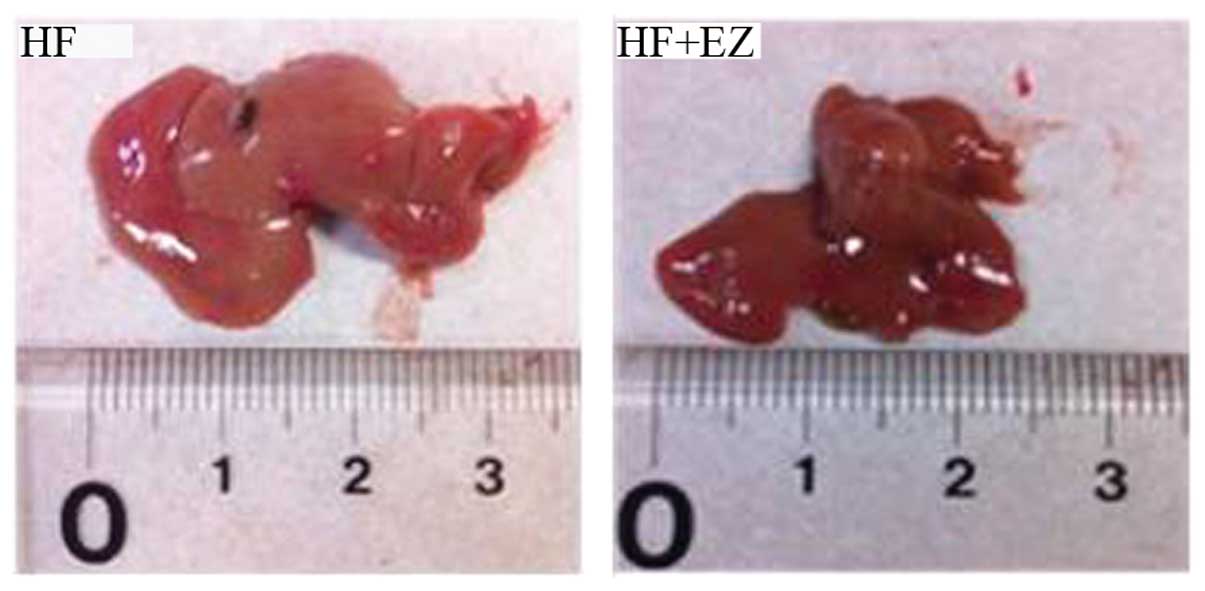
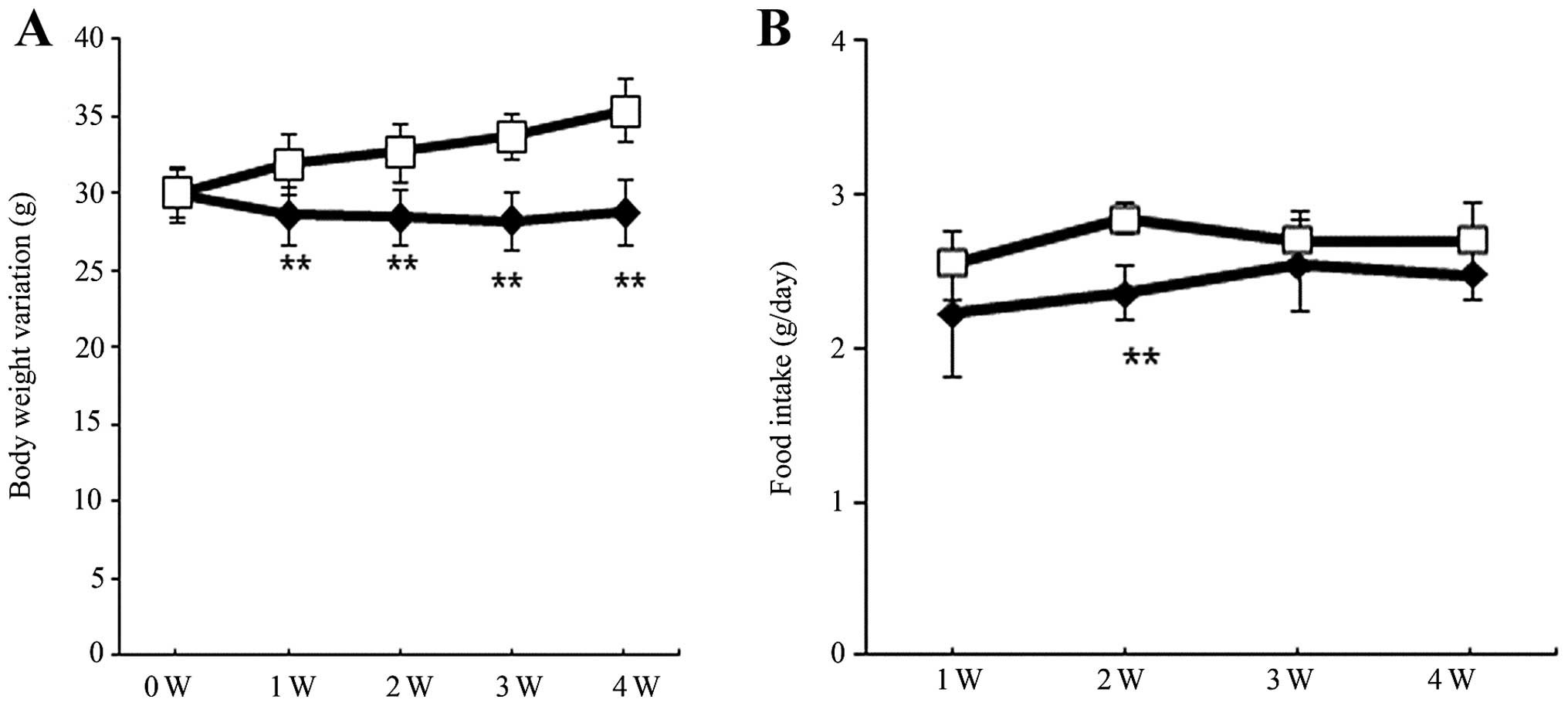
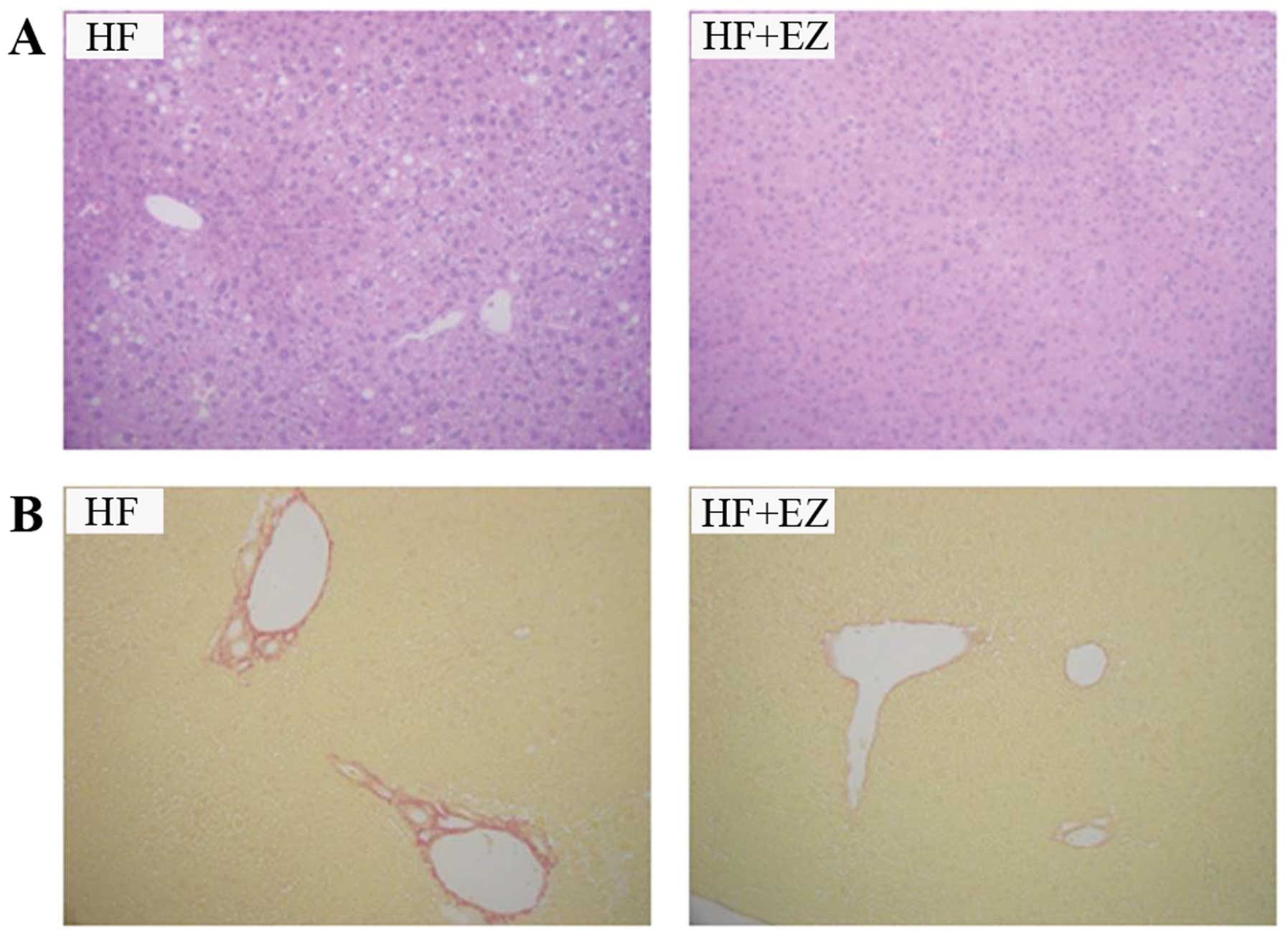
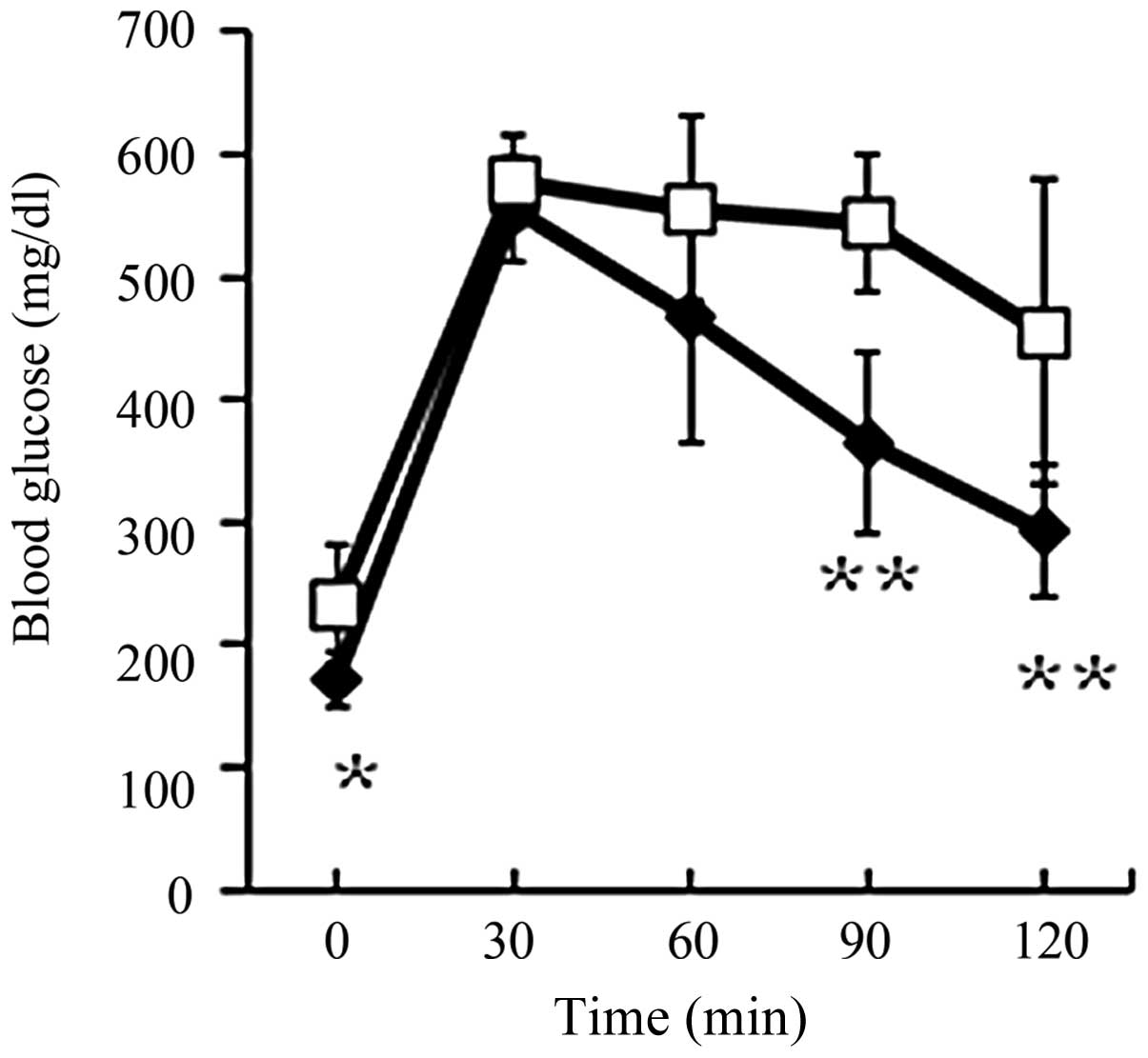
|
1
|
Wieckowska A, McCullough AJ and Feldstein
AE: Noninvasive diagnosis and monitoring of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis: present and future. Hepatology. 46:582–589. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Deushi M, Nomura M, Kawakami A, et al:
Ezetimibe improves liver steatosis and insulin resistance in obese
rat model of metabolic syndrome. FEBS Lett. 581:5664–5670. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Altmann SW, Davis HR Jr, Zhu LJ, et al:
Niemann-Pick C1 Like 1 protein is critical for intestinal
cholesterol absorption. Science. 303:1201–1204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zheng S, Hoos L, Cook J, et al: Ezetimibe
improves high fat and cholesterol diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 584:118–124. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Matono T, Koda M, Tokunaga S, et al:
Therapeutic effects of ezetimibe for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
