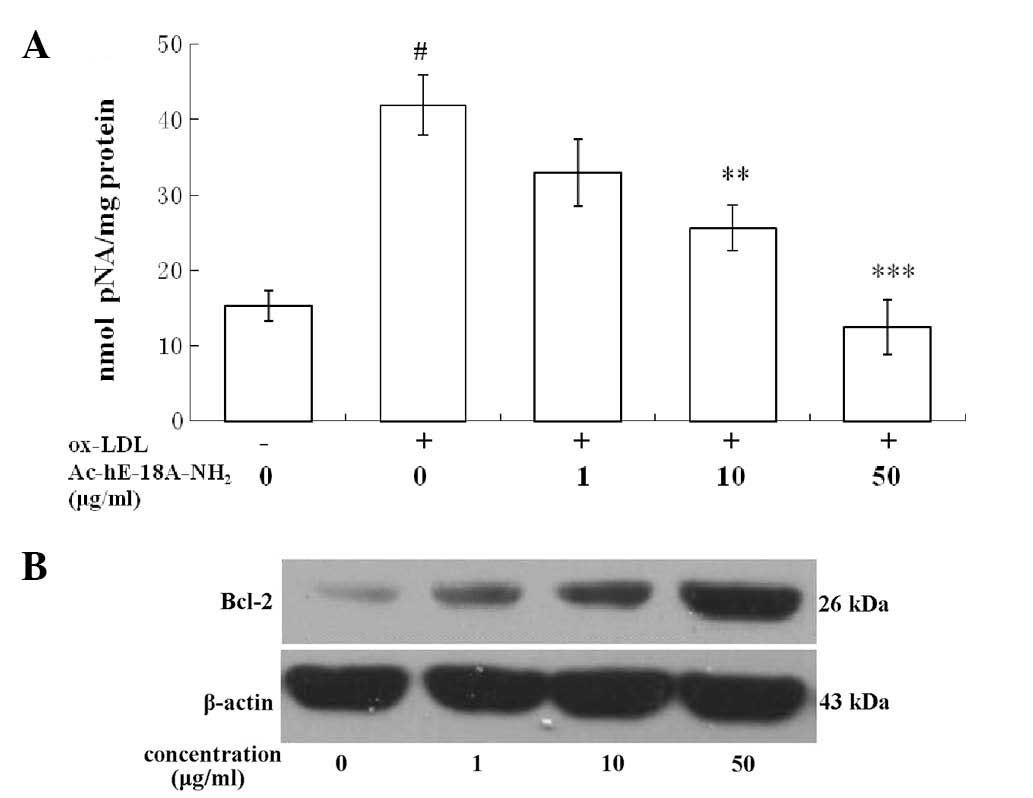
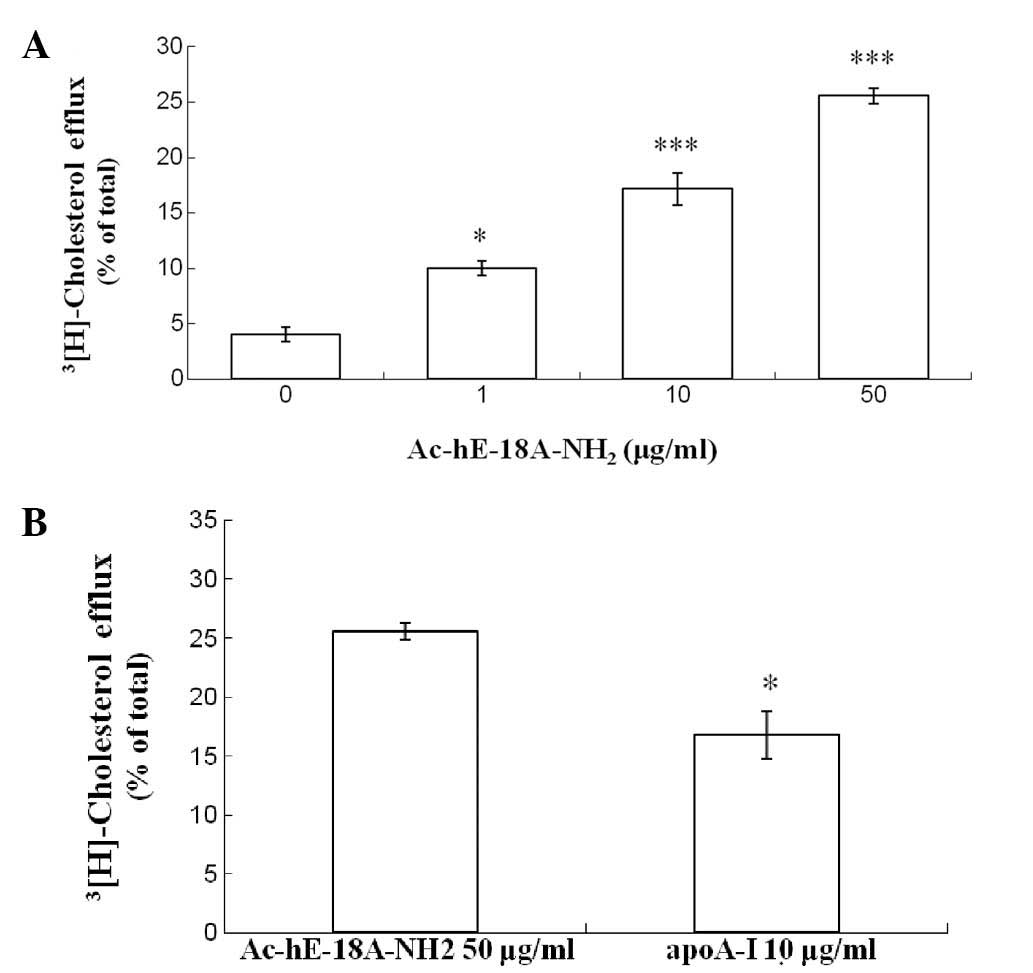
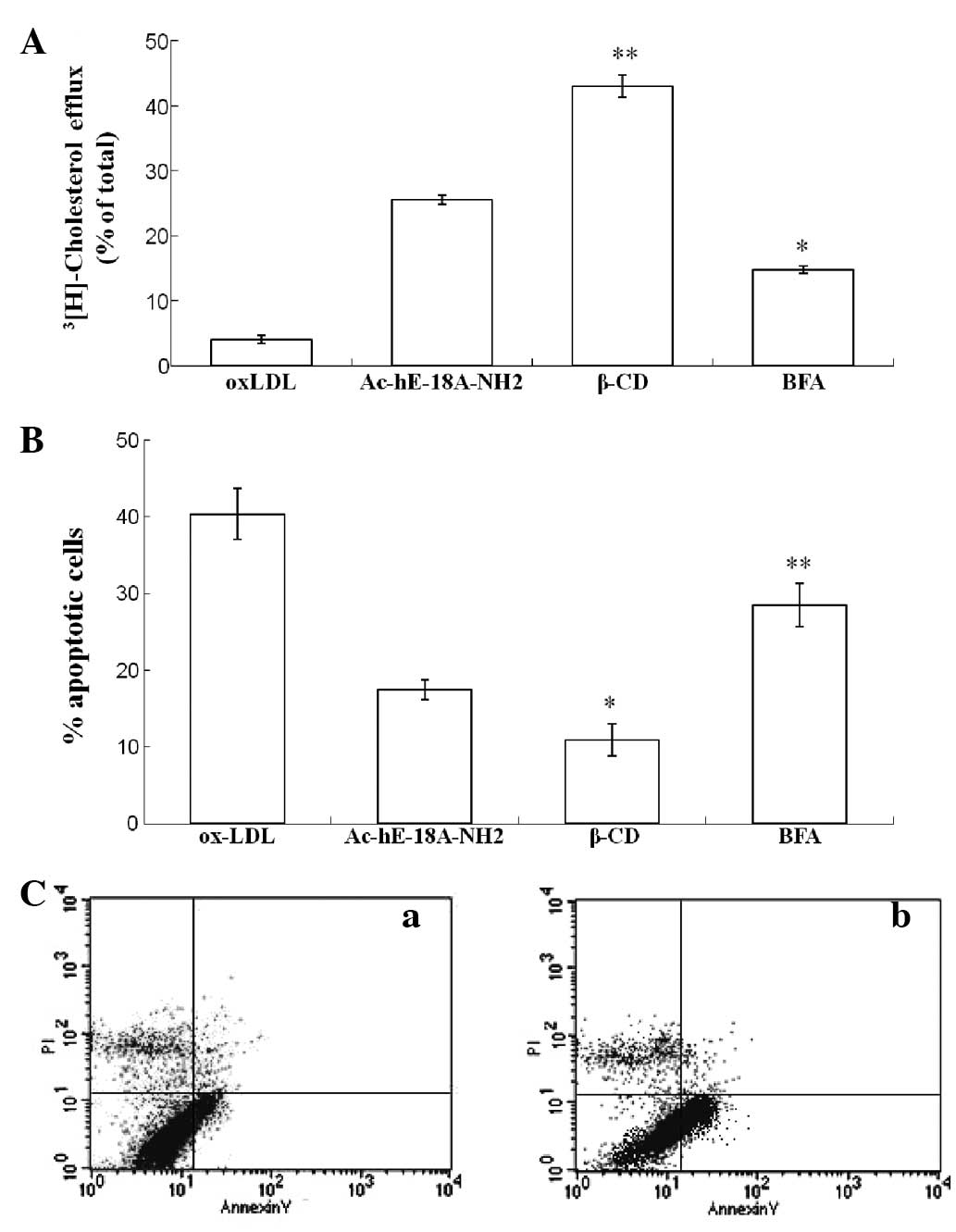
|
1
|
Seimon T and Tabas I: Mechanisms and
consequences of macrophage apoptosis in atherosclerosis. J Lipid
Res. 50(Suppl): S382–S387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tabas I: Consequences and therapeutic
implications of macrophage apoptosis in atherosclerosis: the
importance of lesion stage and phagocytic efficiency. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:2255–2264. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tabas I: Consequences of cellular
cholesterol accumulation: basic concepts and physiological
implications. J Clin Invest. 110:905–911. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kellner-Weibel G, Jerome WG, Small DM, et
al: Effects of intracellular free cholesterol accumulation on
macrophage viability: a model for foam cell death. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 18:423–431. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yao PM and Tabas I: Free cholesterol
loading of macrophages is associated with widespread mitochondrial
dysfunction and activation of the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway.
J Biol Chem. 276:42468–42476. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yao PM and Tabas I: Free cholesterol
loading of macrophages induces apoptosis involving the fas pathway.
J Biol Chem. 275:23807–23813. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Anantharamaiah GM: Synthetic peptide
analogs of apolipoproteins. Methods Enzymol. 128:627–647. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Datta G, Chaddha M, Garber DW, et al: The
receptor binding domain of apolipoprotein E, linked to a model
class A amphipathic helix, enhances internalization and degradation
of LDL in fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 39:213–220. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Datta G, Garber DW, Chung BH, et al:
Cationic domain 141–150 of apoE covalently linked to a class A
amphipathic helix enhances atherogenic lipoprotein metabolism in
vitro and in vivo. J Lipid Res. 42:959–966. 2001.
