Introduction
Osteosarcoma is one of the most frequent types of
malignant cancer and poses a threat to human health (1). It has been revealed that the aberrant
expression of tumor suppressor genes is important in the
progression, invasion and metastasis of osteosarcoma (1). Thus, gene therapy is an effective
strategy for the treatment of osteosarcoma (2).
Tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand (TRAIL) can induce apoptosis in various cancer cells by
binding cellular receptors, death receptor (DR)4 and DR5, and
activating the downstream signal transduction pathway (3,4).
Adenovirus (Ad)-mediated TRAIL delivery has been well documented to
exert antitumor activity against osteosarcoma, both in vitro
and in animal models (5,6). Furthermore, the extensive expression
of DR4 and DR5 in osteosarcoma ensures that TRAIL may be an
effective strategy in future clinical treatment (7).
However, TRAIL has been demonstrated to induce
apoptosis in hepatic cells by inducing the FAS-mediated downstream
molecular pathway (8). The
cytotoxicity of TRAIL to normal liver cells impedes its clinical
application in the treatment of osteosarcoma. Therefore, a novel
gene therapy strategy, which is able to protect normal tissue,
particularly liver tissue, from the side effects of TRAIL
expression is required.
Differential microRNA (miRNA) expression levels have
been revealed between osteosarcoma and normal cells (9). A decrease in the expression of
certain miRNAs enables the selective expression of inserted genes
in osteosarcoma cells by their miRNA response elements (MREs). For
example, miR-34 has been demonstrated to be underexpressed
in osteosarcoma cells (10) and
miR-122 is as a liver-enriched miRNA that can be used to
suppress the expression of TRAIL in liver cells and thus minimize
hepatotoxicity (11). However, to
the best of our knowledge, the effectiveness of MRE-based gene
therapy for the treatment of osteosarcoma has not yet been
investigated.
In the present study, MREs of miR-34 and
miR-122 were used to regulate the expression of TRAIL in
order to confer its expression with osteosarcoma selectivity.
Multidisciplinary experiments were performed to verify its
effectiveness.
Materials and methods
Ad construction
Ad-enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) and
Ad-TRAIL were provided by Dr Zhao (Department of Urology, General
Hospital of Chengdu Military Area Command of Chinese PLA, Chengdu,
China). Ad-TRAIL-34-122 was constructed as follows: A DNA fragment
containing two copies of the MREs of miR-34 and
miR-122 (5′-GCCGATATCACAAACACCCACTGCCACAA
CACCCACTGCCACAAACACCACACTCCACAAACCACAC TCCGATATCGGC-3′) was
synthesized and released from the temporary vector by EcoRV.
The fragment was then inserted into pShuttle-cytomegalovirus
(CMV)-TRAIL at the same site to obtain pShuttle-CMV-TRAIL-34-122.
Subsequently, pShuttle-CMV-TRAIL-34-122 and pAdEasy were
cotransfected into human embryonic kidney (HEK)293 cells (Microbix
Biosystems, Mississauga, ON, Canada). The adenoviral vectors were
purified using a CsCl centrifugation method (30,000 × g, 2.5 h),
following identification by reverse transcription quantitative
polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). The titers of Ad-EGFP,
Ad-TRAIL-34-122 and Ad-TRAIL were determined using a
TCID50 method on HEK293 cells and presented as
pfu/ml.
Cell line cultures
The human osteosarcoma cell lines, KHOS, HOS, SaOS2,
U2OS and MG-63 and the human normal lung fibroblast cell lines,
NHLF and MRC5, were all purchased from the American Type Culture
Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, USA). Normal liver cells, L-02,
were obtained from Shanghai Cell Collection (Shanghai, China). The
cells were cultured using the recommended media (ATCC-formulated
Eagle’s minimum essential medium for KHOS, HOS, MG-63, NHLF, and
MRC5; ATCC-formulated McCoy’s 5a medium modified for Saos-2;
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s minimum essential medium for U2OS, and
HEK-293; RPMI-1640 medium for L-02 (Invitrogen, Grand Island, NY,
USA) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 4 mM glutamine, 100
U/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin (all Invitrogen) at 37°C
and 5% CO2 in a humidified atmosphere.
RT-qPCR
For the detection of miR-34 and
miR-122, fresh osteosarcoma samples were obtained from
surgery (Department of Emergency Surgery, The First Affiliated
Hospital of Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China). Total RNA was
extracted from 10 cancerous samples and corresponding normal
tissues using TRIzol solution (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA)
and pooled as one group for subsequent experiments. In addition,
the KHOS, HOS, SaOS2, U2OS, MG-63, NHLF, MRC5 and L-02 cells were
subjected to RNA extraction using TRIzol. A TaqMan®
MicroRNA Reverse Transcription kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster
City, CA, USA) was applied to perform reverse transcription,
followed by TaqMan® 2X Universal PCR Master mix kit
(Applied Biosystems)-based qPCR assays using a CFX96™ Real-Time PCR
Detection System (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). The
data were processed and analyzed using REST 2009 software (Qiagen,
Hilden, Germany).
