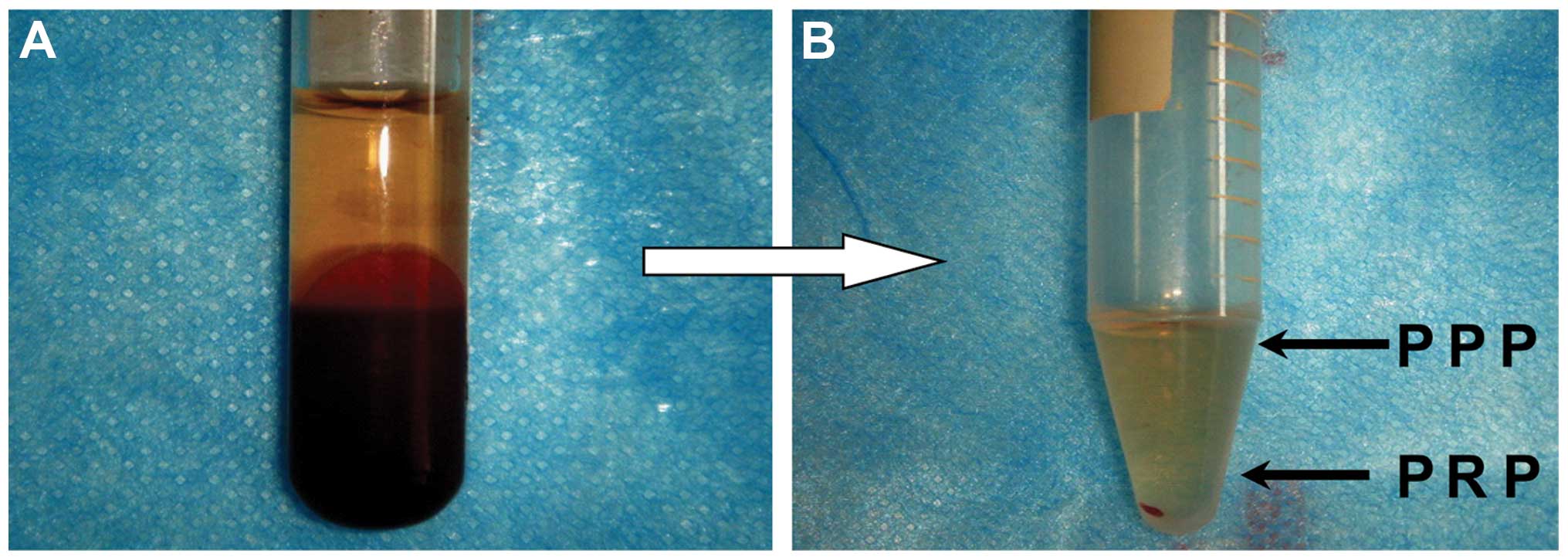
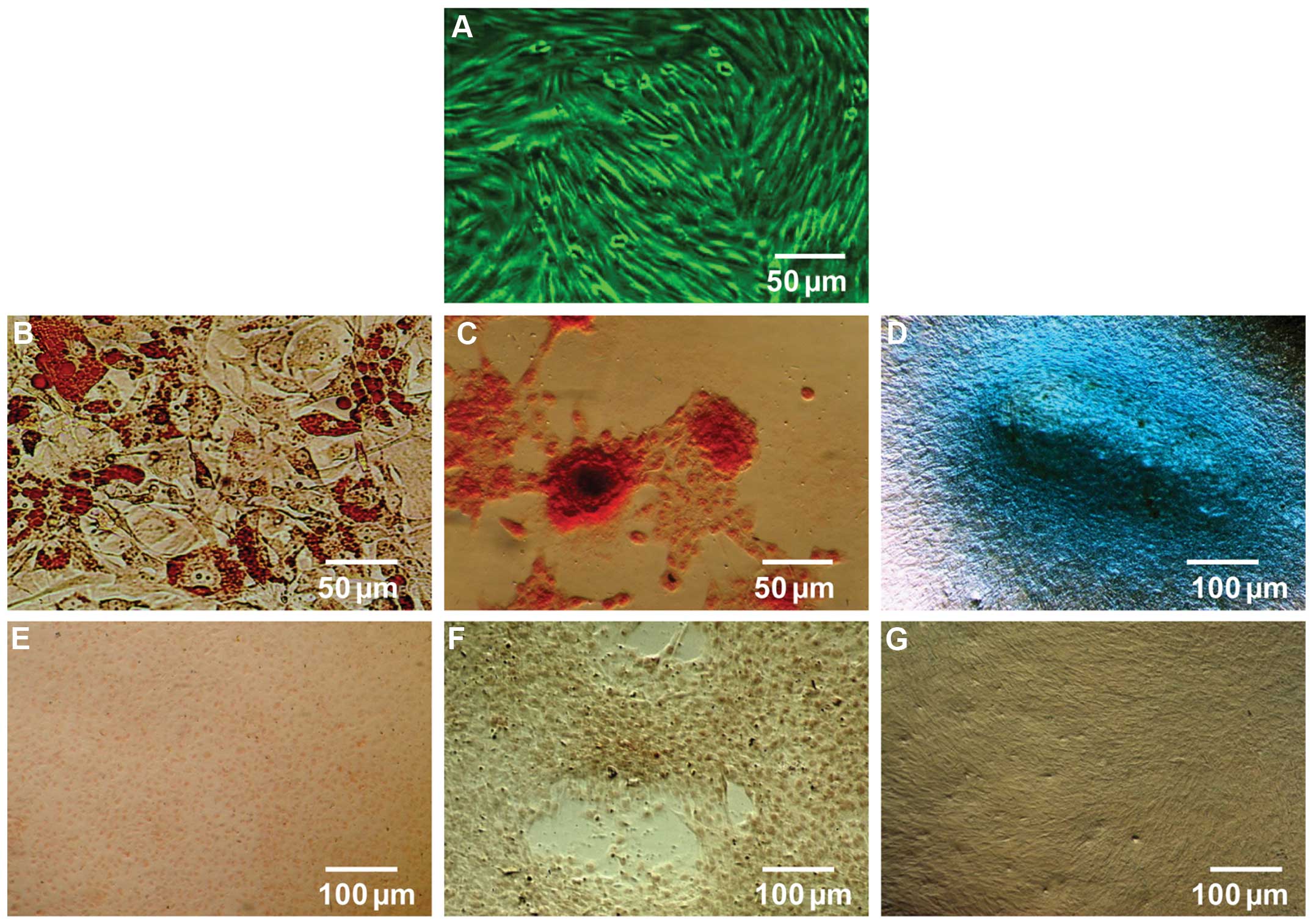
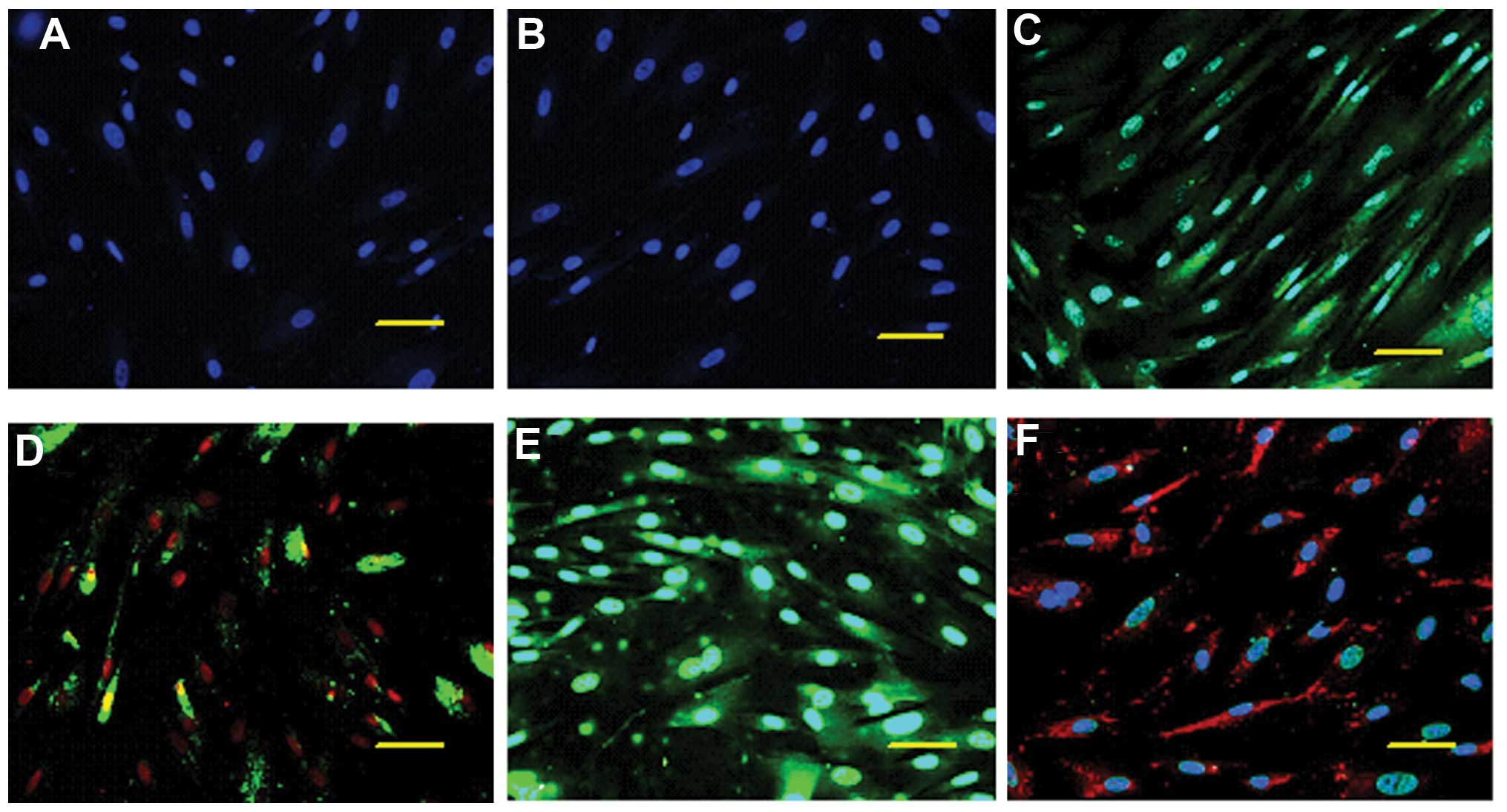
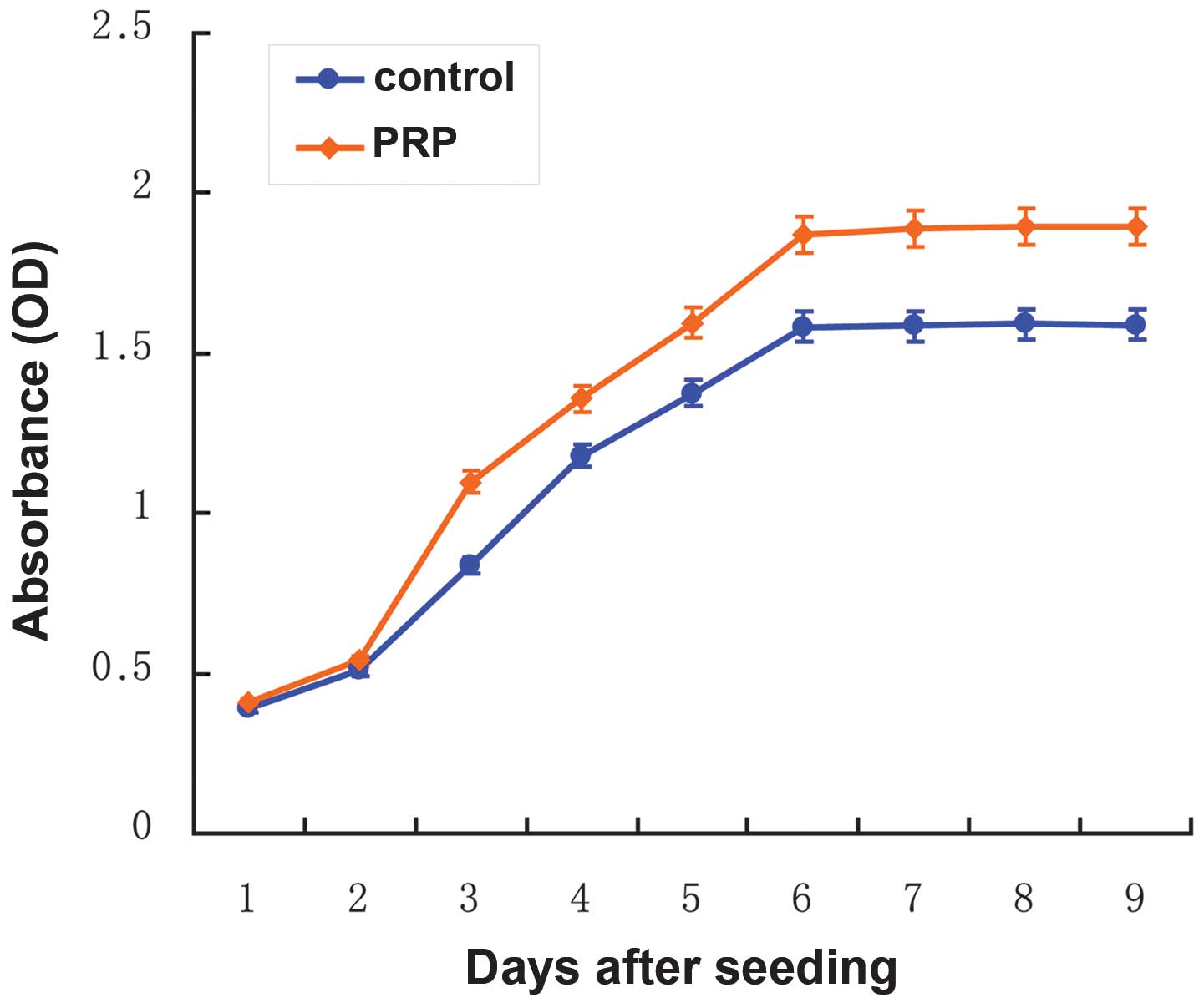
|
1
|
Cordeiro PG: Breast reconstruction after
surgery for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1590–1601. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ren G, Chen X, Dong F, et al: Concise
review: mesenchymal stem cells and translational medicine: emerging
issues. Stem Cells Transl Med. 1:51–58. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dubois SG, Floyd EZ, Zvonic S, Kilroy G,
Wu X, Carling S, Halvorsen YD, Ravussin E and Gimble JM: Isolation
of human adipose-derived stem cells from biopsies and liposuction
specimens. Methods Mol Biol. 449:69–79. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Neupane M, Chang CC, Kiupel M and
Yuzbasiyan-Gurkan V: Isolation and characterization of canine
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng Part A.
14:1007–1015. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peptan IA, Hong L and Mao JJ: Comparison
of osteogenic potentials of visceral and subcutaneous
adipose-derived cells of rabbits. Plast Reconstr Surg.
117:1462–1470. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tholpady SS, Katz AJ and Ogle RC:
Mesenchymal stem cells from rat visceral fat exhibit multipotential
differentiation in vitro. Anat Rec A Discov Mol Cell Evol Biol.
272:398–402. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vidal MA, Kilroy GE, Lopez MJ, Johnson JR,
Moore RM and Gimble JM: Characterization of equine adipose
tissue-derived stromal cells: adipogenic and osteogenic capacity
and comparison with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.
