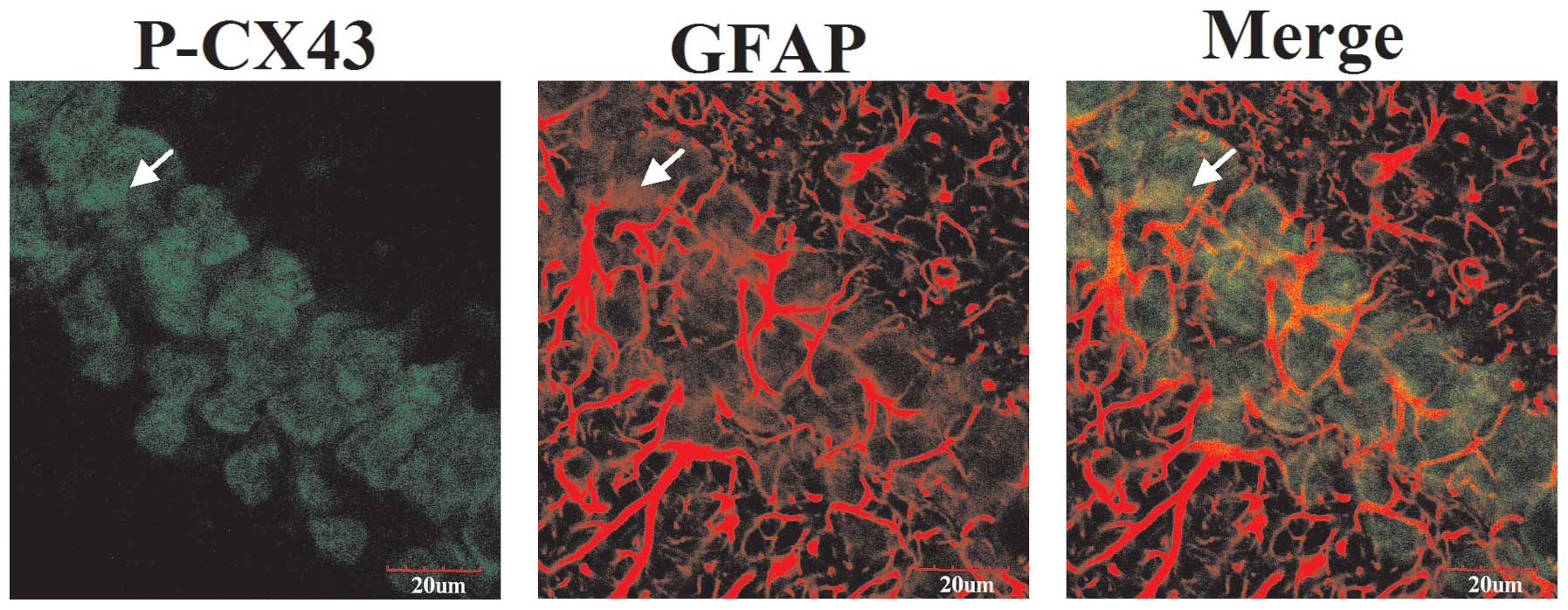
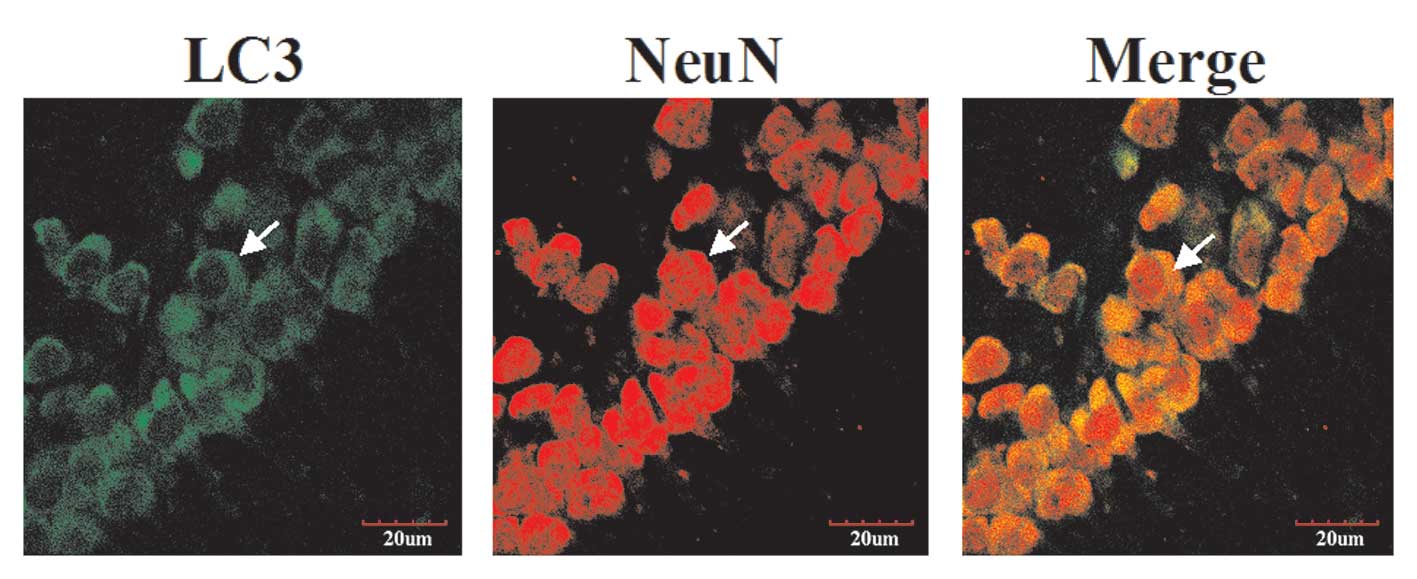
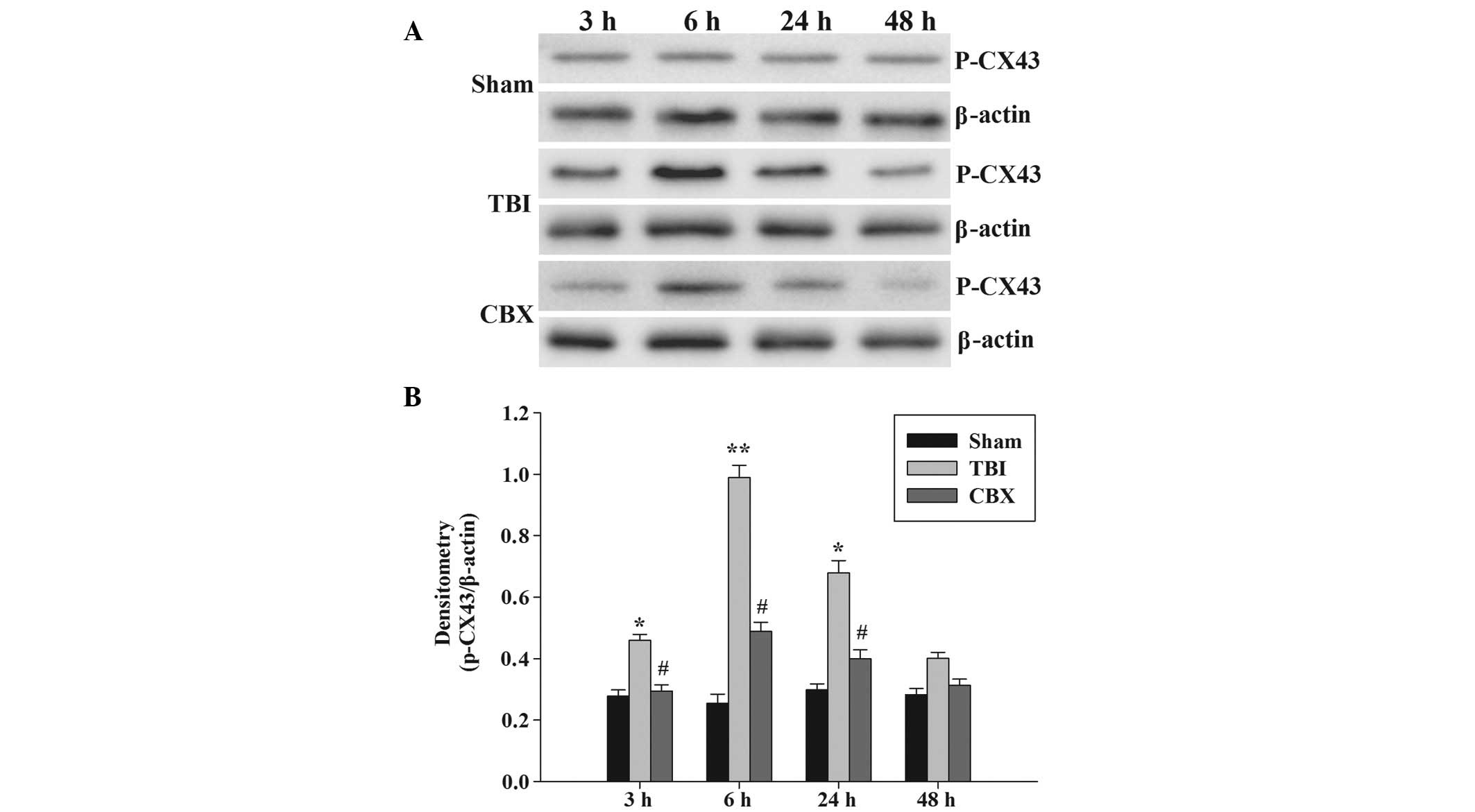
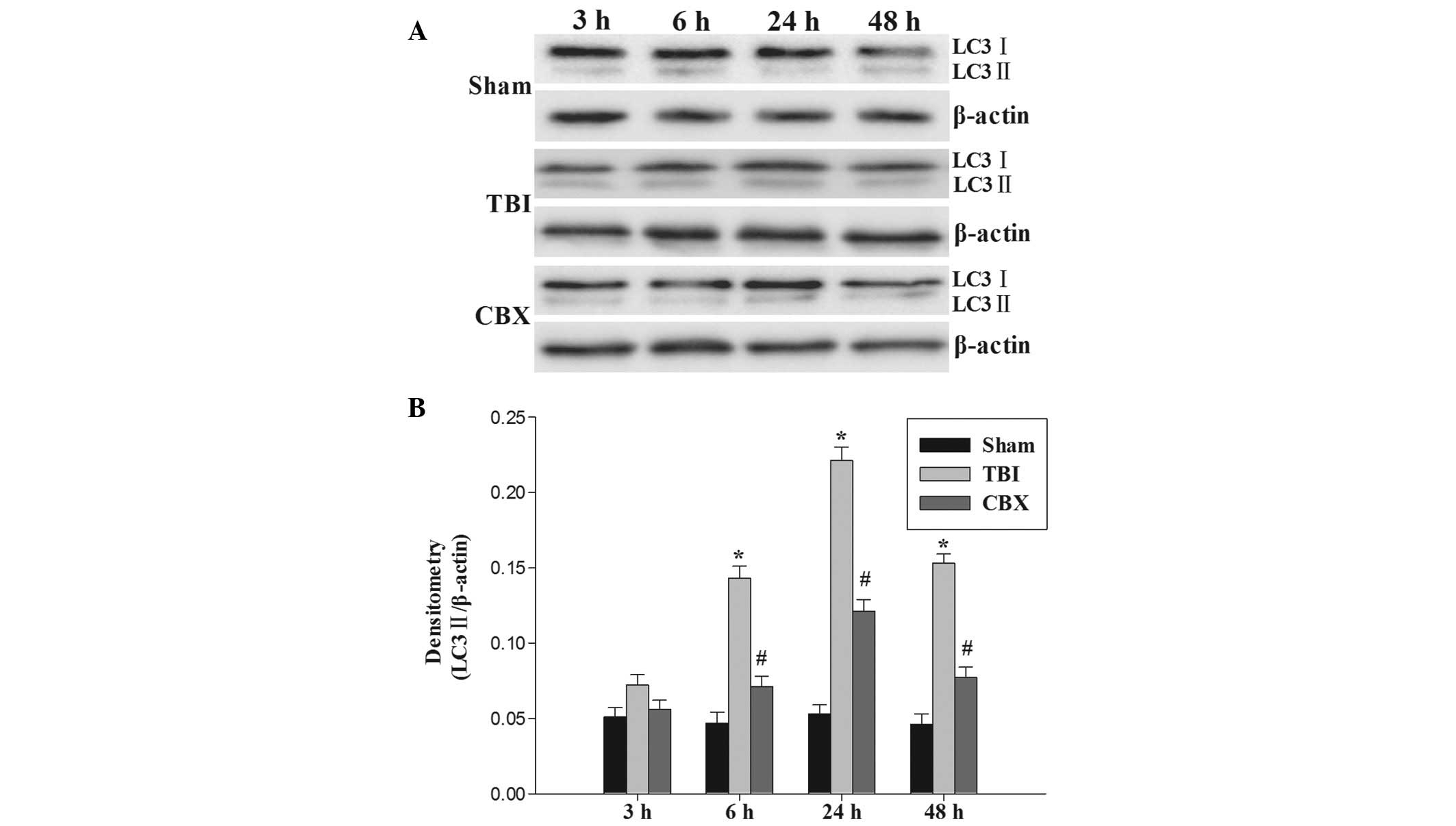
|
1
|
Mammis A, McIntosh TK and Maniker AH:
Erythropoietin as a neuroprotective agent in traumatic brain injury
Review. Surgical Neurol. 71:527–531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Luo CL, Chen XP, Yang R, et al: Cathepsin
B contributes to traumatic brain injury-induced cell death through
a mitochondria-mediated apoptotic pathway. J Neurosci Res.
88:2847–2858. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tehranian R, Rose ME, Vagni V, et al:
Disruption of Bax protein prevents neuronal cell death but produces
cognitive impairment in mice following traumatic brain injury. J
Neurotrauma. 25:755–767. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lai Y, Hickey RW, Chen Y, et al: Autophagy
