Introduction
Cancer of the head and neck is the sixth most common
type of cancer worldwide (1).
Histopathologically, squamous cell carcinoma accounts for >90%
of all head and neck cancers (2,3). The
predominant risk factors of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
(HNSCC) are tobacco and alcohol consumption, which exert a
synergistic effect (4,5). In addition, studies have demonstrated
that human papillomavirus is involved in head and neck cancers
(3,6).
The poor prognosis associated with HNSCC is
primarily due to local invasion, and regional and/or distant
metastatic spread. Surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are
conventional approaches for the treatment of HNSCC; however, the
five-year survival rate is not satisfactory (1). Certain novel approaches, including
minimally invasive surgery (7),
targeted molecular therapy (8),
gene therapy (9) and immunotherapy
(10), have been evaluated in
order to identify a more efficient treatment. These novel therapy
approaches have been promising, but the majority have remained in
the early stages of research. Long-term investigation and safety
evaluations are required for clinical application of these
approaches in HNSCC treatment. Further investigation of the
mechanisms of HNSCC carcinogenesis and identification of key
factors and molecules involved in HNSCC development and progress
may aid in improving HNSCC treatment and reducing mortality.
Head and neck cancer occurs through a complex
multistage process, in which carcinogen exposure, through
activities such as cigarette and alcohol use, as well as host
genetic susceptibility are involved (11). While a number of risk factors have
been identified, mainly determined by epidemiological studies, the
underlying mechanisms of HNSCC carcinogenesis remain elusive.
Activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor, or signal
transducers and activators of transcription signaling pathways, and
the subsequent overexpression of oncogenes have been demonstrated
to contribute to the development and progression of HNSCC (12). In addition, inactivation of tumor
suppressor genes, including p27 (13), p16 (14) and FHIT (15), may also contribute to HNSCC
pathogenesis.
Ubiquitin-specific peptidase 22 (USP22) is a member
of the deubiquitinating enzyme (DUB) gene family and exhibits low
expression in a variety of normal human tissues (16). As a type of DUB, USP22 is the
predominant component of the human Spt-Ada-Gcn5-acetyltransferase
complex and is required for activating transcription and cell cycle
progression by regulating ubiquitination and inducing the
acetylation of certain histones (17). This may further activate
transcription and translation of a number of cancer-associated
genes (17). Overexpression of
USP22 was identified in tumors derived from different tissues, as
determined by DNA microarray analyses (18). In addition, the expression levels
of USP22 were highly correlated with risk of tumor metastasis and
patient prognosis (19). Silencing
of USP22, accomplished with small interfering RNAs (siRNAs),
significantly inhibited tumor cell proliferation and cell cycle
arrest (20,21). At present, the pattern of
expression and the involvement of USP22 in pharyngeal squamous cell
carcinoma is largely unknown. Therefore, in the present study, the
expression levels and role of USP22 in pharyngeal squamous cell
carcinoma tissues and tumor cell lines were investigated.
Materials and methods
Materials
Four sets of pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
tissues and normal tissues adjacent to the cancer cells were
collected from patients with pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
(the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University,
Guangzhou, China) and stored at −80°C for isolation of total RNA
and proteins. The SAS, CAL-33, FaDu, HSC-4, UTSCC-5 and UTSCC-8
human pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines were purchased
from the American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA).
TRIzol, Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium, fetal bovine serum
(FBS), penicillin and streptomycin were purchased from Invitrogen
Life Technologies (Carlsbad, CA, USA). MTT and dimethyl sulfoxide
(DMSO) were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). The
6-, 24- and 96-well plates were purchased from Corning Inc. (Acton,
NY, USA). The reverse transcription kit and 5-bromo-2-deoxyuridine
(BrdU) incorporation cell proliferation kit were supplied by
Promega (Madison, WI, USA). Retinoblastoma (Rb), phospho (p)-Rb,
P21, P27 and tubulin antibodies were purchased from Cell Signaling
Technology, Inc. (Beverly, MA, USA). Polymerase chain reaction
(PCR) primers for USP22 were synthesized by Shanghai Invitrogen
Corporation (Shanghai, China). The green fluorescence protein,
enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL) kit and lentivirus expression
systems were purchased from Guangzhou Yongnuo Biotechnology Limited
Company (Guangzhou, China). The research protocol was approved by
the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Sun Yat-sen
University of Medical Sciences (Guangzhou, China) and all patients
provided written informed consent.
Culture and passage of human pharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines
Pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines were
cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS, 100 U/ml penicillin and 0.1
mg/ml streptomycin at 37°C with 5% CO2 and a relative
humidity of 95%. The cells were passaged every 2–4 days and cells
in the exponential growth phase were used in the experiment.
