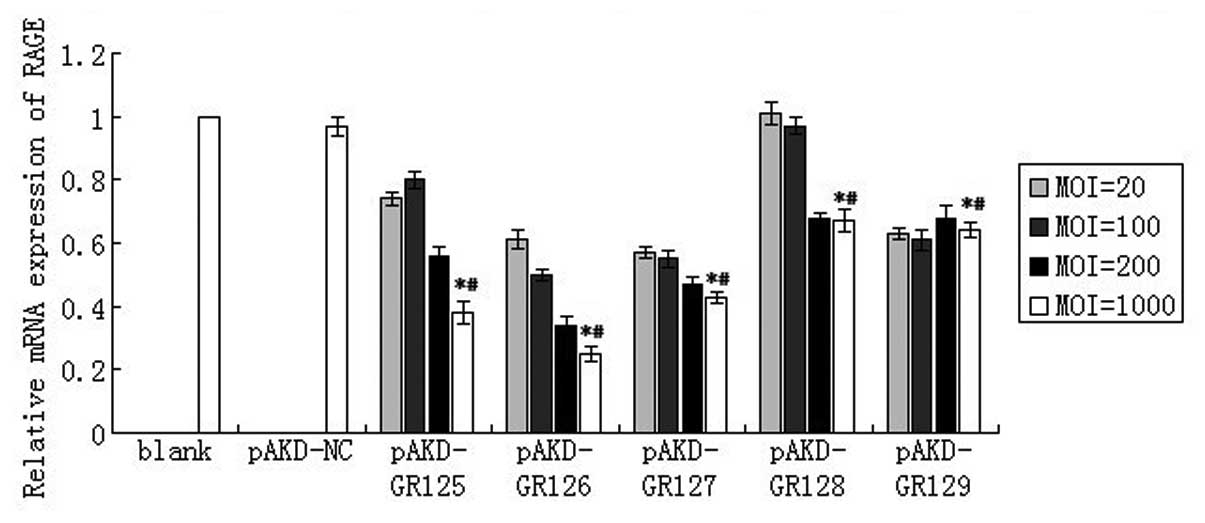
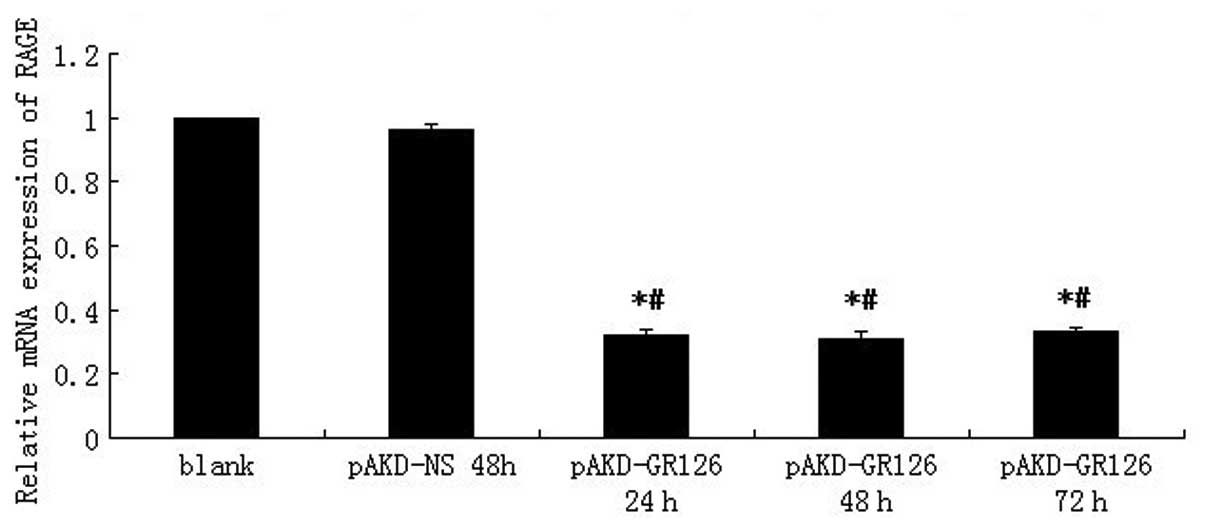
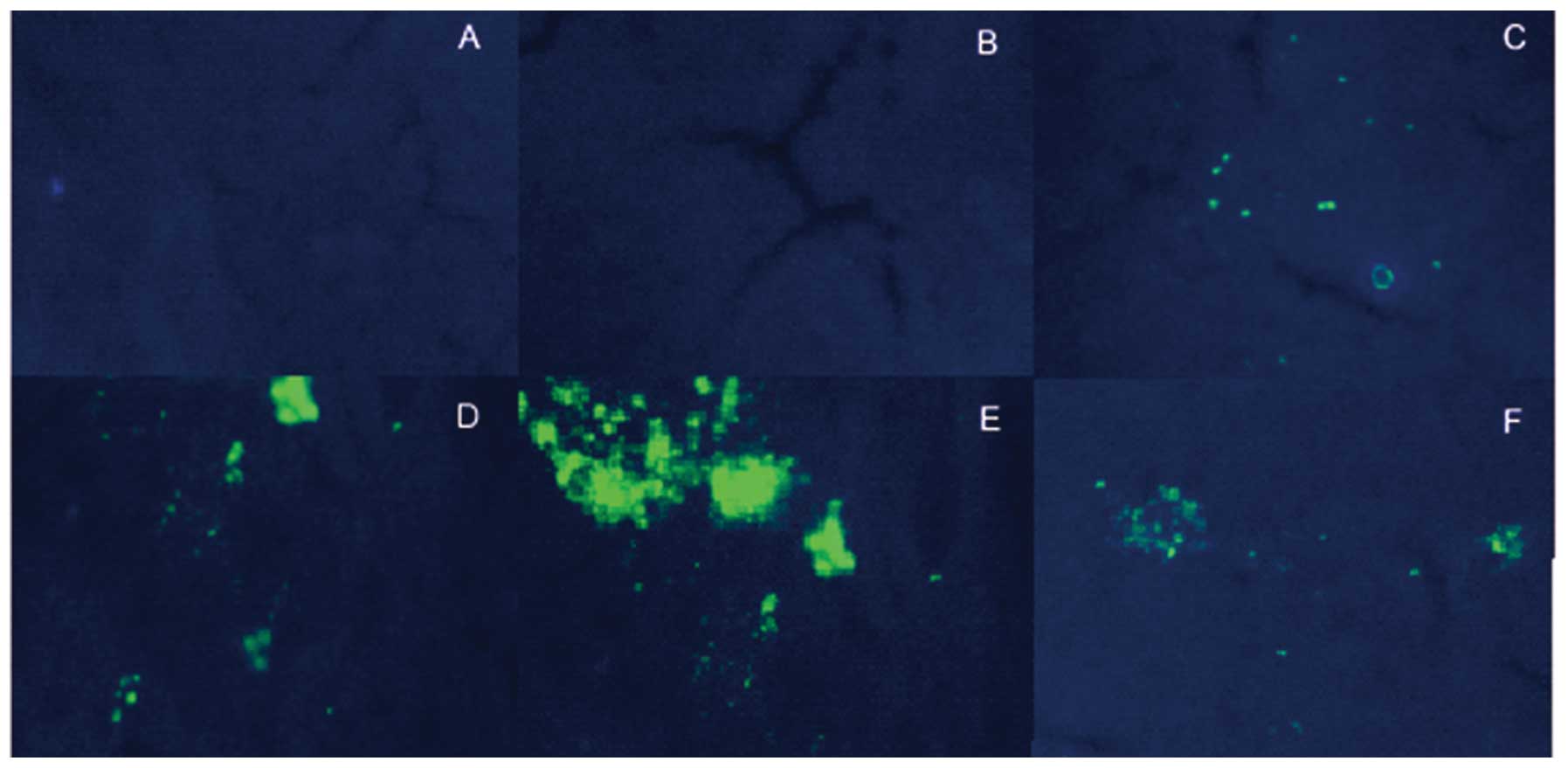
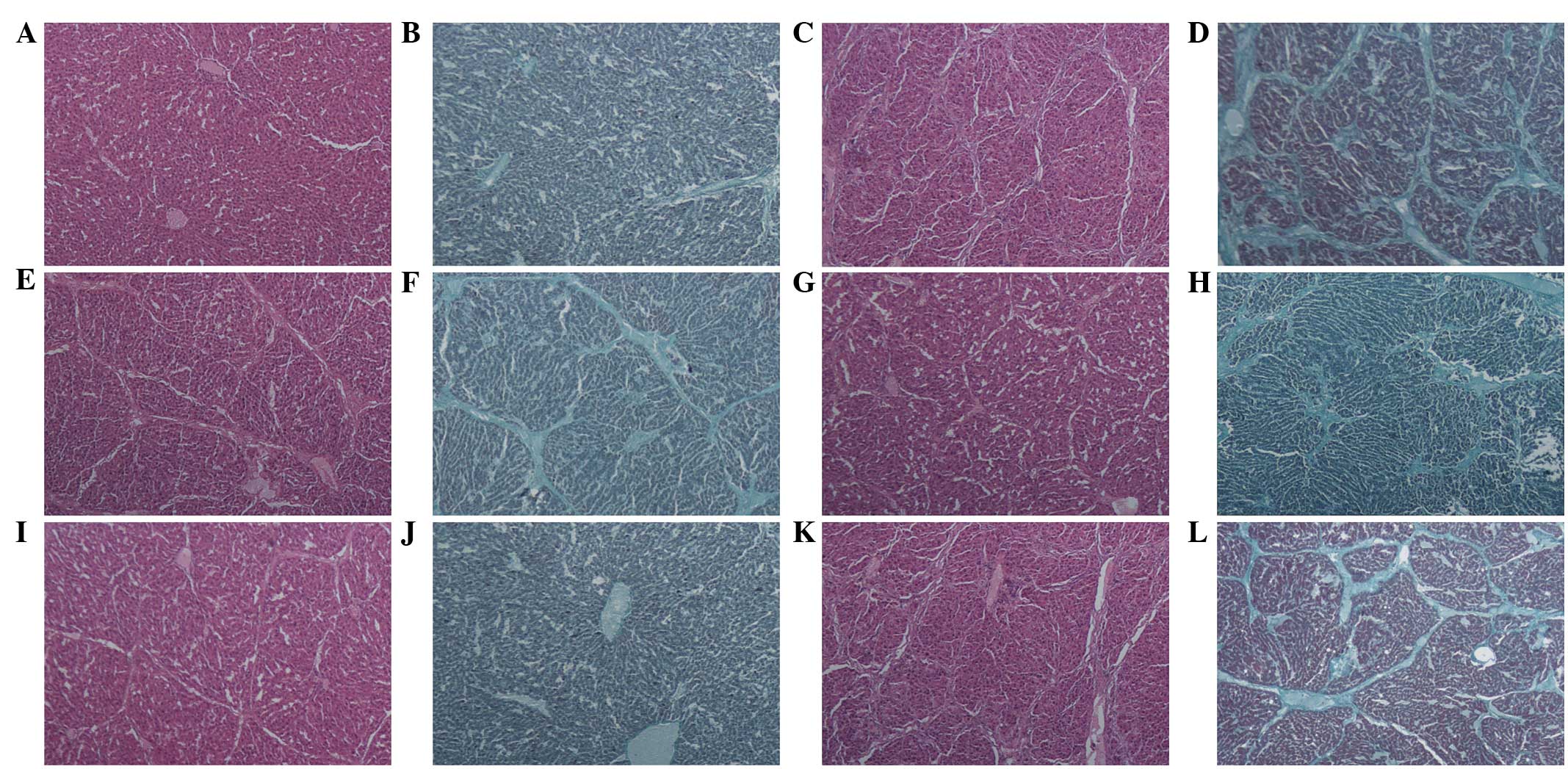
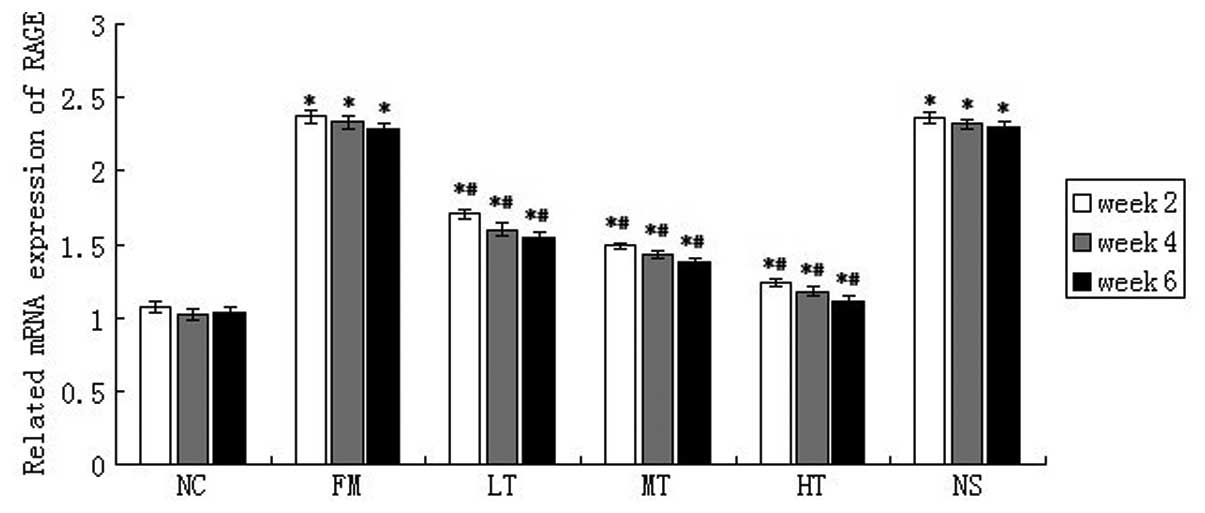
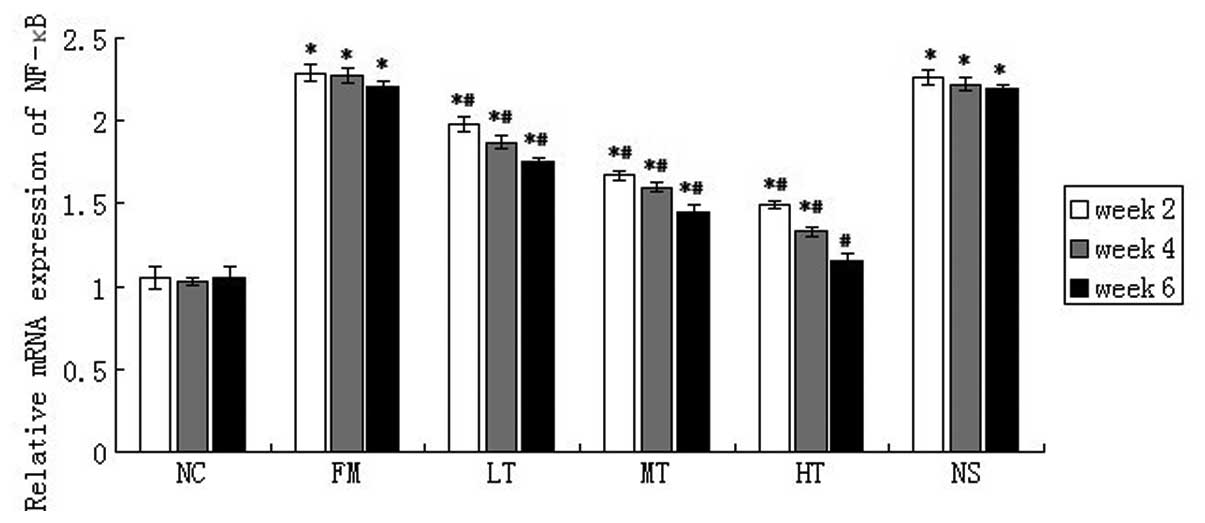
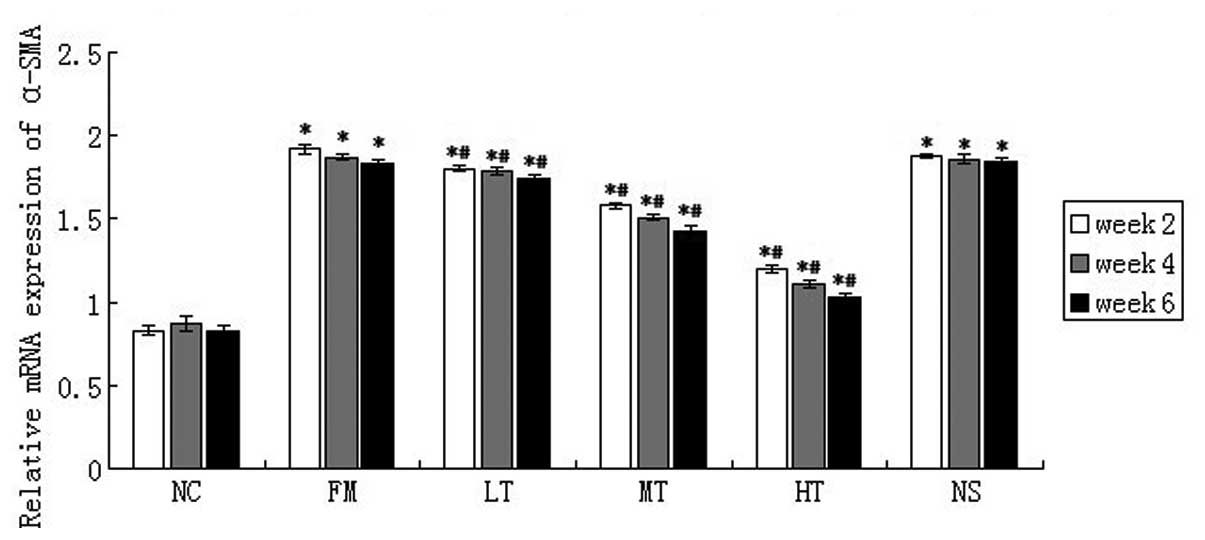
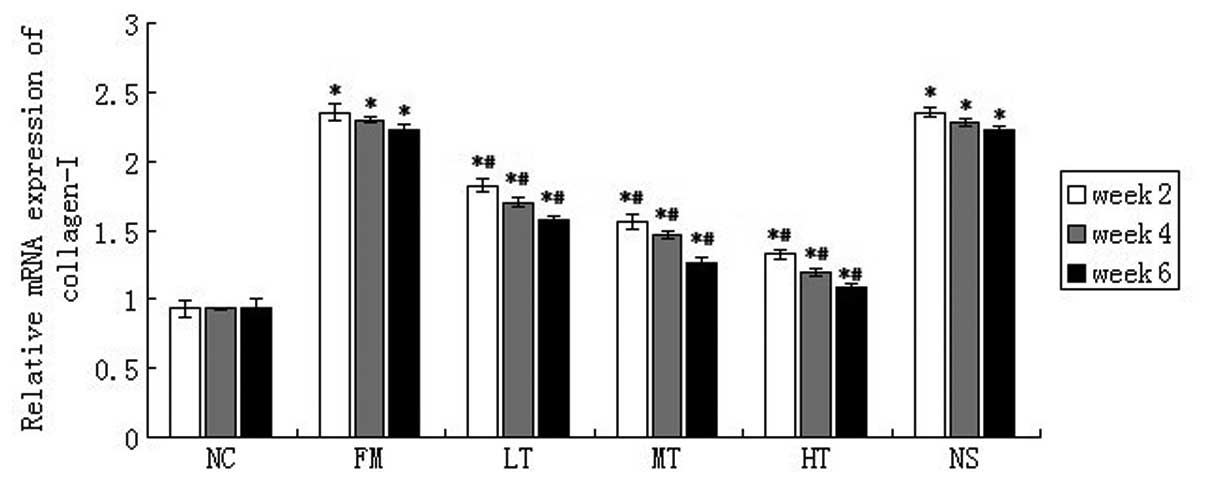
|
1
|
Anthony PP, Ishak KG, Nayak NC, Poulsen
HE, Scheuer PJ and Sobin LH: The morphology of cirrhosis.
Recommendations on definition, nomenclature, and classification by
a working group sponsored by the World Health Organization. J Clin
Pathol. 31:395–414. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friedman SL, Roll FJ, Boyles J and Bissell
DM: Hepatic lipocytes: the principal collagen-producing cells of
normal rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 82:8681–8685. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rippe RA: Life or death: the fate of the
hepatic stellate cell following hepatic injury. Hepatology.
27:1447–1448. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brandão DF, Ramalho LN, Ramalho FS,
Zucoloto S, de Martinelli AL and de Silva OC: Liver cirrhosis and
hepatic stellate cells. Acta Cir Bras. 21(Suppl 1): 54–57.
2006.
|
|
5
|
Lee UE and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic fibrogenesis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
25:195–206. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Neeper M, Schmidt AM, Brett J, et al:
Cloning and expression of a cell surface receptor for advanced
glycosylation end products of proteins. J Biol Chem.