is increased after traumatic brain injury in mice and is partially
inhibited by the antioxidant gamma-glutamylcysteinyl ethyl ester. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 28:540–550. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pozuelo-Rubio M: Regulation of autophagic
activity by 14-3-3ζ proteins associated with class III
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase. Cell Death Differ. 18:479–492.
2011.
|
|
6
|
Liu CL, Chen S, Dietrich D and Hu BR:
Changes in autophagy after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 28:674–683. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cotrina ML and Nedergaard M: Physiological
and pathological functions of P2X7 receptor in the spinal cord.
Purinergic Signal. 5:223–232. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bennett MV, Contreras JE, Bukauskas FF and
Sáez JC: New roles for astrocytes: gap junction hemichannels have
something to communicate. Trends Neurosci. 26:610–617. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cottrell GT, Lin R, Warn-Cramer BJ, Lau AF
and Burt JM: Mechanism of v-Src-and mitogen-activated protein
kinase-induced reduction of gap junction communication. Am J
Physiol Cell Physiol. 284:C511–C520. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao X, Ahram A, Berman RF, Muizelaar JP
and Lyeth BG: Early loss of astrocytes after experimental traumatic
brain injury. Glia. 44:140–152. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Giaume C, Tabernero A and Medina JM:
Metabolic trafficking through astrocytic gap junctions. Glia.
21:114–123. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin JH, Weigel H, Cotrina ML, et al:
Gap-junction-mediated propagation and amplification of cell injury.
Nature Neurosci. 1:494–500. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Marmarou A, Foda MA, van den Brink W,
Campbell J, Kita H and Demetriadou K: A new model of diffuse brain
injury in rats. J Neurosurg. 80:291–300. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khorasani MZ, Hosseinzadeh SA and Vakili
A: Effect of central microinjection of carbenoxolone in an
experimental model of focal cerebral ischemia. Pak J Pharm Sci.
22:349–354. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Milad MR, Vidal-Gonzalez I and Quirk GJ:
Electrical stimulation of medial prefrontal cortex reduces
conditioned fear in a temporally specific manner. Behav Neurosci.
118:389–394. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song SX, Gao JL, Wang KJ, et al:
Attenuation of brain edema and spatial learning deficits by the
inhibition of NADPH oxidase activity using apocynin following
diffuse traumatic brain injury in rats. Mol Med Rep. 327–331.
