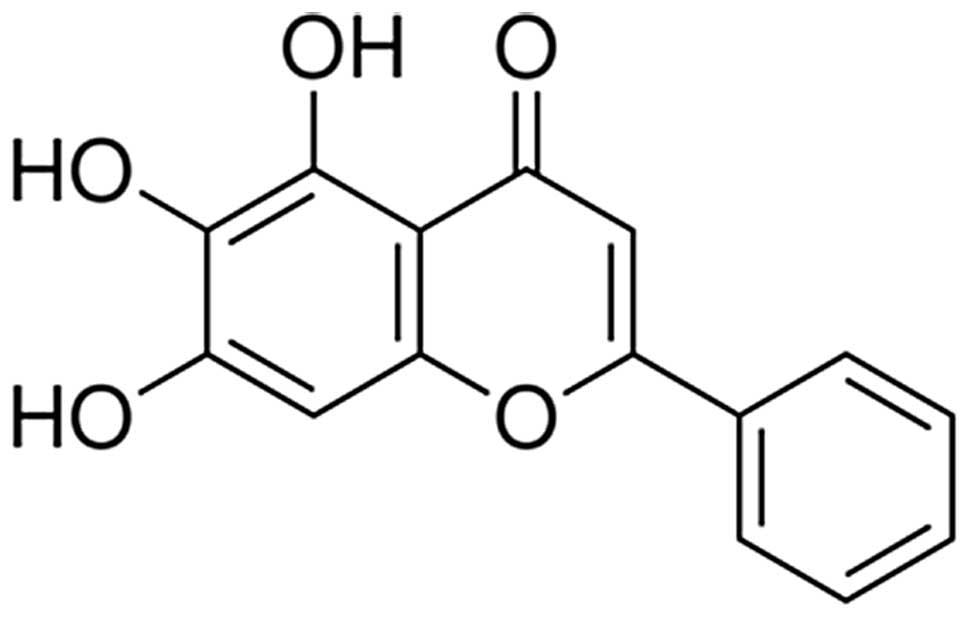
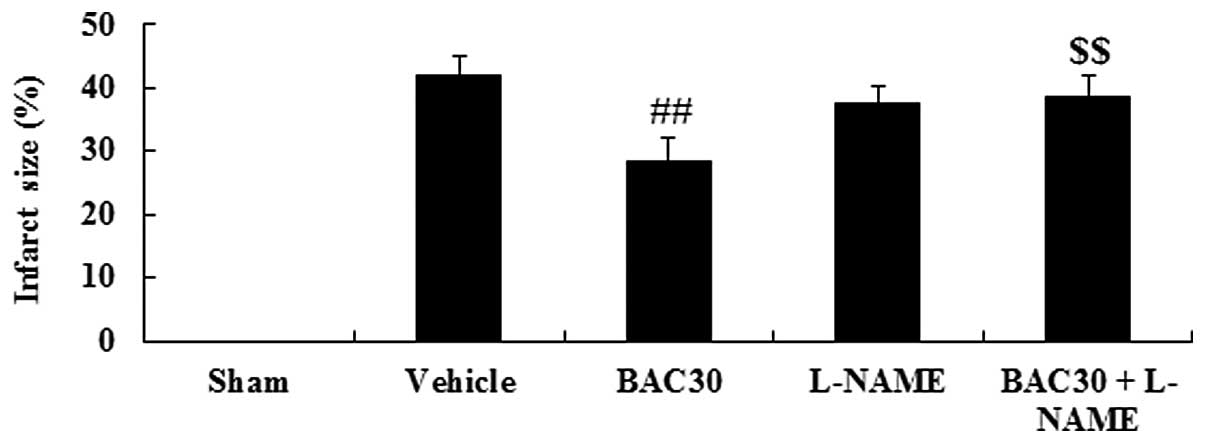
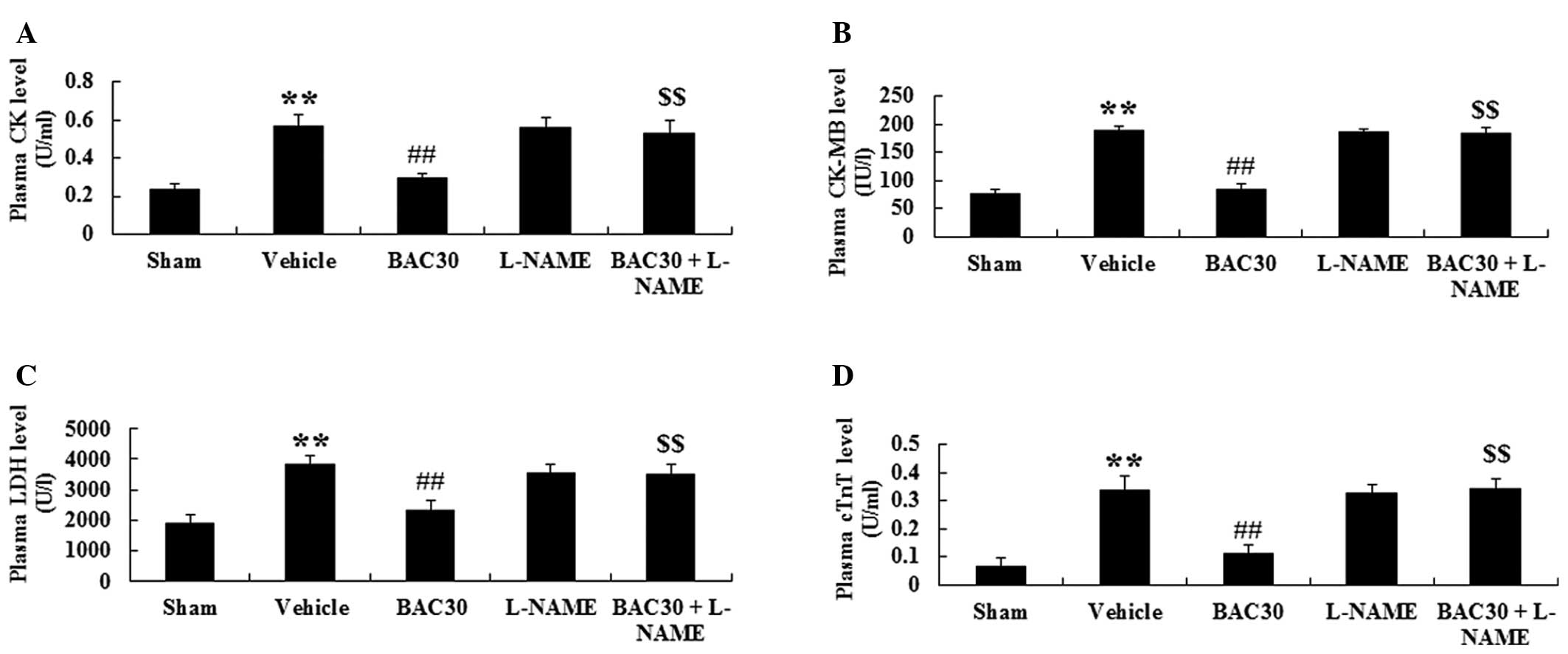
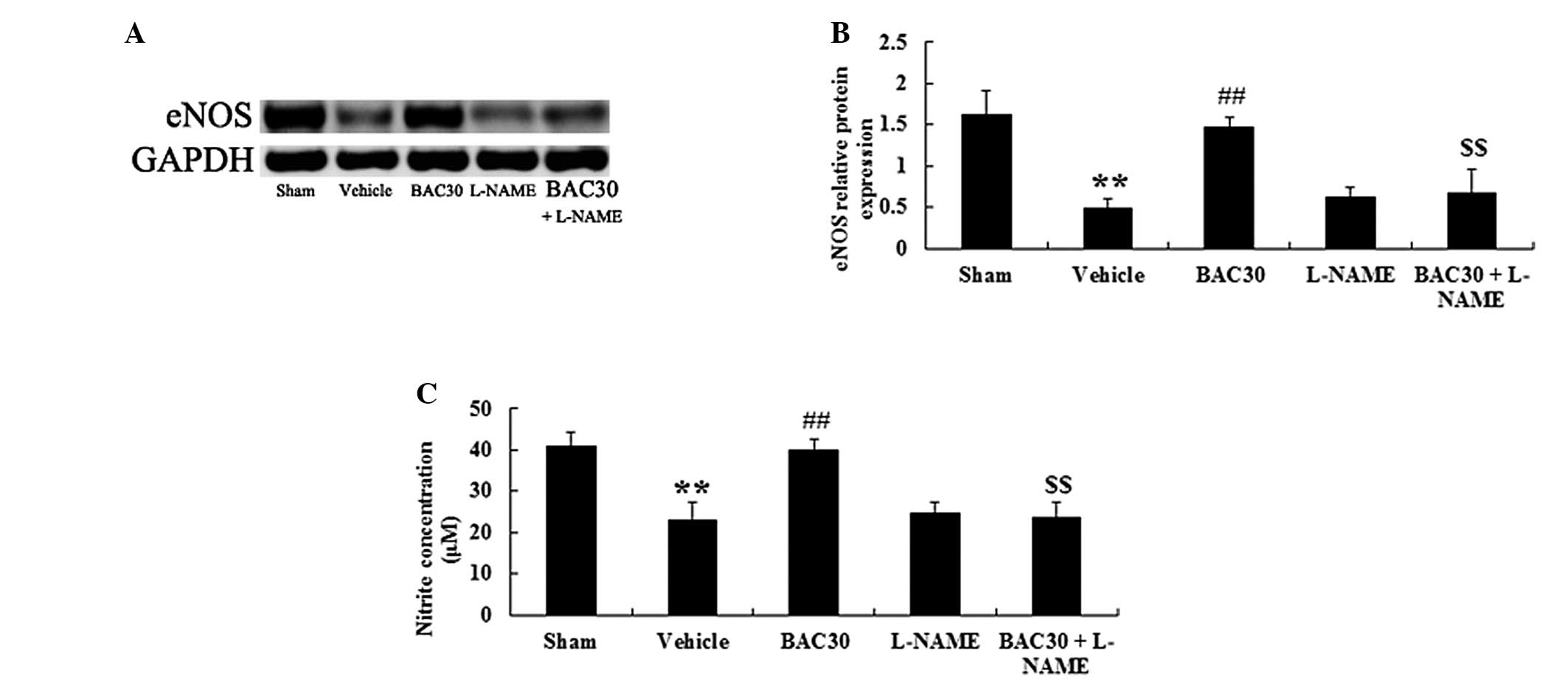
|
1
|
Bulhak AA, Sjöquist PO, Xu CB, Edvinsson L
and Pernow J: Protection against myocardial ischaemia/reperfusion
injury by PPAR-alpha activation is related to production of nitric
oxide and endothelin-1. Basic Res Cardiol. 101:244–252. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gourine AV, Bulhak AA, Gonon AT, Pernow J
and Sjöquist PO: Cardioprotective effect induced by brief exposure
to nitric oxide before myocardial ischemia-reperfusion in vivo.
Nitric Oxide. 7:210–216. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Andelová E, Barteková M, Pancza D, Styk J
and Ravingerová T: The role of NO in ischemia/reperfusion injury in
isolated rat heart. Gen Physiol Biophys. 24:411–426.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Balligand JL and Cannon PJ: Nitric oxide
synthases and cardiac muscle. Autocrine and paracrine influences.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 17:1846–1858. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jones SP, Greer JJ, van Haperen R, Duncker
DJ, de Crom R and Lefer DJ: Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
overexpression attenuates congestive heart failure in mice. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:4891–4896. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sumeray MS, Rees DD and Yellon DM: Infarct
size and nitric oxide synthase in murine myocardium. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 32:35–42. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jones SP, Girod WG, Palazzo AJ, et al:
Myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury is exacerbated in absence of
endothelial cell nitric oxide synthase. Am J Physiol.