The procedure used to detect TRAIL mRNA in the
Ad-TRAIL-34-122-infected cells was as follows: In each well of
24-well plates, 4×104 cells were seeded. These cells
were infected with Ad-TRAIL or AD-TRAIL-34-122 with a multiplicity
of infection (MOI) of 10. After 48 h, total RNA was extracted using
TRIzol® solution (Invitrogen Life Technologies,
Carlsbad, CA, USA), followed by cDNA generation by reverse
transcription using a ReverTra Ace qPCR RT kit (Toyobo Co., Ltd.,
Osaka, Japan) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Subsequently, SYBR premix Ex Taq (Takara Bio, Inc., Otsu, Japan)
was used for RT-qPCR. The primers used for TRAIL detection were as
follows: TRAIL, forward: 5′-GACCTGCGTGCTGATC-3′ and reverse:
5′-TAAAAGAAGATGACAG-3′.
Luciferase assay
A DNA fragment, containing two copies of the
miR-34 and miR-122 MREs
(5′-GCCCTCGAGACAACCAGCTAAGACACTGCCAACAACCAGCTAAGACACTGC
CACAAACACCATTGTCACACTCCACAAACACCATTGT CACACTCCAGCGGCCGCGGC-3′), was
synthesized and inserted into a psiCheck2 vector at the sites
XhoI and NotI (Promega Corporation, Madison, WI, USA)
in order to generate psiCheck2-34-122.
Cells (4×104) were cultured in each well
of a 24-well plate. psiCheck2-34-122 and psiCheck2 were transfected
into the cells using Lipofectamine 2000 (Invitrogen Life
Technologies) and, 48 h later, these cells were treated with lysis
buffer (Promega Corporation). The luciferase activities were then
evaluated using a Dual-Luciferase reporter system kit (Promega
Corporation).
Immunoblot assay
The total proteins were extracted using an
M-PER® Mammalian Protein Extraction reagent (Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Rockford, IL, USA) and then separated on 10%
SDS-PAGE gels (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Subsequently, the
proteins were transferred onto 0.45 μm nitrocellulose membranes
(Thermo Fisher Scientific) and 5% fat-free dry milk was added to
block the membrane. After 1 h, the membranes were incubated with
the primary antibodies for 12 h at 4°C: Monoclonal rabbit
anti-TRAIL, monoclonal rabbit anti-cle-PARP, monoclonal rabbit
anti-cle-caspase 3, and monoclonal mouse anti-GAPDH. On day 2, the
membranes were then incubated with the matched polyclonal goat
anti-mouse or anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G secondary antibodies for
1 h at room temperature and the blots were detected using
SuperSignal West Dura Extended Duration substrate (Thermo Fisher
Scientific). All the above antibodies were all purchased from Cell
Signaling Technology (Boston, MA, USA).
TRAIL determination by ELISA
To determine the concentration of secreted TRAIL,
ELISA was performed. A total of 3.5×105 cells were
cultured in each well of a 6-well plate and different adenoviral
vectors (10 MOI) were added. After 48 h, sandwich ELISA (Thermo
Fisher Scientific) was used to detect the expression level of TRAIL
secreted into the media. The following antibodies were used:
Monoclonal mouse TRAIL antibody and polyclonal goat TRAIL antibody
(R&D Systems, Inc.) Absorbance was measured at a wavelength of
450 nm using a Microplate Reader (model 550; Bio-Rad
Laboratories).
miRNA mimics and inhibitors
The mimics and inhibitors for miR-34 and
miR-122 as well as the control mimics and inhibitors were
purchased from GenePharma (Shanghai, China). Prior to subsequent
experiments, the indicated cells were transfected with the control
mimic (200 nM) or a mixture of the miR-34 mimic (100 nM) and
the miR-122 mimic (100 nM).
Determination of apoptotic rates
The cells (2×105) were cultured in 6-well
plates. After 24 h, the indicated adenoviruses (10 MOI) were added
to the media and, after 48 h, the cells were processed using an
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection kit (BioVision, Inc., Milpitas,
CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The
apoptotic rate was then determined using flow cytometry.
Cell viability assay
The cells (1×104) were cultured in each
well of a 96-well plate. The cells were infected with the indicated
adenoviral vector of different MOI. After 6 days, 50 μl dimethyl
sulfoxide (DMSO) was added to the cell media for 4 h incubation,
and then the media was discarded and 150 μl DMSO was added. The 570
nm absorbance in each well was then assessed using a microplate
reader (Model 550; Bio-Rad Laboratories) with a reference
wavelength of 655 nm. Cell viability was calculated using the
following formula: Cell viability (%) = absorbance value of
infected cells - background absorbance/absorbance of uninfected
control cells - background absorbance.
Animal experiments
The protocols of animal experiments were approved by
the Experimental Animal Ethics Committee of Zhengzhou
University.
To establish osteosarcoma xenografts,
2×106 KHOS cells were injected into the left flanks of
5-week-old BALB/c nude mice. A total of 24 mice were divided
equally into four groups (n=6), once the tumor diameter reached 7–9
mm. Needles were used to intratumorally inject 100 μl PBS either
with or without 2×108 pfu Ad-EGFP, Ad-TRAIL or
Ad-TRAIL-34-122 five times every other day. The total dosage of
adenoviruses reached 1×109 pfu. Calipers were used to
periodically measure the tumor diameters. Tumor volume was then
calculated using the following formula: Tumor volume
(mm3) = maximal length (mm) × perpendicular width
(mm)2/2.
