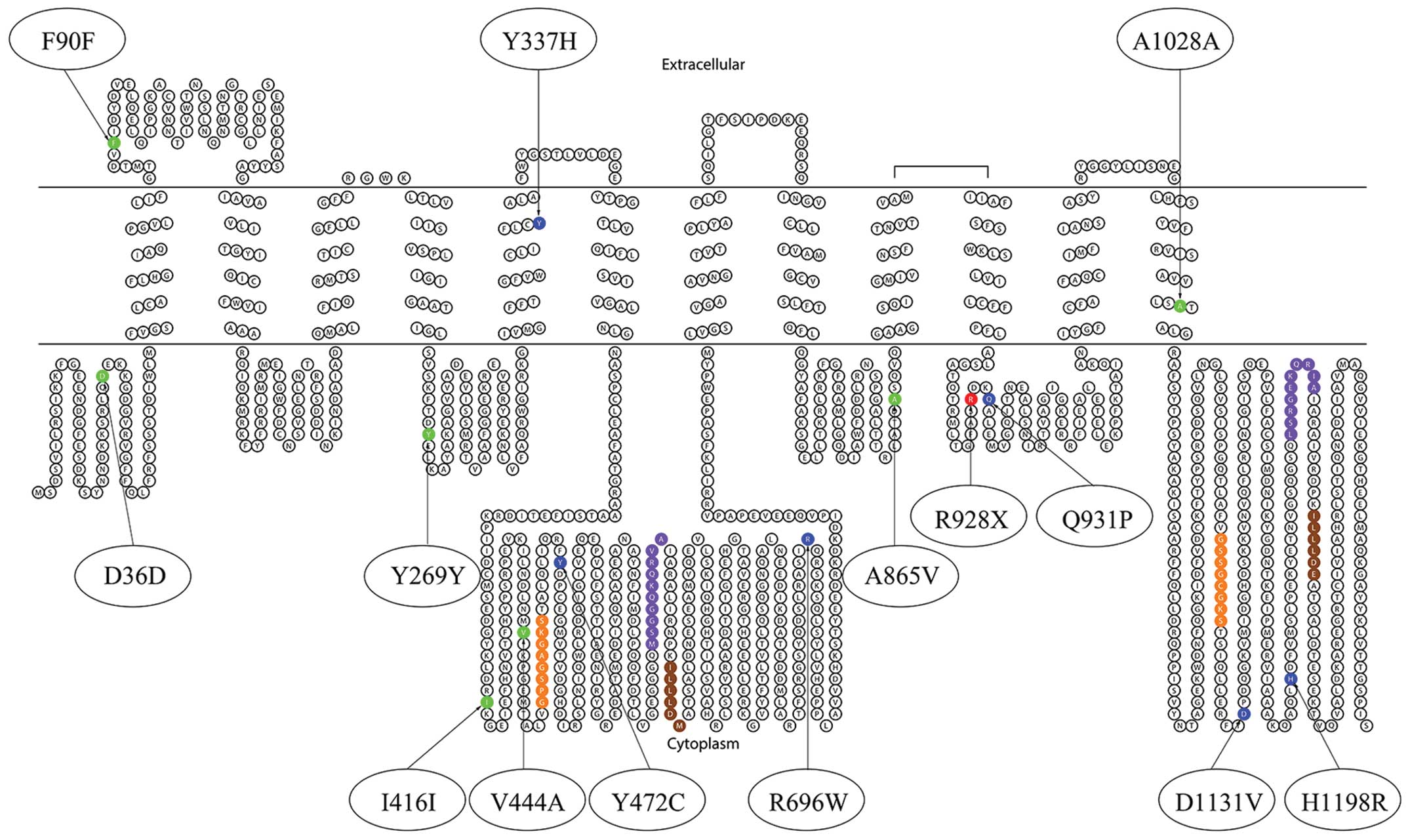
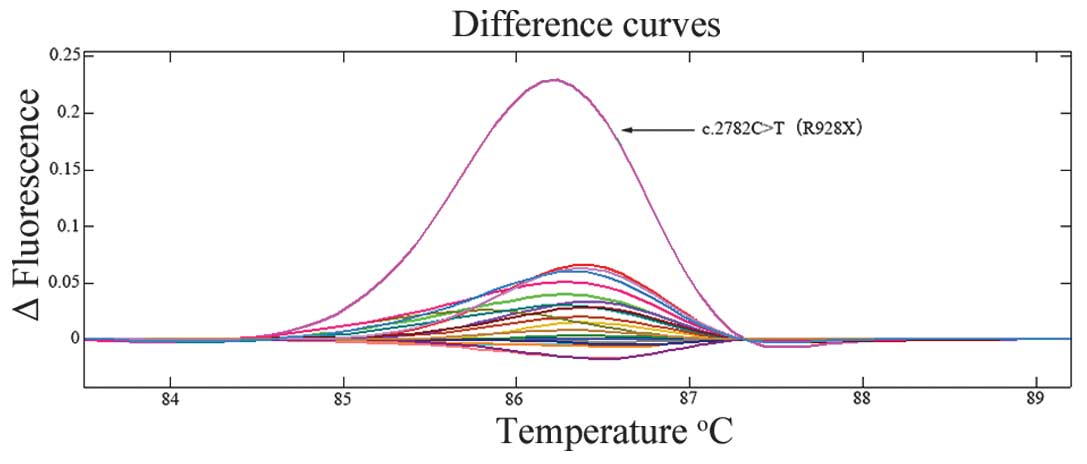
|
1
|
Keitel V, Burdelski M, Vojnisek Z, Schmitt
L, Häussinger D and Kubitz R: De novo bile salt transporter
antibodies as a possible cause of recurrent graft failure after
liver transplantation: a novel mechanism of cholestasis.
