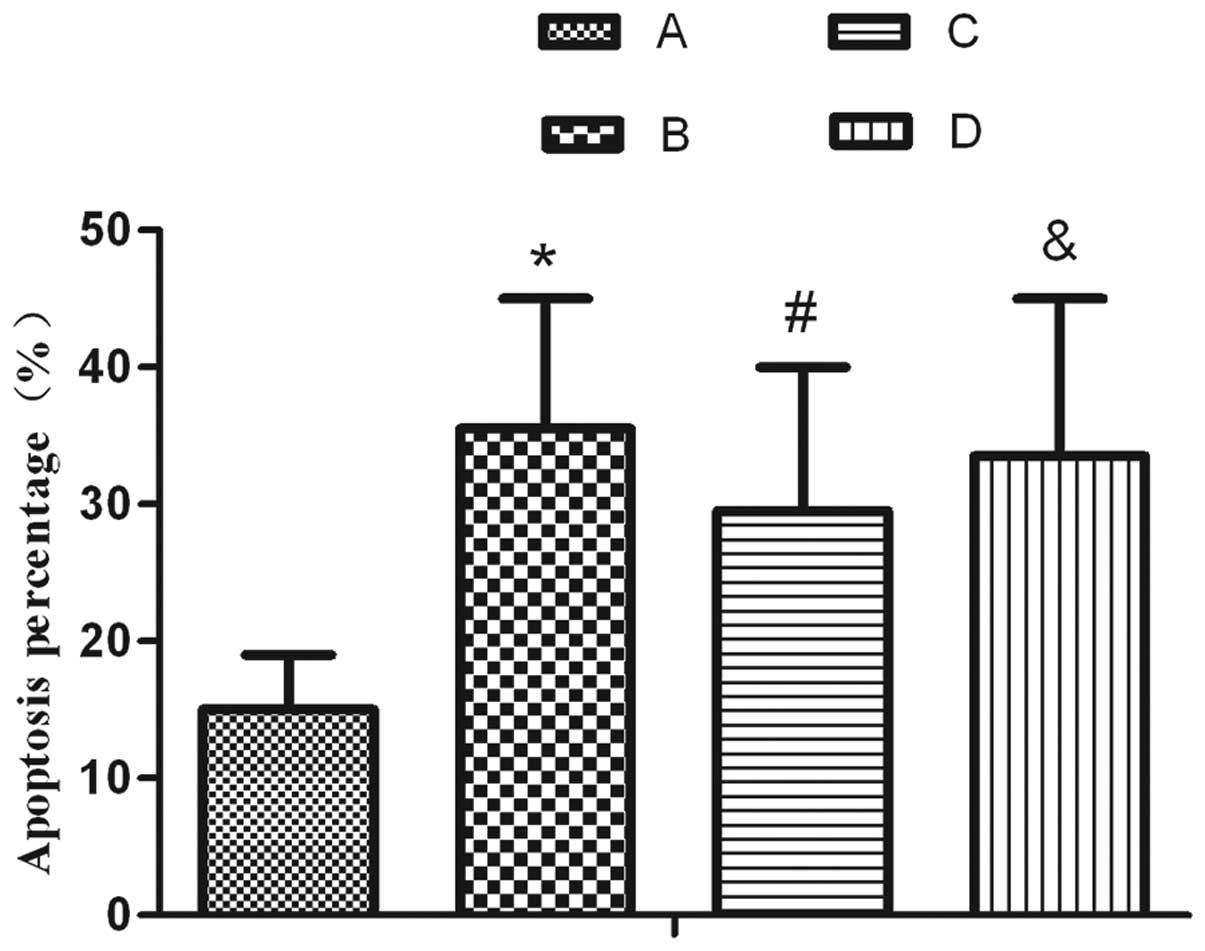
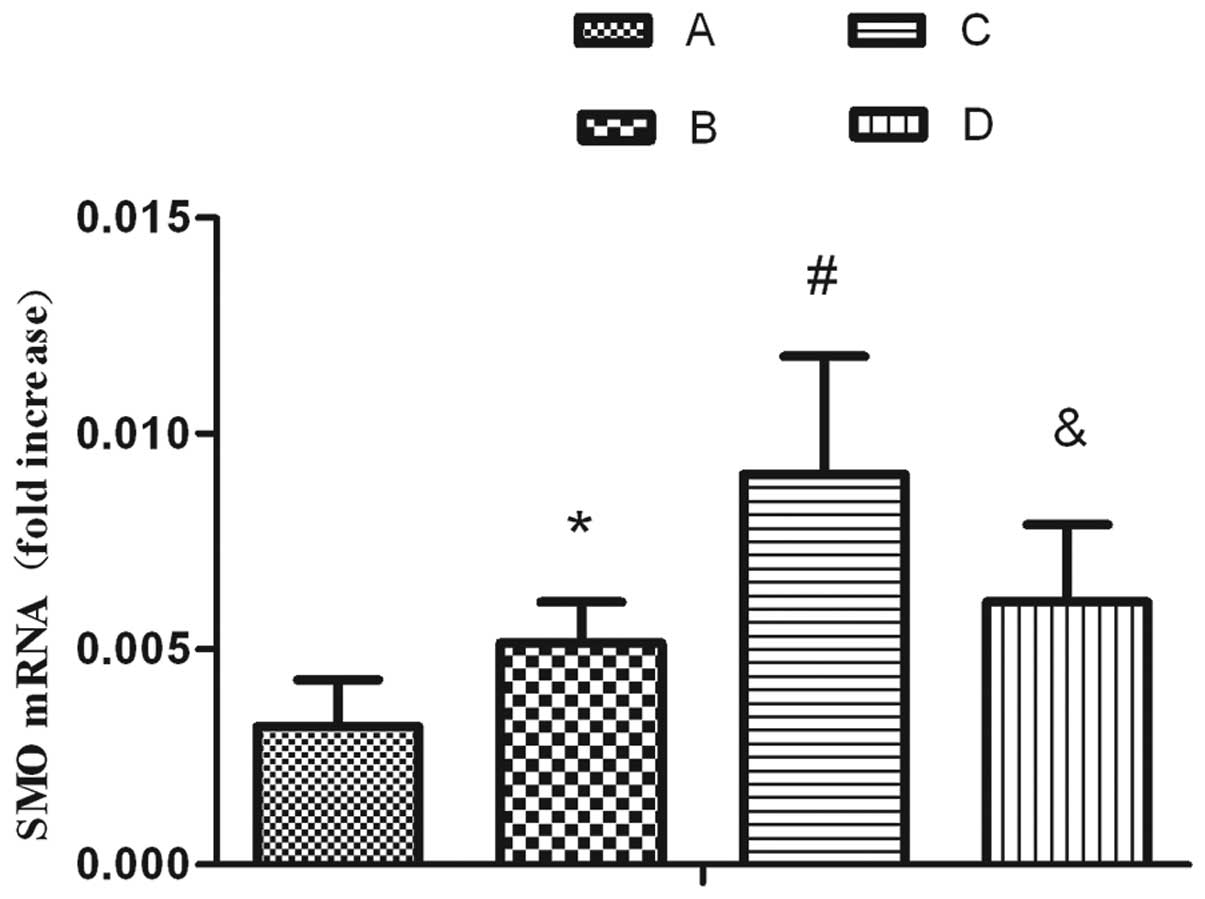
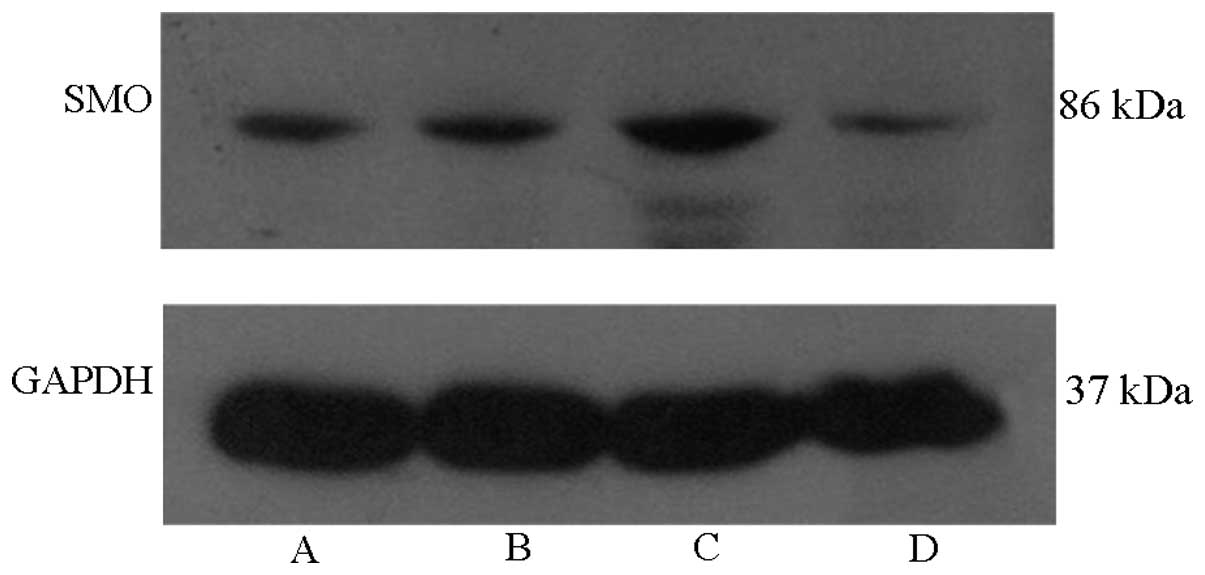
|
1
|
Gordo-Vidal F, Calvo-Herranz E,
Abella-Alvarez A, et al: Hyperoxia-induced pulmonary toxicity. Med
Intensiva. 34:134–138. 2010.(In Spanish).
