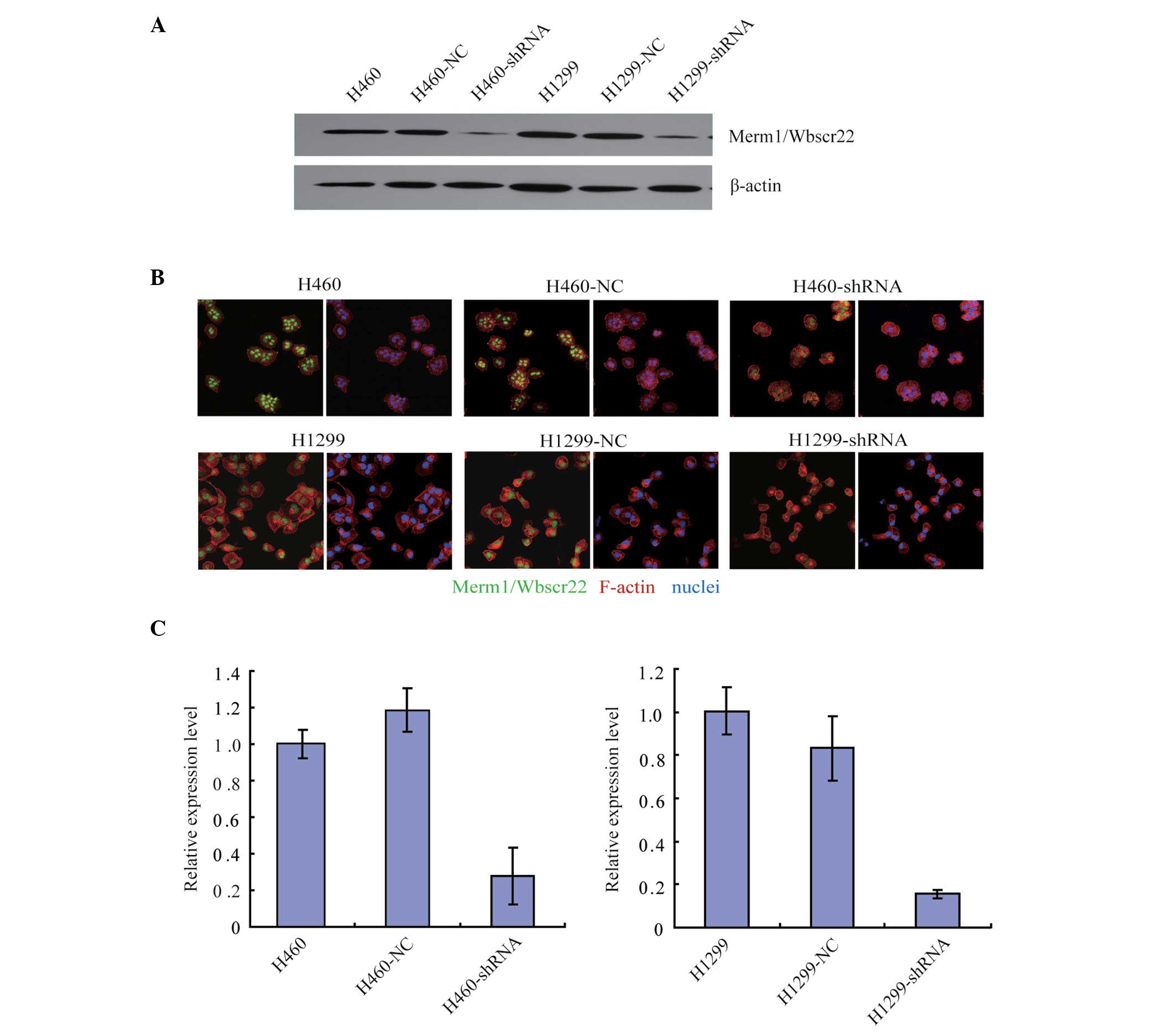
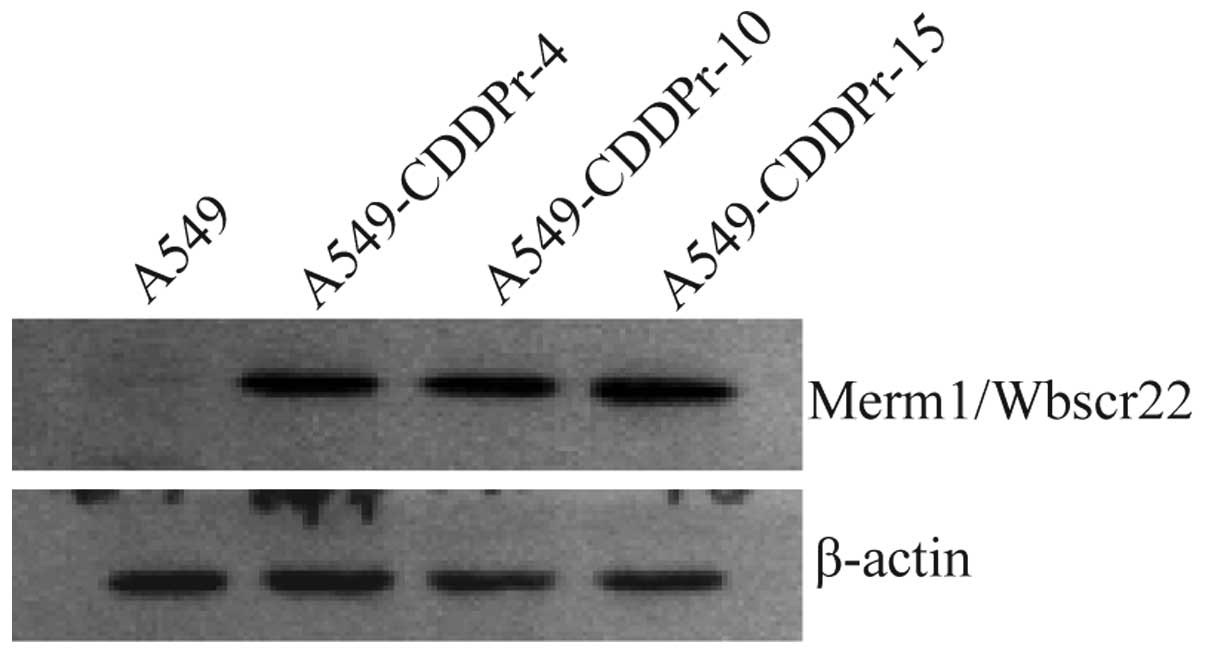