2012.
|
|
17
|
Eghwrudjakpor PO and Allison AB: Oxidative
stress following traumatic brain injury: enhancement of endogenous
antioxidant defense systems and the promise of improved outcome.
Niger J Med. 19:14–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Uryu K, Laurer H, McIntosh T, et al:
Repetitive mild brain trauma accelerates Abeta deposition, lipid
peroxidation, and cognitive impairment in a transgenic mouse model
of Alzheimer amyloidosis. J Neurosci. 22:446–454. 2002.
|
|
19
|
Werner C and Engelhard K: Pathophysiology
of traumatic brain injury. Br J Anaesth. 99:4–9. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Geng J and Klionsky DJ: The Atg8 and Atg12
ubiquitin-like conjugation systems in macroautophagy. ‘Protein
modifications: beyond the usual suspects’ review series. EMBO Rep.
9:859–864. 2008.
|
|
21
|
Mizushima N, Levine B, Cuervo AM and
Klionsky DJ: Autophagy fights disease through cellular
self-digestion. Nature. 451:1069–1075. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Meijer AJ and Codogno P: Autophagy:
regulation and role in disease. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 46:210–240.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Luo CL, Li BX, Li QQ, et al: Autophagy is
involved in traumatic brain injury-induced cell death and
contributes to functional outcome deficits in mice. Neuroscience.
184:54–63. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Clark RS, Bayir H, Chu CT, Alber SM,
Kochanek PM and Watkins SC: Autophagy is increased in mice after
traumatic brain injury and is detectable in human brain after
trauma and critical illness. Autophagy. 4:88–90. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maiuri MC, Criollo A, Tasdemir E, et al:
BH3-only proteins and BH3 mimetics induce autophagy by
competitively disrupting the interaction between Beclin 1 and
Bcl-2/Bcl-X(L). Autophagy. 3:374–376. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Yamamoto A,
Oshitani-Okamoto S, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, GABARAP and
GATE16 localize to autophagosomal membrane depending on form-II
formation. J Cell Sci. 117:2805–2812. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Araque A, Parpura V, Sanzgiri RP and
Haydon PG: Tripartite synapses: glia, the unacknowledged partner.
Trends Neurosci. 22:208–215. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsacopoulos M and Magistretti PJ:
Metabolic coupling between glia and neurons. J Neurosci.
16:877–885. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Dermietzel R and Spray DC: From neuro-glue
(‘Nervenkitt’) to glia: a prologue. Glia. 24:1–7. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Giaume C, Fromaget C, el Aoumari A,
Cordier J, Glowinski J and Gros D: Gap junctions in cultured
astrocytes: single-channel currents and characterization of
channel-forming protein. Neuron. 6:133–143. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Paul DL: New functions for gap junctions.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 7:665–672. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hansson E, Muyderman H, Leonova J, et al:
Astroglia and glutamate in physiology and pathology: aspects on
glutamate transport, glutamate-induced cell swelling and
gap-junction communication. Neurochem Int. 37:317–329. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nakase T, Fushiki S and Naus CC:
Astrocytic gap junctions composed of connexin 43 reduce apoptotic
neuronal damage in cerebral ischemia. Stroke. 34:1987–1993. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rozental R, Srinivas M and Spray DC: How
to close a gap junction channel. Efficacies and potencies of
uncoupling agents. Methods Mol Biol. 154:447–476. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Magistretti PJ: Cellular bases of
functional brain imaging: insights from neuron-glia metabolic
coupling. Brain Res. 886:108–112. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Anderson CM and Swanson RA: Astrocyte
glutamate transport: review of properties, regulation, and
physiological functions. Glia. 32:1–14. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hardingham GE and Bading H: The Yin and
Yang of NMDA receptor signalling. Trends Neurosci. 26:81–89. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rami A, Volkmann T and Winckler J:
Effective reduction of neuronal death by inhibiting gap junctional
intercellular communication in a rodent model of global transient
cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol. 170:297–304. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhang YB, Li SX, Chen XP, et al: Autophagy
is activated and might protect neurons from degeneration after
traumatic brain injury. Neurosci Bull. 24:143–149. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chew SS, Johnson CS, Green CR and
Danesh-Meyer HV: Role of connexin43 in central nervous system
injury. Exp Neurol. 225:250–261. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|