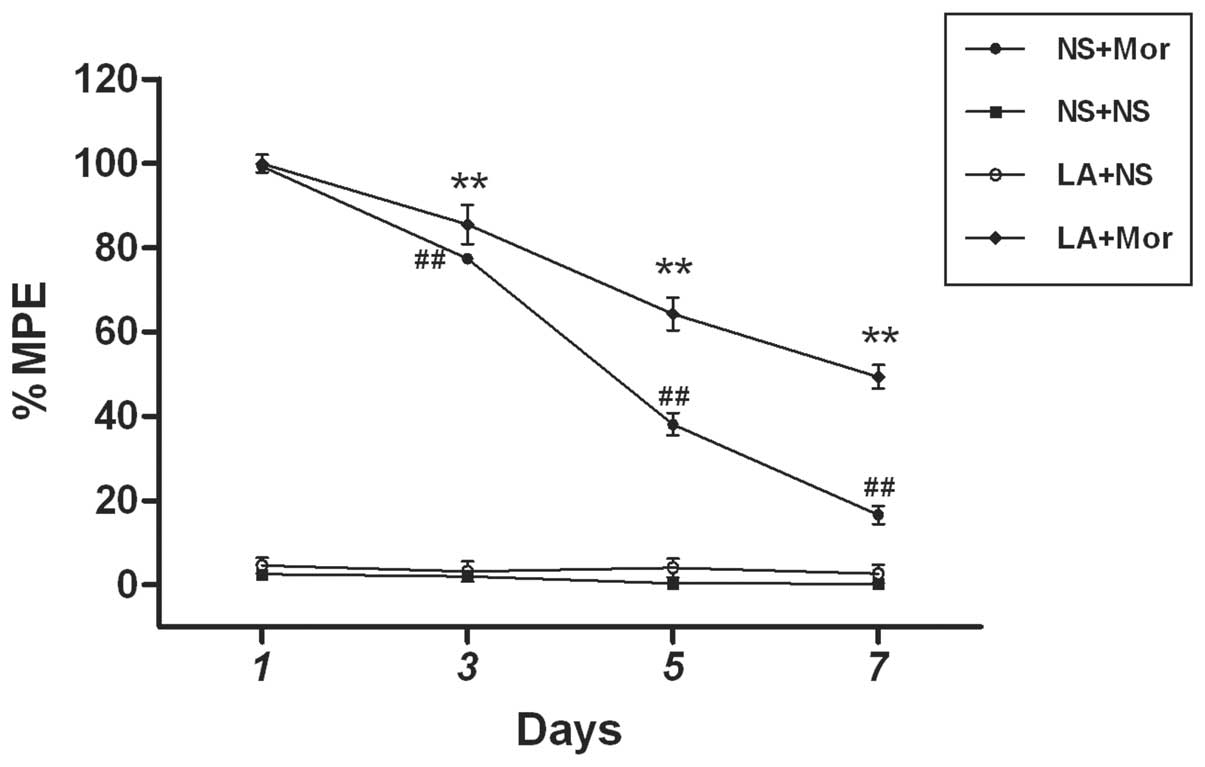
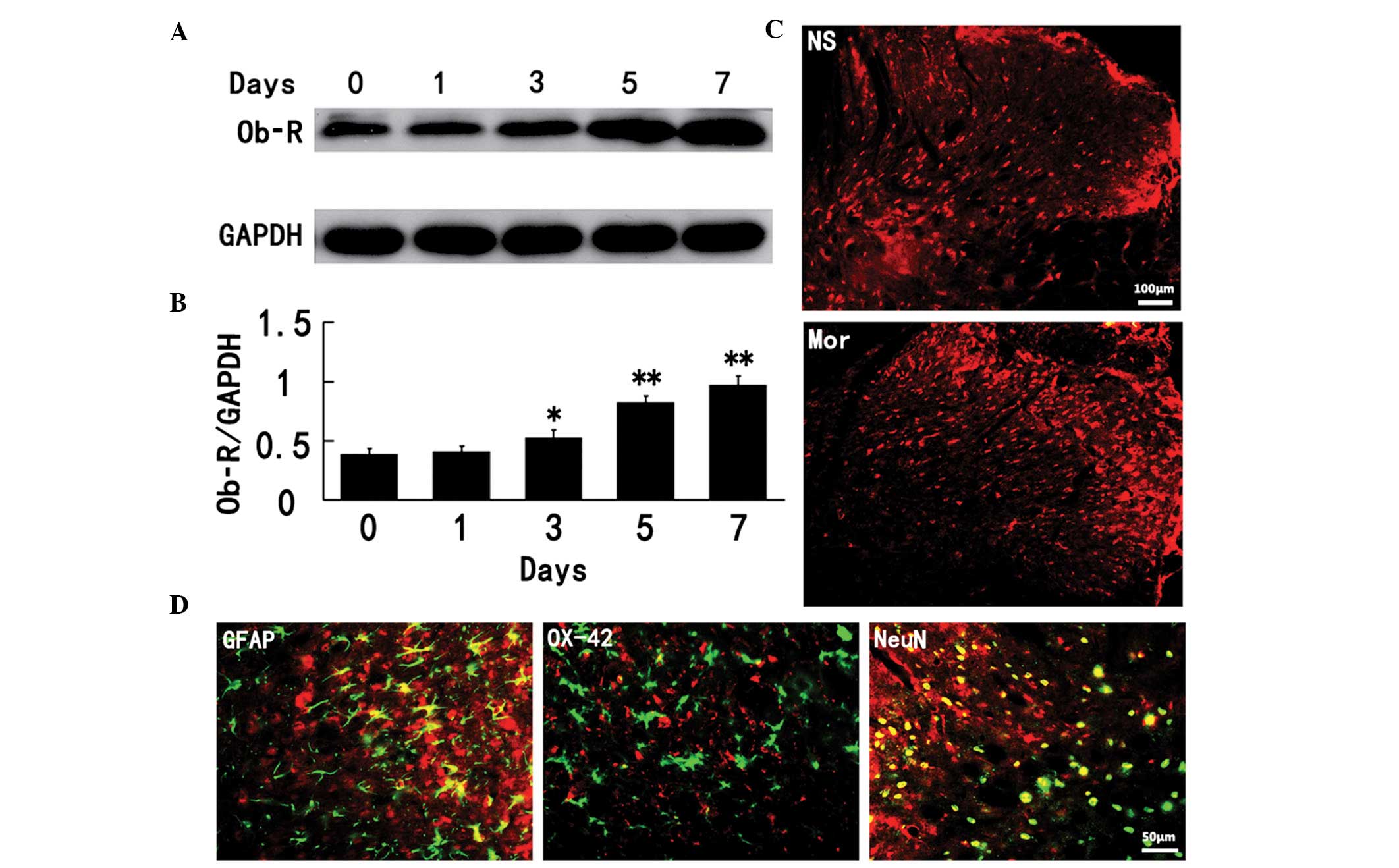
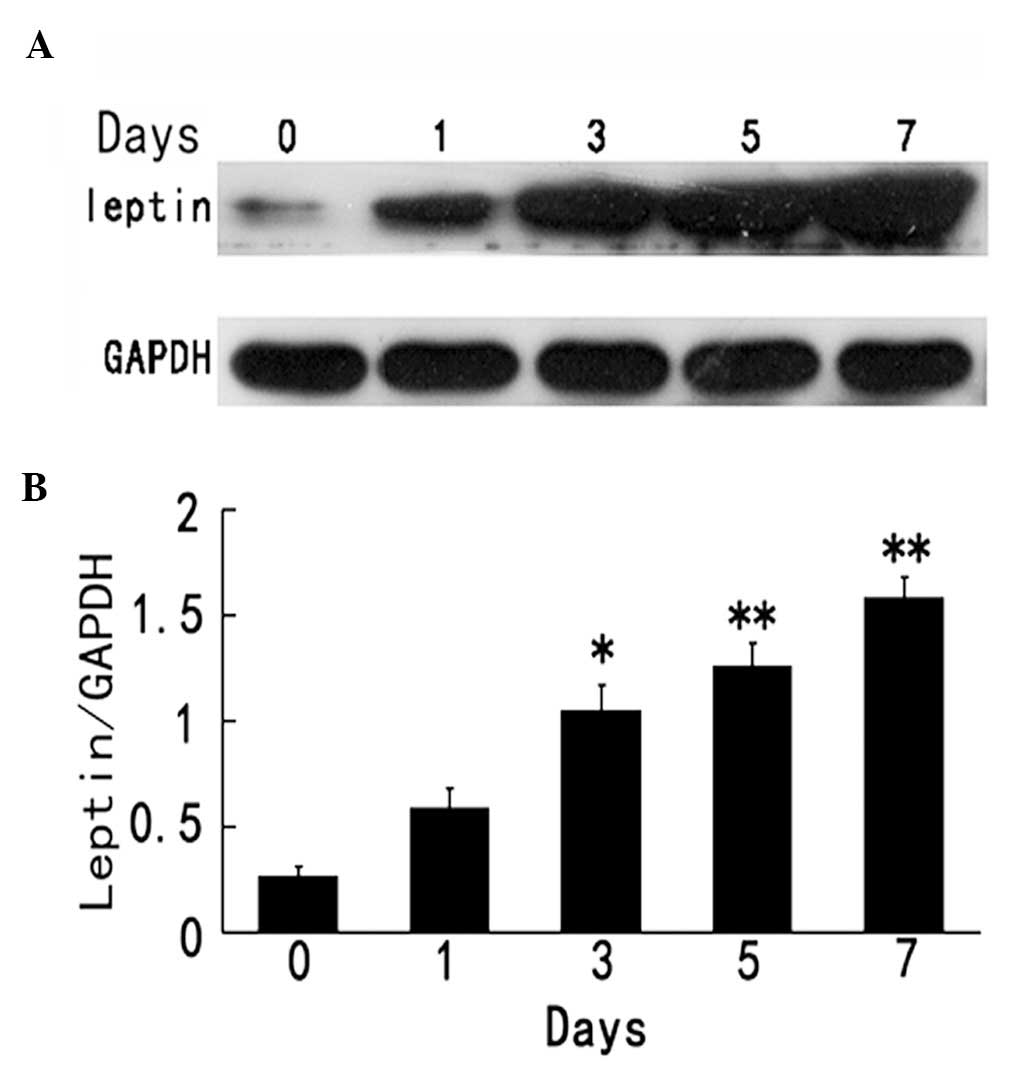
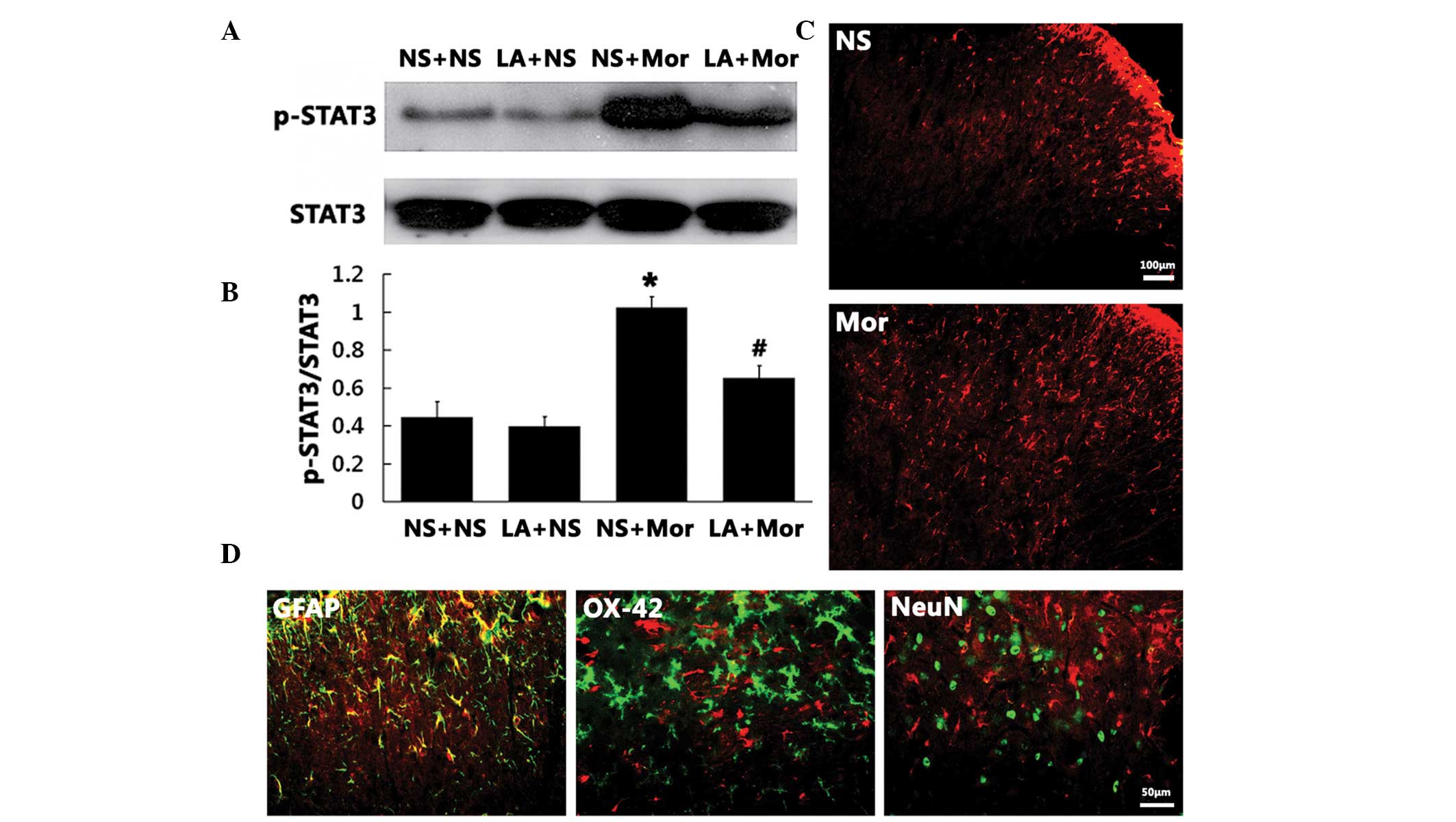
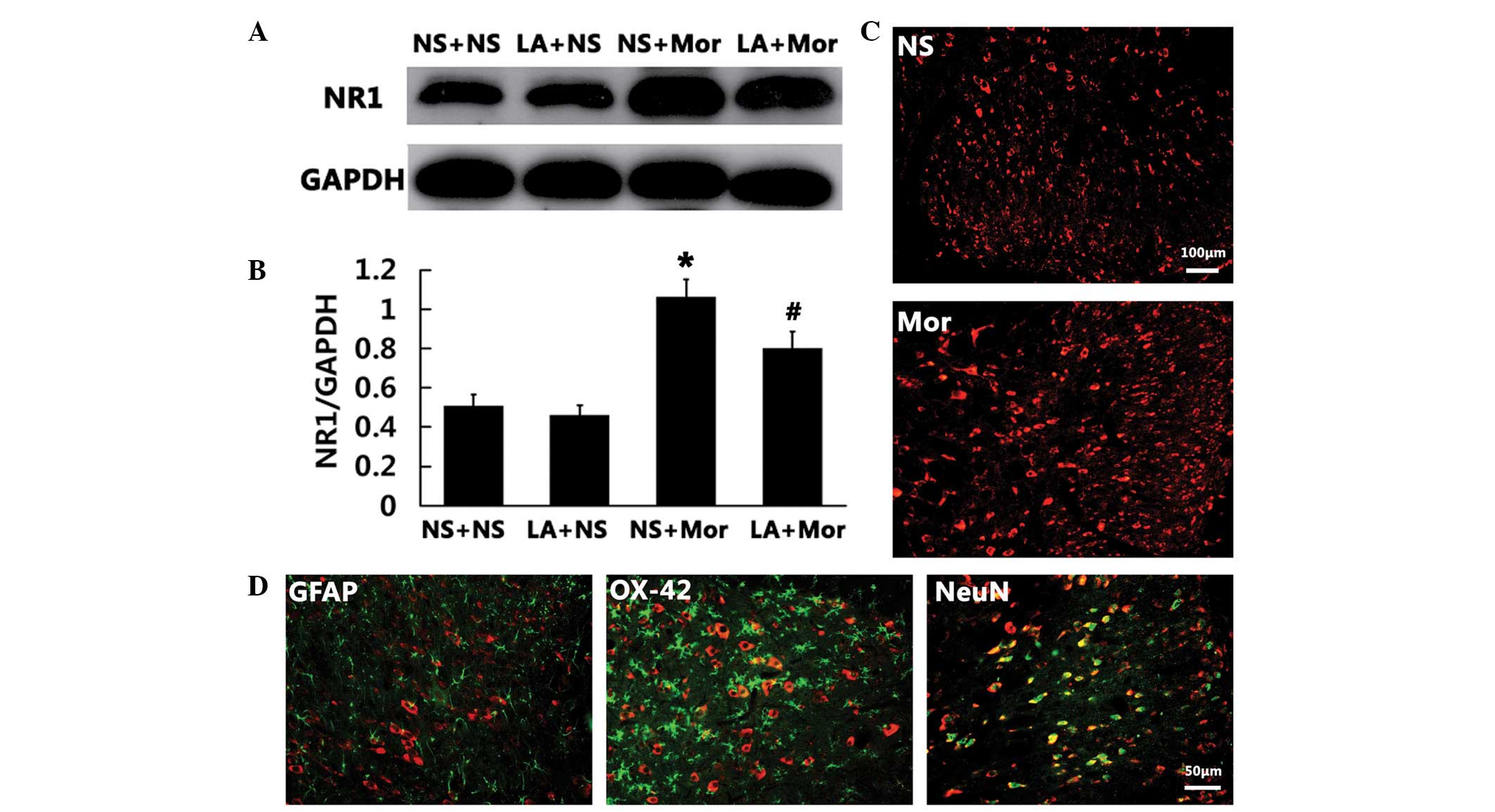