Vet Surg. 36:613–622. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Safford KM, Hicok KC, Safford SD, et al:
Neurogenic differentiation of murine and human adipose-derived
stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 294:371–379. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jurgens WJ, Oedayrajsingh-Varma MJ, Helder
MN, Zandiehdoulabi B, Schouten TE, Kuik DJ, Ritt MJ and van
Milligen FJ: Effect of tissue-harvesting site on yield of stem
cells derived from adipose tissue: implications for cell-based
therapies. Cell Tissue Res. 332:415–426. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grimes BR, Steiner CM, Merfeld-Clauss S,
et al: Interphase FISH demonstrates that human adipose stromal
cells maintain a high level of genomic stability in long-term
culture. Stem Cells Dev. 18:717–724. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al: Human
adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol
Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gimble JM and Guilak F: Differentiation
potential of adipose derived adult stem (ADAS) cells. Curr Top Dev
Biol. 58:137–160. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gimble J and Guilak F: Adipose-derived
adult stem cells: isolation, characterization, and differentiation
potential. Cytotherapy. 5:362–369. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M, et al:
Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem
cells. Keio J Med. 54:132–141. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fraser JK, Schreiber R, Strem B, et al:
Plasticity of human adipose stem cells toward endothelial cells and
cardiomyocytes. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 3(Suppl 1): S33–S37.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jack GS, Almeida FG, Zhang R, Alfonso ZC,
Zuk PA and Rodríguez LV: Processed lipoaspirate cells for tissue
engineering of the lower urinary tract: implications for the
treatment of stress urinary incontinence and bladder
reconstruction. J Urol. 174:2041–2045. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rodríguez LV, Alfonso Z, Zhang R, Leung J,
Wu B and Ignarro LJ: Clonogenic multipotent stem cells in human
adipose tissue differentiate into functional smooth muscle cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12167–12172. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mizuno H, Zuk PA, Zhu M, Lorenz HP,
Benhaim P and Hedrick MH: Myogenic differentiation by human
processed lipoaspirate cells. Plast Reconstr Surg. 109:199–209.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zaman WS, Makpol S, Sathapan S and Chua
KH: Long-term in vitro expansion of human adipose-derived stem
cells showed low risk of tumourigenicity. J Tissue Eng Regen Med.
8:67–76. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee JH and Kemp DM: Human adipose-derived
stem cells display myogenic potential and perturbed function in
hypoxic conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 341:882–888. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu TM, Martina M, Hutmacher DW, Hui JH,
Lee EH and Lim B: Identification of common pathways mediating
differentiation of bone marrow- and adipose tissue-derived human
mesenchymal stem cells into three mesenchymal lineages. Stem Cells.
25:750–760. 2007.
|
|
22
|
Li HX, Luo X, Liu RX, Yang YJ and Yang GS:
Roles of Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in adipogenic differentiation
potential of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 291:116–124. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Karbiener M, Fischer C, Nowitsch S, et al:
microRNA miR-27b impairs human adipocyte differentiation and
targets PPARgamma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 390:247–251. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
James AW, Leucht P, Levi B, et al: Sonic
Hedgehog influences the balance of osteogenesis and adipogenesis in
mouse adipose-derived stromal cells. Tissue Eng Part A.
16:2605–2616. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Davis LA and Zur Nieden NI: Mesodermal
fate decisions of a stem cell: the Wnt switch. Cell Mol Life Sci.
65:2658–2674. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schäffler A and Buchler C: Concise review:
adipose tissue-derived stromal cells - basic and clinical
implications for novel cell-based therapies. Stem Cells.
25:818–827. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cousin B, André MM, Arnaud E, Pénicaud L
and Casteilla L: Reconstitution of lethally irradiated mice by
cells isolated from adipose tissue. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
301:1016–1022. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miranville A, Heeschen C, Sengenès C,
Curat CA, Busse R and Bouloumié A: Improvement of postnatal
neovascularization by human adipose tissue-derived stem cells.
Circulation. 110:349–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Corre J, Barreau C, Cousin B, et al: Human
subcutaneous adipose cells support complete differentiation but not
self-renewal of hematopoietic progenitors. J Cell Physiol.
208:282–288. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li H, Han Z, Liu D, Zhao P, Liang S and Xu
K: Autologous platelet-rich plasma promotes neurogenic
differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in vitro. Int J
Neurosci. 123:184–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu J, Pan Z, Cheng M, et al: Ginsenoside
Rg1 facilitates neural differentiation of mouse embryonic stem
cells via GR-dependent signaling pathway. Neurochem Int. 62:92–102.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shi AW, Gu N, Liu XM, Wang X and Peng YZ:
Ginsenoside Rg1 enhances endothelial progenitor cell angiogenic
potency and prevents senescence in vitro. J Int Med Res.