276:H1567–H1573. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Carden DL and Granger DN: Pathophysiology
of ischaemia-reperfusion injury. J Pathol. 190:255–266. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Collard CD and Gelman S: Pathophysiology,
clinical manifestations, and prevention of ischemia-reperfusion
injury. Anesthesiology. 94:1133–1138. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Panda VS and Naik SR: Cardioprotective
activity of Ginkgo biloba Phytosomes in
isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis in rats: a biochemical
and histoarchitectural evaluation. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 60:397–404.
2008.
|
|
11
|
Priscilla DH and Prince PS:
Cardioprotective effect of gallic acid on cardiac troponin-T,
cardiac marker enzymes, lipid peroxidation products and
antioxidants in experimentally induced myocardial infarction in
Wistar rats. Chem Biol Interact. 179:118–124. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lin CC and Shieh DE: The anti-inflammatory
activity of Scutellaria rivularis extracts and its active
components, baicalin, baicalein and wogonin. Am J Chin Med.
24:31–36. 1996.
|
|
13
|
Gabrielska J, Oszmiański J, Zyłka R and
Komorowska M: Antioxidant activity of flavones from Scutellaria
baicalensis in lecithin liposomes. Z Naturforsch C. 52:817–823.
1997.
|
|
14
|
Shao ZH, Vanden Hoek TL, Qin Y, et al:
Baicalein attenuates oxidant stress in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 282:H999–H1006. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Woo AY, Cheng CH and Waye MM: Baicalein
protects rat cardiomyocytes from hypoxia/reoxygenation damage via a
prooxidant mechanism. Cardiovasc Res. 65:244–253. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu W, Liu Q and Zhu S: Carvacrol protects
against acute myocardial infarction of rats via anti-oxidative and
anti-apoptotic pathways. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:579–584. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kuo CP, Wen LL, Chen CM, et al:
Attenuation of neurological injury with early baicalein treatment
following subarachnoid hemorrhage in rats. J Neurosurg.
199:1028–1037. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maslov LN, Lishmanov YB, Oeltgen PR, et
al: Activation of peripheral delta2 opioid receptors increases
cardiac tolerance to ischemia/reperfusion injury: Involvement of
protein kinase C, NO-synthase, KATP channels and the autonomic
nervous system. Life Sci. 84:657–663. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Papazzo A, Conlan X, Lexis L and
Lewandowski P: The effect of short-term canola oil ingestion on
oxidative stress in the vasculature of stroke-prone spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Lipids Health Dis. 10:1802011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo J, Li HZ, Wang LC, et al: Increased
expression of calcium-sensing receptors in atherosclerosis confers
hypersensitivity to acute myocardial infarction in rats. Mol Cell
Biochem. 366:345–354. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ming X, Tongshen W, Delin W and Ronghua Z:
Cardioprotective effect of the compound yangshen granule in rat
models with acute myocardial infarction. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2012:7171232012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Katus HA, Remppis A, Scheffold T,
Diederich KW and Kuebler W: Intracellular compartmentation of
cardiac troponin T and its release kinetics in patients with
reperfused and nonreperfused myocardial infarction. Am J Cardiol.
67:1360–1367. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wolfrum S, Dendorfer A, Schutt M, et al:
Simvastatin acutely reduces myocardial reperfusion injury in vivo
by activating the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 44:348–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pipaliya H and Vaghasiya J: Cardio
protective effect of vitamin A against isoproterenol-induced
myocardial infarction. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo). 58:402–407.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chang WT, Li J, Vanden Hoek MS, et al:
Baicalein preconditioning protects cardiomyocytes from
ischemia-reperfusion injury via mitochondrial oxidant signaling. Am
J Chin Med. 41:315–331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|