|
1
|
Rosamond W, Flegal K, Furie K, et al;
American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke
Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2008
update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics
Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation.
117:e25–e146. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
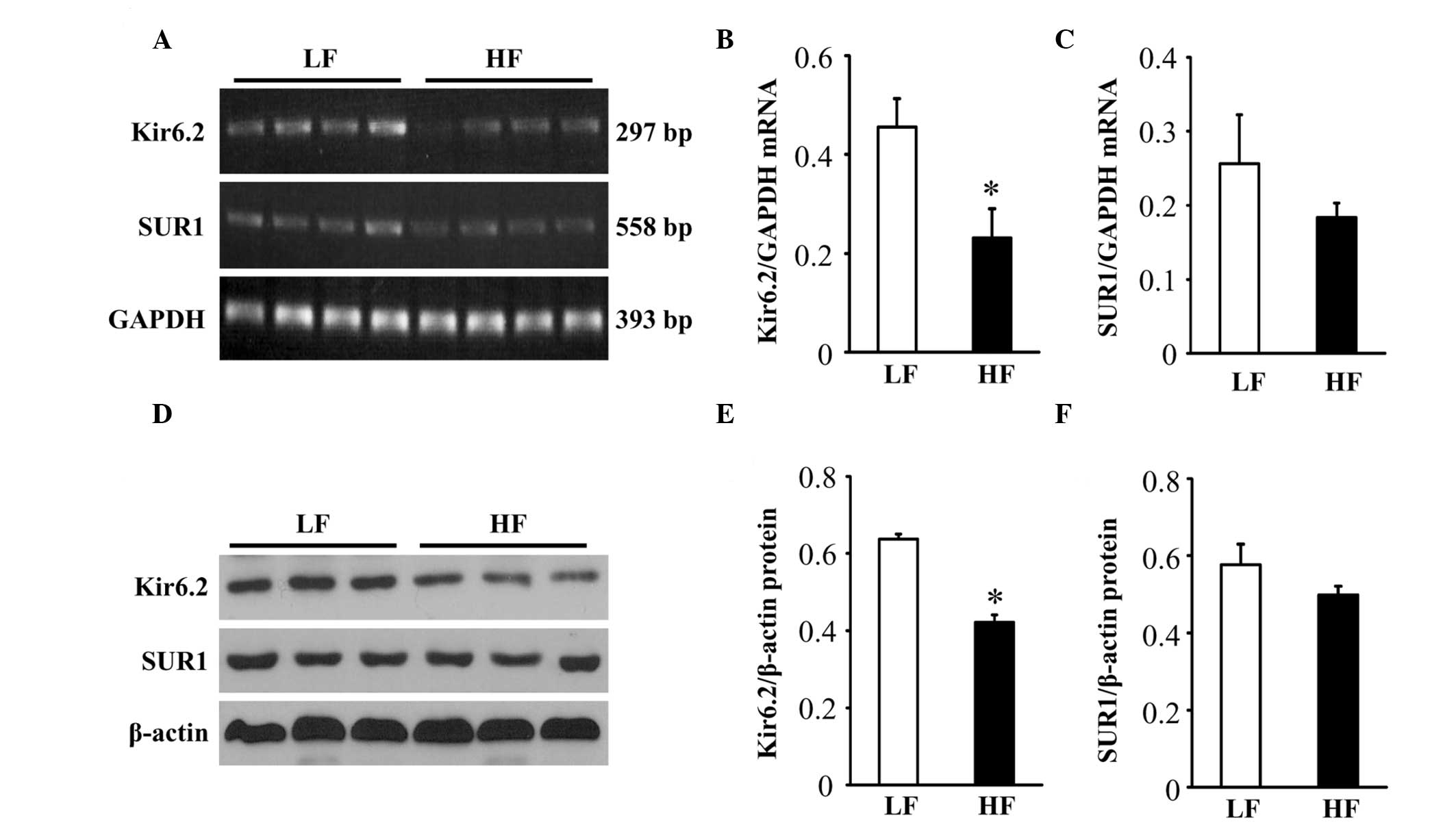
2
|
Katsiki N, Ntaios G and Vemmos K: Stroke,
obesity and gender: a review of the literature. Maturitas.
69:239–243. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Langdon KD, Clarke J and Corbett D:
Long-term exposure to high fat diet is bad for your brain:
exacerbation of focal ischemic brain injury. Neuroscience.