Liver function evaluation
Female BALB/c mice (n=5) were intravenously
administered with Ad-EGFP, Ad-TRAIL or Ad-TRAIL-34-122
(1×109 pfu) five times every other day, in order to
determine the resulting hepatotoxicity. After 10 days, 600 ml serum
was obtained from each mouse by cardiac puncture and then incubated
with heparin (12 U). Serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) was
subsequently quantified at the Clinical Laboratory, The First
Affiliated Hospital of Zhengzhou University.
Histological staining
A single mouse from each group was sacrificed 7 days
after adenovirus administration. The tumor and liver tissues were
fixed using formalin followed by histological staining based on the
streptavidin biotin peroxidase complex method. TRAIL protein
expression and distribution were determined using the TRAIL
antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc., Santa Cruz, CA, USA).
Prior to observation, the sections were counterstained with
hematoxylin.
Statistical analysis
A two-tailed Student’s t-test was used for
statistical analysis in the present study. P<0.05 was considered
to indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Levels of miR-34 are reduced in
osteosarcoma
To confirm the downregulation of miR-34 in
osteosarcoma, the miRNA expression profiles were examined in 10
samples of osteosarcoma. RT-qPCR indicated that the expression
levels of miR-34 were decreased in osteosarcoma, compared
with the corresponding normal tissue (P<0.01; Fig. 1A). Furthermore, the abundance of
miR-34 was quantified in several osteosarcoma cell lines and
levels were also found to be reduced in the cell lines assessed
(Fig. 1B). The differential
expression profile of miR-34 suggested that the application
of these miRNAs regulated the expression of exogenous genes in the
osteosarcoma cells.
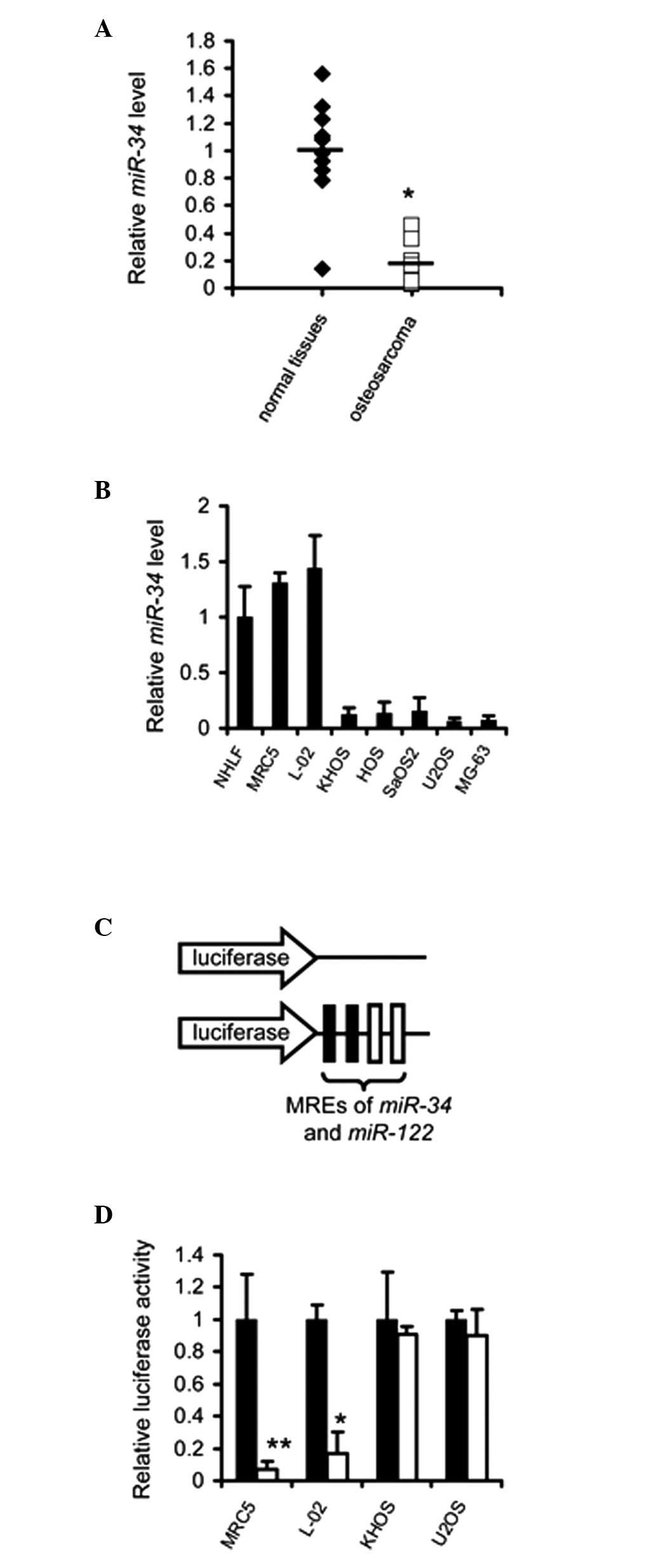 | Figure 1Exogenous genes are selectively
expressed in osteosarcoma cells mediated by the MREs of
miR-34 and miR-122. (A) Expression of miR-34
and miR-122 was detected in the osteosarcoma specimens and
their corresponding normal tissues (n=10). Data are expressed as
the mean ± standard error of the mean of three independent
experiments. (B) Expression of miR-34 and miR-122 was
detected in NHLF, MRC-5, L-02, KHOS, HOS, SaOS2, U2OS and MG-63
cells. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean
of three independent experiments. (C) Structures of the reporter
vectors. (D) Luciferase activity was quantified in the MRC-5, L-02,
KHOS and U2OS cells transfected with the control vector psiCheck2
(■) or psiCheck2-34-122 (□). Data are expressed as the mean ±
standard error of the mean of three independent experiments.
