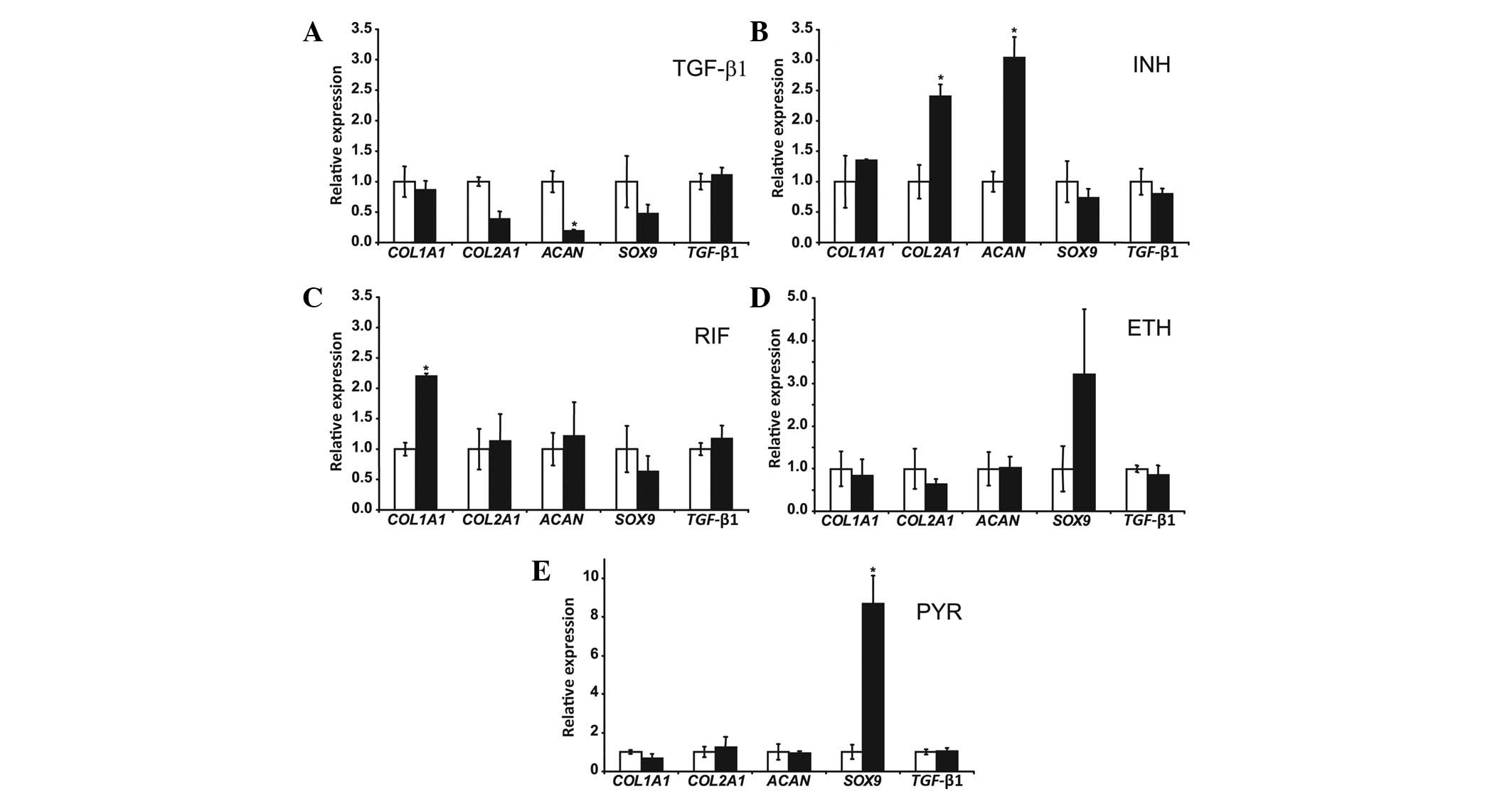
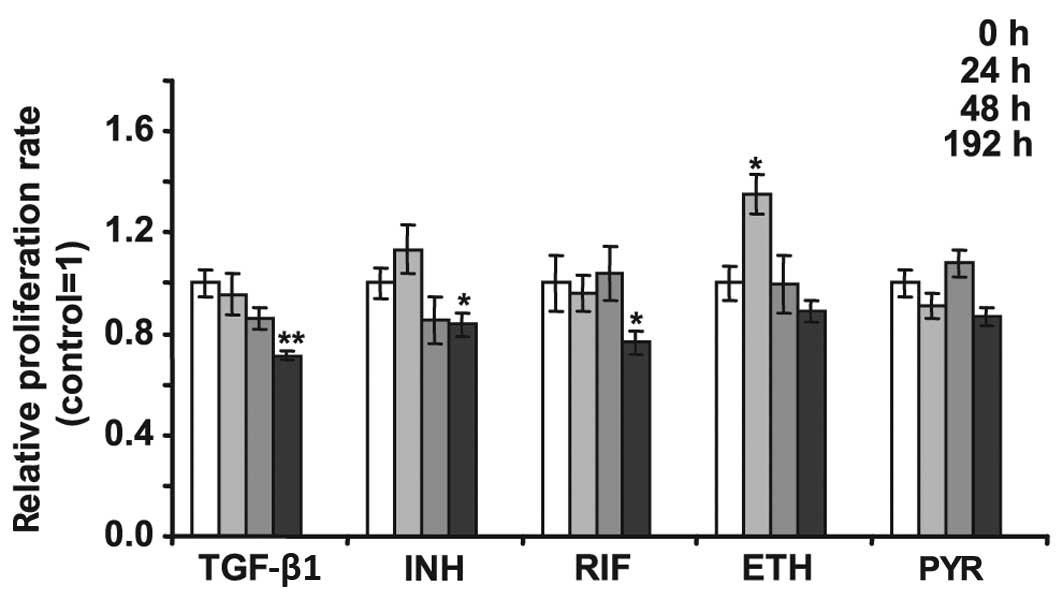
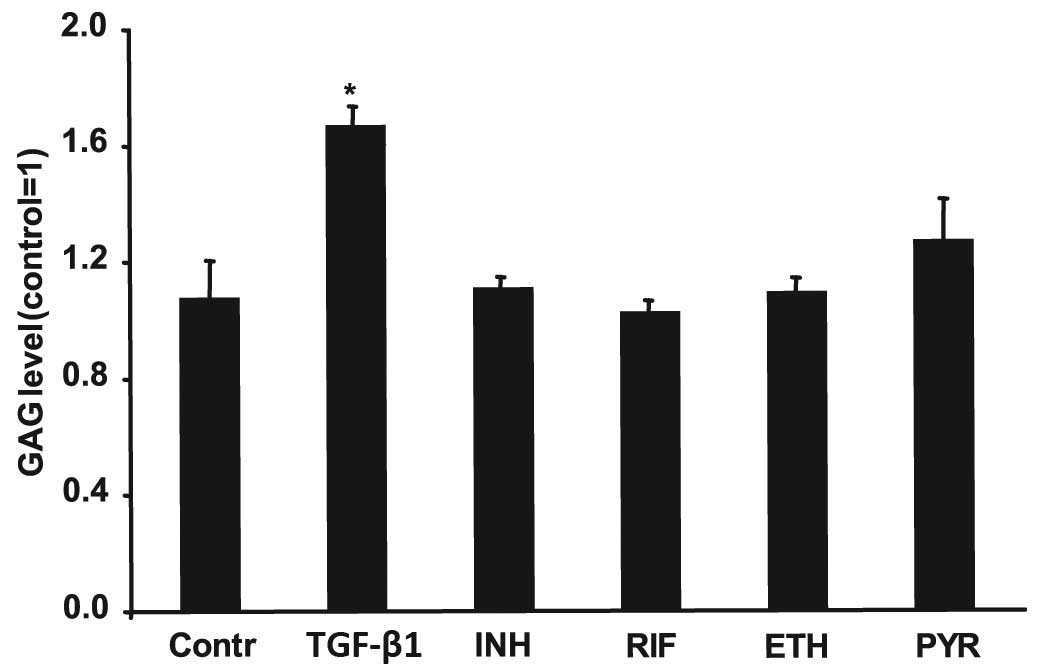
|
1
|
Tostmann A, Boeree MJ, Aarnoutse RE, de
Lange WC, van der Ven AJ and Dekhuijzen R: Antituberculosis
drug-induced hepatotoxicity: concise up-to-date review. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:192–202. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
WHO. Global tuberculosis control.
