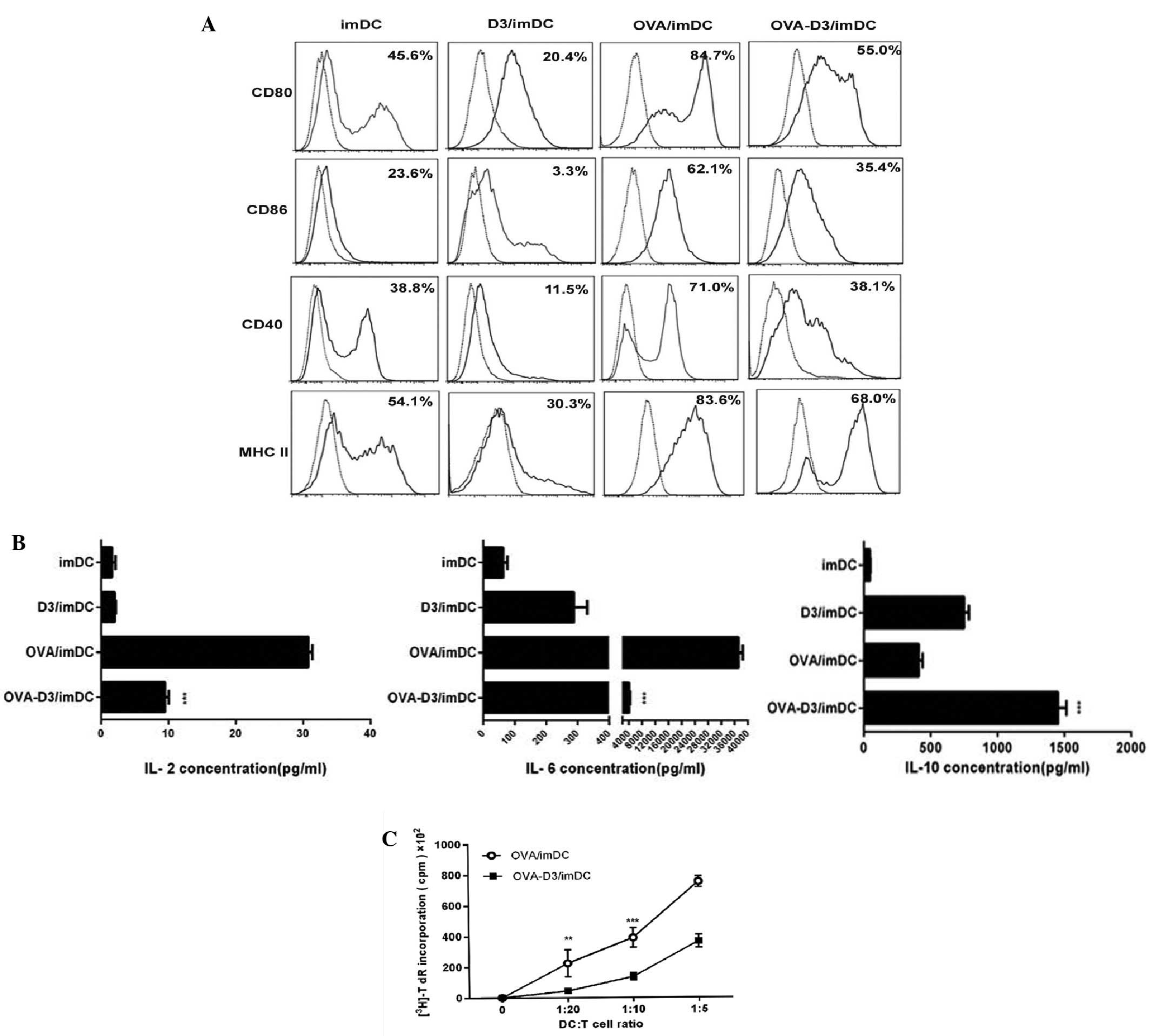
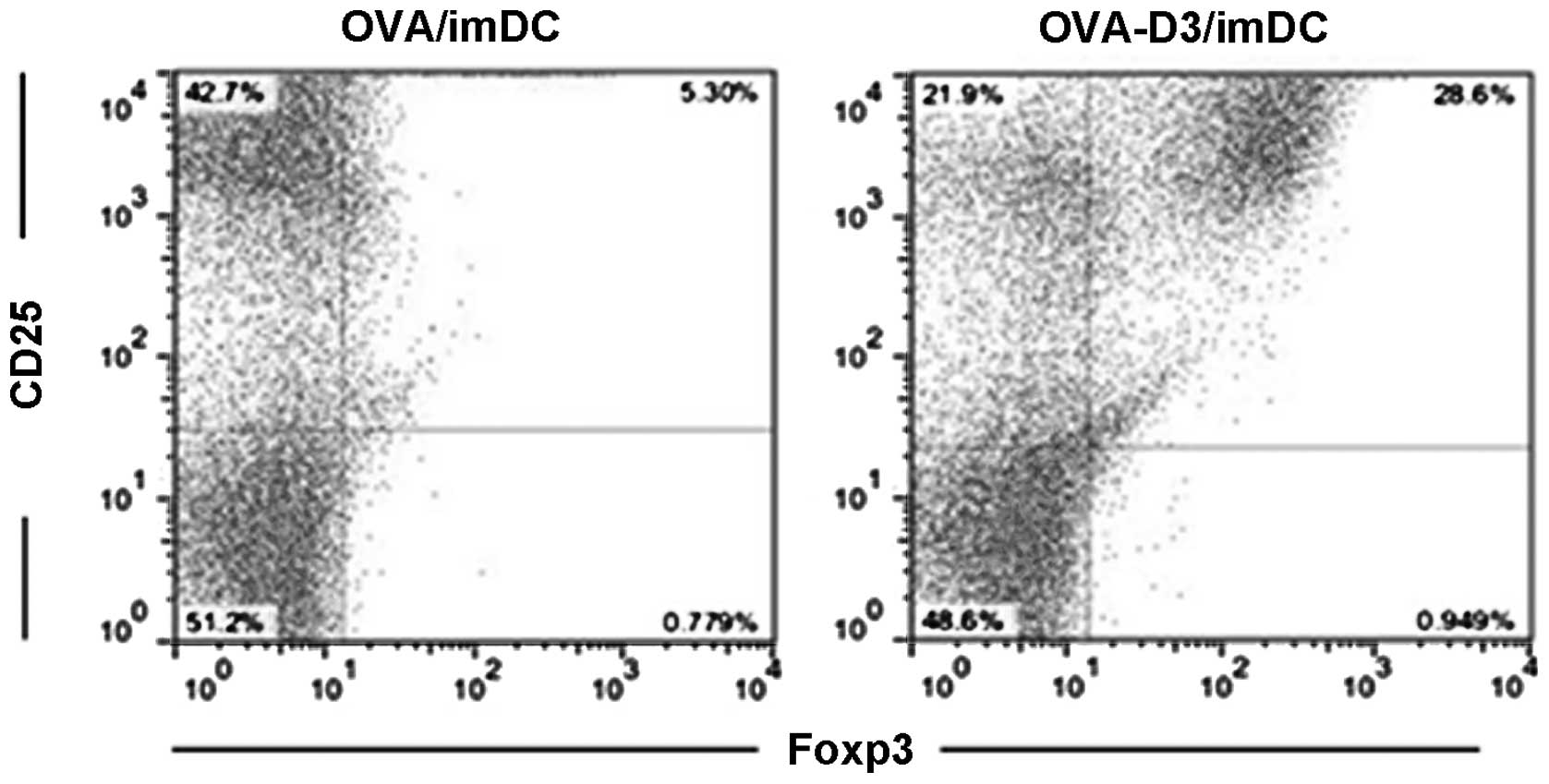
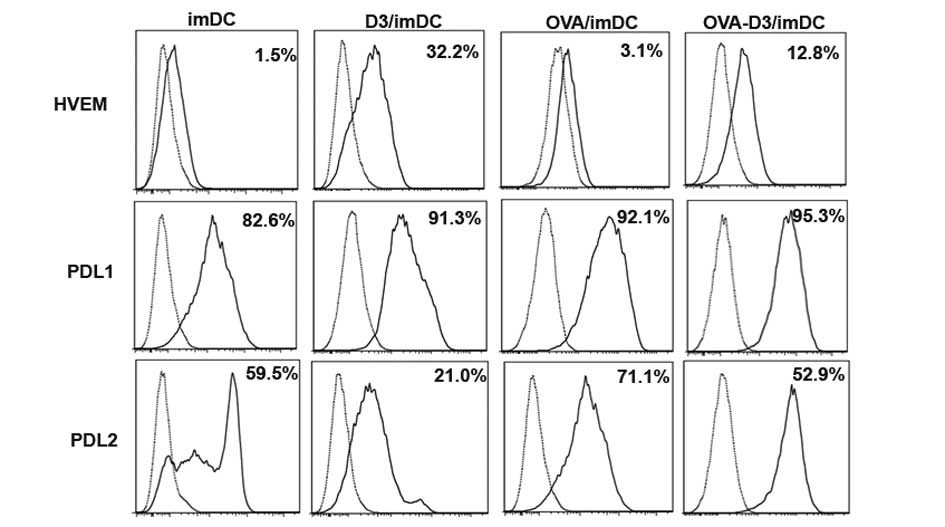
|
1
|
Casteels K, Bouillon R, Waer M and Mathieu
C: Immunomodulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Curr Opin
Nephrol Hypertens. 4:313–318. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Carlberg C: Current understanding of the
function of the nuclear vitamin D receptor in response to its
natural and synthetic ligands. Recent Results Cancer Res.
164:29–42. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Griffin MD, Xing N and Kumar R: Vitamin D
and its analogs as regulators of immune activation and antigen
presentation. Annu Rev Nutr. 23:117–145. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mathieu C and Adorini L: The coming of age
of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 analogs as immunomodulatory agents.
Trends Mol Med. 8:174–179. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adorini L: Immunomodulatory effects of
vitamin D receptor ligands in autoimmune diseases. Int
Immunopharmacol. 2:1017–1028. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adorini L: 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3
