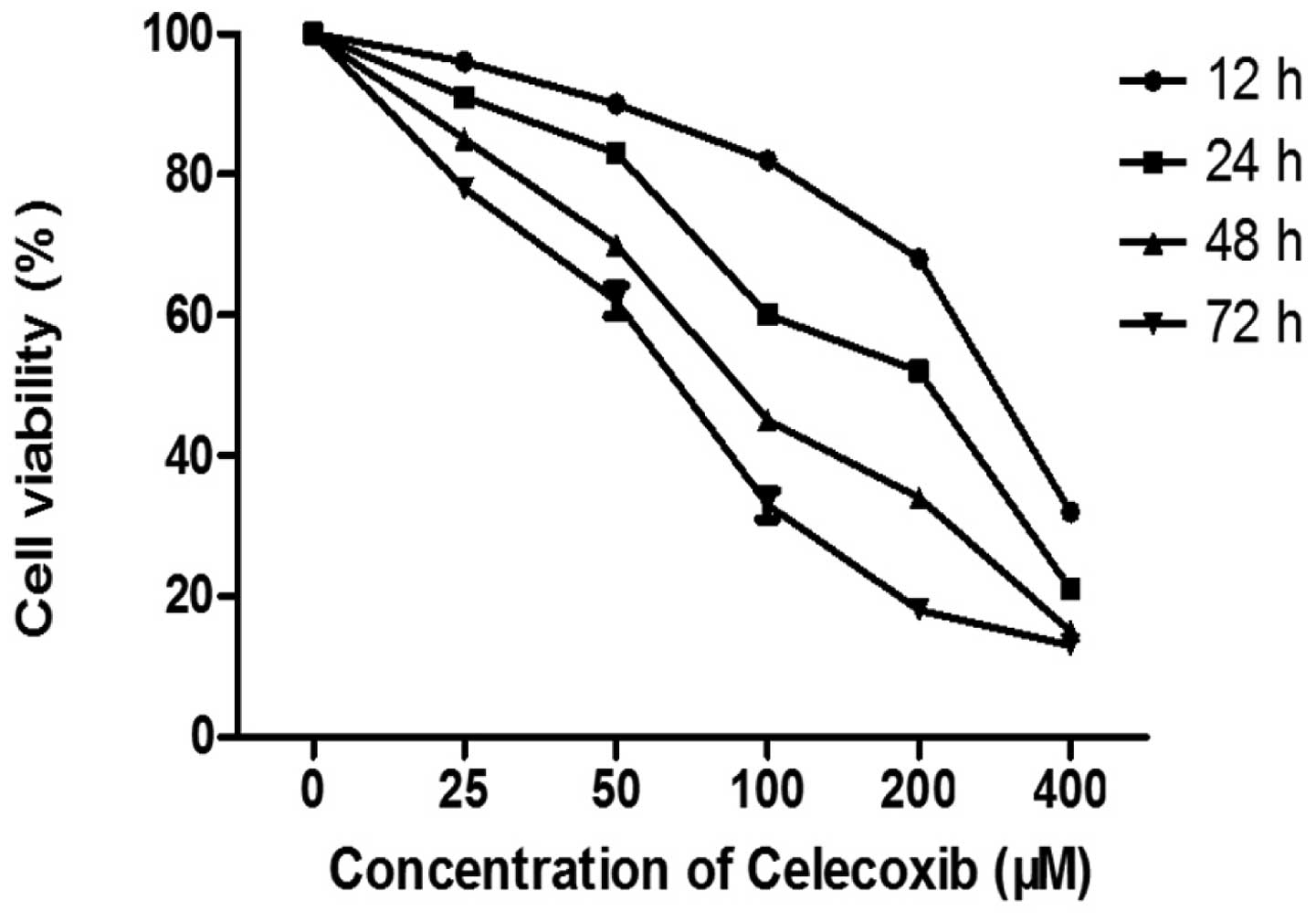
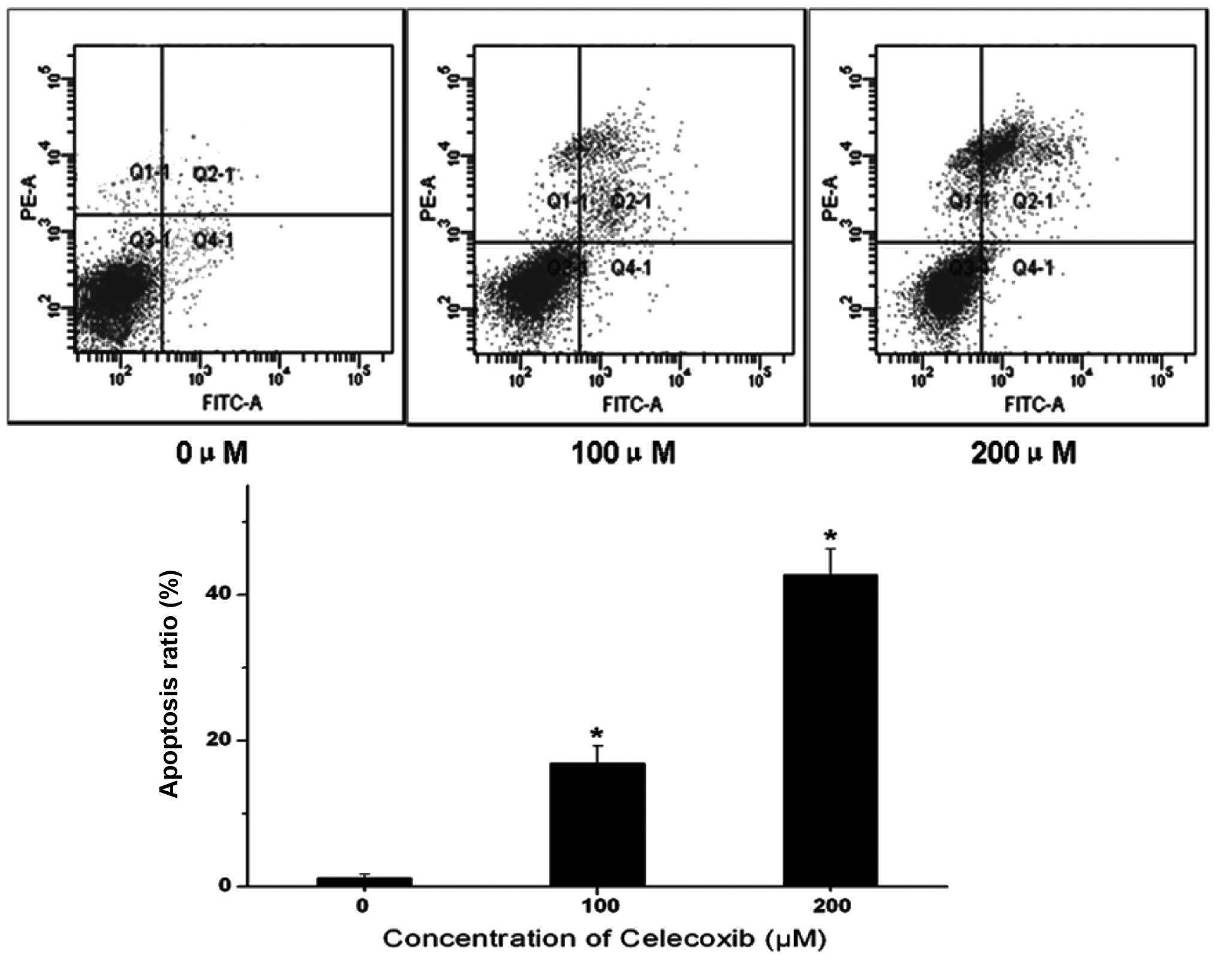
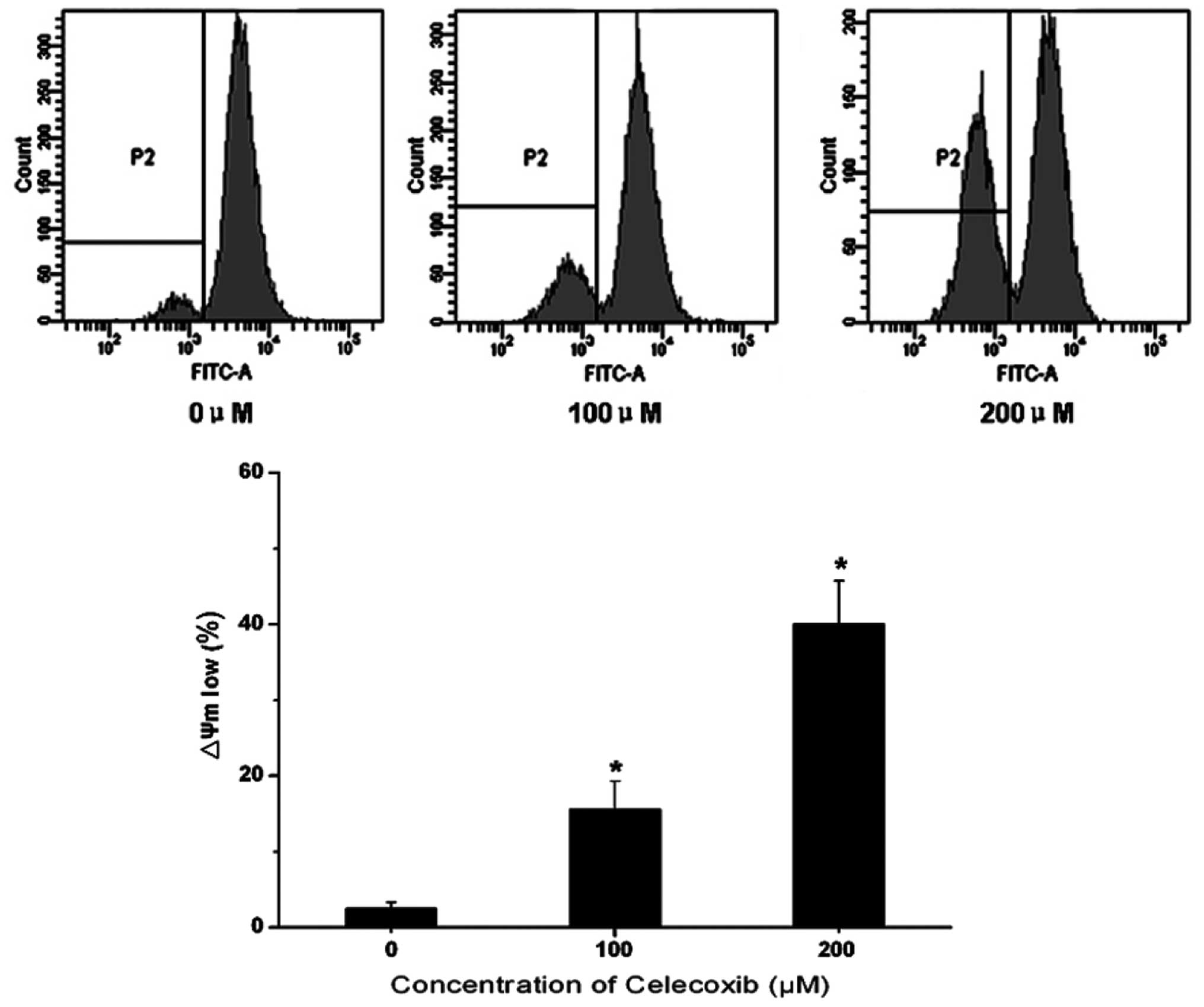
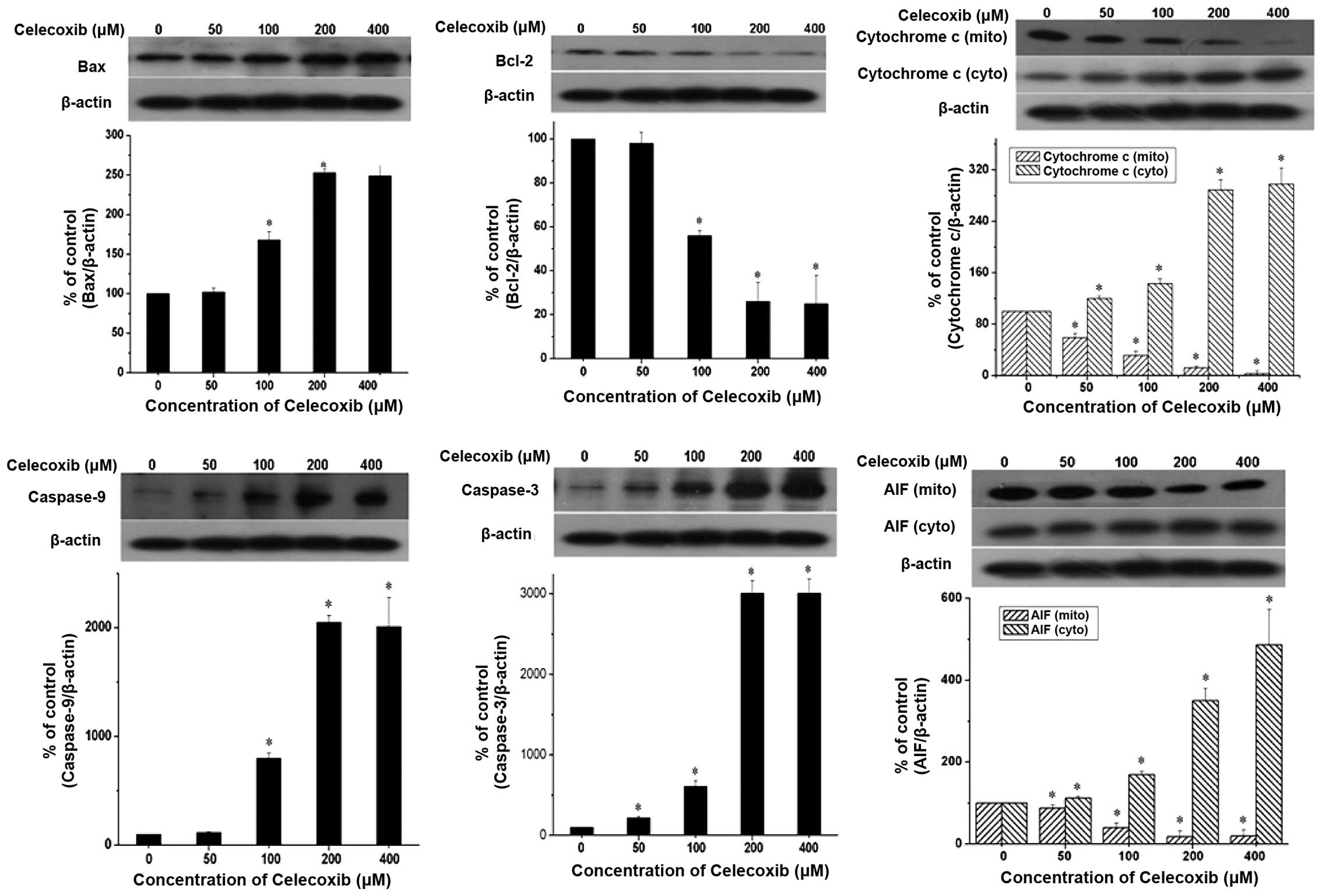
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Grivennikov SI, Greten FR and Karin M:
Immunity, inflammation, and cancer. Cell. 140:883–899. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Raoul JL, Sangro B, Forner A, et al:
Evolving strategies for the management of intermediate-stage
hepatocellular carcinoma: available evidence and expert opinion on
the use of transarterial chemoembolization. Cancer Treat Rev.
37:212–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fort J: Celecoxib, a COX-2-specific
inhibitor: the clinical data. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 28(3
Suppl): 13–18. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chakraborti AK, Garg SK, Kumar R, et al:
Progress in COX-2 inhibitors: a journey so far. Curr Med Chem.