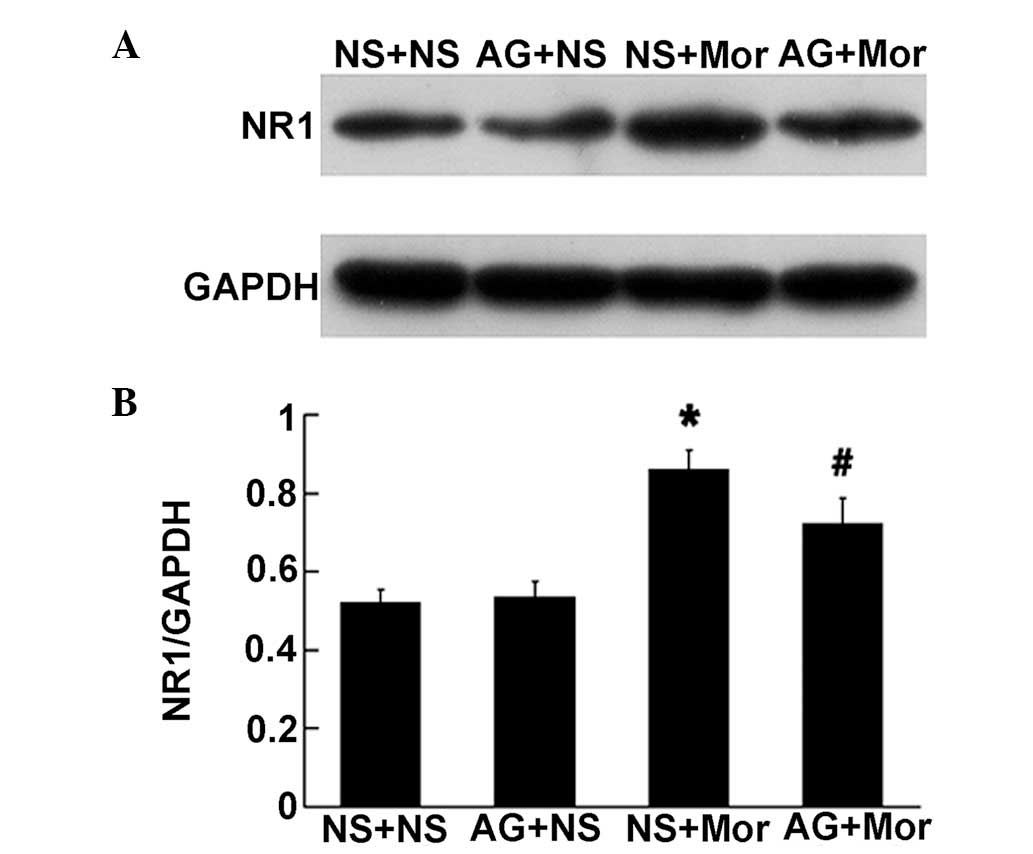
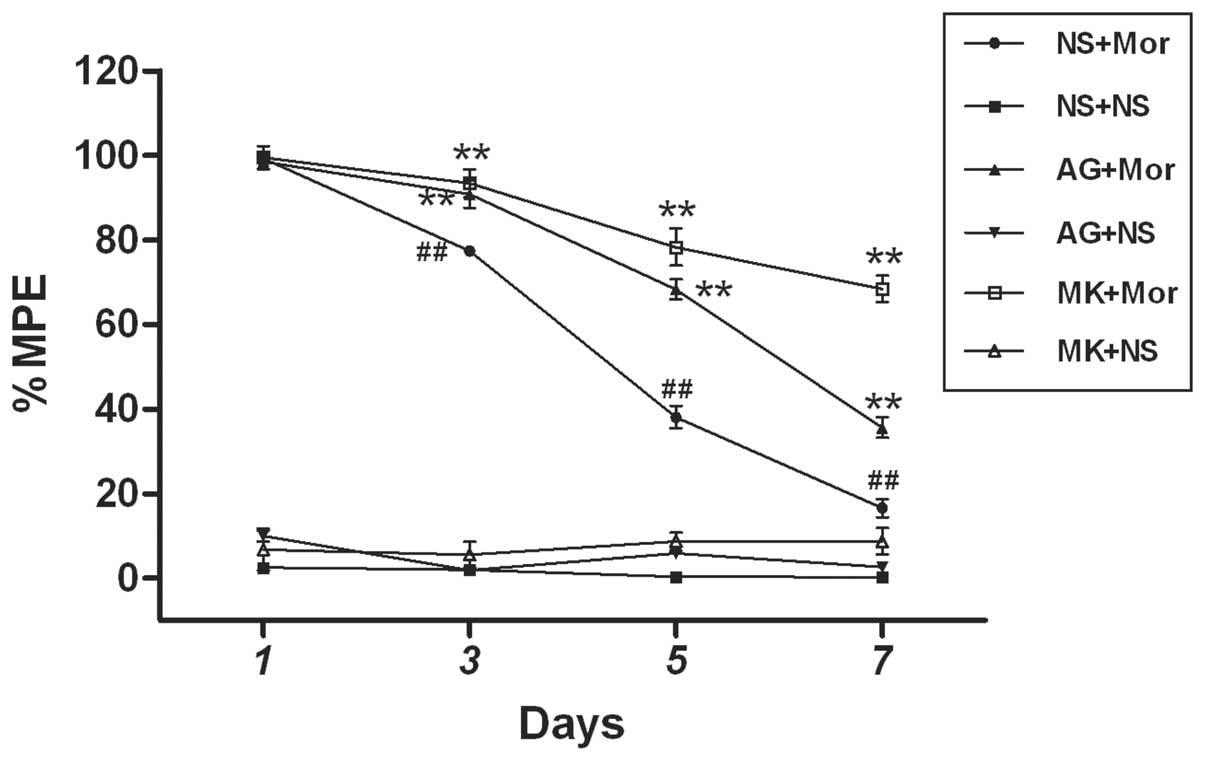
|
1
|
Trujillo KA and Akil H: Inhibition of
morphine tolerance and dependence by the NMDA receptor antagonist
MK-801. Science. 251:85–87. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guo RX, Zhang M, Liu W, Zhao CM, Cui Y,
Wang CH, Feng JQ and Chen PX: NMDA receptors are involved in
upstream of the spinal JNK activation in morphine antinociceptive
tolerance. Neurosci Lett. 467:95–99. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raghavendra V, Rutkowski MD and DeLeo JA:
The role of spinal neuroimmune activation in morphine
tolerance/hyperalgesia in neuropathic and sham-operated rats. J
Neurosci. 22:9980–9989. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Johnston IN, Milligan ED, Wieseler-Frank
J, Frank MG, Zapata V, Campisi J, Langer S, Martin D, Green P,
Fleshner M, et al: A role for proinflammatory cytokines and
fractalkine in analgesia, tolerance, and subsequent pain
facilitation induced by chronic i.t morphine. J Neurosci.
