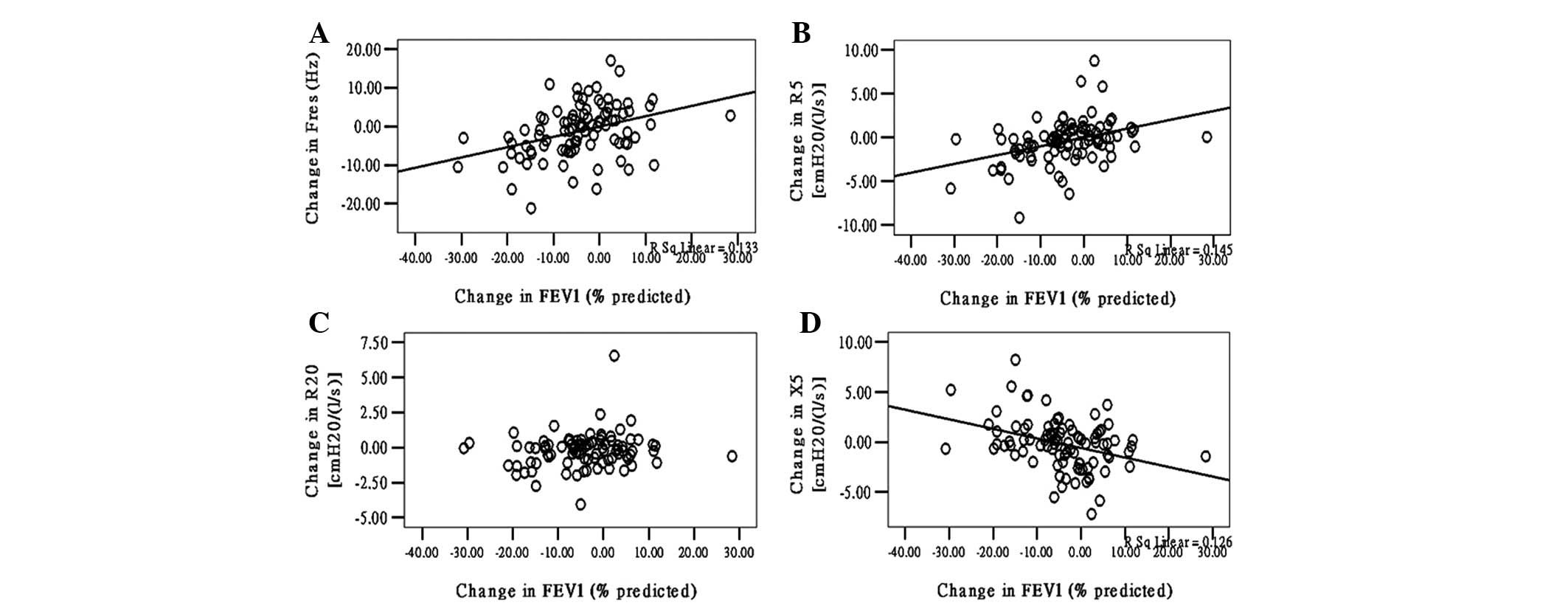
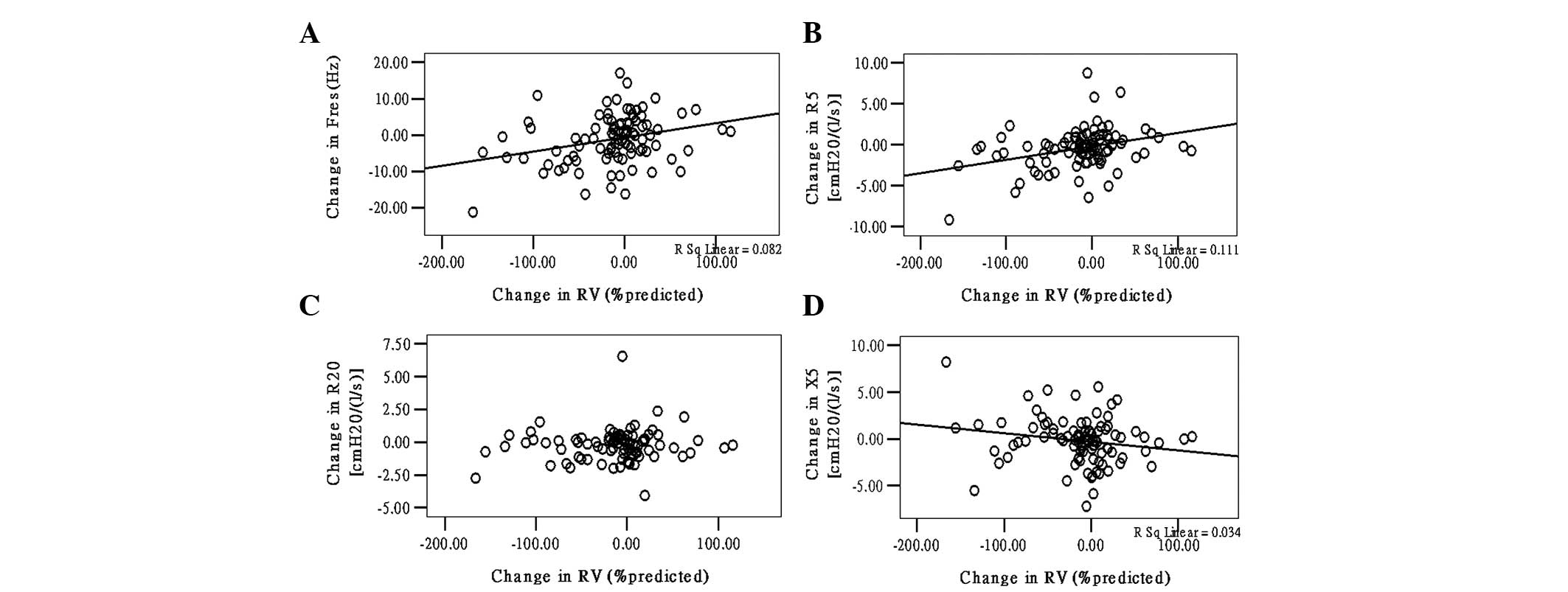
|
1
|
Rabe KF, Hurd S, Anzueto A, et al: Global
strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 176:532–555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cogswell JJ: Forced oscillation technique
for determination of resistance to breathing in children. Arch Dis
Child. 48:259–266. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dubois AB, Brody AW, Lewis DH, et al:
Oscillation mechanics of lungs and chest in man. J Appl Phys.