17:1563–1593. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Xie SQ, Zhang YH, Li Q, et al:
COX-2-independent induction of apoptosis by celecoxib and polyamine
naphthalimide conjugate mediated by polyamine depression in
colorectal cancer cell lines. Int J Colorectal Dis. 27:861–868.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang ZL, Fan ZQ, Jiang HD, et al:
Selective Cox-2 inhibitor celecoxib induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in human lung cancer cells via activating MEK-ERK
signaling. Carcinogenesis. 34:638–646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bocca C, Bozzo F, Bassignana A and
Miglietta A: Antiproliferative effects of COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib
on human breast cancer cell lines. Mol Cell Biochem. 350:59–70.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bastos-Pereira AL, Lugarini D, de
Oliveira-Christoff A, et al: Celecoxib prevents tumor growth in an
animal model by a COX-2 independent mechanism. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 65:267–276. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang AH, Tian XY, Yu JJ, et al: Celecoxib
radiosensitizes the human cervical cancer HeLa cell line via a
mechanism dependent on reduced cyclo-oxygenase-2 and vascular
endothelial growth factor C expression. J Int Med Res. 40:56–66.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jendrossek V: Targeting apoptosis pathways
by Celecoxib in cancer. Cancer Lett. 332:313–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bruix J and Sherman M: American
Association for the Study of Liver Diseases: Management of
hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology. 53:1020–1022.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schattenberg JM, Schuchmann M and Galle
PR: Cell death and hepatocarcinogenesis: Dysregulation of apoptosis
signaling pathways. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26(Suppl 1): 213–219.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tan TT and White E: Therapeutic targeting
of death pathways in cancer: mechanisms for activating cell death
in cancer cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 615:81–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fulda S and Debatin KM: Extrinsic versus
intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene.
25:4798–4811. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu Z, Zhang M, Lv X, et al: The inhibitory
effect of celecoxib on mouse hepatoma H22 cell line on the
arachidonic acid metabolic pathway. Biochem Cell Biol. 88:603–609.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Dai ZJ, Ma XB, Kang HF, et al: Antitumor
activity of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, celecoxib, on
breast cancer in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Cell Int. 12:532012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maier TJ, Schilling K, Schmidt R, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-dependent and -independent
anticarcinogenic effects of celecoxib in human colon carcinoma
cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 67:1469–1478. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cervello M, Bachvarov D, Cusimano A, et
al: COX-2-dependent and COX-2-independent mode of action of
celecoxib in human liver cancer cells. OMICS. 15:383–392. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin MT, Lee RC, Yang PC, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 inducing Mcl-1-dependent survival mechanism in
human lung adenocarcinoma CL1.0 cells. Involvement of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway. J Biol Chem.
276:48997–49002. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan YX, Li WZ, Huang YQ, et al: The COX-2
inhibitor Celecoxib enhances the sensitivity of KB/VCR oral cancer
cell lines to Vincristine by down-regulating P-glycoprotein
expression and function. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat.
97:29–35. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Grosch S, Maier TJ, Schiffmann S and
Geisslinger G: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)-independent
anticarcinogenic effects of selective COX-2 inhibitors. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 98:736–747. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Pyrko P, Soriano N, Kardosh A, et al:
Downregulation of survivin expression and concomitant induction of
apoptosis by celecoxib and its non-cyclooxygenase-2-inhibitory
analog, dimethyl-celecoxib (DMC), in tumor cells in vitro
and in vivo. Mol Cancer. 5:192006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rudner J, Elsaesser SJ, Müller AC, et al:
Differential effects of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family members Mcl-1,
Bcl-2, and Bcl-xL on celecoxib-induced apoptosis. Biochem
Pharmacol. 79:10–20. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Johnson AJ, Hsu AL, Lin HP, et al: The
cyclo-oxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib perturbs intracellular
calcium by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
Ca2+-ATPases: a plausible link with its anti-tumour
effect and cardiovascular risks. Biochem J. 366:831–837.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rahman M, Selvarajan K, Hasan MR, et al:
Inhibition of COX-2 in colon cancer modulates tumor growth and
MDR-1 expression to enhance tumor regression in therapy-refractory
cancers in vivo. Neoplasia. 14:624–633. 2012.
|
|
27
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ricote M, Li AC, Willson TM, et al: The
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma is a negative
regulator of macrophage activation. Nature. 391:79–82. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Birnbaum Y, Long B, Qian J, et al:
Pioglitazone limits myocardial infarct size, activates Akt, and
upregulates cPLA2 and COX-2 in a PPAR-gamma-independent manner.
Basic Res Cardiol. 106:431–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lin Y, Bai L, Chen W and Xu S: The
NF-kappaB activation pathways, emerging molecular targets for
cancer prevention and therapy. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:45–55.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang M, Xu ZG, Shi Z, et al: Inhibitory
effect of celecoxib in lung carcinoma by regulation of
cyclooxygenase-2/cytosolic phospholipase A2 and
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Mol Cell Biochem.
355:233–240. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|