Evaluation of cell viability using an MTT
assay
FaDu cells in the exponential growth phase
(3×104 cells/ml) were seeded into 96-well plates.
Subsequently, 10 μl MTT (5 mg/m1) was added into each well and the
cells were incubated for 4 h. The supernatant was subsequently
removed and DMSO (100 μl/well) was added to terminate the reaction.
The absorbance value at 570 nm was measured using a microplate
reader (Model 680; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA).
Western blot analysis
The frozen pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
tissues and the adjacent normal tissues were homogenized and
digested using radioimmunoprecipitation assay lysis buffer (Sigma
Aldrich). The lysate was centrifuged at 4°C and 14,000 g for 30
min, whereupon the supernatant was collected and the protein
quantities measured using the Bradford method. FaDu cells with and
without USP22 knockdown, as determined by lentiviral-delivered
siRNA, were cultured in six-well plates for 48 h in order to
achieve 80% confluence. The cells were then collected and lysed.
Protein quantitation was determined with the Bradford method.
Subsequently, the proteins were transferred to polyvinylidene
difluoride membranes and electrophoresed at 100 V for 1 h. The
membranes were blocked with 0.5% (w/v) non-fat milk at 4°C for 1 h
and incubated with primary antibodies (mouse anti-USP22 and
-Tubulin; 1:1,000 dilution; Sigma Aldrich) overnight. The membrane
was washed twice with 0.1% (v/v) Tris-buffered saline and Tween 20,
and incubated with secondary antibodies (goat anti-mouse polyclonal
IgG; 1:1,000 dilution; Jackson ImmunoResearch Laboratories, Inc.,
West Grove, PA, USA) at room temperature for 1 h. The membrane was
developed using ECL, subsequent to being washed three times.
Quantitative polymerase chain reaction
(qPCR) assay
Total RNA was isolated from tissues and cancer cell
lines using TRIzol and was then reversely transcribed to cDNA,
using RNA reverse transcription kits (Fermentas, Waltham, MA, USA).
PCR was performed using the following USP22 primers: Forward
5′-GTGGCACAGTCTCGGCTCAC-3′ and reverse 5′-TGGCTCACGCCTATAATCCC-3′
under the following conditions: 94°C for 5 min; 94°C for 30 sec,
60°C for 30 sec, 72°C for 45 sec and 25 amplification cycles; 72°C
for 10 min. The PCR products were analyzed using electrophoresis in
2% agarose gels.
Construction and siRNA transfection
The following USP22 interference sequences were
designed using the DEQOR program (22): si-USP22-1,
5′-GCAAGGCCAAGTCCTGTAT-3′ and si-USP22-2,
5′-GGAGAAAGATCACCTCGAA-3′. Loops were added to the two fragments to
form a complementary structure. The complementary fragment was then
inserted into the pLL3.7 vector (a specific RNA interference vector
containing a U6 promoter; Forevergen, Guangzhou, China.) following
digestion with XhoI and HpaI restriction enzymes
(Fermentas). Clones were isolated and sent for DNA sequencing to
select vectors containing siRNA.
The constructed interference vectors
pLL-USP22-1-siRNA and pLL-USP22-2-siRNA, as well as the
corresponding control vector (without siRNA fragments), were mixed
with packaging plasmids (pGag/Pol, pRev and pVSV-G, respectively;
Fermentas), and co-transfected into FaDu cells (Invitrogen Life
Technologies) with Lipofectamine™ 2000. The successfully
transfected cells were identified using enhanced green fluorescent
protein fluorescence (Forevergen). Following confirmation of
successful transfection, the cells and supernatant were collected
at 72 h and centrifuged at 40,000 g for 120 min. The virus-infected
cells were then subjected to G418 screening (Mediatech Inc.,
Manassas, VA, USA) to obtain laryngeal squamous carcinoma cells
with stable USP22 interference.