analogs as potential therapies in transplantation. Curr Opin
Investig Drugs. 3:1458–1463. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deluca HF and Cantorna MT: Vitamin D: its
role and uses in immunology. FASEB J. 15:2579–2585. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Penna G and Adorini L: 1
Alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits differentiation, maturation,
activation, and survival of dendritic cells leading to impaired
alloreactive T cell activation. J Immunol. 164:2405–2411. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Piemonti L, Monti P, Sironi M, et al:
Vitamin D3 affects differentiation, maturation, and function of
human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol. 164:4443–4451.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Griffin MD, Lutz WH, Phan VA, Bachman LA,
McKean DJ and Kumar R: Potent inhibition of dendritic cell
differentiation and maturation by vitamin D analogs. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 270:701–708. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
van Halteren AG, van Etten E, de Jong EC,
Bouillon R, Roep BO and Mathieu C: Redirection of human
autoreactive T-cells Upon interaction with dendritic cells
modulated by TX527, an analog of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D(3).
Diabetes. 51:2119–2125. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gauzzi MC, Purificato C, Donato K, et al:
Suppressive effect of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on type I
IFN-mediated monocyte differentiation into dendritic cells:
impairment of functional activities and chemotaxis. J Immunol.
174:270–276. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dai H, Zhu H, Lei P, et al: Programmed
death-1 signaling is essential for the skin allograft protection by
alternatively activated dendritic cell infusion in mice.
Transplantation. 88:864–873. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang L, Pino-Lagos K, de Vries VC, Guleria
I, Sayegh MH and Noelle RJ: Programmed death 1 ligand signaling
regulates the generation of adaptive Foxp3+CD4+ regulatory T cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:9331–9336. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen C, Qu QX, Huang JA, et al: Expression
of programmed-death receptor ligands 1 and 2 may contribute to the
poor stimulatory potential of murine immature dendritic cells.