http://www.who.int/tb/publications/global_report/2011/gtbr11_main.pdf.
Accessed October 9, 2013
|
|
3
|
Donald PR: The chemotherapy of
osteo-articular tuberculosis with recommendations for treatment of
children. J Infect. 62:411–439. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hadjipavlou AG, Mader JT, Necessary JT and
Muffoletto AJ: Hematogenous pyogenic spinal infections and their
surgical management. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:1668–1679. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hoelscher GL, Gruber HE, Coldham G,
Grigsby JH and Hanley EN Jr: Effects of very high antibiotic
concentrations on human intervertebral disc cell proliferation,
viability, and metabolism in vitro. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
25:1871–1877. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schaberg T, Rebhan K and Lode H: Risk
factors for side-effects of isoniazid, rifampin and pyrazinamide in
patients hospitalized for pulmonary tuberculosis. Eur Respir J.
9:2026–2030. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Riley LH III, Banovac K, Martinez OV and
Eismont FJ: Tissue distribution of antibiotics in the
intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 19:2619–2625. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Walters R, Moore R and Fraser R:
Penetration of cephazolin in human lumbar intervertebral disc.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31:567–570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Black M, Mitchell JR, Zimmerman HJ, Ishak
KG and Epler GR: Isoniazid-associated hepatitis in 114 patients.
Gastroenterology. 69:289–302. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aristoff PA, Garcia GA, Kirchhoff PD and
Hollis Showalter HD: Rifamycins - obstacles and opportunities.
Tuberculosis (Edinb). 90:94–118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Frydenberg AR and Graham SM: Toxicity of
first-line drugs for treatment of tuberculosis in children: review.
Trop Med Int Health. 14:1329–1337. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Griffith DE, Brown-Elliott BA, Shepherd S,
McLarty J, Griffith L and Wallace RJ Jr: Ethambutol ocular toxicity
in treatment regimens for Mycobacterium avium complex lung disease.
Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 172:250–253. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sive JI, Baird P, Jeziorsk M, Watkins A,
Hoyland JA and Freemont AJ: Expression of chondrocyte markers by
cells of normal and degenerate intervertebral discs. Mol Pathol.
55:91–97. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gruber HE, Norton HJ, Ingram JA and Hanley
EN Jr: The SOX9 transcription factor in the human disc: decreased
immunolocalization with age and disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 30:625–630. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen WH, Lo WC, Lee JJ, et al:
Tissue-engineered intervertebral disc and chondrogenesis using
human nucleus pulposus regulated through TGF-beta1 in platelet-rich
plasma. J Cell Physiol. 209:744–754. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Freyria AM and Mallein-Gerin F:
Chondrocytes or adult stem cells for cartilage repair: the
indisputable role of growth factors. Injury. 43:259–265. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang SH, Lin CC, Hu MH, Shih TT, Sun YH
and Lin FH: Influence of age-related degeneration on regenerative
potential of human nucleus pulposus cells. J Orthop Res.
28:379–383. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang SH, Wu CC, Shih TT, Sun YH and Lin
FH: In vitro study on interaction between human nucleus pulposus
cells and mesenchymal stem cells through paracrine stimulation.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:1951–1957. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bujía J, Sittinger M, Wilmes E and Hammer
C: Effect of growth factors on cell proliferation by human nasal
septal chondrocytes cultured in monolayer. Acta Otolaryngol.