Statistical analysis
SPSS statistical software 19.0 (SPSS, Inc., Chicago,
IL, USA) was used for statistical analysis. Values are presented as
the mean ± standard deviation. One-way analysis of variance was
used to compare the mean values of multiple groups and P<0.05
was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
USP22 mRNA and protein expression levels
in pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma tissues
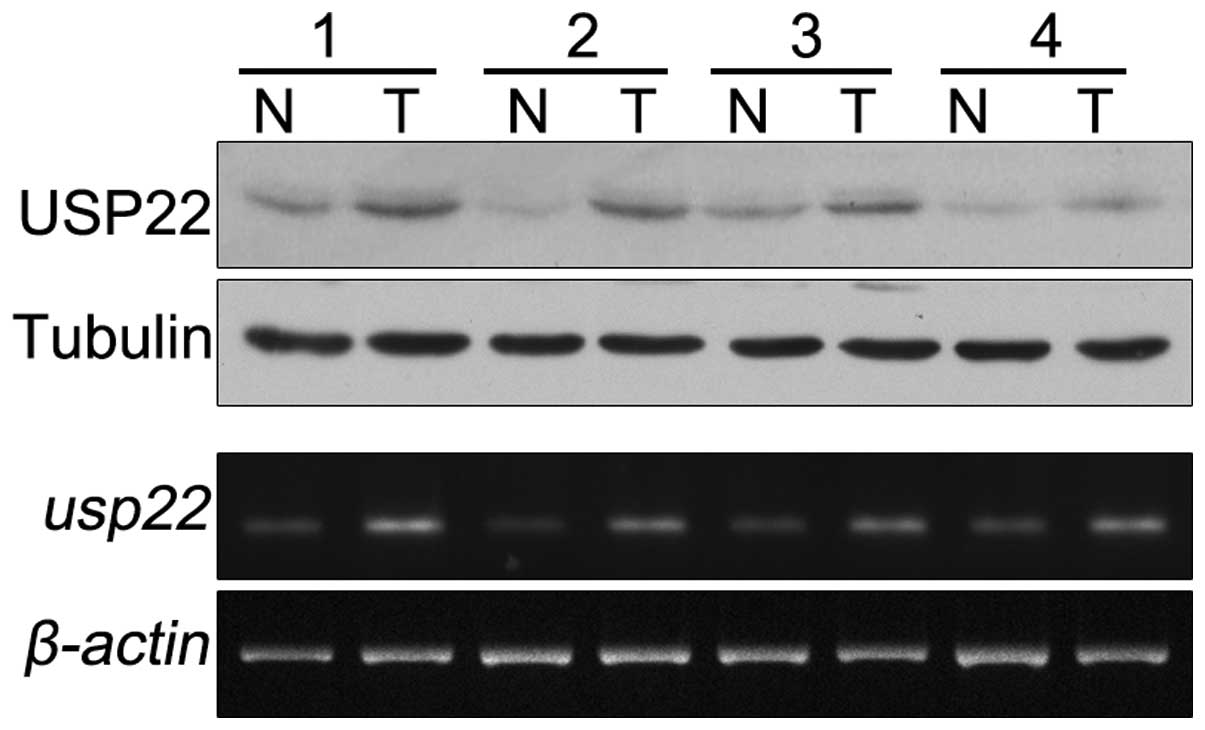
Four pairs of pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
tissues and the adjacent normal mucosa tissues were included to
evaluate USP22 protein and mRNA expression levels using western
blot and qPCR analyses. As shown in Fig. 1, the expression levels of USP22
protein and mRNA were increased in human pharyngeal squamous cell
carcinoma tissues (T) compared with adjacent normal mucosal tissues
(N).