in fatty liver shionogi-ob/ob mice. Hepatol Res. 41:1240–1248.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Muraoka T, Aoki K, Iwasaki T, et al:
Ezetimibe decreases SREBP-1c expression in liver and reverses
hepatic insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet. Metabolism.
60:617–628. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oza N, Takahashi H, Eguchi Y, et al:
Efficacy of ezetimibe for reducing serum low-density lipoprotein
cholesterol levels resistant to lifestyle intervention in patients
with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatol Res. 44:812–817.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ushio M, Nishio Y, Sekine O, et al:
Ezetimibe prevents hepatic steatosis induced by a high-fat but not
a high-fructose diet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 305:E293–E304.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kishino Y, Tanaka Y, Ikeda T, et al:
Ezetimibe increases hepatic iron levels in mice fed a high-fat
diet. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 345:483–491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
George V, Tremblay A, Després JP, Leblanc
C and Bouchard C: Effect of dietary fat content on total and
regional adiposity in men and women. Int J Obes. 14:1085–1094.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tucker LA and Kano MJ: Dietary fat and
body fat: a multivariate study of 205 adult females. Am J Clin
Nutr. 56:616–622. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Takahashi Y, Soejima Y and Fukusato T:
Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 18:2300–2308. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Buettner R, Schölmerich J and Bollheimer
LC: High-fat diets: modeling the metabolic disorders of human
obesity in rodents. Obesity (Silver Spring). 15:798–808. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Sugimoto K, Fujisawa T, et al:
Novel effect of ezetimibe to inhibit the development of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Fatty Liver Shionogi mouse.
Hepatol Res. 44:102–113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, et al:
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Clinical Research Network: Design and
validation of a histological scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease. Hepatology. 41:1313–1321. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shindo N, Fujisawa T, Sugimoto K, et al:
Involvement of microsomal triglyceride transfer protein in
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in novel spontaneous mouse model. J
Hepatol. 52:903–912. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Oze-Fukai A, Fujisawa T, Sugimoto K, et
al: A novel mouse model for type 2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease: spontaneous amelioration of diabetes by augmented
beta cell mass. Endocr J. 56:227–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jung HY, Kim YH, Kim IB, et al: The Korean
mistletoe (Viscum album coloratum) extract has an
antiobesity effect and protects against hepatic steatosis in mice
with high-fat diet-induced obesity. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2013:1682072013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jia L, Betters JL and Yu L: Niemann-pick
C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) protein in intestinal and hepatic cholesterol
transport. Annu Rev Physiol. 73:239–259. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oosterveer MH, van Dijk TH, Tietge UJ, et
al: High fat feeding induces hepatic fatty acid elongation in mice.
