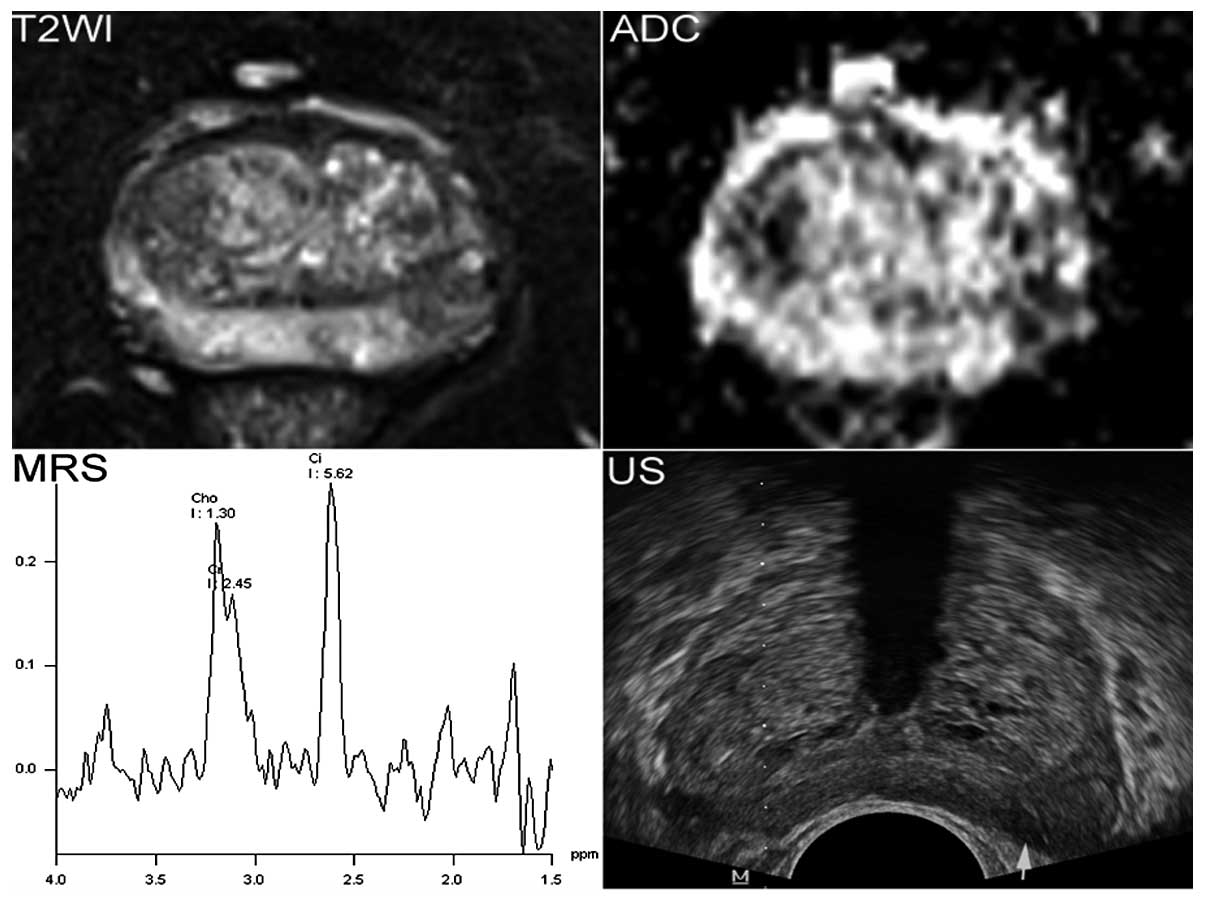
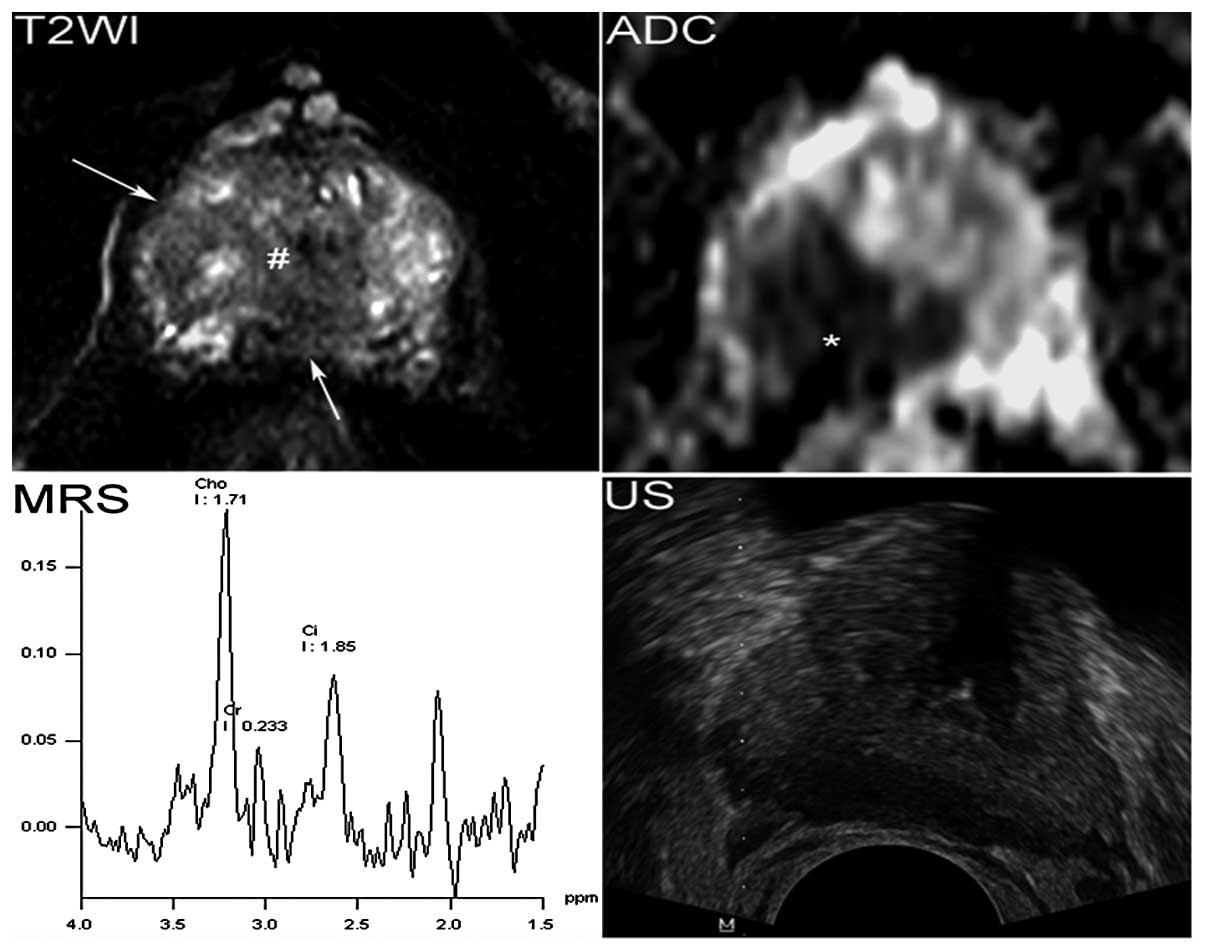
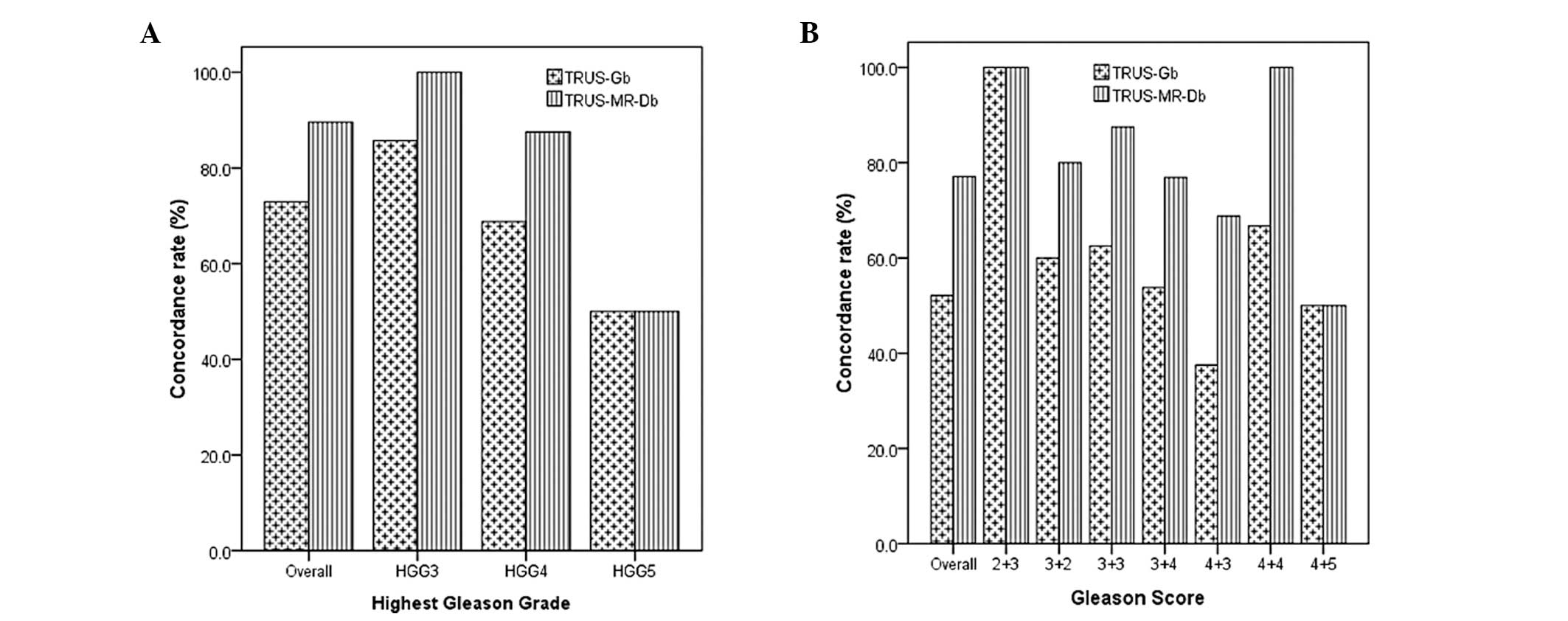
|
1
|
Gleason DF and Mellinger GT: Prediction of
prognosis for prostatic adenocarcinoma by combined histological
grading and clinical staging. J Urol. 111:58–64. 1974.
|
|
2
|
Egevad L, Granfors T, Karlberg L, Bergh A
and Stattin P: Prognostic value of the Gleason score in prostate
cancer. BJU Int. 89:538–542. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang CW, Lin TP, Huang YH, et al: Does
extended prostate needle biopsy improve the concordance of Gleason
scores between biopsy and prostatectomy in the Taiwanese
population? J Chin Med Assoc. 75:97–101. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Divrik RT, Eroglu A, Sahin A, Zorlu F and
Ozen H: Increasing the number of biopsies increases the concordance
of Gleason scores of needle biopsies and prostatectomy specimens.
Urol Oncol. 25:376–382. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Delongchamps NB, Rouanne M, Flam T, et al:
Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the detection and
localization of prostate cancer: combination of T2-weighted,
dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted imaging. BJU Int.
107:1411–1418. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mazaheri Y, Shukla-Dave A, Hricak H, et
al: Prostate cancer: identification with combined
diffusion-weighted MR imaging and 3D 1H MR spectroscopic
imaging - correlation with pathologic findings. Radiology.
246:480–488. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park BK, Park JW, Park SY, et al:
Prospective evaluation of 3-T MRI performed before initial
transrectal ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy in patients with high
prostate-specific antigen and no previous biopsy. AJR Am J
Roentgenol. 197:W876–W881. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Haffner J, Lemaitre L, Puech P, et al:
Role of magnetic resonance imaging before initial biopsy:
comparison of magnetic resonance imaging-targeted and systematic
biopsy for significant prostate cancer detection. BJU Int.
108:E171–E178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pinto PA, Chung PH, Rastinehad AR, et al:
Magnetic resonance imaging/ultrasound fusion guided prostate biopsy
improves cancer detection following transrectal ultrasound biopsy
and correlates with multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging. J
Urol. 186:1281–1285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vourganti S, Rastinehad A, Yerram NK, et
al: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and ultrasound
fusion biopsy detect prostate cancer in patients with prior
negative transrectal ultrasound biopsies. J Urol. 188:2152–2157.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kobus T, Vos PC, Hambrock T, et al:
Prostate cancer aggressiveness: in vivo assessment of MR
spectroscopy and diffusion-weighted imaging at 3 T. Radiology.