Detection of USP22 protein and mRNA
expression levels in pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma cell
lines
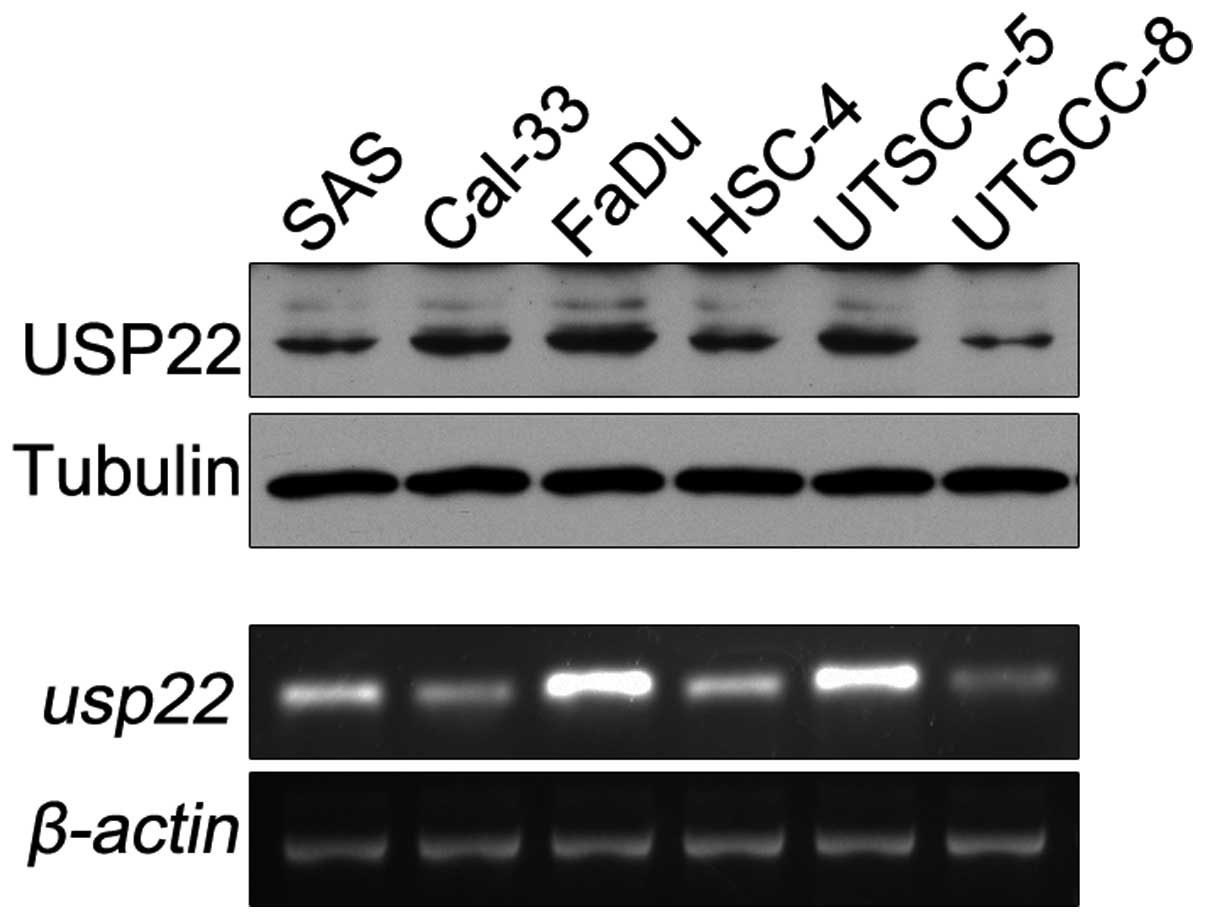
Protein and mRNA were isolated from six pharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma cell lines (SAS, Cal-33, FaDu, HSC-4,
UTSCC-5 and UTSCC-8) and analyzed using western blot and qPCR
analyses. As shown in Fig. 2,
USP22 protein and mRNA were detected in all six pharyngeal squamous
cell carcinoma cell lines. Among the six cell lines, the FaDu line
exhibited the highest USP22 protein and mRNA expression levels.
RNA interference-mediated USP22 gene
silencing
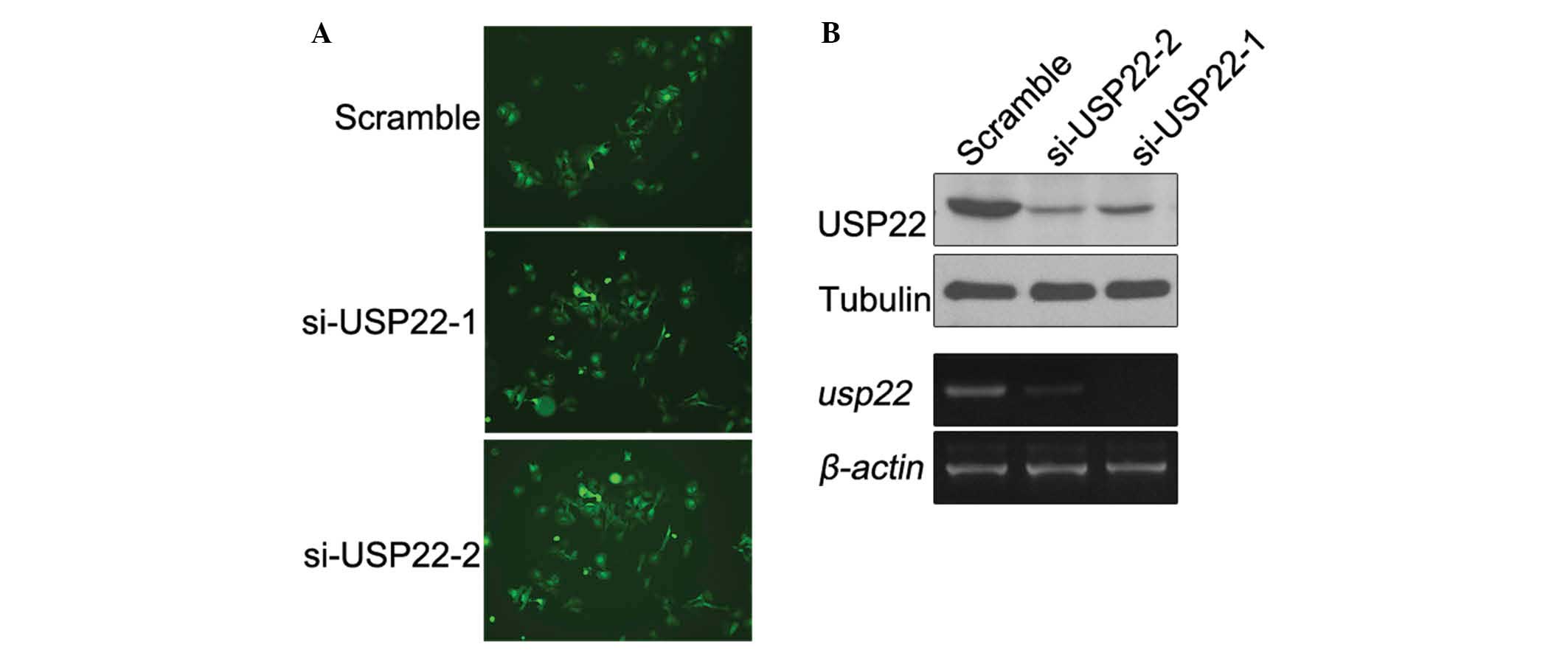
To investigate the role of USP22 in pharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma, two siRNA fragments, si-USP-22-1 and
si-USP-22-2, were designed to be used in the FaDu cancer cell line.
