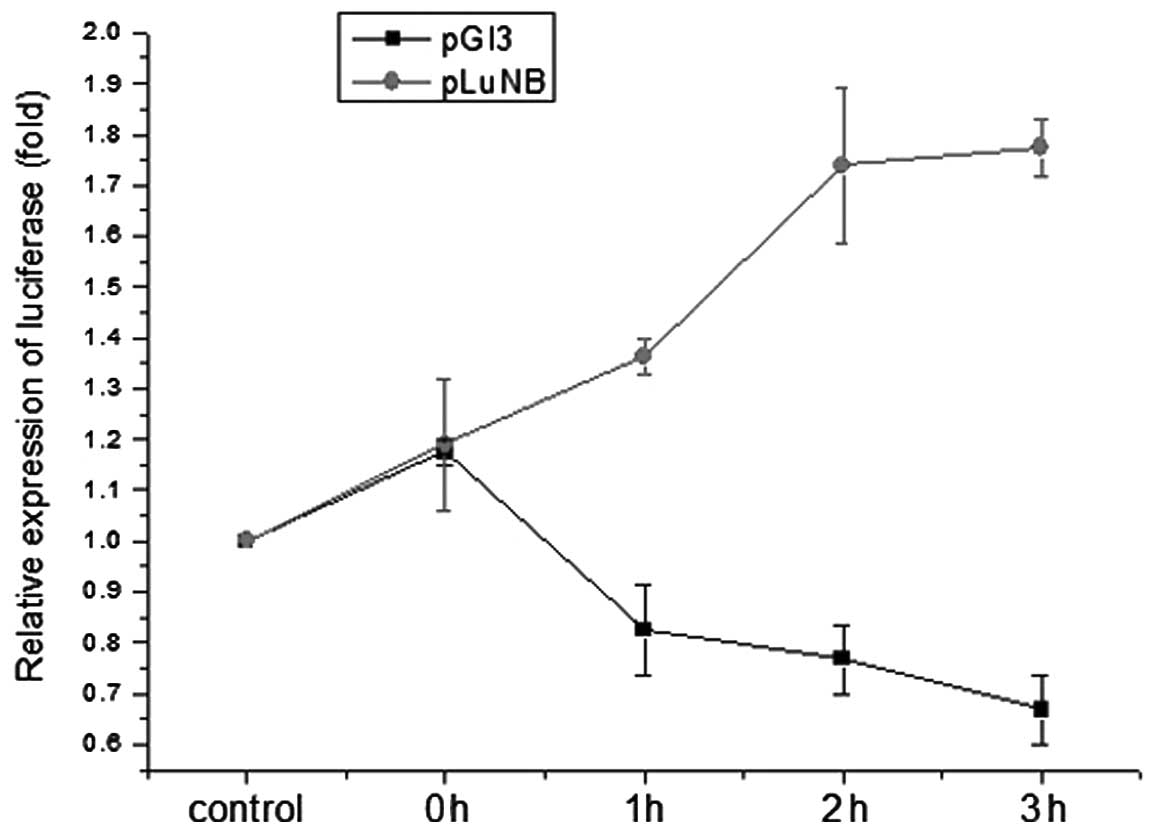
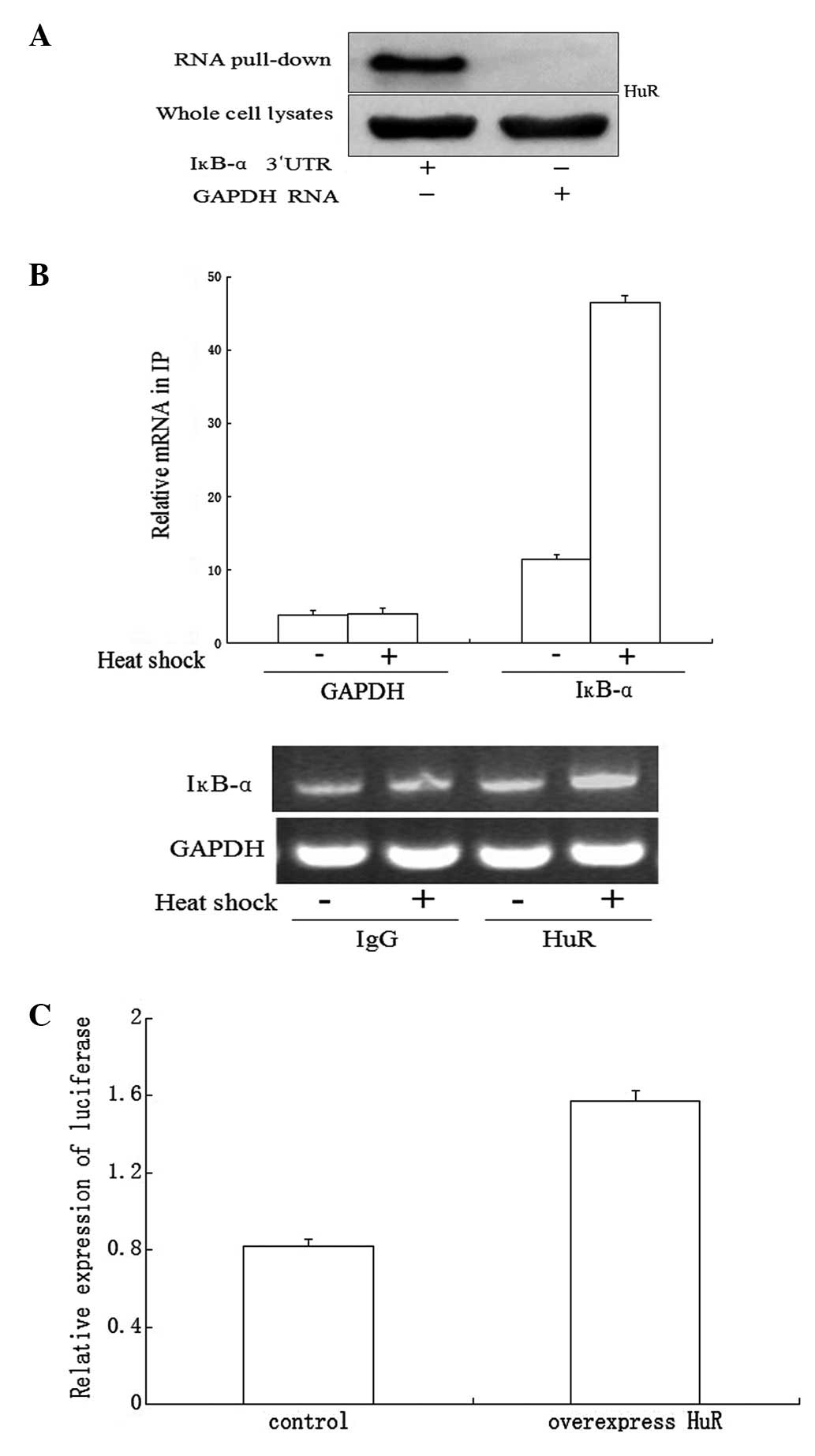
