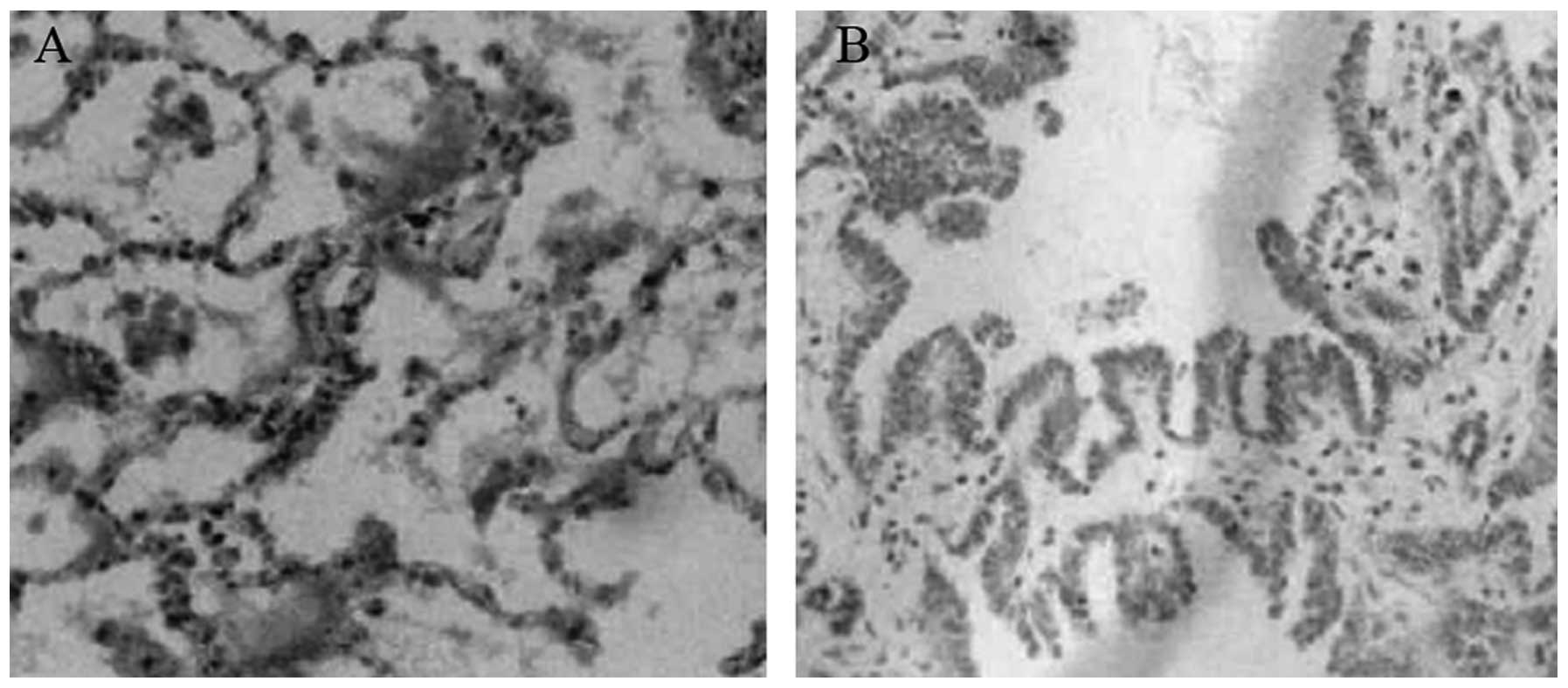
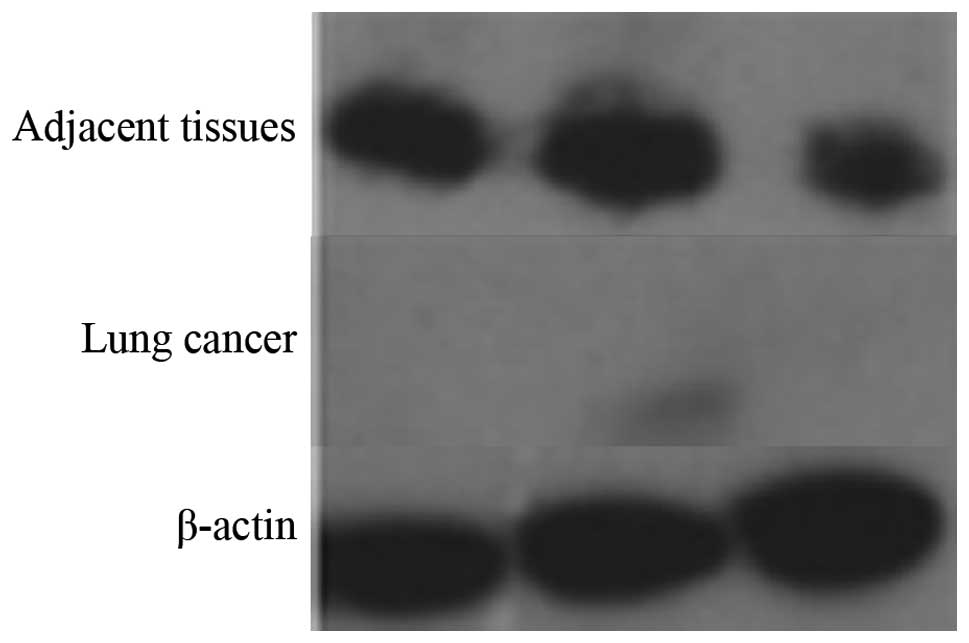
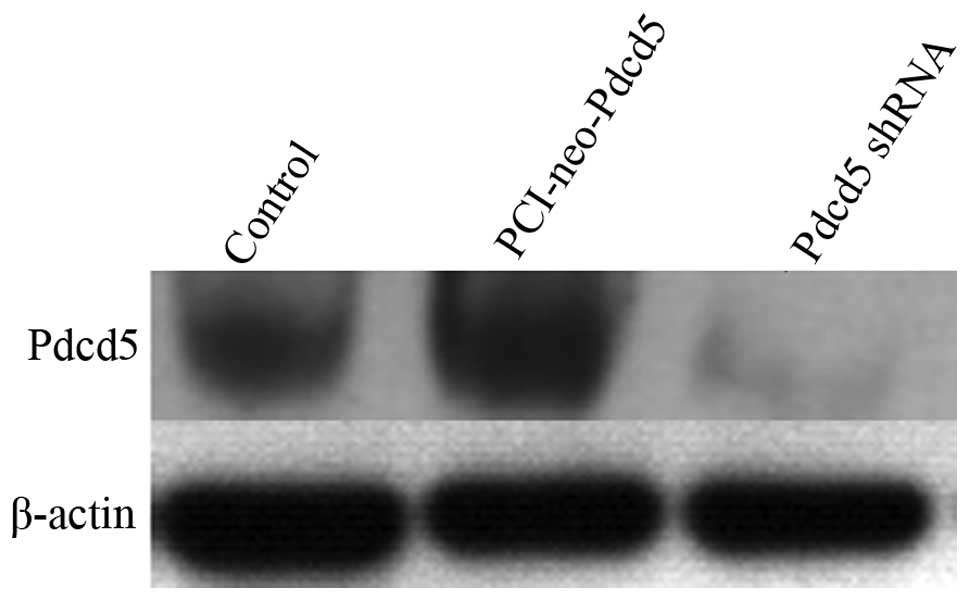
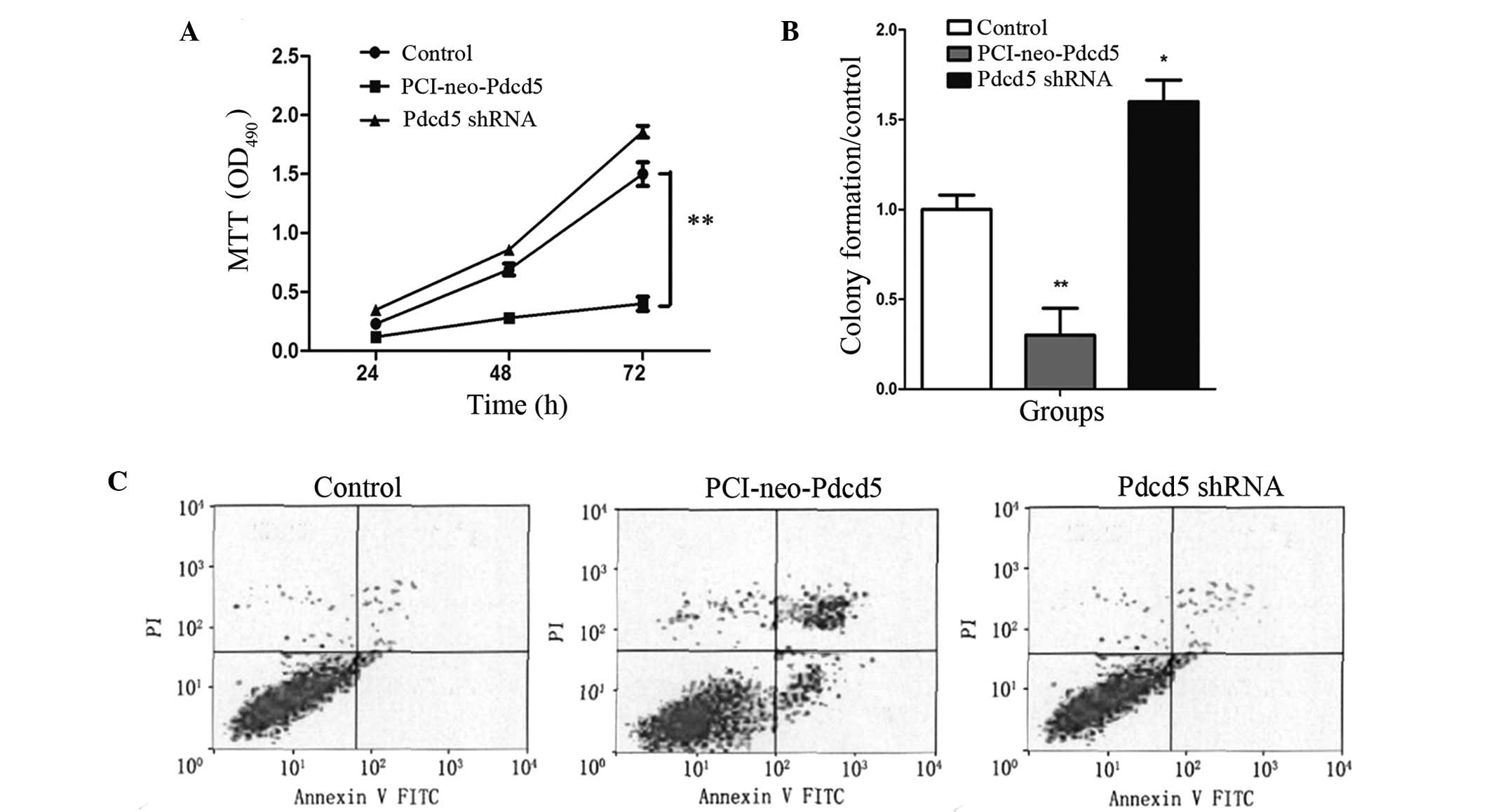
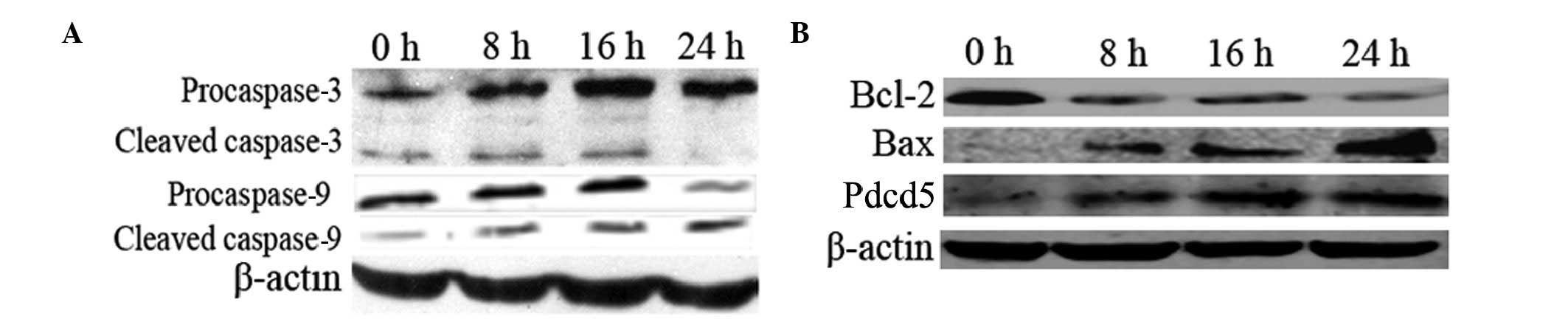
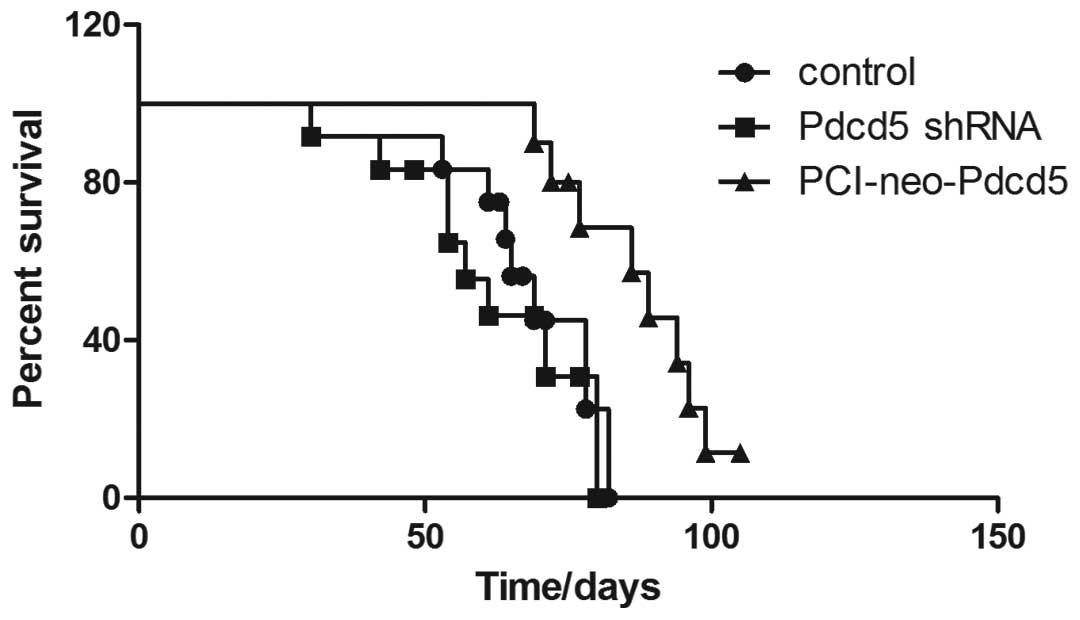
|
1
|
Marshall HM, Bowman RV, Yang IA, Fong KM
and Berg CD: Screening for lung cancer with low-dose computed
tomography: a review of current status. J Thorac Dis. 5:S524–S539.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee PN and Forey BA: Indirectly estimated
absolute lung cancer mortality rates by smoking status and
