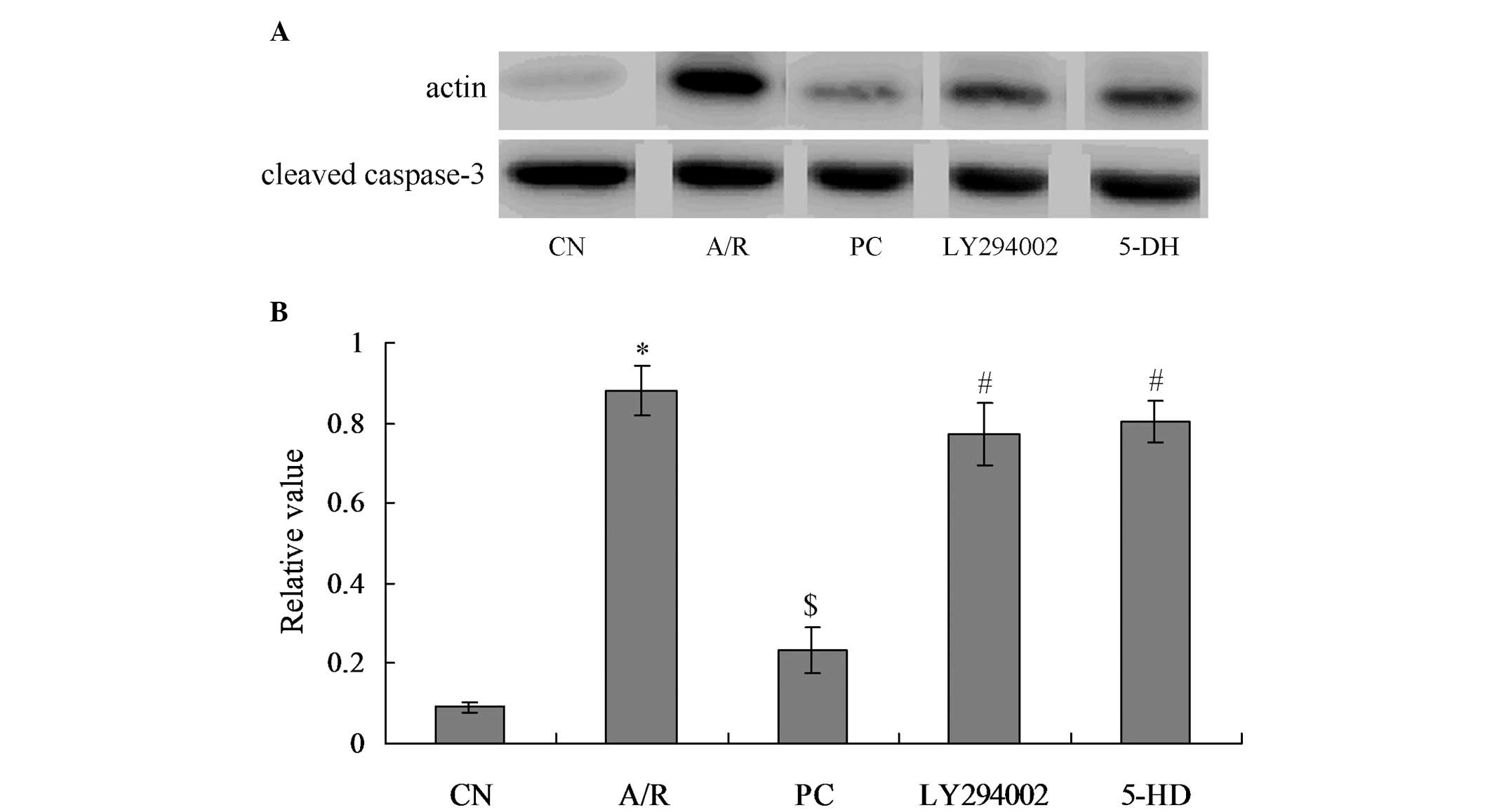
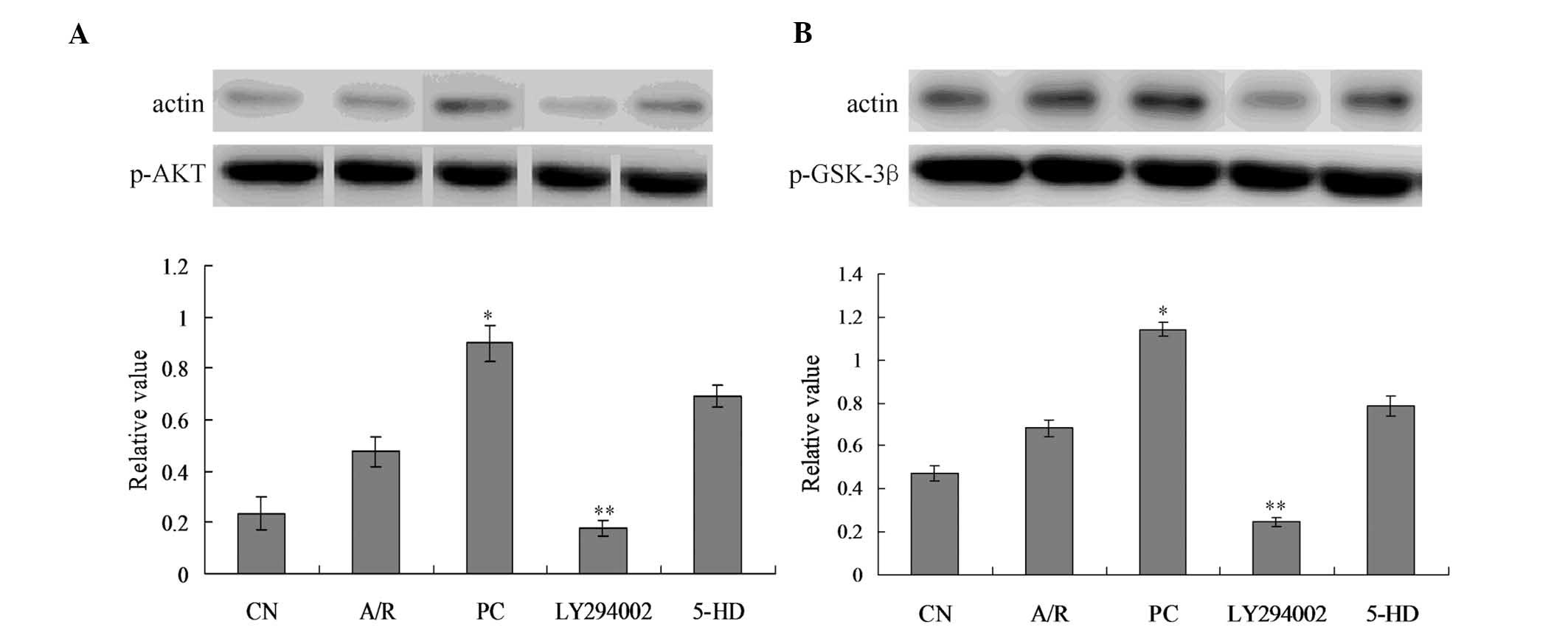
|
1
|
Zhang LN, Liu PP, Zhou J, Huang RS, Yuan
F, Fei LJ, Huang Y, Xu L, Hao LM, Qiu XJ, et al: Positive
correlation between variants of lipid metabolism-related genes and
coronary heart disease. Mol Med Rep. 8:260–266. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang S, Liu X, Goldstein S, Li Y, Ge J,
He B, Fei X, Wang Z and Ruiz G: Role of JAK/STAS signaling pathway
in the pathogenesis of acute myocardial infarction in rats and its
effect on NF-κB expression. Mol Med Rep. 7:93–98. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rao SV, Hess CN, Dai D, Green CL, Peterson
ED and Douglas PS: Temporal trends in percutaneous coronary
intervention outcomes among older patients in the United States. Am
Heart J. 166:273–281. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang N, Min, Li D, He P and Zhao L:
Geranylgeranylacetone protects against myocardial ischemia and
reperfusion injury by inhibiting high-mobility group box 1 protein
in rats. Mol Med Rep. 5:521–524. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Turer AT and Hill JA: Pathogenesis of
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy.
Am J Cardiol. 106:360–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xu Z, Du P, Meiser P and Jacob C:
proanthocyanidins: oligomeric structures with unique biochemical
properties and great therapeutic promise. Nat Prod Commun.
7:381–388. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Louch WE, Sheehan KA and Wolska BM:
