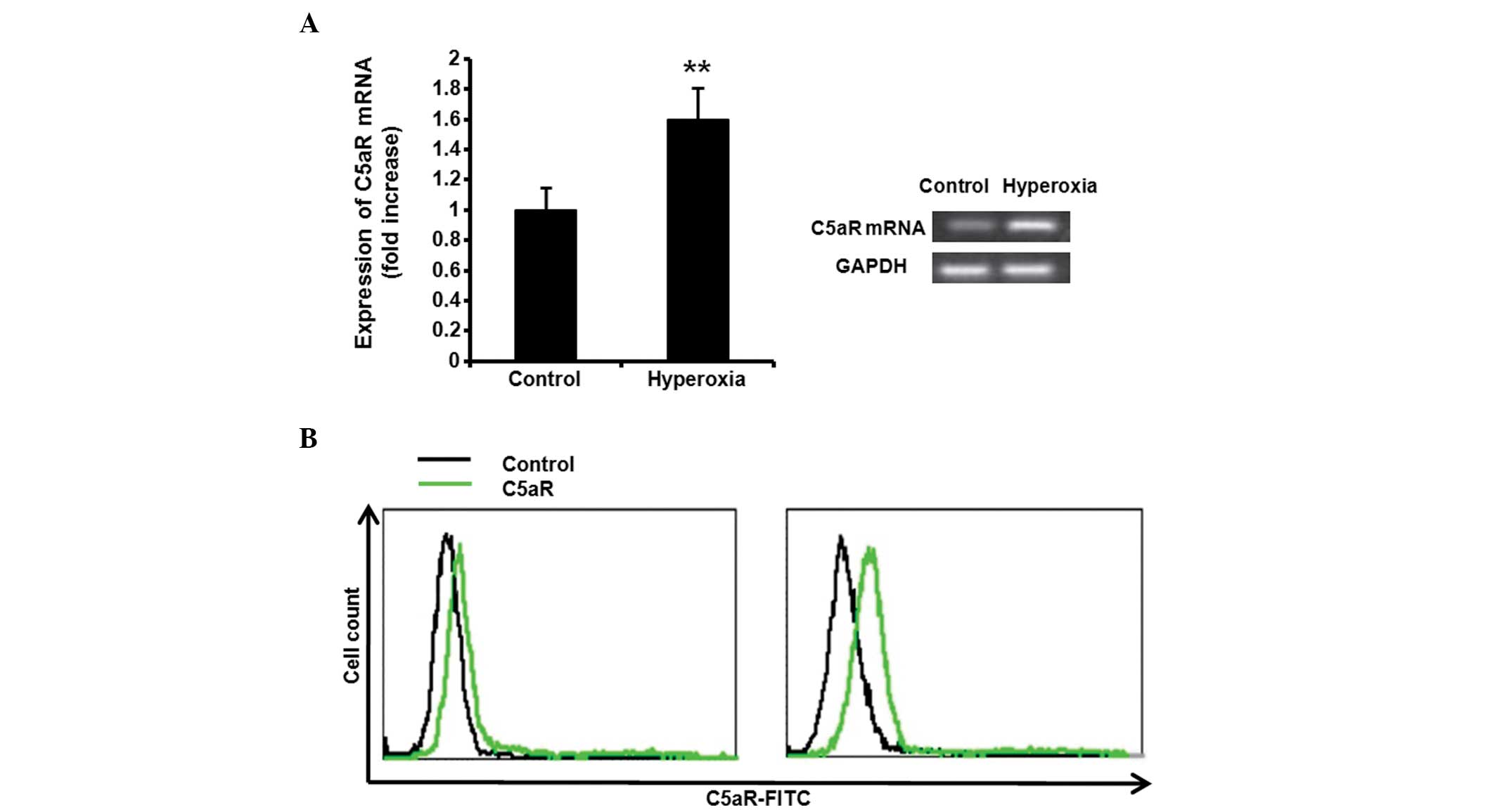
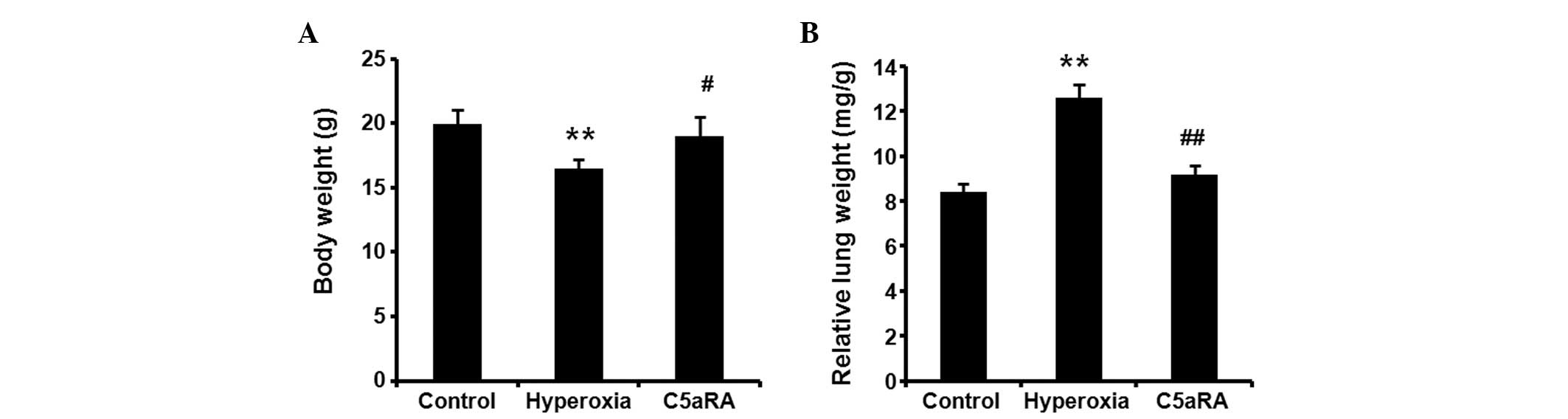
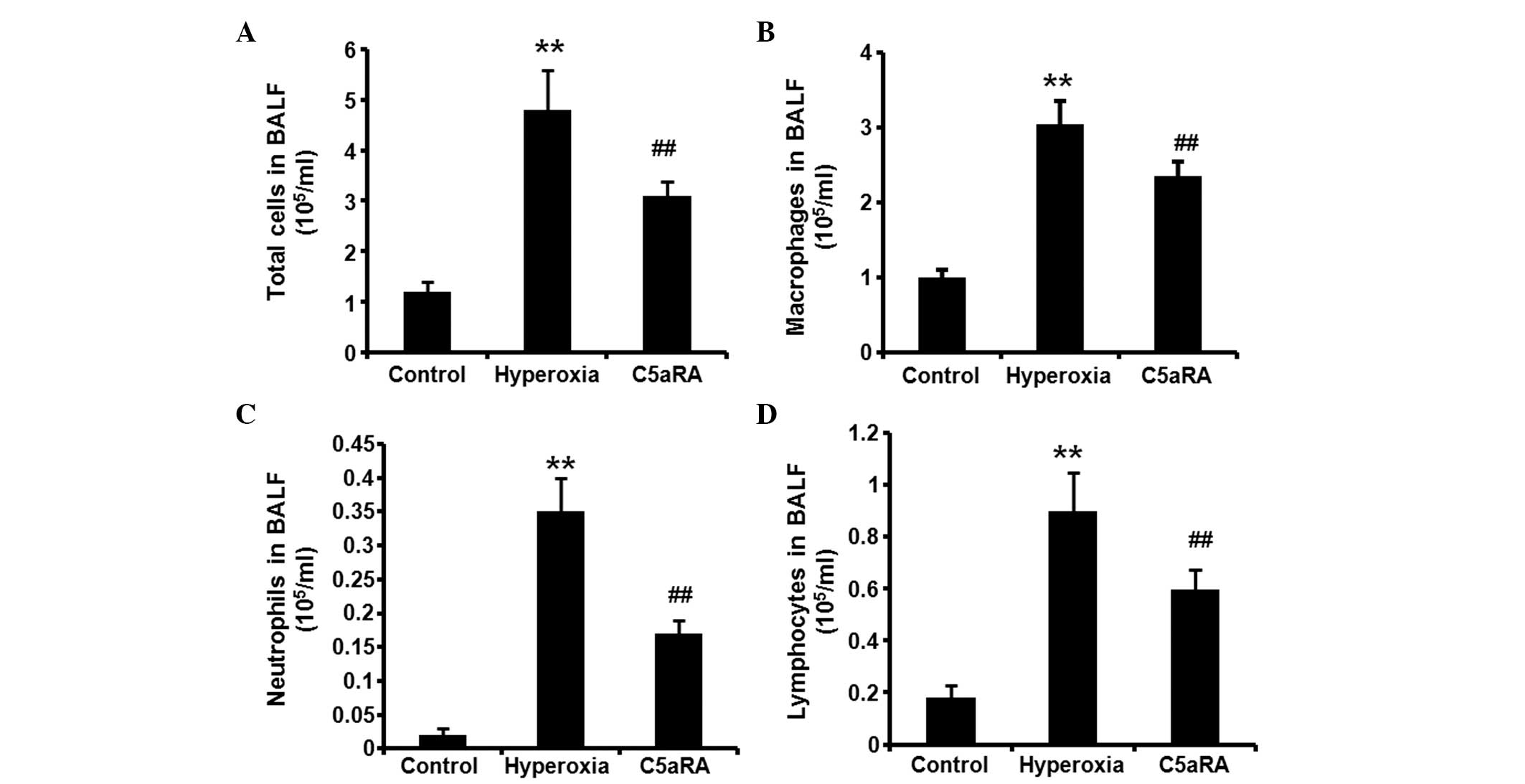