The siRNA was delivered by a lentiviral vector to silence the USP22
gene. The stably silenced cells were selected as determined by GFP
fluorescence. As shown in Fig. 3A,
the cells were successfully transfected with the virus. Western
blotting and qPCR results demonstrated that the si-USP-22-1 and
si-USP-22-2 fragments effectively inhibited the expression of
USP-22 protein and mRNA, compared with the scrambled control
(Fig. 3B).
Proliferation of the FaDu cell line is
reduced following RNA interference-mediated USP22 gene
silencing
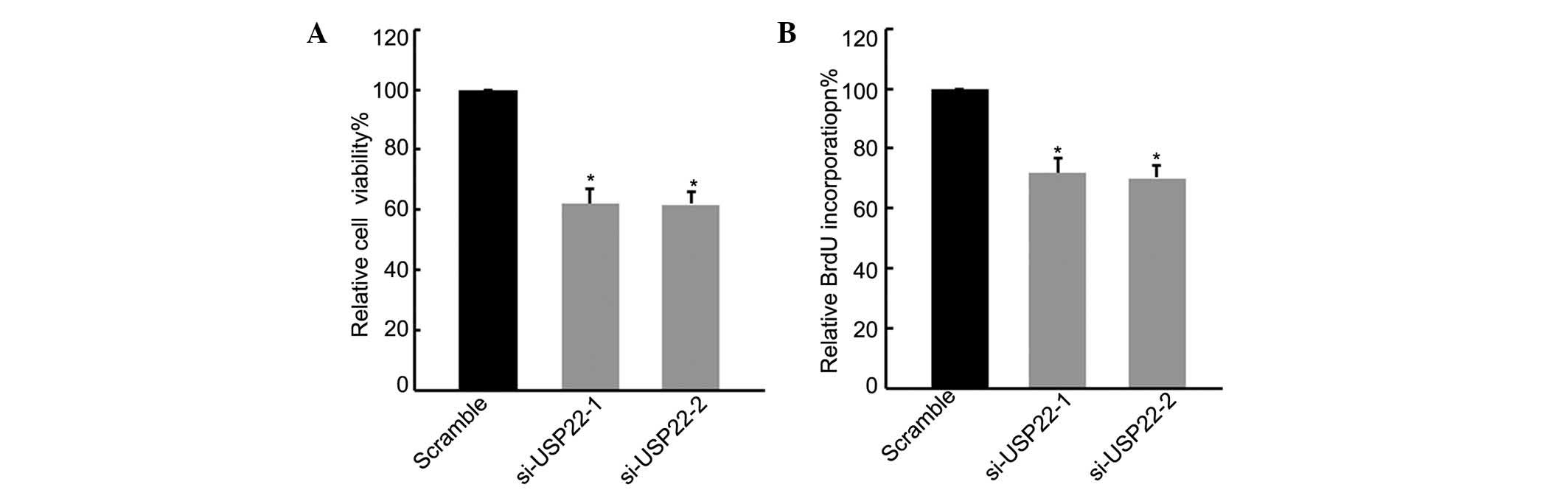
To investigate whether RNA interference-mediated
USP22 gene silencing affected the proliferation of the FaDu cell
line, the MTT assay was used to analyze the viability of FaDu cells
after 48 h of culture. As shown in Fig. 4A, the viability of FaDu cells with
silenced USP22 was significantly reduced compared with the
scrambled control groups (P<0.05). The BrdU incorporation assay
was used to address whether USP22 silencing inhibited cell
proliferation and further reduced the number of FaDu cells. As
shown in Fig. 4B, USP22 gene
silencing inhibited the proliferation of FaDu cells. This
demonstrated that RNA interference reduced the number of cells
through the suppression of cell proliferation.
