. Dev Biol. 304:394–408. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang J, Woodhead GJ, Swaminathan SK, et
al: Cortical neural precursors inhibit their own differentiation
via N-cadherin maintenance of beta-catenin signaling. Dev Cell.
18:472–479. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang X, Kopinke D, Lin J, et al: Wnt
signaling regulates postembryonic hypothalamic progenitor
differentiation. Dev Cell. 23:624–636. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang M, Villaescusa JC, Luo SX, et al:
Interactions of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and sonic hedgehog
regulate the neurogenesis of ventral midbrain dopamine neurons. J
Neurosci. 30:9280–9291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pöschl J, Grammel D, Dorostkar MM,
Kretzschmar HA and Schüller U: Constitutive activation of β-catenin
in neural progenitors results in disrupted proliferation and
migration of neurons within the central nervous system. Dev Biol.
374:319–332. 2013.
|
|
9
|
Zhao S, Fu J, Liu X, Wang T, Zhang J and
Zhao Y: Activation of Akt/GSK-3beta/beta-catenin signaling pathway
is involved in survival of neurons after traumatic brain injury in
rats. Neurol Res. 34:400–407. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pérez-Álvarez MJ, del Maza MC, Anton M,
Ordoñez L and Wandosell F: Post-ischemic estradiol treatment
reduced glial response and triggers distinct cortical and
hippocampal signaling in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:1572012.
|
|
11
|
Mavila N, James D, Utley S, et al:
Fibroblast growth factor receptor-mediated activation of
AKT-β-catenin-CBP pathway regulates survival and proliferation of
murine hepatoblasts and hepatic tumor initiating stem cells. PloS
One. 7:e504012012.
|
|
12
|
Lei ZN, Liu F, Zhang LM, Huang YL and Sun
FY: Bcl-2 increases stroke-induced striatal neurogenesis in adult
brains by inhibiting BMP-4 function via activation of β-catenin
signaling. Neurochem Int. 61:34–42. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kingsbury Ma, Rehen SK, Contos JJ, Higgins
CM and Chun J: Non-proliferative effects of lysophosphatidic acid
enhance cortical growth and folding. Nat Neurosci. 6:1292–1299.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Valenta T, Hausmann G and Basler K: The
many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 31:2714–2736.
2012.
|
|
15
|
Jin T, George Fantus I and Sun J: Wnt and
beyond Wnt: multiple mechanisms control the transcriptional
property of beta-catenin. Cell Signal. 20:1697–1704. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Eves EM, Boise LH, Thompson CB, Wagner AJ,
Hay N and Rosner MR: Apoptosis induced by differentiation or serum
deprivation in an immortalized central nervous system neuronal cell
line. J Neurochem. 67:1908–1920. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rhee HJ, Nam JS, Sun Y, et al:
Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates cAMP accumulation and cAMP
response element-binding protein phosphorylation in immortalized
hippocampal progenitor cells. Neuroreport. 17:523–526. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang M, Zhong WW, Srivastava N, et al: G
protein-coupled lysophosphatidic acid receptors stimulate
proliferation of colon cancer cells through the β-catenin pathway.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:6027–6032. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Desbois-Mouthon C, Cadoret A, Blivet-Van
Eggelpoël MJ, et al: Insulin and IGF-1 stimulate the beta-catenin
pathway through two signalling cascades involving GSK-3beta
inhibition and Ras activation. Oncogene. 20:252–259. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Castellone MD, Teramoto H, Williams BO,
Druey KM and Gutkind JS: Prostaglandin E2 promotes colon cancer
cell growth through a Gs-axin-beta-catenin signaling axis. Science.
310:1504–1510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verras M and Sun Z: Beta-catenin is
involved in insulin-like growth factor 1-mediated transactivation
of the androgen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 19:391–398. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ortega F, Pérez-Sen R and Miras-Portugal
MT: Gi-coupled P2Y-ADP receptor mediates GSK-3 phosphorylation and
beta-catenin nuclear translocation in granule neurons. J Neurochem.
104:62–73. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yi F, Sun J, Lim GE, Fantus IG, Brubaker
PL and Jin T: Cross talk between the insulin and Wnt signaling
pathways: evidence from intestinal endocrine L cells.
Endocrinology. 149:2341–2351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iqbal S, Zhang S, Driss A, et al: PDGF
upregulates Mcl-1 through activation of β-catenin and
HIF-1α-dependent signaling in human prostate cancer cells. PloS
One. 7:e307642012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hur EM and Zhou FQ: GSK3 signalling in
neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci. 11:539–551. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu D and Pan W: GSK3: a multifaceted
kinase in Wnt signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 35:161–168. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ng SS, Mahmoudi T, Danenberg E, et al:
Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling does not activate the wnt
cascade. J Biol Chem. 284:35308–35313. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gherzi R, Trabucchi M, Ponassi M, et al:
The RNA-binding protein KSRP promotes decay of beta-catenin mRNA
and is inactivated by PI3K-AKT signaling. PLoS Biol. 5:e52006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Takemaru K, Fischer V and Li FQ:
Fine-tuning of nuclear-catenin by Chibby and 14-3-3. Cell Cycle.
8:210–213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Luna-Ulloa LB, Hernández-Maqueda JG,
Santoyo-Ramos P, Castañeda-Patlán MC and Robles-Flores M: Protein
kinase C ζ is a positive modulator of canonical Wnt signaling
pathway in tumoral colon cell lines. Carcinogenesis. 32:1615–1624.
2011.
|
|
31
|
Paek H, Hwang JY, Zukin RS and Hébert JM:
β-Catenin-dependent FGF signaling sustains cell survival in the
anterior embryonic head by countering Smad4. Dev Cell. 20:689–699.
2011.
|
|
32
|
Holowacz T, Huelsken J, Dufort D and van
der Kooy D: Neural stem cells are increased after loss of
β-catenin, but neural progenitors undergo cell death. Eur J
Neurosci. 33:1366–1375. 2011.
|
|
33
|
Chen BY, Wang X, Wang ZY, Wang YZ, Chen LW
and Luo ZJ: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor stimulates
proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells, possibly by
triggering the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Neurosci Res.
91:30–41. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|