265:457–467. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hambrock T, Somford DM, Huisman HJ, et al:
Relationship between apparent diffusion coefficients at 3.0-T MR
imaging and Gleason grade in peripheral zone prostate cancer.
Radiology. 259:453–461. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kobus T, Hambrock T, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa
CA, et al: In vivo assessment of prostate cancer aggressiveness
using magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging at 3 T with an
endorectal coil. Eur Urol. 60:1074–1080. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Scheenen TW, Heijmink SW, Roell SA, et al:
Three-dimensional proton MR spectroscopy of human prostate at 3 T
without endorectal coil: feasibility. Radiology. 245:507–516. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang XZ, Wang B, Gao ZQ, et al:
Diffusion-weighted imaging of prostate cancer: correlation between
apparent diffusion coefficient values and tumor proliferation. J
Magn Reson Imaging. 29:1360–1366. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang XZ, Wang B, Gao ZQ, et al:
1H-MRSI of prostate cancer: the relationship between
metabolite ratio and tumor proliferation. Eur J Radiol. 73:345–351.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Stackhouse DA, Sun L, Schroeck FR, et al:
Factors predicting prostatic biopsy Gleason sum under grading. J
Urol. 182:118–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zakian KL, Sircar K, Hricak H, et al:
Correlation of proton MR spectroscopic imaging with gleason score
based on step-section pathologic analysis after radical
prostatectomy. Radiology. 234:804–814. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Delongchamps NB, Peyromaure M, Schull A,
et al: Prebiopsy magnetic resonance imaging and prostate cancer
detection: comparison of random and targeted biopsies. J Urol.
189:493–499. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moore CM, Robertson NL, Arsanious N, et
al: Image-guided prostate biopsy using magnetic resonance
imaging-derived targets: a systematic review. Eur Urol. 63:125–140.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Verma S, Rajesh A, Morales H, et al:
Assessment of aggressiveness of prostate cancer: correlation of
apparent diffusion coefficient with histologic grade after radical
prostatectomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 196:374–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
San Francisco IF, DeWolf WC, Rosen S,
Upton M and Olumi AF: Extended prostate needle biopsy improves
concordance of Gleason grading between prostate needle biopsy and
radical prostatectomy. J Urol. 169:136–140. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Park BK, Lee HM, Kim CK, Choi HY and Park
JW: Lesion localization in patients with a previous negative
transrectal ultrasound biopsy and persistently elevated prostate
specific antigen level using diffusion-weighted imaging at three
Tesla before rebiopsy. Invest Radiol. 43:789–793. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Prando A, Kurhanewicz J, Borges AP,
Oliveira EM Jr and Figueiredo E: Prostatic biopsy directed with
endorectal MR spectroscopic imaging findings in patients with
elevated prostate specific antigen levels and prior negative biopsy
findings: early experience. Radiology. 236:903–910. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tamada T, Sone T, Jo Y, et al: Apparent
diffusion coefficient values in peripheral and transition zones of
the prostate: comparison between normal and malignant prostatic
tissues and correlation with histologic grade. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 28:720–726. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hambrock T, Hoeks C, Hulsbergen-van de Kaa
C, et al: Prospective assessment of prostate cancer aggressiveness
using 3-T diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging-guided
biopsies versus a systematic 10-core transrectal ultrasound
prostate biopsy cohort. Eur Urol. 61:177–184. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Na R, Jiang H, Kim ST, et al: Outcomes and
treands of prostate biopsy for prostate cancer in Chinese men from
2003 to 2011. PLoS One. 7:e499142012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miyagawa T, Ishikawa S, Kimura T, et al:
Real-time Virtual Sonography for navigation during targeted
prostate biopsy using magnetic resonance imaging data. Int J Urol.
17:855–860. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rastinehad AR, Baccala AA Jr, Chung PH, et
al: D’Amico risk stratification correlates with degree of suspicion
of prostate cancer on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging. J
Urol. 185:815–820. 2011.
|