PLoS One. 4:e60662009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia L, Ma Y, Rong S, et al: Niemann-Pick
C1-Like 1 deletion in mice prevents high-fat diet-induced fatty
liver by reducing lipogenesis. J Lipid Res. 51:3135–3144. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miquilena-Colina ME, Lima-Cabello E,
Sánchez-Campos S, et al: Hepatic fatty acid translocase CD36
upregulation is associated with insulin resistance,
hyperinsulinaemia and increased steatosis in non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis and chronic hepatitis C. Gut. 60:1394–1402. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Inoue M, Ohtake T, Motomura W, et al:
Increased expression of PPARgamma in high fat diet-induced liver
steatosis in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 336:215–222. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Buqué X, Martínez MJ, Cano A, et al: A
subset of dysregulated metabolic and survival genes is associated
with severity of hepatic steatosis in obese Zucker rats. J Lipid
Res. 51:500–513. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Degrace P, Moindrot B, Mohamed I, et al:
Upregulation of liver VLDL receptor and FAT/CD36 expression in
LDLR−/− apoB100/100 mice fed trans-10, cis-12 conjugated linoleic
acid. J Lipid Res. 47:2647–2655. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu LF, Purushotham A, Wendel AA and
Belury MA: Combined effects of rosiglitazone and conjugated
linoleic acid on adiposity, insulin sensitivity, and hepatic
steatosis in high-fat-fed mice. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 292:G1671–G1682. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
López-Parra M, Titos E, Horrillo R, et al:
Regulatory effects of arachidonate 5-lipoxygenase on hepatic
microsomal TG transfer protein activity and VLDL-triglyceride and
apoB secretion in obese mice. J Lipid Res. 49:2513–2523.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nozaki Y, Fujita K, Yoneda M, et al:
Long-term combination therapy of ezetimibe and acarbose for
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 51:548–556. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Higuchi N, Kato M, Tanaka M, et al:
Effects of insulin resistance and hepatic lipid accumulation on
hepatic mRNA expression levels of apoB, MTP and L-FABP in
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Exp Ther Med. 2:1077–1081.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Calvisi DF, Ladu S, Pinna F, et al: SKP2
and CKS1 promote degradation of cell cycle regulators and are
associated with hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis.
Gastroenterology. 137:1816–1826. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gao D, Inuzuka H, Tseng A, Chin RY, Toker
A and Wei W: Phosphorylation by Akt1 promotes cytoplasmic
localization of Skp2 and impairs APCCdh1-mediated Skp2 destruction.
Nat Cell Biol. 11:397–408. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang G, Ayala G, De Marzo A, et al:
Elevated Skp2 protein expression in human prostate cancer:
association with loss of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27
and PTEN and with reduced recurrence-free survival. Clin Cancer
Res. 8:3419–3426. 2002.
|
|
33
|
Li SH, Li CF, Sung MT, et al: Skp2 is an
independent prognosticator of gallbladder carcinoma among
p27(Kip1)-interacting cell cycle regulators: an immunohistochemical
study of 62 cases by tissue microarray. Mod Pathol. 20:497–507.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Masuda TA, Inoue H, Sonoda H, et al:
Clinical and biological significance of S-phase kinase-associated
protein 2 (Skp2) gene expression in gastric carcinoma: modulation
of malignant phenotype by Skp2 overexpression, possibly via p27
proteolysis. Cancer Res. 62:3819–3825. 2002.
|
|
35
|
Shigemasa K, Gu L, O’Brien TJ and Ohama K:
Skp2 overexpression is a prognostic factor in patients with ovarian
adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 9:1756–1763. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Calvisi DF, Pinna F, Ladu S, et al: The
degradation of cell cycle regulators by SKP2/CKS1 ubiquitin ligase
is genetically controlled in rodent liver cancer and contributes to
determine the susceptibility to the disease. Int J Cancer.
126:1275–1281. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gstaiger M, Jordan R, Lim M, et al: Skp2
is oncogenic and overexpressed in human cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 98:5043–5048. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhu L: Skp2 knockout reduces cell
proliferation and mouse body size: and prevents cancer? Cell Res.
20:605–607. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Koga H, Harada M, Ohtsubo M, et al:
Troglitazone induces p27Kip1-associated cell-cycle arrest through
down-regulating Skp2 in human hepatoma cells. Hepatology.
37:1086–1096. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Signoretti S, Di Marcotullio L, Richardson
A, et al: Oncogenic role of the ubiquitin ligase subunit Skp2 in
human breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 110:633–641. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|