Hepatology. 50:510–517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Morotti RA, Suchy FJ and Magid MS:
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis (PFIC) type 1, 2, and
3: a review of the liver pathology findings. Semin Liver Dis.
31:3–10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harris MJ, Le Couteur DG and Arias IM:
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: genetic disorders of
biliary transporters. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 20:807–817. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hori T, Nguyen JH and Uemoto S:
Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 9:570–578. 2010.
|
|
5
|
Nicolaou M, Andress EJ, Zolnerciks JK,
Dixon PH, Williamson C and Linton KJ: Canalicular ABC transporters
and liver disease. J Pathol. 226:300–315. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jankowska I and Socha P: Progressive
familial intrahepatic cholestasis and inborn errors of bile acid
synthesis. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 36:271–274. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Strautnieks SS, Bull LN, Knisely AS, et
al: A gene encoding a liver-specific ABC transporter is mutated in
progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. Nat Genet.
20:233–238. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van Mil SW, van der Woerd WL, van der
Brugge G, et al: Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis type 2
is caused by mutations in ABCB11. Gastroenterology. 127:379–384.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Andrade RJ, Robles M, Ulzurrun E and
Lucena MI: Drug-induced liver injury: insights from genetic
studies. Pharmacogenomics. 10:1467–1487. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dixon PH, van Mil SW, Chambers J, et al:
Contribution of variant alleles of ABCB11 to susceptibility to
intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gut. 58:537–544. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Meier Y, Zodan T, Lang C, et al: Increased
susceptibility for intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and
contraceptive-induced cholestasis in carriers of the 1331T>C
polymorphism in the bile salt export pump. World J Gastroenterol.
14:38–45. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stieger B and Geier A: Genetic variations
of bile salt transporters as predisposing factors for drug-induced
cholestasis, intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy and therapeutic
response of viral hepatitis. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol.
7:411–425. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Müllenbach R, Weber SN, Krawczyk M, et al:
A frequent variant in the human bile salt export pump gene ABCB11
is associated with hepatitis C virus infection, but not liver
stiffness in a German population. BMC Gastroenterol. 12:632012.
|
|
14
|
Byrne JA, Strautnieks SS, Ihrke G, et al:
Missense mutations and single nucleotide polymorphisms in ABCB11
impair bile salt export pump processing and function or disrupt
pre-messenger RNA splicing. Hepatology. 49:553–567. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pauli-Magnus C, Kerb R, Fattinger K, et
al: BSEP and MDR3 haplotype structure in healthy Caucasians,
primary biliary cirrhosis and primary sclerosing cholangitis.
Hepatology. 39:779–791. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen HL, Liu YJ, Su YN, et al: Diagnosis
of BSEP/ABCB11 mutations in Asian patients with cholestasis using
denaturing high performance liquid chromatography. J Pediatr.
153:825–832. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu LY, Wang ZL, Wang XH, Zhu QR and Wang
JS: ABCB11 gene mutations in Chinese children with progressive
intrahepatic cholestasis and low gamma glutamyltransferase. Liver
Int. 30:809–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Nguyen-Dumont T, Calvez-Kelm FL, Forey N,
et al: Description and validation of high-throughput simultaneous
genotyping and mutation scanning by high-resolution melting curve
analysis. Hum Mutat. 30:884–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen HL, Liu YJ, Su YN, et al: Diagnosis
of BSEP/ABCB11 mutations in Asian patients with cholestasis using
denaturing high performance liquid chromatograph. J Pediatr.
