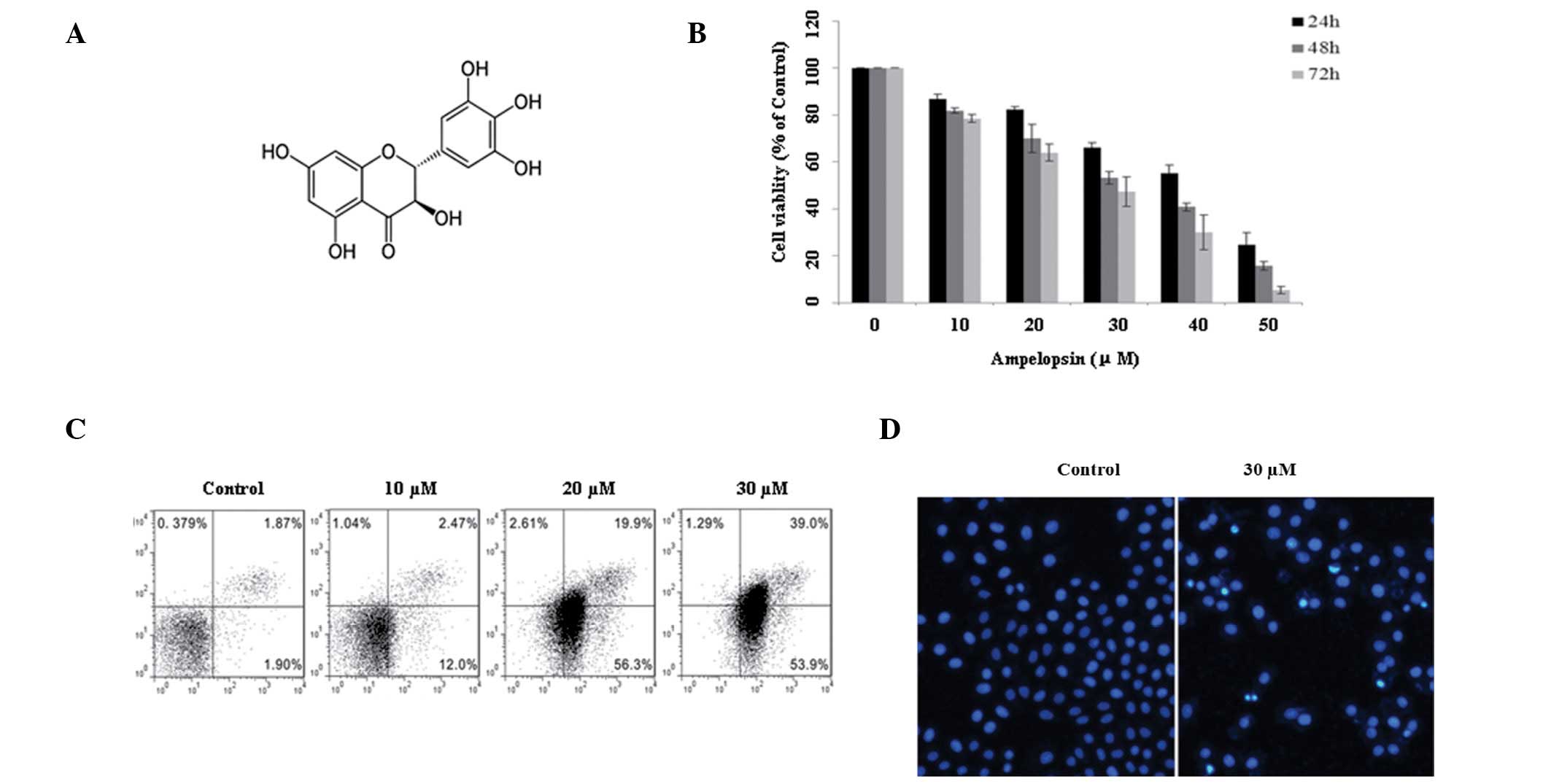
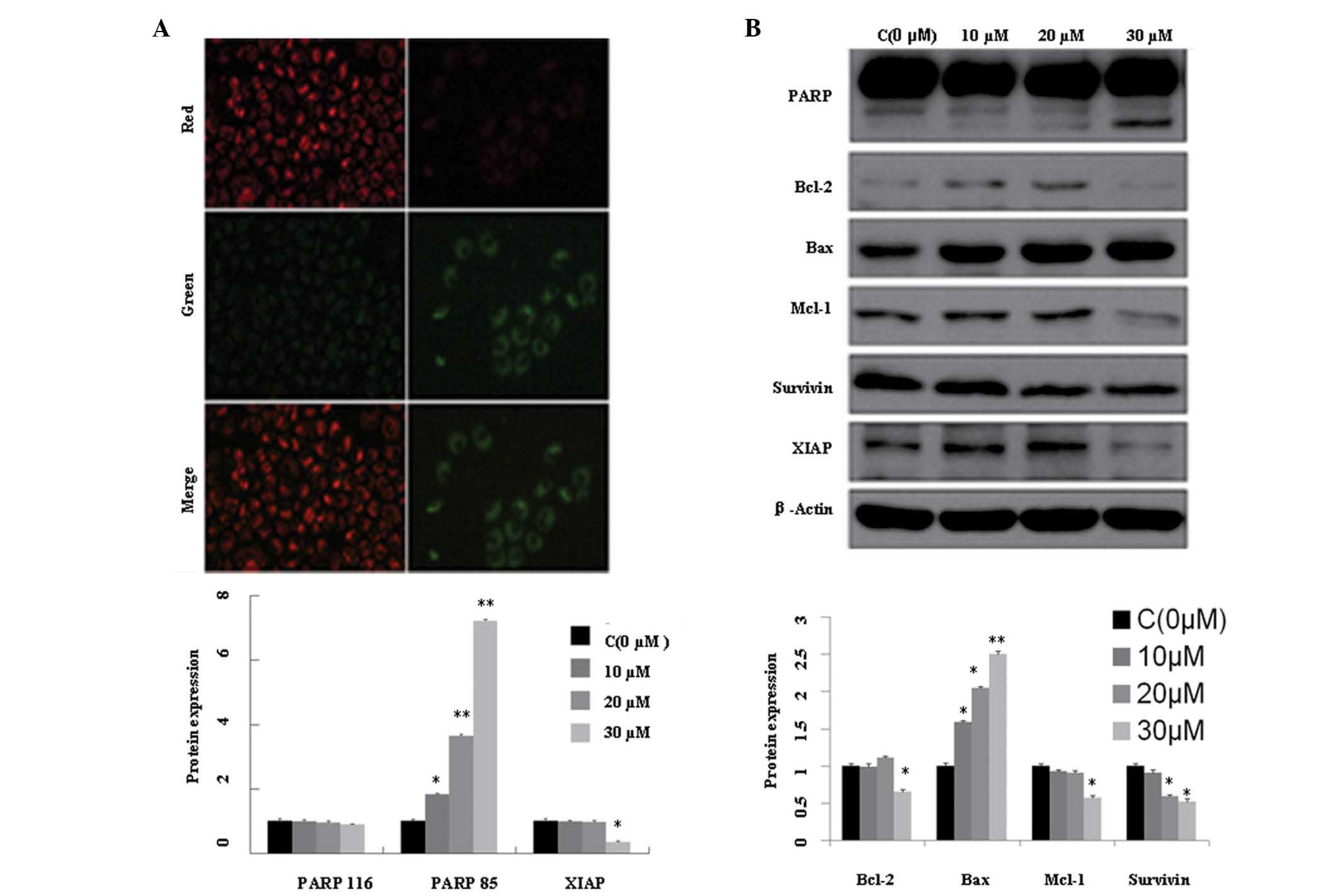
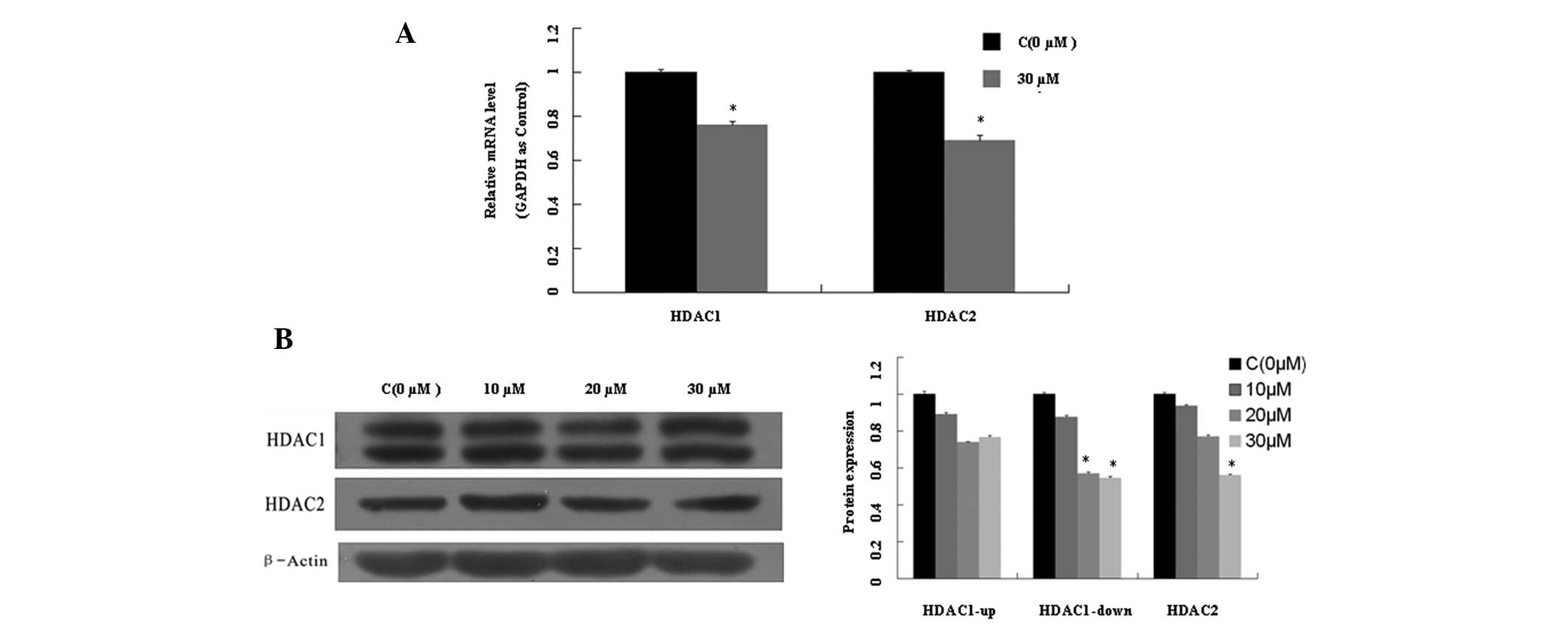
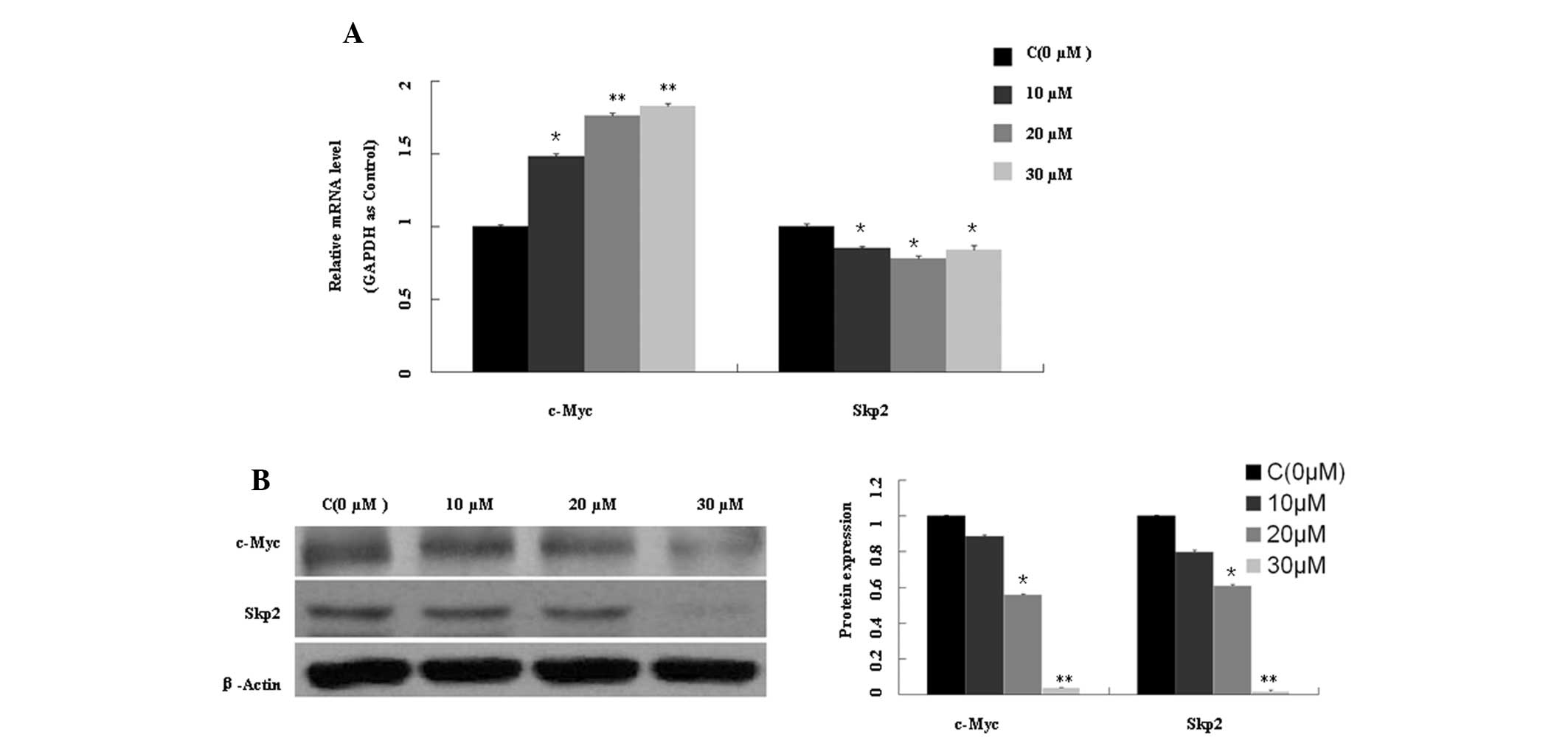
|
1
|
Juergens R and Brahmer J: Targeting the
epidermal growth factor receptor in non-small-cell lung cancer:
who, which, when, and how? Curr Oncol Rep. 4:255–264. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crocetti E and Paci E: Trends in lung
adenocarcinoma incidence and survival. Lung Cancer. 2:215–216.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ruthenburg AJ, Li H, Patel DJ and Allis
CD: Multivalent engagement of chromatin modifications by linked
binding modules. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 8:983–994. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Marks PA and Xu WS: Histone deacetylase
inhibitors: Potential in cancer therapy. J Cell Biochem.
107:600–608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Slingerland M, Guchelaar HJ and Gelderblom