114:539–543. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang R, Ruan D and Zhang C: Effects of
TGF-beta1 and IGF-1 on proliferation of human nucleus pulposus
cells in medium with different serum concentrations. J Orthop Surg
Res. 1:92006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boatright KM and Salvesen GS: Mechanisms
of caspase activation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 15:725–731. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Le Maitre CL, Pockert A, Buttle DJ,
Freemont AJ and Hoyland JA: Matrix synthesis and degradation in
human intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Soc Trans.
35:652–655. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu Q, Wang J, Skubutyte R, et al: SMAD3
controls β-1, 3-glucuronosyltransferase 1 expression in nucleus
pulposus cells: implications of dysregulated expression in disc
disease. Arthritis Rheum. 64:3324–3333. 2012.
|
|
24
|
Boxenbaum HG, Berkersky I, Mattaliano V
and Kaplan SA: Plasma and salivary concentrations of isoniazid in
man: preliminary findings in two slow acetylator subjects. J
Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 3:443–456. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Klenø TG, Kiehr B, Baunsgaard D and
Sidelmann UG: Combination of ‘omics’ data to investigate the
mechanism(s) of hydrazine-induced hepatotoxicity in rats and to
identify potential biomarkers. Biomarkers. 9:116–138. 2004.
|
|
26
|
Knowles SR, Uetrecht J and Shear NH:
Idiosyncratic drug reactions: the reactive metabolite syndromes.
Lancet. 356:1587–1591. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boman G: Serum concentration and half-life
of rifampicin after simultaneous oral administration of
aminosalicylic acid or isoniazid. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 7:217–225.
1974. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Holdiness MR: Clinical pharmacokinetics of
the antituberculosis drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 9:511–544. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Trnka L, Mison P and Staflova S:
Interaction aspects of antimycobacterial drugs in the chemotherapy
of tuberculosis. II The role of rifampicin and other drugs in the
dependent or independent action of drug associations in vitro.
Chemotherapy. 20:82–91. 1974.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Westphal JF, Vetter D and Brogard JM:
Hepatic side-effects of antibiotics. J Antimicrob Chemother.
33:387–401. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhuang W, Jia Z, Feng H, et al: The
mechanism of the G0/G1 cell cycle phase arrest induced by
activation of PXR in human cells. Biomed Pharmacother. 65:467–473.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Clouet J, Pot-Vaucel M, Grimandi G, et al:
Characterization of the age-dependent intervertebral disc changes
in rabbit by correlation between MRI, histology and gene
expression. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 12:1472011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Conte JE Jr, Golden JA, Kipps J, Lin ET
and Zurlinden E: Effects of AIDS and gender on steady-state plasma
and intrapulmonary ethambutol concentrations. Antimicrob Agents
Chemother. 45:2891–2896. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
McIlleron H, Wash P, Burger A, Norman J,
Folb PI and Smith P: Determinants of rifampin, isoniazid,
pyrazinamide, and ethambutol pharmacokinetics in a cohort of
tuberculosis patients. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 50:1170–1177.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Peloquin CA, Bulpitt AE, Jaresko GS,
Jelliffe RW, Childs JM and Nix DE: Pharmacokinetics of ethambutol
under fasting conditions, with food, and with antacids. Antimicrob
Agents Chemother. 43:568–572. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shayakhmetova GM, Bondarenko LB and
Kovalenko VM: Damage of testicular cell macromolecules and
reproductive capacity of male rats following co-administration of
ethambutol, rifampicin, isoniazid and pyrazinamide. Interdiscip
Toxicol. 5:9–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ellard GA and Haslam RM: Observations on
the reduction of the renal elimination of urate in man caused by
the administration of pyrazinamide. Tubercle. 57:97–103. 1976.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shi W, Zhang X, Jiang X, et al:
Pyrazinamide inhibits trans-translation in Mycobacterium
tuberculosis. Science. 333:1630–1632. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Watts HG and Lifeso RM: Tuberculosis of
bones and joints. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 78:288–298. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu G, Codina M and Fisher S: Multiple
enhancers associated with ACAN suggest highly redundant
transcriptional regulation in cartilage. Matrix Biol. 31:328–337.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|