Methods in cardiomyocyte isolation, culture, and gene transfer. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 51:288–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cantin M, Ballak M, Beuzeron-Mangina J,
Anand-Srivastava MB and Tautu C: DNA synthesis in cultured adult
cardiocytes. Science. 214:569–570. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Piper HM, Probst I, Schwartz P, Hütter FJ
and Spieckermann PG: Culturing of calcium stable adult cardiac
myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 14:397–412. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Dong CF, Shi Q, Shi S, Wang GR,
Lei YJ, Xu K, An R, Chen JM, Jiang HY, et al: Cytosolic prion
protein induces apoptosis in human neuronal cell SH-SY5Y via
mitochondrial disruption pathway. BMP Rep. 42:444–449. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang W, Shi Q, Xu K, Gao C, Chen C, Li XL,
et al: Familial CJD associated PrP mutants within the transmembrane
region induced Ctm-PrP retention in ER and trigger apoptosis by ER
stress in SH-SY5Y cells. PLoS One. 6:e146022011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang HJ, Kang PF, Wu WJ, Tang Y, Pan QQ,
Ye HW, Tang B, Li ZH and Gao Q: Changes in cardiac mitochondrial
aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 activity in relation to oxidative stress
and inflammatory injury in diabetic rats. Mol Med Rep. 8:686–690.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Decoursey TE and Ligeti E: Regulation and
termination of NADPH oxidase activity. Cell Mol Life Sci.