*P<0.05, **P<0.01. miR, microRNA; MREs,
miRNA response elements. |
Application of miR-34 and miR-122 MREs
regulates the expression of TRAIL in an osteosarcoma-selective
manner
To investigate whether the MREs of miR-34 and
miR-122 can be applied for osteosarcoma-specific expression
of exogenous genes, psiCkeck2-34-122 U, a luciferase reporter
vector regulated by the MREs of miR-34 and miR-122,
was constructed (Fig. 1C). The
results demonstrated that luciferase activity was not significantly
affected in the psiCkeck2-34-122-transfected osteosarcoma cells.
However, its activity was markedly suppressed in the normal cell
lines (Fig. 1D).
MREs of miR-34 and miR-122 restrict the
expression of TRAIL mediated by adenoviral vectors within
osteosarcoma cells
To confirm whether the application of miR-34
and miR-122 MREs enabled the selective expression of TRAIL
in osteosarcoma cells, an adenoviral vector was constructed by
inserting two copies of the miR-34 and miR-122 MREs
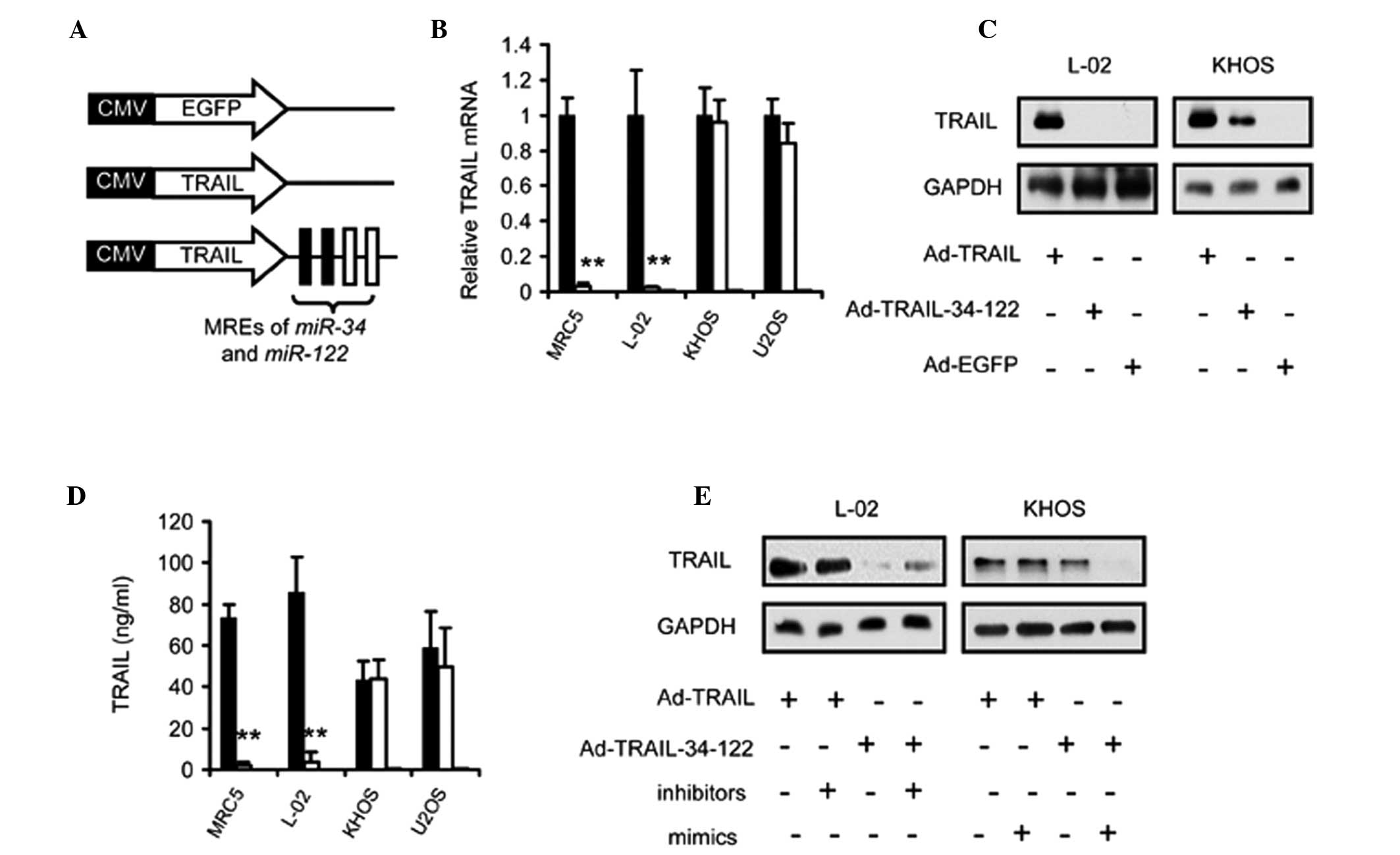
at the end of the TRAIL-encoding sequence (Fig. 2A). The RT-qPCR assay revealed no
difference in the expression of TRAIL between the Ad-TRAIL-34-122
and Ad-TRAIL-infected osteosarcoma cells (Fig. 2B). By contrast, Ad-TRAIL-34-122
suppressed the expression of TRAIL protein in normal cells
(Fig. 2B). Immunoblotting and
ELISA further demonstrated that Ad-TRAIL-34-122 treatment led to
the selective expression of TRAIL in osteosarcoma (Fig. 2C and D). To verify that TRAIL
expression was regulated by the abundance of endogenous
miR-34 and miR-122, the inhibitors or mimics of these
miRNAs were added to the cell cultures. The data demonstrated that
increasing the abundance of miR-34 and miR-122 in
osteosarcoma cells led to a reduction in the expression of TRAIL
proteins, while suppression of miR-34 and miR-122 by
inhibitors resulted in the restoration of TRAIL in normal cells
(Fig. 2E).