24:7353–7365. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang Z, Ma W, Chabot JG and Quirion R:
Calcitonin gene-related peptide as a regulator of neuronal
CaMKII-CREB, microglial p38-NFκB and astroglial ERK-Stat1/3
cascades mediating the development of tolerance to morphine-induced
analgesia. Pain. 151:194–205. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cui Y, Liao XX, Liu W, Guo RX, Wu ZZ, Zhao
CM, Chen PX and Feng JQ: A novel role of minocycline: attenuating
morphine antinociceptive tolerance by inhibition of p38 MAPK in the
activated spinal microglia. Brain Behav Immun. 22:114–123. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cui Y, Chen Y, Zhi JL, Guo RX, Feng JQ and
Chen PX: Activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase in
spinal microglia mediates morphine antinociceptive tolerance. Brain
Res. 1069:235–243. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M,
Leopold L and Friedman JM: Positional cloning of the mouse obese
gene and its human homologue. Nature. 372:425–432. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bjørbaek C, Uotani S, da Silva B and Flier
JS: Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms
of the leptin receptor. J Biol Chem. 272:32686–32695.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Maeda T, Kiguchi N, Kobayashi Y, Ikuta T,
Ozaki M and Kishioka S: Leptin derived from adipocytes in injured
peripheral nerves facilitates development of neuropathic pain via
macrophage stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13076–13081.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lim G, Wang S, Zhang Y, Tian Y and Mao J:
Spinal leptin contributes to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain
in rodents. J Clin Invest. 119:295–304. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tian Y, Wang S, Ma Y, Lim G, Kim H and Mao
J: Leptin enhances NMDA-induced spinal excitation in rats: A
functional link between adipocytokine and neuropathic pain. Pain.
152:1263–1271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mao J, Price DD and Mayer DJ: Mechanisms
of hyperalgesia and morphine tolerance: a current view of their
possible interactions. Pain. 62:259–274. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mayer DJ, Mao J, Holt J and Price DD:
Cellular mechanisms of neuropathic pain, morphine tolerance, and
their interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:7731–7736. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Harvey J: Leptin: a diverse regulator of
neuronal function. J Neurochem. 100:307–313. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tartaglia LA, Dembski M, Weng X, et al:
Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R.
Cell. 83:1263–1271. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Myers MG Jr: Leptin receptor signaling and
the regulation of mammalian physiology. Recent Prog Horm Res.
59:287–304. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ahima RS, Qi Y, Singhal NS, Jackson MB and
Scherer PE: Brain adipocytokine action and metabolic regulation.
Diabetes. 55(Suppl 2): S145–154. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wolsk E, Mygind H, Grøndahl TS, Pedersen
BK and van Hall G: Human skeletal muscle releases leptin in vivo.
Cytokine. 60:667–673. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Purdham DM, Zou MX, Rajapurohitam V and
Karmazyn M: Rat heart is a site of leptin production and action. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 287:H2877–H2884. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Morash B, Li A, Murphy PR, Wilkinson M and
Ur E: Leptin gene expression in the brain and pituitary gland.
Endocrinology. 140:5995–5998. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ur E, Wilkinson DA, Morash BA and
Wilkinson M: Leptin immunoreactivity is localized to neurons in rat
brain. Neuroendocrinology. 75:264–272. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bjorbaek C: Central leptin receptor action
and resistance in obesity. J Investig Med. 57:789–794.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Robertson SA, Leinninger GM and Myers MG
Jr: Molecular and neural mediators of leptin action. Physiol Behav.
94:637–642. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fisher K, Coderre TJ and Hagen NA:
Targeting the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor for chronic pain
management. Preclinical animal studies, recent clinical experience
and future research directions. J Pain Symptom Manage. 20:358–373.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hewitt DJ: The use of NMDA-receptor
antagonist in the treatment of chronic pain. Clin J Pain.
16(Suppl): s73–79. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Houghton AK, Parsons CG and Headley PM:
Mrz 2/579, a fast kinetic NMDA channel blocker, reduces the
development of morphine tolerance in awake rats. Pain. 91:201–207.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Goldin M, Segal M and Avignone E:
Functional plasticity triggers formation and pruning of dendritic
spines in cultured hippocampal networks. J Neurosci. 21:186–193.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Elmquist JK, Maratos-Flier E, Saper CB and
Flier JS: Unraveling the central nervous system pathways underlying
responses to leptin. Nat Neurosci. 1:445–450. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|