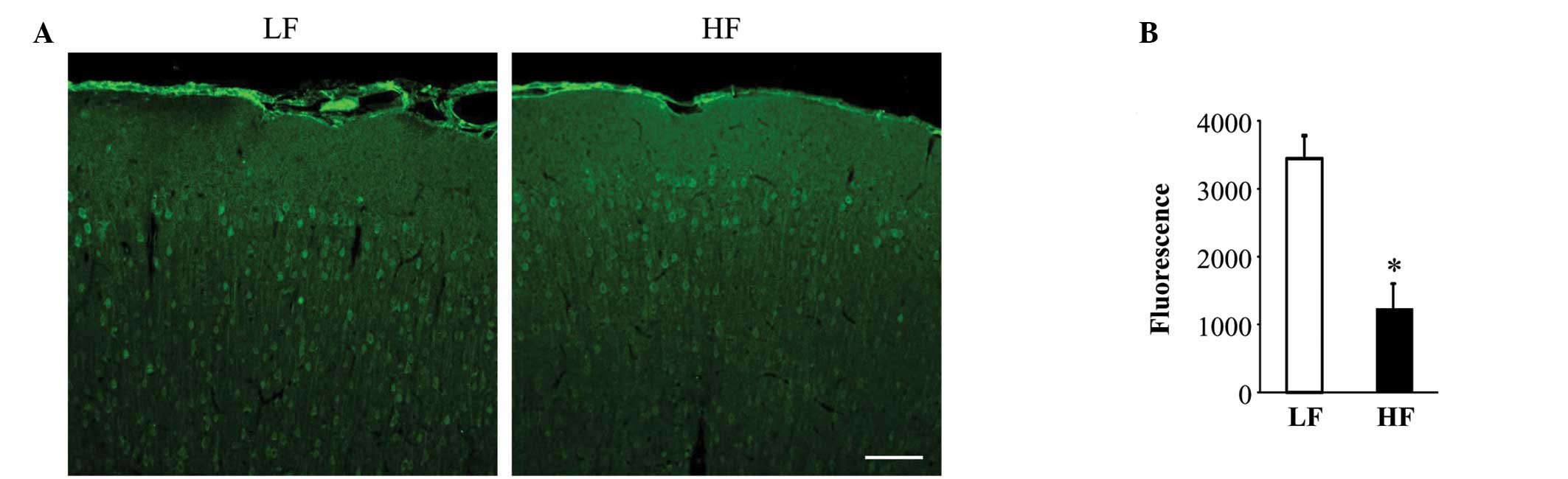
182:82–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Adamczyk S, Robin E, Simerabet M, et al:
Sevoflurane pre- and post-conditioning protect the brain via the
mitochondrial K ATP channel. Br J Anaesth. 104:191–200. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Codaccioni JL, Velly LJ, Moubarik C,
Bruder NJ, Pisano PS and Guillet BA: Sevoflurane preconditioning
against focal cerebral ischemia: inhibition of apoptosis in the
face of transient improvement of neurological outcome.
Anesthesiology. 110:1271–1278. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Canas PT, Velly LJ, Labrande CN, et al:
Sevoflurane protects rat mixed cerebrocortical neuronal-glial cell
cultures against transient oxygen-glucose deprivation: involvement
of glutamate uptake and reactive oxygen species. Anesthesiology.
105:990–998. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bouhidel O, Pons S, Souktani R, Zini R,
Berdeaux A and Ghaleh B: Myocardial ischemic postconditioning
against ischemia-reperfusion is impaired in ob/ob mice. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1580–H1586. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Song T, Lv LY, Xu J, et al: Diet-induced
obesity suppresses sevoflurane preconditioning against myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury: role of AMP-activated protein kinase
pathway. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 236:1427–1436. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Robin E, Simerabet M, Hassoun SM, et al:
Postconditioning in focal cerebral ischemia: role of the
mitochondrial ATP-dependent potassium channel. Brain Res.
1375:137–146. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee JJ, Li L, Jung HH and Zuo Z:
Postconditioning with isoflurane reduced ischemia-induced brain
injury in rats. Anesthesiology. 108:1055–1062. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gyte A, Pritchard LE, Jones HB, Brennand
JC and White A: Reduced expression of the KATP channel subunit,
Kir6.2, is associated with decreased expression of neuropeptide Y
and agouti-related protein in the hypothalami of Zucker diabetic
fatty rats. J Neuroendocrinol. 19:941–951. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fan LH, Tian HY, Yang ML, et al: High-fat
diet may impair K(ATP) channels in vascular smooth muscle cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 63:165–170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hodnett BL, Xiang L, Dearman JA, Carter CB
and Hester RL: K(ATP)-mediated vasodilation is impaired in obese
Zucker rats. Microcirculation. 15:485–494. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Madsen AN, Hansen G, Paulsen SJ, et al:
Long-term characterization of the diet-induced obese and
diet-resistant rat model: a polygenetic rat model mimicking the
human obesity syndrome. J Endocrinol. 206:287–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
World Medical Association and American
Physiological Society. Guiding principles for research involving
animals and human beings. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
283:R281–R283
|
|
16
|
Li L and Zuo Z: Isoflurane preconditioning
improves short-term and long-term neurological outcome after focal
brain ischemia in adult rats. Neuroscience. 164:497–506. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Patzer A, Zhao Y, Stöck I, Gohlke P,
Herdegen T and Culman J: Peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptors gamma (PPARgamma) differently modulate the interleukin-6
expression in the peri-infarct cortical tissue in the acute and
delayed phases of cerebral ischaemia. Eur J Neurosci. 28:1786–1794.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Katakam PV, Jordan JE, Snipes JA, Tulbert
CD, Miller AW and Busija DW: Myocardial preconditioning against
ischemia-reperfusion injury is abolished in Zucker obese rats with
insulin resistance. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol.
292:R920–R926. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Odermatt A: The Western-style diet: a
major risk factor for impaired kidney function and chronic kidney
disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 301:F919–F931. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng S and Zuo Z: Isoflurane
preconditioning induces neuroprotection against ischemia via
activation of P38 mitogen-activated protein kinases. Mol Pharmacol.
65:1172–1180. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Costa AD, Quinlan CL, Andrukhiv A, West
IC, Jabůrek M and Garlid KD: The direct physiological effects of
mitoK(ATP) opening on heart mitochondria. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 290:H406–H415. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou M, He HJ, Hirano M, et al:
Localization of ATP-sensitive K+ channel subunits in rat
submandibular gland. J Histochem Cytochem. 58:499–507. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sun HS, Feng ZP, Barber PA, Buchan AM and
French RJ: Kir6.2-containing ATP-sensitive potassium channels
protect cortical neurons from ischemic/anoxic injury in vitro and
in vivo. Neuroscience. 144:1509–1515. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ploug KB, Baun M, Hay-Schmidt A, Olesen J
and Jansen-Olesen I: Presence and vascular pharmacology of KATP
channel subtypes in rat central and peripheral tissues. Eur J
Pharmacol. 637:109–117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|