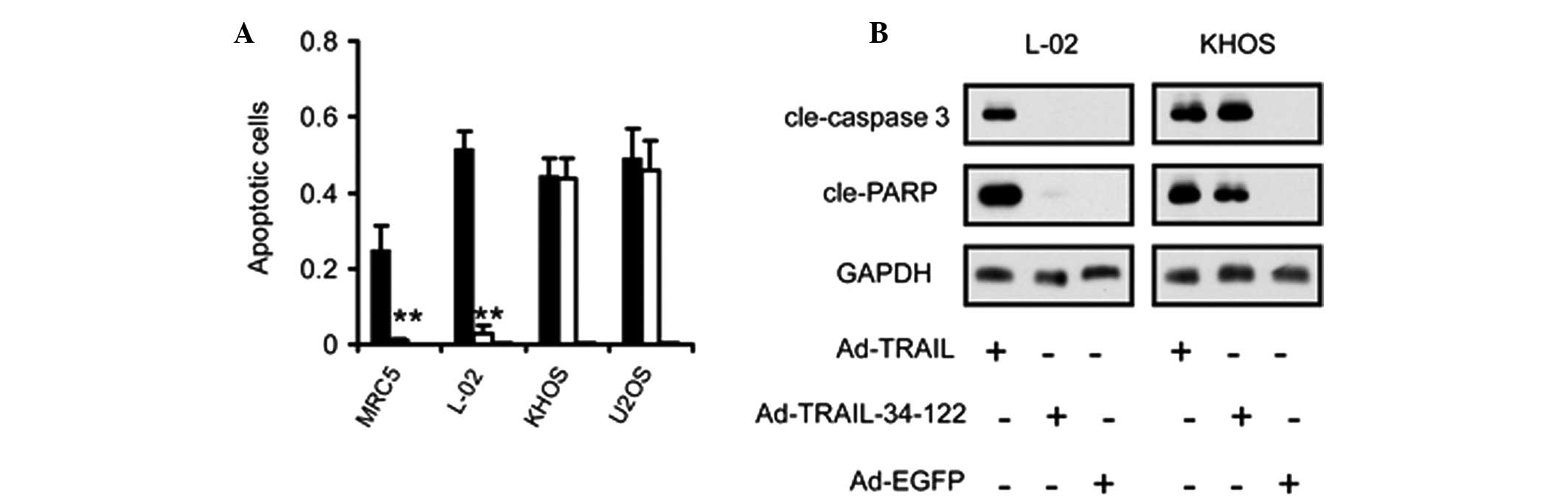
Selective apoptosis in osteosarcoma cells
is induced by miRNA-regulated expression of TRAIL
As TRAIL initiates apoptosis in a wide range of
cells, the present study investigated the activation of the
apoptotic pathway in osteosarcoma and normal cell lines. Flow
cytometric analysis of apoptotic rates revealed that apoptosis
occurred specifically in the osteosarcoma cells, but not in the
normal cells, infected with Ad-TRAIL-34-122 (Fig. 3A). By contrast, Ad-TRAIL induced
apoptosis in osteosarcoma and normal cells (Fig. 3A).
Furthermore, immunoblot assays were also employed to
confirm the activation status of the apoptotic pathway in
osteosarcoma cells infected with TRAIL-expressing adenoviruses.
Caspase-3 and poly ADP-ribose polymerase were found to be markedly
cleaved in the Ad-TRAIL and Ad-TRAIL-34-122-transduced osteosarcoma
cells and in the Ad-TRAIL-infected normal cells. However, no
cleavage was observed in the normal cells infected with
Ad-TRAIL-34-122 (Fig. 3B).