62:2173–2193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marczin N, E1-Habashi N, Hoare GS, Bundy
RE and Yacoub M: Antioxidants in myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury: therapeutic potential and basic mechanisms. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 420:222–236. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yang H, Fan S, Song D, Wang Z, Ma S, Li S,
Li X, Xu M, Xu M and Wang X: Long-term streptozotocin-induced
diabetes in rats leads to severe damage of brain blood vessels and
neurons via enhanced oxidative stress. Mol Med Rep. 7:431–440.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scarabelli TM, Stephanou A, Pasini E, et
al: Minocycline inhibits caspase activation and reactivation,
increases the ratio of XIAP to smac/DIABLO, and reduces the
mitochondrial leakage of cytochrome C and smac/DIABLO. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 43:865–874. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao ZQ, Morris CD, Budde JM, Wang NP,
Muraki S and Sun HY: Inhibition of myocardial apoptosis reduces
infarct size and improves regional contractile dysfunction during
reperfusion. Cardiovasc Res. 59:132–142. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Arguad L, Gateau-Roesh O, Raisky O,
Loufouat J, Robert D and Ovize M: Postconditioning inhibits
mitochondrial permeability transition. Circulation. 111:194–197.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang X and Huang N: Berberine induces
selective apoptosis through the AMPK-mediated mitochondrial/caspase
pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Mep Rep. 8:505–510.
2013.
|
|
20
|
Assaly R, de Tassigny AD, Paradis S,
Jacquin S, Berdeaux A and Morin D: Oxidative stress, mitochondrial
permeability transition pore opening and cell death during
hypoxia-reoxygenation in adult cardiomyocytes. Eur J Pharmacol.
675:6–14. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bergmann MW, Rechner C, Freund C, Baurand
A, El Jamali A and Dietz R: Statins inhibit reoxygenation-induced
cardiomyocyte apoptosis: role for glycogen synthase kinase 3beta
and transcription factor beta-catenin. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
37:681–690. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu ZL, Mao JH, Peng AF, Yin QS, Zhou Y,
Long XH and Huang SH: Inhibition of fatty acid synthase suppresses
osteosarcoma cell invasion and migration via downregulation of the
PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 7:608–612.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Efthymiou CA, Mocanu MM and Yellon DM:
Atorvastatin and myocardial reperfusion injury: new pleiotropic
effect implicating multiple prosurvival sinaling. J Cardiovasc
Pharmac. 45:247–252. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Abdallah Y, Wolf C, Meuter K, Piper HM,
Reusch HP and Ladilov Y: Preconditioning with diazoxide prevents
reoxygenation-induced rigor-type hypercontracture. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 48:270–276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alizadeh AM, Faghihi M, Khori V, Sohanaki
H, Pourkhalili K, Mohammadghasemi F and Mohsenikia M: Oxytocin
protects cardiomyocytes from apoptosis induced by
ischemia-reperfusion in rat heart: role of mitochondrial
ATP-dependent potassium channel and permeability transition pore.
Peptides. 36:71–77. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Grossini E, Pollesello P, Bellofatto K, et
al: Protective effects elicited by levosimendan against liver
ischemia/reperfusion injury in anesthetized rats. Liver Transpl.
20:361–375. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Amani M, Jeddi S, Ahmadiasl N, Usefzade N
and Zaman J: Effect of HEMADO on level of CK-MB and LDH enzymes
after ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart.
Bioimpacts. 3:101–104. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zeng Z, Huang HF, He F, et al: Diazoxide
attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury via upregulation of heme
oxygenase-1 after liver transplantation in rats. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:1765–1772. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sato M, Maulik G, Ray PS, Bagchi D and Das
DK: Cardioprotective effects of grape seed proanthocyanidin against
ischemic reperfusion injury. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 31:1289–1297.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Qiu J, Zhao S, You B, Ji X, Wang Y,
Cui X, Wang Q and Gao H: Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract
alleviates ouabain-induced vascular remodeling through regulation
of endothelial function. Mol Med Rep. 6:949–954. 2012.
|