H: Histone deacetylase inhibitors: an overview of the clinical
studies in solid tumors. Anticancer Drugs. 2:140–149. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
de Ruijter AJ, van Gennip AH, Caron HN,
Kemp S and van Kuilenburg AB: Histone deacetylases (HDACs):
characterization of the classical HDAC family. Biochem J.
370:737–749. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dang CV, Resar LM, Emison E, Kim S, Li Q,
Prescott JE, Wonsey D and Zeller K: Function of the c-Myc oncogenic
transcription factor. Exp Cell Res. 253:63–77. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nesbit CE, Tersak JM and Prochownik EV:
MYC oncogenes and human neoplastic disease. Oncogene. 18:3004–3016.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Flinn EM, Busch CM and Wright AP: Myc
boxes, which are conserved in Myc family proteins, are signals for
protein degradation via the proteasome. Mol Cell Biol.
18:5961–5969. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jones TR and Cole MD: Rapid cytoplasmic
turnover of c-Myc mRNA: requirement of the 3′ untranslated
sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 7:4513–4521. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kelly K, Cochran H, Stiles CD and Leder P:
Cell-specific regulation of the c-Myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens
and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 35:603–610. 1983.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Amati B: Myc degradation: Dancing with
ubiquitin ligases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:8843–8844. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carrano AC, Eytan E, Hershko A and Pagano
M: Skp2 is required for ubiquitin-mediated degradation of the CDK
inhibitor p27. Nat Cell Biol. 1:193–199. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kamura T, Hara T, Kotoshiba S, Yada M,
Ishida N, Imaki H, Hatakeyama S, Nakayama K and Nakayama KI:
Degradation of p57 Kip2 mediated by SCFSkp2-dependent
ubiquitylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:10231–10236. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tedesco D, Lukas J and Reed SI: The
pRb-related protein p130 is regulated by phosphorylation-dependent
proteolysis via the protein-ubiquitin ligase SCF (Skp2). Genes Dev.
16:2946–2957. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hiramatsu Y, Kitagawa K, Suzuki T, Uchida
C, Hattori T, Kikuchi H, Oda T, Hatakeyama S, Nakayama KI, Yamamoto
T, et al: Degradation of Tob1 mediated by SCFSkp2-dependent
ubiquitination. Cancer Res. 66:8477–8483. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao D, Zheng HQ, Zhou Z and Chen C: The
Fbw7 tumor suppressor targets KLF5 for ubiquitin-mediated
degradation and suppresses breast cell proliferation. Cancer Res.