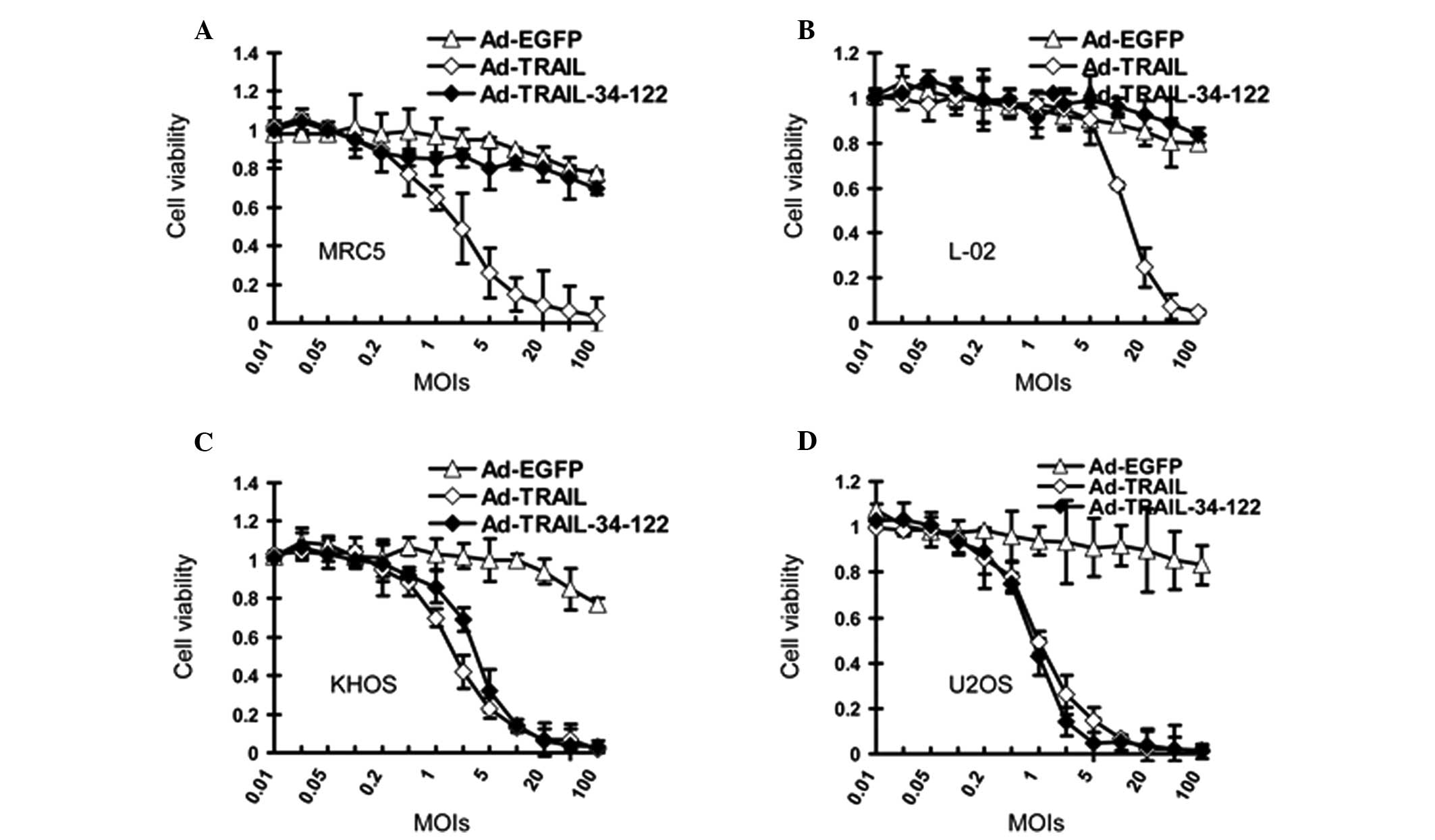
Ad-TRAIL-34-122 compromises the viability
of osteosarcoma cells without significant cytotoxicity to normal
cells
MTT assays were subsequently performed to determine
the suppressive effect of Ad-TRAIL and Ad-TRAIL-34-122 on
osteosarcoma cells and normal cells. According to the data, the
viability of the osteosarcoma cells was inhibited when Ad-TRAIL and
Ad-TRAIL-34-122 were added to the cell culture (Fig. 4A and B). However, the effect of
Ad-TRAIL and Ad-TRAIL-34-122 on normal cells differed. Ad-TRAIL
reduced the survival of normal cell lines, whereas their viability
was not affected by Ad-TRAIL-34-122 (Fig. 4C and D).
TRAIL expression suppresses the growth of
osteosarcoma xenografts in vivo
Subsequently, the effect of Ad-TRAIL-34-122 on the
growth of osteosarcoma xenografts in mice was investigated. KHOS
cells were used to establish the osteosarcoma xenografts. Mice were
then intravenously injected with PBS, Ad-EGFP, Ad-TRAIL and
Ad-TRAIL-34-122 and the tumor diameter was periodically measured.
The data revealed that Ad-TRAIL and Ad-TRAIL-34-122 suppressed KHOS
tumor growth in mice (Fig. 5A).
The expression of TRAIL was also confirmed in the tumor sections
using immunohistological staining (Fig. 5B).