39:1306–1318. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang L and Kisaalita WS: Administration of
BDNF/ginsenosides combination enhanced synaptic development in
human neural stem cells. J Neurosci Methods. 194:274–282. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shi AW, Wang XB, Lu FX, Zhu MM, Kong XQ
and Cao KJ: Ginsenoside Rg1 promotes endothelial progenitor cell
migration and proliferation. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:299–306. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Moshtagh PR, Emami SH and Sharifi AM:
Differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell into
insulin-producing cells: an in vitro study. J Physiol Biochem.
69:451–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Scuderi N, Ceccarelli S, Onesti MG, et al:
Human adipose-derived stromal cells for cell-based therapies in the
treatment of systemic sclerosis. Cell Transplant. 22:779–795. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kisiel AH, McDuffee LA, Masaoud E, Bailey
TR, Esparza Gonzalez BP and Nino-Fong R: Isolation,
characterization, and in vitro proliferation of canine mesenchymal
stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, muscle, and
periosteum. Am J Vet Res. 73:1305–1317. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Heneidi S, Simerman AA, Keller E, Singh P,
Li X, Dumesic DA and Chazenbalk G: Awakened by cellular stress:
isolation and characterization of a novel population of pluripotent
stem cells derived from human adipose tissue. PLoS One.
8:e647522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hanson SE, Kim J and Hematti P:
Comparative analysis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
isolated from abdominal and breast tissue. Aesthet Surg J.
33:888–898. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
41
|
Smith SE and Roukis TS: Bone and wound
healing augmentation with platelet-rich plasma. Clin Podiatr Med
Surg. 26:559–588. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Gentile P, Orlandi A, Scioli MG, Di
Pasquali C, Bocchini I and Cervelli V: Concise review:
adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cells and platelet-rich
plasma: basic and clinical implications for tissue engineering
therapies in regenerative surgery. Stem Cells Transl Med.
1:230–236. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Mardani M, Kabiri A, Esfandiari E,
Esmaeili A, Pourazar A, Ansar M and Hashemibeni B: The effect of
platelet rich plasma on chondrogenic differentiation of human
adipose derived stem cells in transwell culture. Iran J Basic Med
Sci. 16:1163–1169. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gaiba S, França LP, França JP and Ferreira
LM: Characterization of human adipose-derived stem cells. Acta Cir
Bras. 27:471–476. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mafi P, Hindocha S, Mafi R, Griffin M and
Khan WS: Adult mesenchymal stem cells and cell surface
characterization - a systematic review of the literature. Open
Orthop J. 5:253–260. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hass R, Kasper C, Böhm S and Jacobs R:
Different populations and sources of human mesenchymal stem cells
(MSC): A comparison of adult and neonatal tissue-derived MSC. Cell
Commun Signal. 9:122011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Dimri G, Band H and Band V: Mammary
epithelial cell transformation: insights from cell culture and
mouse models. Breast Cancer Res. 7:171–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Péchoux C, Gudjonsson T, Ronnov-Jessen L,
Bissell MJ and Petersen OW: Human mammary luminal epithelial cells
contain progenitors to myoepithelial cells. Dev Biol. 206:88–99.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tobita M, Orbay H and Mizuno H:
Adipose-derived stem cells: current findings and future
perspectives. Discov Med. 11:160–170. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Mizuno H, et al:
Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for
cell-based therapies. Tissue Eng. 7:211–228. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Halvorsen YD, Franklin D, Bond AL, et al:
Extracellular matrix mineralization and osteoblast gene expression
by human adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Tissue Eng.
7:729–741. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Baer PC, Döring C, Hansmann ML, Schubert R
and Geiger H: New insights into epithelial differentiation of human
adipose-derived stem cells. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 7:271–278.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Baer PC, Brzoska M and Geiger H:
Epithelial differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells.
Methods Mol Biol. 702:289–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|