Immunobiology. 212:159–165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kwon BS, Tan KB, Ni J, et al: A newly
identified member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily
with a wide tissue distribution and involvement in lymphocyte
activation. J Biol Chem. 272:14272–14276. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Morel Y, Schiano de Colella JM, Harrop J,
et al: Reciprocal expression of the TNF family receptor herpes
virus entry mediator and its ligand LIGHT on activated T cells:
LIGHT down-regulates its own receptor. J Immunol. 165:4397–4404.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Jung HW, La SJ, Kim JY, et al: High levels
of soluble herpes virus entry mediator in sera of patients with
allergic and autoimmune diseases. Exp Mol Med. 35:501–508. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Subudhi SK, Anders RA, et al: The
role of herpesvirus entry mediator as a negative regulator of T
cell-mediated responses. J Clin Invest. 115:711–717. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sedy JR, Gavrieli M, Potter KG, et al: B
and T lymphocyte attenuator regulates T cell activation through
interaction with herpesvirus entry mediator. Nat Immunol. 6:90–98.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cai G, Wang H, Qin Q, et al: Amelioration
of myocarditis by HVEM-overexpressing dendritic cells through
induction of IL-10-producing cells. Cardiovasc Res. 84:425–433.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang M, Tang H, Guo Z, et al: Splenic
stroma drives mature dendritic cells to differentiate into
regulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol. 5:1124–1133. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, et al:
PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-1 and inhibits T cell activation.
Nat Immunol. 2:261–268. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Freeman GJ, Long AJ, Iwai Y, et al:
Engagement of the PD-1 immunoinhibitory receptor by a novel B7
family member leads to negative regulation of lymphocyte
activation. J Exp Med. 192:1027–1034. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kaliński P, Hilkens CM, Wierenga EA and
Kapsenberg ML: T-cell priming by type-1 and type-2 polarized
dendritic cells: the concept of a third signal. Immunology Today.
20:561–567. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lutz MB and Schuler G: Immature,
semi-mature and fully mature dendritic cells: which signals induce
tolerance or immunity? Trends Immunol. 23:445–449. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Anderson AE, Swan DJ, Sayers BL, et al:
LPS activation is required for migratory activity and antigen
presentation by tolerogenic dendritic cells. J Leukoc Biol.
85:243–250. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Alroy I, Towers TL and Freedman LP:
Transcriptional repression of the interleukin-2 gene by vitamin D3:
direct inhibition of NFATp/AP-1 complex formation by a nuclear
hormone receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 15:5789–5799. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wölfle SJ, Strebovsky J, Bartz H, et al:
PD-L1 expression on tolerogenic APCs is controlled by STAT-3. Eur J
Immunol. 41:413–424. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Unger WW, Laban S, Kleijwegt FS, van der
Slik AR and Roep BO: Induction of Treg by monocyte-derived DC
modulated by vitamin D3 or dexamethasone: differential role for
PD-L1. Eur J Immunol. 39:3147–3159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kuipers H, Muskens F, Willart M, et al:
Contribution of the PD-1 ligands/PD-1 signaling pathway to
dendritic cell-mediated CD4+ T cell activation. Eur J
Immunol. 36:2472–2482. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sadeghi K, Wessner B, Laggner U, et al:
Vitamin D3 down-regulates monocyte TLR expression and triggers
hyporesponsiveness to pathogen-associated molecular patterns. Eur J
Immunol. 36:361–370. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hewison M, Freeman L, Hughes SV, et al:
Differential regulation of vitamin D receptor and its ligand in
human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. J Immunol. 170:5382–5390.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dong X, Craig T, Xing N, et al: Direct
transcriptional regulation of RelB by 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3
and its analogs: physiologic and therapeutic implications for
dendritic cell function. J Biol Chem. 278:49378–49385. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Griffin MD, Lutz W, Phan VA, Bachman LA,
McKean DJ and Kumar R: Dendritic cell modulation by 1alpha,25
dihydroxyvitamin D3 and its analogs: a vitamin D receptor-dependent
pathway that promotes a persistent state of immaturity in vitro and
in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:6800–6805. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Szeles L, Keresztes G, Töröcsik D, et al:
1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 is an autonomous regulator of the
transcriptional changes leading to a tolerogenic dendritic cell
phenotype. J Immunol. 182:2074–2083. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|