70:4728–4738. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Akhoondi S, Lindström L, Widschwendter M,
Corcoran M, Bergh J, Spruck C, Grandér D and Sangfelt O:
Inactivation of FBXW7/hCDC4-beta expression by promoter
hypermethylation is associated with favorable prognosis in primary
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 12:R1052010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inuzuka H, Shaik S, Onoyama I, et al:
SCF(FBW7) regulates cellular apoptosis by targeting MCL1 for
ubiquitylation and destruction. Nature. 471:104–109. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sancho R, Jandke A, Davis H, Diefenbacher
ME, Tomlinson I and Behrens A: F-box and WD repeat
domain-containing 7 regulates intestinal cell lineage commitment
and is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor. Gastroenterology.
139:929–941. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
O’Neil J and Look AT: Mechanisms of
transcription factor deregulation in lymphoid cell transformation.
Oncogene. 26:6838–6849. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Z, Fukushima H, Gao D, Inuzuka H, Wan
L, Lau AW, Liu P and Wei W: The two faces of FBW7 in cancer drug
resistance. Bioessays. 11:851–859. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wertz IE, Kusam S, Lam C, et al:
Sensitivity to antitubulin chemotherapeutics is regulated by MCL1
and FBW7. Nature. 471:110–114. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pulverer BJ, Fisher C, Vousden K,
Littlewood T, Evan G and Woodgett JR: Site-specific modulation of
c-Myc cotransformation by residues phosphorylated in vivo.
Oncogene. 9:59–70. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim SY, Herbst A, Tworkowski KA, Salghetti
SE and Tansey WP: Skp2 regulates Myc protein stability and
activity. Mol Cell. 11:1177–1188. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Spruck CH, Strohmaier H, Sangfelt O,
Müller HM, Hubalek M, Müller-Holzner E, Marth C, Widschwendter M
and Reed SI: hCDC4 gene mutations in endometrial cancer. Cancer
Res. 62:4535–4539. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Welcker M, Orian A, Grim JE, Eisenman RN
and Clurman BE: A nucleolar isoform of the Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase
regulates c-Myc and cell size. Curr Biol. 14:1852–1857. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang B, Dong S, Cen X, Wang X, Liu X,
Zhang H, Zhao X and Wu Y: Ampelopsin sodium exhibits antitumor
effects against bladder carcinoma in orthotopic xenograft models.
Anticancer Drugs. 6:590–596. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zheng HQ and Liu DY: Anti-invasive and
anti-metastatic effect of ampelopsin on melanoma. Ai Zheng.
22:363–367. 2003.(In Chinese).
|
|
30
|
Zeng S, Liu D, Ye Y, Wang L and Wang W:
Anti-tumor effects of ampelopsin on human lung cancer GLC-82
implanted in nude mice. Zhong Yao Cai. 27:842–845. 2004.(In
Chinese).
|
|
31
|
Luo GQ, Zeng S and Liu DY: Inhibitory
effects of ampelopsin on angiogenesis. Zhong Yao Cai. 29:146–150.
2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Ye J, Zheng Y and Liu D: Reversal effect
and its mechanism of ampelopsin on multidrug resistance in K562/ADR
cells. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 34:761–765. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Ni F, Gong Y, Li L, Abdolmaleky HM and
Zhou JR: Flavonoid ampelopsin inhibits the growth and metastasis of
prostate cancer in vitro and in mice. PLoS One. 7:e388022012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kou X, Shen K, An Y, Qi S, Dai WX and Yin
Z: Ampelopsin inhibits H2O2-induced apoptosis
by ERK and Akt signaling pathways and up-regulation of heme
oxygenase-1. Phytother Res. 7:988–994. 2012.
|
|
35
|
Gregory MA, Qi Y and Hann SR:
Phosphorylation by glycogen synthase kinase-3 controls c-myc
proteolysis and subnuclear localization. J Biol Chem.
51:51606–51612. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kamemura K, Hayes BK, Comer FI and Hart
GW: Dynamic interplay between O-glycosylation and O-phosphorylation
of nucleocytoplasmic proteins: alternative
glycosylation/phosphorylation of THR-58, a known mutational hot
spot of c-Myc in lymphomas, is regulated by mitogens. J Biol Chem.
21:19229–19235. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen XM, Bai Y, Zhong YJ, Xie XL, Long HW,
Yang YY, Wu SG, Jia Q and Wang XH: Wogonin has multiple anti-cancer
effects by regulating c-Myc/SKP2/Fbw7a and HDAC1/HDAC2 pathways and
inducing apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell line A549.
PLoS One. 8:e792012013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Q, Kluz T, Sun H and Costa M:
Mechanisms of c-Myc degradation by nickel compounds and hypoxia.
PLoS One. 4:e85312009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|