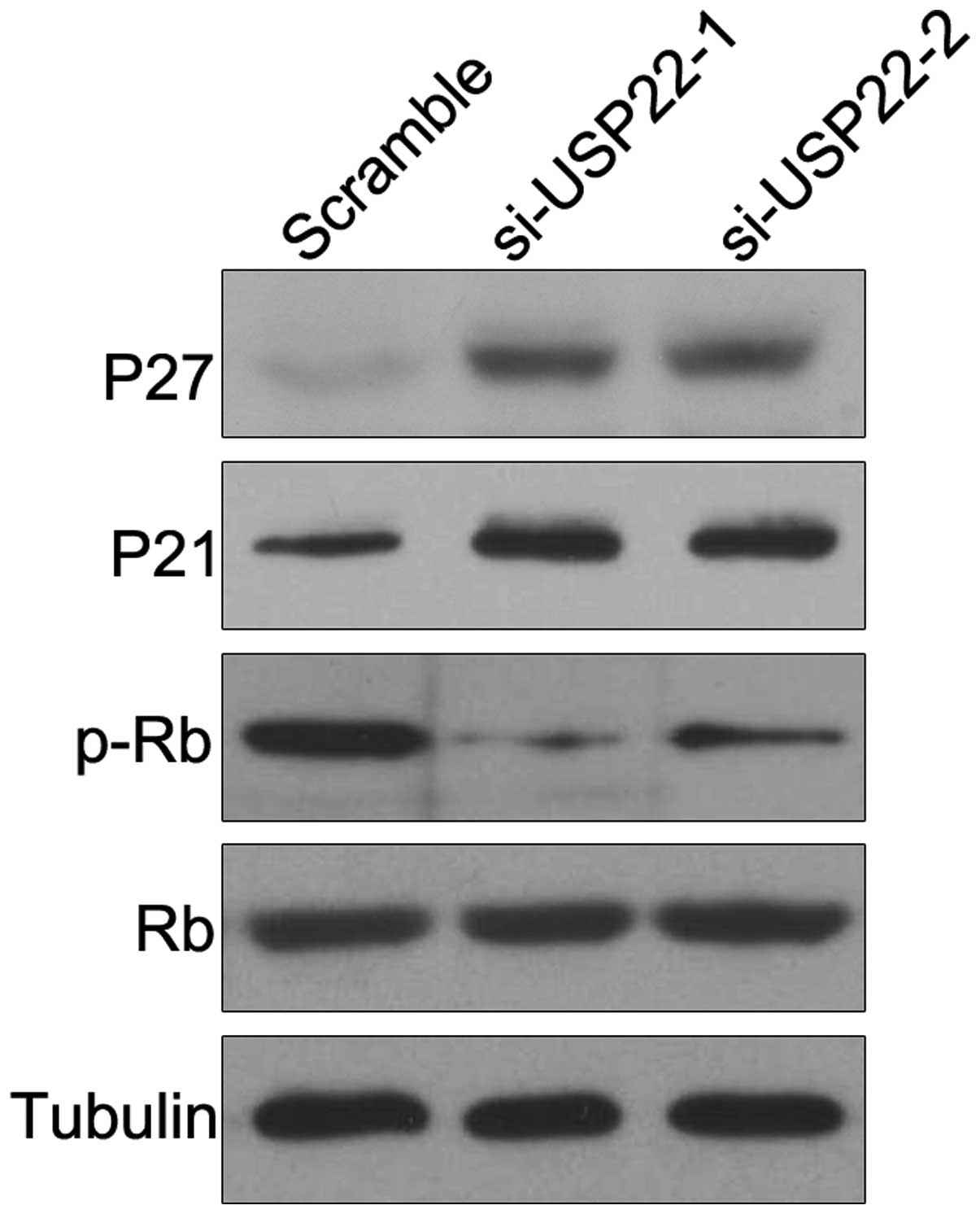
RNA interference affects the
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor protein (CDKI)/Rb signaling
pathway
To elucidate the underlying mechanism by which USP22
gene silencing resulted in inhibition of FaDu cell proliferation,
the expression levels of key cell cycle regulatory proteins,
including Rb, p-Rb, P21 and P27, were evaluated using western
blotting. As compared with the scramble control group, the P21 and
P27 CDKIs were significantly upregulated, whereas Rb
phosphorylation was markedly reduced in USP22 siRNA-transfected
FaDu cells (Fig. 5). The total Rb
protein and internal reference tubulin protein levels remained
unchanged. These results suggested that inhibition of FaDu cell
proliferation by USP22 gene silencing was mediated through the
CDKI/Rb signaling pathway.