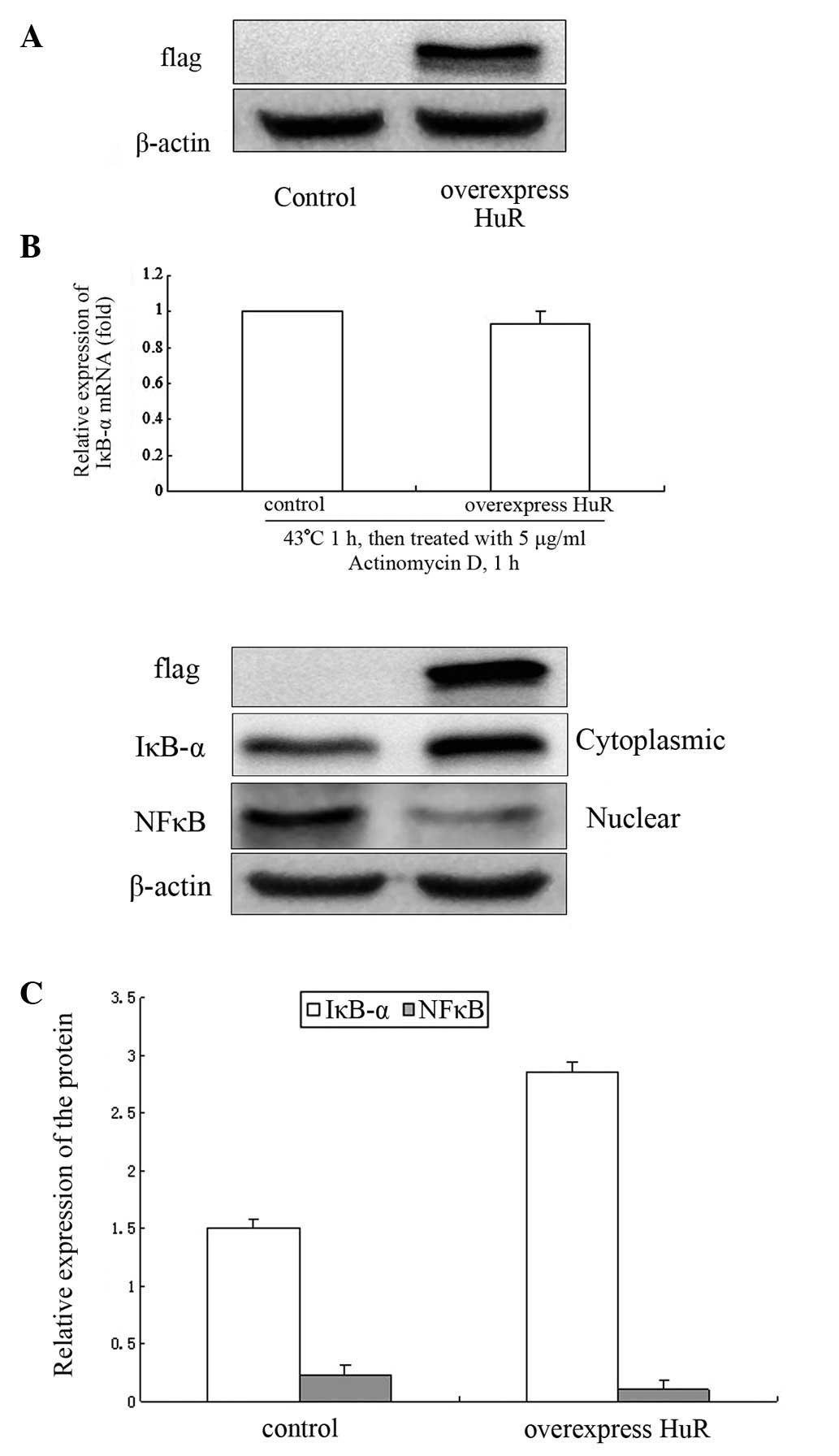
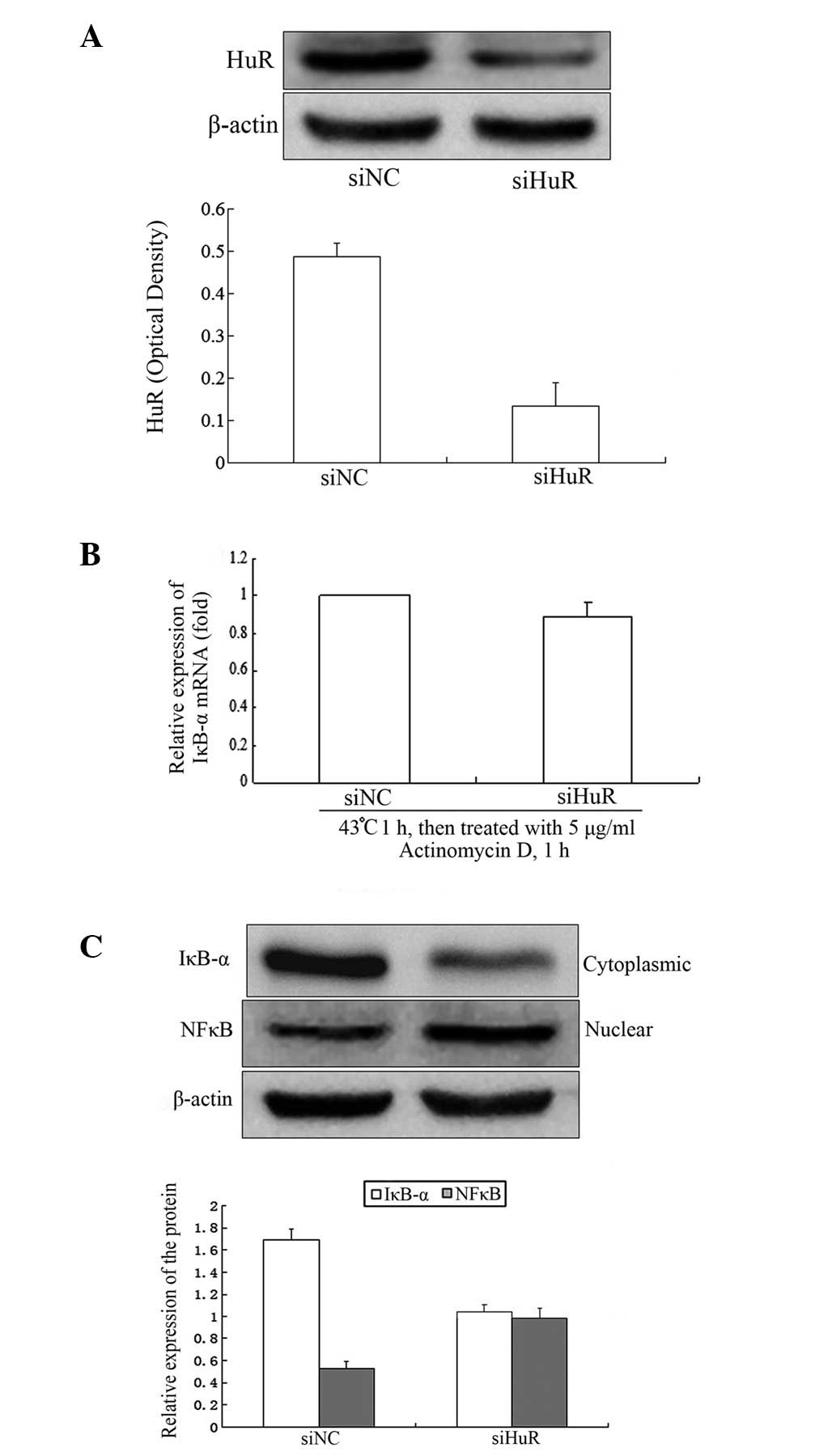
|
1
|
Shanley TP, Ryan MA, Eaves-Pyles T and
Wong HR: Heat shock inhibits phosphorylation of IkappaBalpha.