8:587–594. 1956.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van Noord JA, Clément J, Van de Woestijne
KP, et al: Total respiratory resistance and reactance in patients
with asthma, chronic bronchitis, and emphysema. Am Rev Respir Dis.
143:922–927. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zerah F, Lorino AM, Lorino H, et al:
Forced oscillation technique vs spirometry to assess
bronchodilatation in patients with asthma and COPD. Chest.
108:41–47. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Di Mango AM, Lopes AJ, Jansen JM, et al:
Changes in respiratory mechanics with increasing degrees of airway
obstruction in COPD: detection by forced oscillation technique.
Respir Med. 100:399–410. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goldman MD: Clinical application of forced
oscillation. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 14:341–350. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hellinckx J, Cauberghs M, De Boeck K, et
al: Evaluation of impulse oscillation system: comparison with
forced oscillation technique and body plethysmography. Eur Respir
J. 18:564–570. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
MacLeod D and Birch M: Respiratory input
impedance measurement: forced oscillation methods. Med Biol Eng
Comput. 39:505–516. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dellacà RL, Santus P, Aliverti A, et al:
Detection of expiratory flow limitation in COPD using the forced
oscillation technique. Eur Respir J. 23:232–240. 2004.
|
|
11
|
Dellacà RL, Rotger M, Aliverti A, et al:
Noninvasive detection of expiratory flow limitation in COPD
patients during nasal CPAP. Eur Respir J. 27:983–991.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dellacà RL, Duffy N, Pompilio PP, et al:
Expiratory flow limitation detected by forced oscillation and
negative expiratory pressure. Eur Respir J. 29:363–374.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Houghton CM, Woodcock AA and Singh D: A
comparison of lung function methods for assessing dose-response
effects of salbutamol. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 58:134–141. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Houghton CM, Woodcock AA and Singh D: A
comparison of plethysmography, spirometry and oscillometry for
assessing the pulmonary effects of inhaled ipratropium bromide in
healthy subjects and patients with asthma. Br J Clin Pharmacol.
59:152–159. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Borrill ZL, Houghton CM, Woodcock AA, et
al: Measuring bronchodilation in COPD clinical trials. Br J Clin
Pharmacol. 59:379–384. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Park JW, Lee YW, Jung YH, et al: Impulse
oscillometry for estimation of airway obstruction and
bronchodilation in adults with mild obstructive asthma. Ann Allergy
Asthma Immunol. 98:546–552. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Al-Mutairi SS, Sharma PN, Al-Alawi A, et
al: Impulse oscillometry: an alternative modality to the
conventional pulmonary function test to categorise obstructive
pulmonary disorders. Clin Exp Med. 7:56–64. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Clément J, Làndsér FJ and Van de Woestijne
KP: Total resistance and reactance in patients with respiratory
complaints with and without airways obstruction. Chest. 83:215–220.
1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kolsum U, Borrill Z, Roy K, et al: Impulse
oscillometry in COPD: Identification of measurements related to
airway obstruction, airway conductance and lung volumes. Respir
Med. 103:136–143. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lándsér FJ, Nagles J, Demedts M, et al: A
new method to determine frequency characteristics of the
respiratory system. J Appl Physiol. 41:101–106. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duiverman EJ, Neijens HJ, Van der Snee-van
Smaalen M, et al: Comparison of forced oscillometry and forced
expirations for measuring dose-related responses to inhaled
methacholine in asthmatic children. Bull Eur Physiopathol Respir.
22:433–436. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ortiz G and Menendez R: The effects of
inhaled albuterol and salmeterol in 2- to 5-year-old asthmatic
children as measured by impulse oscillometry. J Asthma. 39:531–536.
2002.
|