Discussion
Head and neck cancer is the sixth most common type
of cancer in humans. The majority of cases of hypopharyngeal head
and neck cancer are squamous cell carcinomas, which have a high
invasion and growth rate. Currently, surgery, radiotherapy and
chemical therapy are used in treatments for hypopharyngeal head and
neck tumors. However, the five-year survival rate remains low,
which is mainly due to poor understanding of HNSCC pathogenesis
mechanisms, preventing efficient treatment (23). In the present study, ubiquitin
hydrolase USP22 levels were found to be upregulated in pharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma samples as compared with those in normal
adjacent tissue samples. The FaDu pharyngeal squamous cell
carcinoma cell line was also observed to express high levels of
USP22. Following USP22 knockdown by lentiviral vector-mediated
small RNA interference, the expression levels of the cyclin
proteins P21 and P27 in FaDu cells were increased, the p-Rb
expression levels were reduced and cell proliferation was
inhibited. According to these observations, USP22 may be considered
a key protein in the carcinogenesis of pharyngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Modification of USP22 may provide a novel approach for
efficiently treating this type of carcinoma.
The USP22 gene is located on chromosome 17 and
consists of 14 exons. The product of the USP22 gene is a type of
DUB (16). USP22 has been widely
analyzed in a number of human cancer types and has been shown to
indirectly affect chromatin structure via histone ubiquitination
(H2A and H2B), thereby regulating the transcriptional activation of
numerous genes and affecting a wide range of biological functions
(17,24). Therefore, USP22 is an important
component of cell cycle regulation. Zhang et al (17) found that interference with USP22
expression significantly inhibited tumor cell proliferation by cell
cycle arrest in the G1 phase. Ovaa et al (25) observed that USP22 promoted
proliferation and immortalization of human lymphocytes, mainly due
to high USP22 expression levels and the resulting effects on cell
cycle gene regulation. In addition, Lee et al (16) demonstrated that USP22 exhibits
periodic expression in mouse embryogenesis, suggesting that USP22
may be involved in the regulation of cell growth and development.
Recent studies have shown that USP22 modifies telomeric
repeat-binding factor 2, a telomeric DNA binding protein, to affect
the balance of telomeres (26,27).
In conclusion, USP22 is a cell-signaling molecule important in cell
proliferation and differentiation.
Previous studies have demonstrated that USP22 is
involved in the tumorigenesis and progress of particular types of
cancer, exhibiting a specific expression pattern. As determined by
expression analysis using microarray, two studies by Glinsky
(28,29) revealed that USP22 expression levels
were increased in the majority of tumors and were associated with
solid tumor metastasis, drug resistance and patient prognosis.
Thus, USP22 was classified as a stem cell marker gene, similar to
BMI-1 and cyclinB1 (28). Abnormal
USP22 expression levels are considered to be an indicator of
malignant transformation and a possible predictor of tumorigenesis
and infiltration (30).
In the present study, to the best of our knowledge,
USP22 was observed for the first time to be upregulated in squamous
cell carcinoma of the pharynx. USP22 may be a key protein involved
in the tumorigenesis of pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. The
results demonstrated that USP22 knockout promoted the upregulation
of the cell cycle-associated proteins P21 and P27, thereby
inhibiting Rb phosphorylation and pharyngeal squamous cell
proliferation. This biological activity of USP22 is consistent with
studies demonstrating that USP22 affects chromatin structure and
regulates gene transcription activation (31). This is also concurrent with studies
revealing the effect of USP22 on the proliferation of pharyngeal
squamous cell carcinoma by regulating the cell cycle (32). However, the present study has
certain limitations. For example, whether USP22 upregulation in
pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma is associated with poorer
prognosis or other clinical parameters remains elusive. To answer
these questions, more detailed analysis is required. In conclusion,
the results of the present study demonstrated that USP22 is a key
protein involved in pharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma, which may
provide novel methods for the treatment of this disease.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Forevergen
Biosciences for assistance with the experiments and for valuable
discussion.
References
|
1
|
Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J and Pisani P:
Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 55:74–108. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hunter KD, Parkinson EK and Harrison PR:
Profiling early head and neck cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:127–135.
2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Pai SI and Westra WH: Molecular pathology
of head and neck cancer: implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and
treatment. Annu Rev Pathol. 4:49–70. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stadler ME, Patel MR, Couch ME and Hayes
DN: Molecular biology of head and neck cancer: risks and pathways.
Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 22:1099–1124. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tuyns AJ: Aetiology of head and neck
cancer: tobacco, alcohol and diet. Adv Otorhinolaryngol. 46:98–106.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
D’Souza G and Dempsey A: The role of HPV
in head and neck cancer and review of the HPV vaccine. Prev Med.
53(Suppl 1): S5–S11. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Goh HK, Ng YH and Teo DT: Minimally
invasive surgery for head and neck cancer. Lancet Oncol.