Shock. 14:447–450. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grossman BJ, Shanley TP, Odoms K, Dunsmore
KE, Denenberg AG and Wong HR: Temporal and mechanistic effects of
heat shock on LPS-mediated degradation of IkappaBalpha in
macrophages. Inflammation. 26:129–137. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kohn G, Wong HR, Bshesh K, Zhao B, Vasi N,
Denenberg A, Morris C, Stark J and Shanley TP: Heat shock inhibits
tnf-induced ICAM-1 expression in human endothelial cells via
Ikappakinase inhibition. Shock. 17:91–97. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pittet JF, Lee H, Pespeni M, O’Mahony A,
Roux J and Welch WJ: Stress-induced inhibition of the NF-kappaB
signaling pathway results from the insolubilization of the IkappaB
kinase complex following its dissociation from heat shock protein
90. J Immunol. 174:384–394. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Deng L, Wang C, Spencer E, Yang L, Braun
A, Slaughter C, Pickart C and Chen ZJ: Activation of the IkappaB
kinase complex by TRAF6 requires a dimeric ubiquitin conjugating
enzyme complex and a unique polyubiquitin chain. Cell. 103:351–361.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ouaaz F, Arron J, Zheng Y, Choi Y and Beg
AA: Dendritic cell development and survival require distinct
NF-kappaB subunits. Immunity. 16:257–270. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wong HR: Potential protective role of the
heat shock response in sepsis. New Horiz. 6:194–200.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wong HR and Wispé JR: The stress response
and the lung. Am J Physiol Lung. 273:L1–L9. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Malhotra V and Wong HR: Interactions
between the heat shock response and the nuclear factor-kappaB
signaling pathway. Crit Care Med. 30(1 Supp): S89–S95. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Beg AA, Sha WC, Bronson RT and Baltimore
D: Constitutive NF-kappaB activation, enhanced granulopoiesis and
neonatal lethality in IkappaBalpha-deficient mice. Genes Dev.
9:2736–2746. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peng B, Ling J, Lee AJ, Wang Z, Chang Z,
Jin W, Kang Y, Zhang R, Shim D, Wang H, Fleming JB, Zheng H, Sun SC
and Chiao PJ: Defective feedback regulation of NF-kappaB underlies
Sjogren’s syndrome in mice with mutated kappaB enhancers of the
IkappaBalpha promoter. Proc Natl Acad USA. 107:15193–15198.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hoffmann A, Levchenko A, Scott ML and
Baltimore D: The IkappaB-NF-kappaB signaling module: temporal
control and selective gene activation. Science. 298:1241–1245.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Moore MJ: From birth to death: the complex
lives of eukaryotic mRNAs. Science. 309:1514–1518. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moore MJ and Proudfoot NJ: Pre-mRNA
processing reaches back to transcription and ahead to translation.
Cell. 136:688–700. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Glisovic T, Bachorik JL, Yong J and
Dreyfuss G: RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene
regulation. FEBS Lett. 582:1977–1986. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sanchez-Diaz P and Penalva LO:
Post-transcription meets post-genomic: the saga of RNA binding
proteins in a new era. RNA Biol. 3:101–109. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
López de Silanes I, Zhan M, Lal A, Yang X
and Gorospe M: Identification of a target RNA motif for RNA-binding
protein HuR. Proc Natl Acad USA. 101:2987–2992. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Anderson P and Kedersha N: Stressful
initiations. Cell. 115:3227–3234. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|