histological type based on a systematic review. BMC Cancer.
13:1892013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Amorin Kajatt E: Lung cancer: a review of
current knowledge, diagnostic methods and therapeutic perspectives.
Rev Peru Med Exp Salud Publica. 30:85–92. 2013.(In Spanish).
|
|
4
|
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
(CDC). State-specific trends in lung cancer incidence and smoking -
United States, 1999–2008. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 60:1243–1247.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jankovic M, Samarzija M, Jakopovic M,
Kulis T and Znaor A: Trends in lung cancer incidence and mortality
in Croatia, 1988–2008. Croat Med J. 53:93–99. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kern DG, Kern E, Crausman RS and Clapp RW:
A retrospective cohort study of lung cancer incidence in nylon
flock workers, 1998–2008. Int J Occup Environ Health. 17:345–351.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Han R, Zheng R, Zhang S, Wu M and Chen W:
Trend analyses on the differences of lung cancer incidence between
gender, area and average age in China during 1989–2008. Zhongguo
Fei Ai Za Zhi. 16:445–451. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Chang S, Dai M, Ren JS, Chen YH and Guo
LW: Estimates and prediction on incidence, mortality and prevalence
of lung cancer in China in 2008. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi.
33:391–394. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
She J, Yang P, Hong Q and Bai C: Lung
cancer in China: challenges and interventions. Chest.
143:1117–1126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huncharek M, Muscat J and Geschwind JF:
K-ras oncogene mutation as a prognostic marker in non-small cell
lung cancer: a combined analysis of 881 cases. Carcinogenesis.