267:14998–15004. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sparvero LJ, Asafu-Adjei D, Kang R, et al:
RAGE (Receptor for Advanced Glycation Endproducts), RAGE ligands,
and their role in cancer and inflammation. J Transl Med. 7:172009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Schmidt AM, Yan SD, Yan SF and Stern DM:
The biology of the receptor for advanced glycation end products and
its ligands. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1498:99–111. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wautier MP, Chappey O, Corda S, Stern DM,
Schmidt AM and Wautier JL: Activation of NADPH oxidase by AGE links
oxidant stress to altered gene expression via RAGE. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 280:E685–E694. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mohamed AK, Bierhaus A, Schiekofer S,
Tritschler H, Ziegler R and Nawroth PP: The role of oxidative
stress and NF-kappaB activation in late diabetic complications.
Biofactors. 10:157–167. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fehrenbach H, Weiskirchen R, Kasper M and
Gressner AM: Up-regulated expression of the receptor for advanced
glycation end products in cultured rat hepatic stellate cells
during transdifferentiation to myofibroblasts. Hepatology.
34:943–952. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brett J, Schmidt AM, Yan SD, et al: Survey
of the distribution of a newly characterized receptor for advanced
glycation end products in tissues. Am J Pathol. 143:1699–1712.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lohwasser C, Neureiter D, Popov Y, Bauer M
and Schuppan D: Role of the receptor for advanced glycation end
products in hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol. 15:5789–5798.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guimarães EL, Empsen C, Geerts A and van
Grunsven LA: Advanced glycation end products induce production of
reactive oxygen species via the activation of NADPH oxidase in
murine hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol. 52:389–397.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xia JR, Liu NF and Zhu NX: Specific siRNA
targeting the receptor for advanced glycation end products inhibits
experimental hepatic fibrosis in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 9:638–661.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Barouch DH, Liu J, Li H, et al: Vaccine
protection against acquisition of neutralization-resistant SIV
challenges in rhesus monkeys. Nature. 482:89–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Desmet VJ, Knodell RG, Ishak KG, Black WC,
Chen TS, Craig R, Kaplowitz N, Kiernan TW and Wollman J:
Formulation and application of a numerical scoring system for
assessing histological activity in asymptomatic chronic active
hepatitis. [Hepatology 1981;1:431–435]. J Hepatol. 38:382–386.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ishak K, Baptista A, Bianchi L, et al:
Histological grading and staging of chronic hepatitis. J Hepatol.
22:696–699. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karin M and Lin A: NF-kappaB at the
crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 3:221–227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Luo JL, Kamata H and Karin M: The
anti-death machinery in IKK/NF-kappaB signaling. J Clin Immunol.
25:541–550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Haskill S, Beg AA, Tompkins SM, et al:
Characterization of an immediate-early gene induced in adherent
monocytes that encodes I kappa B-like activity. Cell. 65:1281–1289.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beg AA, Finco TS, Nantermet PV and Baldwin
AS Jr: Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to
phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for
NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 13:3301–3310. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappaB: the
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yan SD, Schmidt AM, Anderson GM, et al:
Enhanced cellular oxidant stress by the interaction of advanced
glycation end products with their receptors/binding proteins. J
Biol Chem. 269:9889–9897. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yan SD, Stern D and Schmidt AM: What’s the
RAGE? The receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and
the dark side of glucose. Eur J Clin Invest. 27:179–181. 1997.
|
|
26
|
Li J and Schmidt AM: Characterization and
functional analysis of the promoter of RAGE, the receptor for
advanced glycation end products. J Biol Chem. 272:16498–16506.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hellerbrand C, Jobin C, Licato LL, Sartor
RB and Brenner DA: Cytokines induce NF-kappaB in activated but not
in quiescent rat hepatic stellate cells. Am J Physiol.
275:G269–G278. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hellerbrand, Wang SC, Tsukamoto H, Brenner
DA and Rippe RA: Expression of intracellular adhesion molecule 1 by
activated hepatic stellate cells. Hepatology. 24:670–676. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu C, Tao Q, Sun M, et al: Kupffer cells
are associated with apoptosis, inflammation and fibrotic effects in
hepatic fibrosis in rats. Lab Invest. 90:1805–1816. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Senoo H, Yoshikawa K, Morii M, Miura M,
Imai K and Mezaki Y: Hepatic stellate cell (vitamin A-storing cell)
and its relative - past, present and future. Cell Biol Int.
34:1247–1272. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Otogawa K, Ogawa T, Shiga R, Ikeda K and
Kawada N: Induction of tropomyosin during hepatic stellate cell
activation and the progression of liver fibrosis. Hepatol Int.
3:378–383. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|