|
|
2
|
Buccellato LJ, Tso M, Akinci OI, et al:
Reactive oxygen species are required for hyperoxia-induced Bax
activation and cell death in alveolar epithelial cells. J Biol
Chem. 279:6753–6760. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miyake Y, Kaise H, Isono K, et al:
Protective role of macrophages in noninflammatory lung injury
caused by selective ablation of alveolar epithelial type II Cells.
J Immunol. 178:5001–5009. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Scott JR, Muangman P and Gibran NS: Making
sense of hypertrophic scar: a role for nerves. Wound Repair Regen.
15(Suppl 1): S27–S31. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Scott JR, Muangman PR, Tamura RN, et al:
Substance P levels and neutral endopeptidase activity in acute burn
wounds and hypertrophic scar. Plast Reconstr Surg. 115:1095–1102.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang M, Wang H, Teng H, et al: Expression
of SHH signaling pathway components in the developing human lung.
Histochem Cell Biol. 134:327–335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Zhang H, Choi SC, et al: Sonic
hedgehog signaling regulates Gli3 processing, mesenchymal
proliferation, and differentiation during mouse lung organogenesis.
Dev Biol. 270:214–231. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Le H, Kleinerman R, Lerman OZ, et al:
Hedgehog signaling is essential for normal wound healing. Wound
Repair Regen. 16:768–773. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo JD, Hu TP, Wang L, et al: Sonic
hedgehog improves delayed wound healing via enhancing cutaneous
nitric oxide function in diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
297:e525–e531. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kusano KF, Pola R, Murayama T, et al:
Sonic hedgehog myocardial gene therapy: tissue repair through
transient reconstitution of embryonic signaling. Nat Med.
11:1197–1204. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Corti M, Brody AR and Harrison JH:
Isolation and primary culture of murine alveolar type II cells. Am
J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 14:309–315. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pagano A and Barazzone-Argiroffo C:
Alveolar cell death in hyperoxia-induced lung injury. Ann N Y Acad
Sci. 1010:405–416. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bishop AE: Pulmonary epithelial stem
cells. Cell Prolif. 37:89–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hökfelt T, Pernow B and Wahren J:
Substance P: a pioneer amongst neuropeptides. J Intern Med.
249:27–40. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hafstrom I, Ringertz B, Lundeberg T and
Palmblad J: The effect of endothelin, neuropeptide Y, calcitonin
gene-related peptide and substance P on neutrophil functions. Acta
Physiol Scand. 148:341–346. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Oslund KL, Hyde DM, Putney LF, et al:
Activation of neurokinin-1 receptors during ozone inhalation
contributes to epithelial injury and repair. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 39:279–288. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yaraee R and Ghazanfari T: Substance P
potentiates TGFβ-1 production in lung epithelial cell lines. Iran J
Allergy Asthma Immunol. 8:19–24. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dib M, Zsengeller Z, Mitsialis A, et al: A
paradoxical protective role for the proinflammatory peptide
substance P receptor (NK1R) in acute hyperoxic lung injury. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 297:L687–L697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang L, Liu C, Dang H, et al: Substance P
attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in neonatal rats. Mol Med
Rep. 9:595–599. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bellusci S, Furuta Y, Rush MG, et al:
Involvement of Sonic hedgehog (Shh) in mouse embryonic lung growth
and morphogenesis. Development. 124:53–63. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Litingtung Y, Lei L, Westphal H and Chiang
C: Sonic hedgehog is essential to foregut development. Nat Genet.
20:58–61. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pepicelli CV, Lewis PM and McMahon AP:
Sonic hedgehog regulates branching morphogenesis in the mammalian
lung. Curr Biol. 8:1083–1086. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Grindley JC, Bellusci S, Perkins D and
Hogan BL: Evidence for the involvement of the Gli gene family in
embryonic mouse lung development. Dev Biol. 188:337–348. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Warburton D, Zhao J, Berberich MA, et al:
Molecular embryology of the lung: then, now, and in the future. Am
J Physiol. 276:L697–L704. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|