|
|
10
|
Garber DW, Handattu S, Aslan I, Datta G,
Chaddha M and Anantharamaiah GM: Effect of an arginine-rich
amphipathic helical peptide on plasma cholesterol in dyslipidemic
mice. Atherosclerosis. 168:229–237. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gupta H, White CR, Handattu S, et al:
Apolipoprotein E mimetic Peptide dramatically lowers plasma
cholesterol and restores endothelial function in watanabe heritable
hyperlipidemic rabbits. Circulation. 111:3112–3118. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sharifov OF, Nayyar G, Garber DW, et al:
Apolipoprotein E mimetics and cholesterol-lowering properties. Am J
Cardiovasc Drugs. 11:371–381. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Navab M, Hama SY, Anantharamaiah GM, et
al: Normal high density lipoprotein inhibits three steps in the
formation of mildly oxidized low density lipoprotein: steps 2 and
3. J Lipid Res. 41:1495–1508. 2000.
|
|
14
|
Datta G, Epand RF, Epand RM, et al:
Aromatic residue position on the nonpolar face of class A
amphipathic helical peptides determines biological activity. J Biol
Chem. 279:26509–26517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Marcil M, Bissonnette R, Vincent J,
Krimbou L and Genest J: Cellular phospholipid and cholesterol
efflux in high-density lipoprotein deficiency. Circulation.
107:1366–1371. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yancey PG, Rodrigueza WV, Kilsdonk EP,
Stoudt GW, Johnson WJ, Phillips MC and Rothblat GH: Cellular
cholesterol efflux mediated by cyclodextrins. Demonstration of
kinetic pools and mechanism of efflux. J Biol Chem.
271:16026–16234. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mendez AJ: Monensin and brefeldin A
inhibit high density lipoprotein-mediated cholesterol efflux from
cholesterol-enriched cells. J Biol Chem. 270:5891–5900.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hung YC, Hong MY and Huang GS: Cholesterol
loading augments oxidative stress in macrophages. FEBS Letters.
580:849–861. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li D and Mehta JL: Upregulation of
endothelial receptor for oxidized LDL (LOX-1) by oxidized LDL and
implications in apoptosis of human coronary artery endothelial
cells: evidence from use of antisense LOX-1 mRNA and chemical
inhibitors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 20:1116–1122. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kataoka H, Kume N, Miyamoto S, et al:
Oxidized LDL modulates Bax/Bcl-2 through the lectinlike Ox-LDL
receptor-1 in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 21:955–960. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hardwick SJ, Hegyi L, Clare K, et al:
Apoptosis in human monocyte-macrophages exposed to oxidized low
density lipoprotein. J Pathol. 179:294–302. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wintergerst ES, Jelk J, Rahner C and Asmis
R: Apoptosis induced by oxidized low density lipoprotein in human
monocyte-derived macrophages involves CD36 and activation of
caspase-3. Eur J Biochem. 267:6050–6059. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Napoli C, Quehenberger O, De Nigris F,
Abete P, Glass CK and Palinski W: Mildly oxidized low density
lipoprotein activates multiple apoptotic signaling pathways in
human coronary cells. FASEB J. 14:1996–2007. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yancey PG and Jerome WG: Lysosomal
sequestration of free and esterified cholesterol from oxidized low
density lipoprotein in macrophages of different species. J Lipid
Res. 39:1349–1361. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sanossian N, Saver JL, Navab M and
Ovbiagele B: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol: an emerging
target for stroke treatment. Stroke. 38:1104–1109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Terasaka N, Wang N, Yvan-Charvet L and
Tall AR: High-density lipoprotein protects macrophages from
oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis by promoting
efflux of 7-ketocholesterol via ABCG1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:15093–15098. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang P, Yan PK, Chen JX, et al: High
density lipoprotein 3 inhibits oxidized low density
lipoprotein-induced apoptosis via promoting cholesterol efflux in
RAW264.7 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 27:151–157. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Christian AE, Haynes MP, Phillips MC and
Rothblat GH: Use of cyclodextrins for manipulating cellular
cholesterol content. J Lipid Res. 38:2264–2272. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tsujikawa H, Song Y, Watanabe M, et al:
Cholesterol depletion modulates basal L-type Ca2+
current and abolishes its -adrenergic enhancement in ventricular
myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 294:H285–H292. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Verghese PB, Arrese EL, Howard AD and
Soulages JL: Brefeldin A inhibits cholesterol efflux without
affecting the rate of cellular uptake and re-secretion of
apolipoprotein A-I in adipocytes. Arch Biochem Biophys.
478:161–166. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|