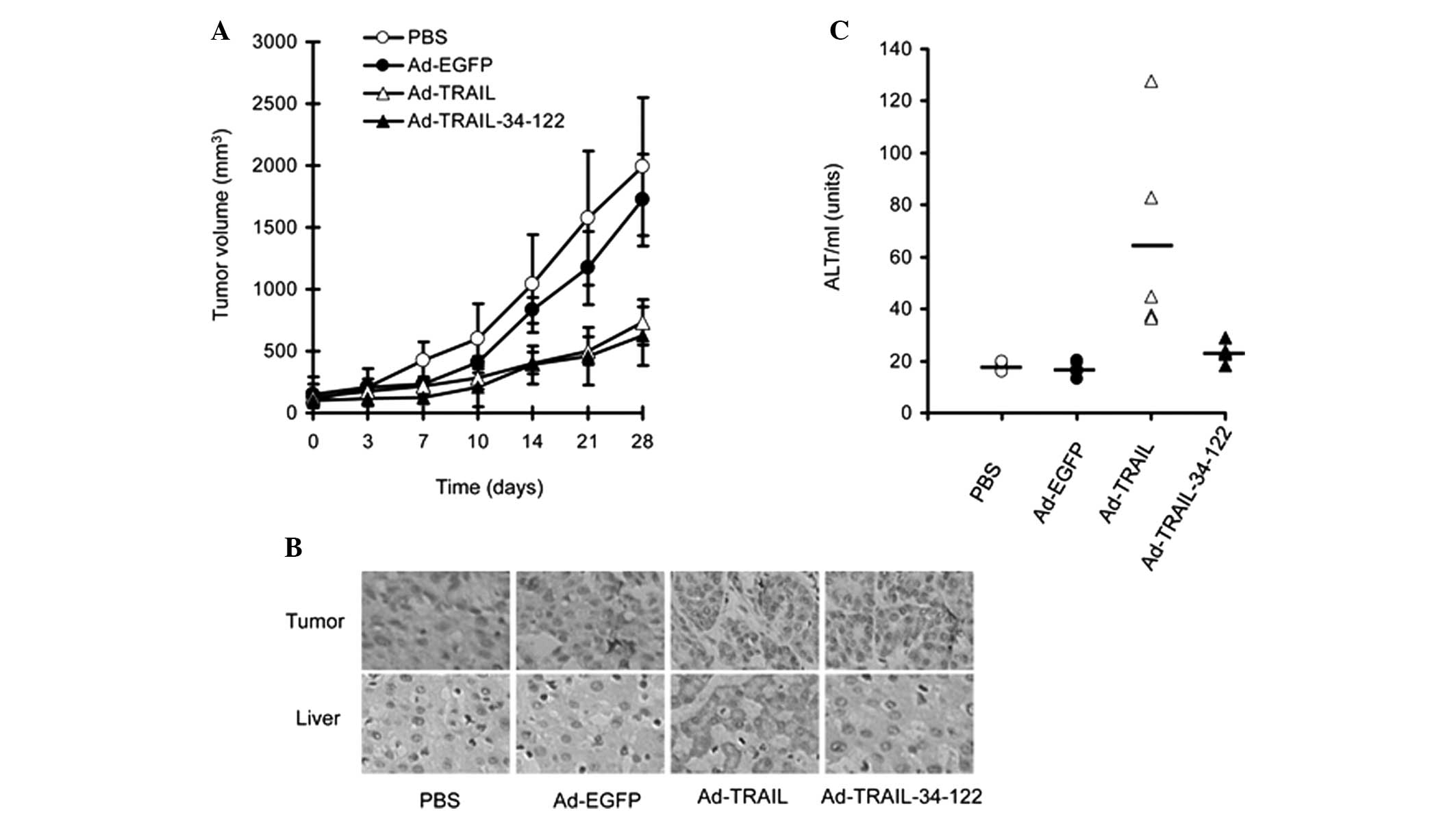 | Figure 5Ad-TRAIL-34-122 suppresses the growth
of osteosarcoma xenografts in mouse models without hepatotoxicity.
(A) Different adenoviruses (1×109 pfu) were
intratumorally injected into mice bearing KHOS tumors and the tumor
volumes were periodically measured. Data are expressed as the mean
± standard error of the mean of tumor sizes. (B) Histological
staining was performed to detect the expression of TRAIL in tumor
and liver sections from the KHOS tumor-bearing mice and the
tumor-free mice, respectively, following treatment with PBS,
Ad-EGFP, Ad-TRAIL and Ad-TRAIL-34-122. Representative images are
presented (magnification, ×200). (C) ALT levels were detected in
mice bearing no tumors following injection of different
adenoviruses. Data are expressed as the mean ± standard error of
the mean of ALT serum levels. PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; Ad,
adenovirus; TRAIL, tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand; EGFP, enhanced green fluorescent protein; ALT, alanine
aminotransferase. |
Ad-TRAIL-34-122 exhibits no
hepatotoxicity in mice
Finally, the present study investigated whether
these adenoviral vectors led to hepatotoxicity in mice. PBS,
Ad-EGFP, Ad-TRAIL and Ad-TRAIL-34-122 were injected into the tail
vein of tumor-free BALB/c mice. The blood was harvested for
analysis of serum ALT levels. The results revealed that Ad-TRAIL
induced significant hepatotoxicity, evidenced by the elevated
levels of ALT in the blood. However, Ad-TRAIL-MRE-34-122 did not
alter the levels of ALT in the blood (Fig. 5C). Furthermore, immuohistological
staining indicated that TRAIL was not expressed in the liver
tissues from the mice injected with Ad-TRAIL-34-122 (Fig. 5B).