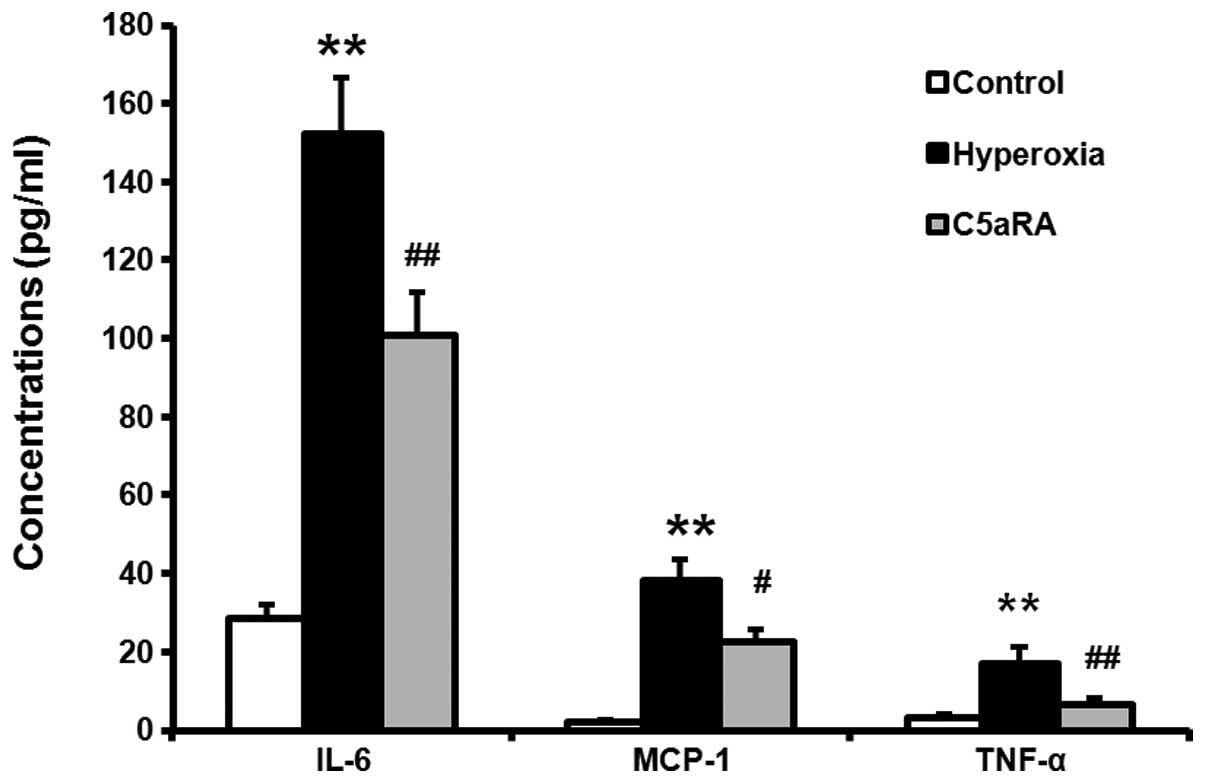
|
1
|
Imakiire K, Uto H, Sato Y, et al:
Difference in serum complement component C4a levels between
hepatitis C virus carriers with persistently normal alanine
aminotransferase levels or chronic hepatitis C. Mol Med Rep.