11:281–286. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Le Tourneau C, Faivre S and Siu LL:
Molecular targeted therapy of head and neck cancer: review and
clinical development challenges. Eur J Cancer. 43:2457–2466.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chisholm E, Bapat U, Chisholm C, Alusi G
and Vassaux G: Gene therapy in head and neck cancer: a review.
Postgrad Med J. 83:731–737. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
De Costa AM and Young MR: Immunotherapy
for head and neck cancer: advances and deficiencies. Anticancer
Drugs. 22:674–681. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brennan P and Boffetta P: Mechanistic
considerations in the molecular epidemiology of head and neck
cancer. IARC Sci Publ; pp. 393–414. 2004
|
|
12
|
Leong PL, Xi S, Drenning SD, et al:
Differential function of STAT5 isoforms in head and neck cancer
growth control. Oncogene. 21:2846–2853. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fan GK, Fujieda S, Sunaga H, et al:
Expression of protein p27 is associated with progression and
prognosis in laryngeal cancer. Laryngoscope. 109:815–820. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yuen PW, Man M, Lam KY and Kwong YL:
Clinicopathological significance of p16 gene expression in the
surgical treatment of head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. J
Clin Pathol. 55:58–60. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pavelić K, Krizanac S, Cacev T, et al:
Aberration of FHIT gene is associated with increased tumor
proliferation and decreased apoptosis-clinical evidence in lung and
head and neck carcinomas. Mol Med. 7:442–453. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee HJ, Kim MS, Shin JM, et al: The
expression patterns of deubiquitinating enzymes, USP22 and Usp22.
Gene Expr Patterns. 6:277–284. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang XY, Varthi M, Sykes SM, et al: The
putative cancer stem cell marker USP22 is a subunit of the human
SAGA complex required for activated transcription and cell-cycle
progression. Mol Cell. 29:102–111. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Glinsky GV, Berezovska O and Glinskii AB:
Microarray analysis identifies a death-from-cancer signature
predicting therapy failure in patients with multiple types of
cancer. J Clin Invest. 115:1503–1521. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ning J, Zhang J, Liu W, Lang Y, Xue Y and
Xu S: Overexpression of ubiquitin-specific protease 22 predicts
poor survival in patients with early-stage non-small cell lung
cancer. Eur J Histochem. 56:e462012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li ZH, Yu Y, Du C, et al: RNA
interference-mediated USP22 gene silencing promotes human brain
glioma apoptosis and induces cell cycle arrest. Oncol Lett.
5:1290–1294. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ling SB, Sun DG, Tang B, et al: Knock-down
of USP22 by small interfering RNA interference inhibits HepG2 cell
proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 58(Suppl): OL1803–OL1808. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Henschel A, Buchholz F and Habermann B:
DEQOR: a web-based tool for the design and quality control of
siRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:W113–W120. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Arens C: Transoral treatment strategies
for head and neck tumors. GMS Curr Top Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck
Surg. 11:Doc052012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao Y, Lang G, Ito S, et al: A TFTC/STAGA
module mediates histone H2A and H2B deubiquitination, coactivates
nuclear receptors, and counteracts heterochromatin silencing. Mol
Cell. 29:92–101. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ovaa H, Kessler BM, Rolén U, et al:
Activity-based ubiquitin-specific protease (USP) profiling of
virus-infected and malignant human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2253–2258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Atanassov BS, Evrard YA, Multani AS, et
al: Gcn5 and SAGA regulate shelterin protein turnover and telomere
maintenance. Mol Cell. 35:352–364. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Smith S: The SAGA continues... to the end.
Mol Cell. 35:256–258. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Glinsky GV: Genomic models of metastatic
cancer: functional analysis of death-from-cancer signature genes
reveals aneuploid, anoikis-resistant, metastasis-enabling phenotype
with altered cell cycle control and activated Polycomb Group (PcG)
protein chromatin silencing pathway. Cell Cycle. 5:1208–1216.
2006.
|
|
29
|
Glinsky GV: Death-from-cancer signatures
and stem cell contribution to metastatic cancer. Cell Cycle.
4:1171–1175. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang J, Zhang X, Xie S, et al:
Ubiquitin-specific protease 22: a novel molecular biomarker in
glioma prognosis and therapeutics. Med Oncol. 31:8992014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chipumuro E and Henriksen MA: The
ubiquitin hydrolase USP22 contributes to 3′-end processing of
JAK-STAT-inducible genes. FASEB J. 26:842–854. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Schrecengost RS, Dean JL, Goodwin JF, et
al: USP22 regulates oncogenic signaling pathways to drive lethal
cancer progression. Cancer Res. 74:272–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|