Discussion
The present study initially verified that the
expression of miR-34 and miR-122 was underexpressed
in osteosarcoma compared with in normal tissues. These results were
consistent with a previous study (10). The difference in the levels of
miR-34 and miR-122 between cancer and normal tissues
suggested that the application of their MREs may confer the
expression of inserted genes with specificity.
Further investigation using a luciferase reporter
revealed that the MREs of miR-34 and miR-122 were
able to suppress exogenous gene expression in the normal cells
rather than in the osteosarcoma cells. This effect of MREs on the
expression of inserted genes has been confirmed in other types of
cancer (12,13).
As expected, Ad-TRAIL-34-122 suppressed the
viability of osteosarcoma cells by activating the apoptotic pathway
and had no significant effect on the survival of normal cells,
indicating high tumor selectivity. The use of MREs of tumor
suppressor miRNAs, including TRAIL, to regulate exogenous
expression, mediated by adenoviral vectors, has been assessed in
bladder cancer and glioma (13,14).
The therapeutic effect has been further verified in mice
(13.14).
In addition to TRAIL, certain cytokines can also be
used in MRE-regulated gene therapy for osteosarcoma, including
dickkopf-1 and interleukin-24 (15,16).
Furthermore, adenoviral vectors from other serotypes are also
suitable for MRE-regulated TRAIL therapy (15,17)
due to their improved infectivity towards cancer cells.
In the present study, an MRE-regulated adenoviral
vector that selectively expressed TRAIL in osteosarcoma cells was
constructed. The results confirmed that this strategy was effective
and safe and demonstrated that this miRNA-based anti-tumor gene
therapy may be promising for the treatment of osteosarcoma.
References
|
1
|
Ando K, Heymann MF, Stresing V, Mori K,
Redini F and Heymann D: Current therapeutic strategies and novel
approaches in osteosarcoma. Cancers (Basel). 5:591–616. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang J and Zhang W: New molecular insights
into osteosarcoma targeted therapy. Curr Opin Oncol. 25:398–406.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Muzio M, Chinnaiyan AM, Kischkel FC, et
al: FLICE, a novel FADD-homologous ICE/CED-3-like protease, is
recruited to the CD95 (Fas/APO-1) death - inducing signaling
complex. Cell. 85:817–827. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li C, Cheng Q, Liu J, Wang B, Chen D and
Liu Y: Potent growth-inhibitory effect of TRAIL therapy mediated by
double-regulated oncolytic adenovirus on osteosarcoma. Mol Cell
Biochem. 364:337–344. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu J, Zeng T, Wu X, Gao Q, Zhai W and Ding
Z: Ether à go-go 1 silencing in combination with TRAIL
overexpression has synergistic antitumor effects on osteosarcoma.
Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 28:65–70. 2012.
|
|
7
|
Mitsiades N, Poulaki V, Mitsiades C and
Tsokos M: Ewing’s sarcoma family tumors are sensitive to tumor
necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand and express death
receptor 4 and death receptor 5. Cancer Res. 61:2704–2712.
2001.
|
|
8
|
Zheng SJ, Wang P, Tsabary G and Chen YH:
Critical roles of TRAIL in hepatic cell death and hepatic
inflammation. J Clin Invest. 113:58–64. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miao J, Wu S, Peng Z, Tania M and Zhang C:
MicroRNAs in osteosarcoma: diagnostic and therapeutic aspects.
Tumour Biol. 34:2093–2098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
He C, Xiong J, Xu X, et al: Functional
elucidation of MiR-34 in osteosarcoma cells and primary tumor
samples. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 388:35–40. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma L, Liu J, Shen J, et al: Expression of
miR-122 mediated by adenoviral vector induces apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest of cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 9:554–561. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu J, Ma L, Li C, Zhang Z, Yang G and
Zhang W: Tumor-targeting TRAIL expression mediated by miRNA
response elements suppressed growth of uveal melanoma cells. Mol
Oncol. 7:1043–1055. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bo Y, Guo G and Yao W: MiRNA-mediated
tumor specific delivery of TRAIL reduced glioma growth. J
Neurooncol. 112:27–37. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhao Y, Li Y, Wang L, et al: microRNA
response elements-regulated TRAIL expression shows specific
survival-suppressing activity on bladder cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 32:102013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang B, Liu J, Ma LN, et al: Chimeric 5/35
adenovirus-mediated Dickkopf-1 overexpression suppressed
tumorigenicity of CD44(+) gastric cancer cells via
attenuating Wnt signaling. J Gastroenterol. 48:798–808. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lou W, Chen Q, Ma L, et al: Oncolytic
adenovirus co-expressing miRNA-34a and IL-24 induces superior
antitumor activity in experimental tumor model. J Mol Med (Berl).
91:715–725. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
He X, Liu J, Yang C, et al: 5/35
fiber-modified conditionally replicative adenovirus armed with p53
shows increased tumor-suppressing capacity to breast cancer cells.
Hum Gene Ther. 22:283–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|