153:825–832. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schwarz JM, Rödelsperger C, Schuelke M and
Seelow D: MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of
sequence alterations. Nat Methods. 7:575–576. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ng PC and Henikoff S: SIFT: Predicting
amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3812–3814. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Castellana S and Mazza T: Congruency in
the prediction of pathogenic missense mutations: state-of-the-art
web-based tools. Brief Bioinform. 14:448–459. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Adzhubei I, Jordan DM and Sunyaev SR:
2013.Predicting Functional Effect of Human Missense Mutations Using
PolyPhen-2. Curr Protocols in Human Genetics. 76:7.20.1–7.20.41
|
|
24
|
Calabrese R, Capriotti E, Fariselli P,
Martelli PL and Casadio R: Functional annotations improve the
predictive score of human disease-related mutations in proteins.
Hum Mutat. 30:1237–1244. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leabman MK, Huang CC, DeYoung J, et al:
Natural variation in human membrane transporter genes reveals
evolutionary and functional constraints. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
100:5896–5901. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Evason K, Bove KE, Finegold MJ, et al:
Morphologic findings in progressive familial intrahepatic
cholestasis 2 (PFIC2): correlation with genetic and
immunohistochemical studies. Am J Surg Pathol. 35:687–696. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Strautnieks SS, Byrne JA, Pawlikowska L,
et al: Severe bile salt export pump deficiency: 82 different ABCB11
mutations in 109 families. Gastroenterology. 134:1203–1214. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu C, Aronow BJ, Jegga AG, et al: Novel
resequencing chip customized to diagnose mutations in patients with
inherited syndromes of intrahepatic cholestasis. Gastroenterology.
132:119–126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Acalovschi M, Tirziu S, Chiorean E,
Krawczyk M, Grünhage F and Lammert F: Common variants of ABCB4 and
ABCB11 and plasma lipid levels: a study in sib pairs with
gallstones, and controls. Lipids. 44:521–526. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wheeler DA, Srinivasan M, Egholm M, et al:
The complete genome of an individual by massively parallel DNA
sequencing. Nature. 452:872–876. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
van der Stoep N, van Paridon CD, Janssens
T, et al: Diagnostic guidelines for high-resolution melting curve
(HRM) analysis: an interlaboratory validation of BRCA1 mutation
scanning using the 96-well LightScanner. Hum Mutat. 30:899–909.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van der Stoep N, van Paridon CD, Janssens
T, et al: Diagnostic guidelines for high-resolution melting curve
(HRM) analysis: an interlaboratory validation of BRCA1 mutation
scanning using the 96-well LightScanner. Hum Mutat. 30:899–909.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zolnerciks JK, Andress EJ, Nicolaou M and
Linton KJ: Structure of ABC transporters. Essays Biochem. 50:43–61.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matte U, Mourya R, Miethke A, et al:
Analysis of gene mutations in children with cholestasis of
undefined etiology. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 51:488–493. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Treepongkaruna S, Gaensan A, Pienvichit P,
et al: Novel ABCB11 mutations in a Thai infant with progressive
familial intrahepatic cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol.
15:4339–4342. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nobili V, Di Giandomenico S, Francalanci
P, Callea F, Marcellini M and Santorelli FM: A new ABCB11 mutation
in two Italian children with familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J
Gastroenterol. 41:598–603. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Goto K, Sugiyama K, Sugiura T, et al: Bile
salt export pump gene mutations in two Japanese patients with
progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. J Pediatr
Gastroenterol Nutr. 36:647–650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Saito S, Iida A, Sekine A, et al: Three
hundred twenty-six genetic variations in genes encoding nine
members of ATP-binding cassette, subfamily B (ABCB/MDR/TAP), in the
Japanese population. J Hum Genet. 47:38–50. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kim SR, Saito Y, Itoda M, et al: Genetic
variations of the ABC transporter gene ABCB11 encoding the human
bile salt export pump (BSEP) in a Japanese population. Drug Metab
Pharmacokinet. 24:277–281. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen HL, Chang PS, Hsu HC, et al: FIC1 and
BSEP defects in Taiwanese patients with chronic intrahepatic
cholestasis with low gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase levels. J
Pediatr. 140:119–124. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen ST, Chen HL, Su YN, et al: Prenatal
diagnosis of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis type 2.
J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23:1390–1393. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu LY, Wang XH, Lu Y, Zhu QR and Wang JS:
Association of variants of ABCB11 with transient neonatal
cholestasis. Pediatr Int. 55:138–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ananthanarayanan M and Li Y: PFIC2 and
ethnicity-specific bile salt export pump (BSEP, ABCB11) mutations:
where do we go from here? Liver Int. 30:777–779. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lang T, Haberl M, Jung D, et al: Genetic
variability, haplotype structures, and ethnic diversity of hepatic
transporters MDR3 (ABCB4) and bile salt export pump (ABCB11). Drug
Metab Dispos. 34:1582–1599. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lang C, Meier Y, Stieger B, et al:
Mutations and polymorphisms in the bile salt export pump and the
multidrug resistance protein 3 associated with drug-induced liver
injury. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 17:47–60. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|