20:1507–1510. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Suda K, Tomizawa K, Osada H, et al:
Conversion from the ‘oncogene addiction’ to ‘drug addiction’ by
intensive inhibition of the EGFR and MET in lung cancer with
activating EGFR mutation. Lung Cancer. 76:292–299. 2012.
|
|
12
|
You L, He B, Xu Z, et al: Inhibition of
Wnt-2-mediated signaling induces programmed cell death in
non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Oncogene. 23:6170–6174. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu L, Hu J, Zhao Y, et al: PDCD5 interacts
with p53 and functions as a positive regulator in the p53 pathway.
Apoptosis. 17:1235–1245. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liu H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, et al: TFAR19, a
novel apoptosis-related gene cloned from human leukemia cell line
TF-1, could enhance apoptosis of some tumor cells induced by growth
factor withdrawal. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 254:203–210. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen CH, Jiang Z, Yan JH, et al: The
involvement of programmed cell death 5 (PDCD5) in the regulation of
apoptosis in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. CNS Neurosci
Ther. 19:566–576. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao F, Ding L, Zhao M, Qu Z, Huang S and
Zhang L: The clinical significance of reduced programmed cell death
5 expression in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncol Rep.
28:2195–2199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhuge C, Chang Y, Li Y, Chen Y and Lei J:
PDCD5-regulated cell fate decision after
ultraviolet-irradiation-induced DNA damage. Biophys J.
101:2582–2591. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi L, Song Q, Zhang Y, et al: Potent
antitumor activities of recombinant human PDCD5 protein in
combination with chemotherapy drugs in K562 cells. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 396:224–230. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saleem M, Maddodi N, Abu Zaid M, et al:
Lupeol inhibits growth of highly aggressive human metastatic
melanoma cells in vitro and in vivo by inducing apoptosis. Clin
Cancer Res. 14:2119–2127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adhami VM, Siddiqui IA, Ahmad N, Gupta S
and Mukhtar H: Oral consumption of green tea polyphenols inhibits
insulin-like growth factor-I-induced signaling in an autochthonous
mouse model of prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 64:8715–8722. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ahmadian S, Barar J, Saei AA, Fakhree MA
and Omidi Y: Cellular toxicity of nanogenomedicine in MCF-7 cell
line: MTT assay. J Vis Exp. 26:e11912009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Verma A, Prasad KN, Singh AK, Nyati KK,
Gupta RK and Paliwal VK: Evaluation of the MTT lymphocyte
proliferation assay for the diagnosis of neurocysticercosis. J
Microbiol Methods. 81:175–178. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seidl K and Zinkernagel AS: The MTT assay
is a rapid and reliable quantitative method to assess
Staphylococcus aureus induced endothelial cell damage. J
Microbiol Methods. 92:307–309. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishitani H, Sugimoto N, Roukos V, et al:
Two E3 ubiquitin ligases, SCF-Skp2 and DDB1-Cul4, target human Cdt1
for proteolysis. EMBO J. 25:1126–1136. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Peng L, Xu Z, Zhou Y, Yang T, Liang ZQ and
Zhang M: Effect of rosiglitazone on cells cycle, apoptosis and
expression of Skp2 and p27Kip1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell
line. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 18:148–149. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Schulman BA, Carrano AC, Jeffrey PD, et
al: Insights into SCF ubiquitin ligases from the structure of the
Skp1-Skp2 complex. Nature. 408:381–386. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng A, Wang Y, Ma D, Zhou H and Lou S:
Characterization of programmed cell death 5 (PDCD5) gene in human
cartilage and its possible significance. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao.
35:481–484. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Ruan GR, Qin YZ, Chen SS, et al: Abnormal
expression of the programmed cell death 5 gene in acute and chronic
myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 30:1159–1165. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li H, Wang Q, Gao F, et al: Reduced
expression of PDCD5 is associated with high-grade astrocytic
gliomas. Oncol Rep. 20:573–579. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Du YJ, Xiong L, Lou Y, Tan WL and Zheng
SB: Reduced expression of programmed cell death 5 protein in tissue
of human prostate cancer. Chin Med Sci J. 24:241–245. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao F, Ding L, Zhao M, Qu Z, Huang S and
Zhang L: The clinical significance of reduced programmed cell death
5 expression in human gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Oncol Rep.
28:2195–2199. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen C, Zhou H, Xu L, et al: Recombinant
human PDCD5 sensitizes chondrosarcomas to cisplatin chemotherapy in
vitro and in vivo. Apoptosis. 15:805–813. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yin A, Jiang Y, Zhang X, Zhao J and Luo H:
Transfection of PDCD5 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol.
649:120–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|