6:259–264. 2012.
|
|
2
|
Hugli TE: Biochemistry and biology of
anaphylatoxins. Complement. 3:111–127. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shagdarsuren E, Bidzhekov K, Mause SF, et
al: C5a receptor targeting in neointima formation after arterial
injury in atherosclerosis-prone mice. Circulation. 122:1026–1036.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Monk PN, Scola AM, Madala P and Fairlie
DP: Function, structure and therapeutic potential of complement C5a
receptors. Br J Pharmacol. 152:429–448. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vitacca M, Bianchi L, Bazza A and Clini
EM: Advanced COPD patients under home mechanical ventilation and/or
long term oxygen therapy: Italian healthcare costs. Monaldi Arch
Chest Dis. 75:207–214. 2011.
|
|
6
|
Vosdoganes P, Lim R, Koulaeva E, et al:
Human amnion epithelial cells modulate hyperoxia-induced neonatal
lung injury in mice. Cytotherapy. 15:1021–1029. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pushparaj PN, Tay HK, Wang CC, Hong W and
Melendez AJ: VAMP8 is essential in anaphylatoxin-induced
degranulation, TNF-alpha secretion, peritonitis, and systemic
inflammation. J Immunol. 183:1413–1418. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lee H, Whitfeld PL and Mackay CR:
Receptors for complement C5a. The importance of C5aR and the
enigmatic role of C5L2. Immunol Cell Biol. 86:153–160. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mikawa K, Nishina K, Maekawa N and Obara
H: Attenuation of hyperoxic lung injury in rabbits with superoxide
dismutase: effects on inflammatory mediators. Acta Anaesthesiol
Scand. 39:317–322. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takao Y, Mikawa K, Nishina K, Maekawa N
and Obara H: Lidocaine attenuates hyperoxic lung injury in rabbits.
Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 40:318–325. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dolinay T, Wu W, Kaminski N, et al:
Mitogen-activated protein kinases regulate susceptibility to
ventilator-induced lung injury. PLoS One. 3:e16012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rünzi M, Raptopoulos V, Saluja AK, et al:
Evaluation of necrotizing pancreatitis in the opossum by dynamic
contrast-enhanced computed tomography: correlation between
radiographic and morphologic changes. J Am Coll Surg. 180:673–682.
1995.
|
|
13
|
Laemmli UK: Cleavage of structural
proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4.
Nature. 227:680–685. 1970. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kyhse-Andersen J: Electroblotting of
multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid
transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J
Biochem Biophys Methods. 10:203–209. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Manthey HD, Woodruff TM, Taylor SM and
Monk PN: Complement component 5a (C5a). Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
41:2114–2117. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Naik N, Giannini E, Brouchon L and Boulay
F: Internalization and recycling of the C5a anaphylatoxin receptor:
evidence that the agonist-mediated internalization is modulated by
phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain. J Cell Sci.
110:2381–2390. 1997.
|
|
17
|
Sun S, Wang H, Zhao G, et al: Complement
inhibition alleviates paraquat-induced acute lung injury. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 45:834–842. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Rittirsch D, Flierl MA, Day DE, et al:
Acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide is independent of
complement activation. J Immunol. 180:7664–7672. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Levitt JE, Calfee CS, Goldstein BA, Vojnik
R and Matthay MA: Early acute lung injury: criteria for identifying
lung injury prior to the need for positive pressure ventilation.
Crit Care Med. 41:1929–1937. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Janssen WJ, Barthel L, Muldrow A, et al:
Fas determines differential fates of resident and recruited
macrophages during resolution of acute lung injury. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 184:547–560. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Piguet PF, Collart MA, Grau GE, Sappino AP
and Vassalli P: Requirement of tumour necrosis factor for
development of silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Nature.
344:245–247. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jones SA: Directing transition from innate
to acquired immunity: defining a role for IL-6. J Immunol.
175:3463–3468. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wolters PJ, Wray C, Sutherland RE, et al:
Neutrophil-derived IL-6 limits alveolar barrier disruption in
experimental ventilator-induced lung injury. J Immunol.
182:8056–8062. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Halbertsma FJ, Vaneker M, Scheffer GJ and
van der Hoeven JG: Cytokines and biotrauma in ventilator-induced
lung injury: a critical review of the literature. Neth J Med.
63:382–392. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Frank JA, Parsons PE and Matthay MA:
Pathogenetic significance of biological markers of
ventilator-associated lung injury in experimental and clinical
studies. Chest. 130:1906–1914. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Tanaka J, Tajima S, Asakawa K, et al:
Preventive effect of irbesartan on bleomycin-induced lung injury in
mice. Respir Investig. 51:76–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|