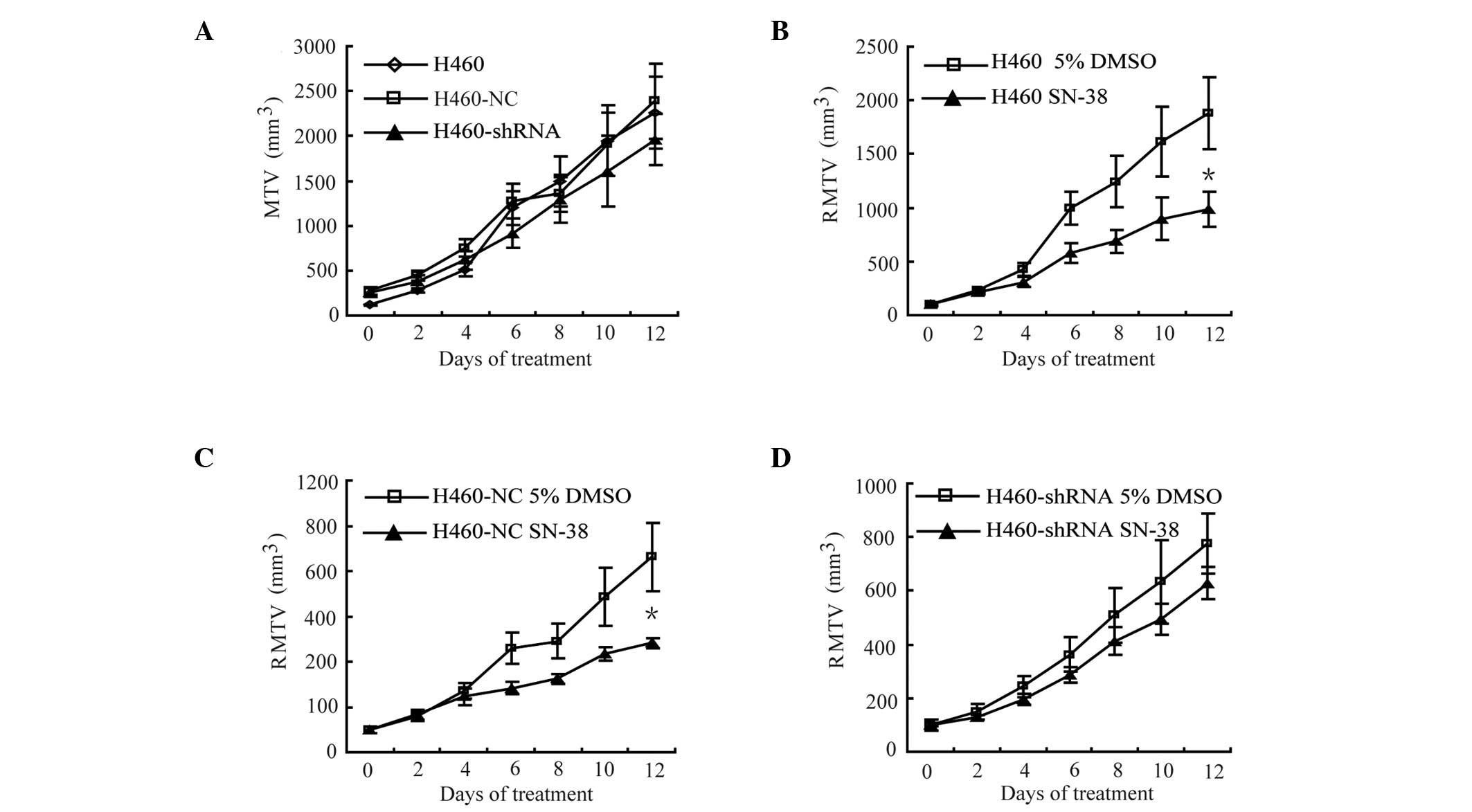
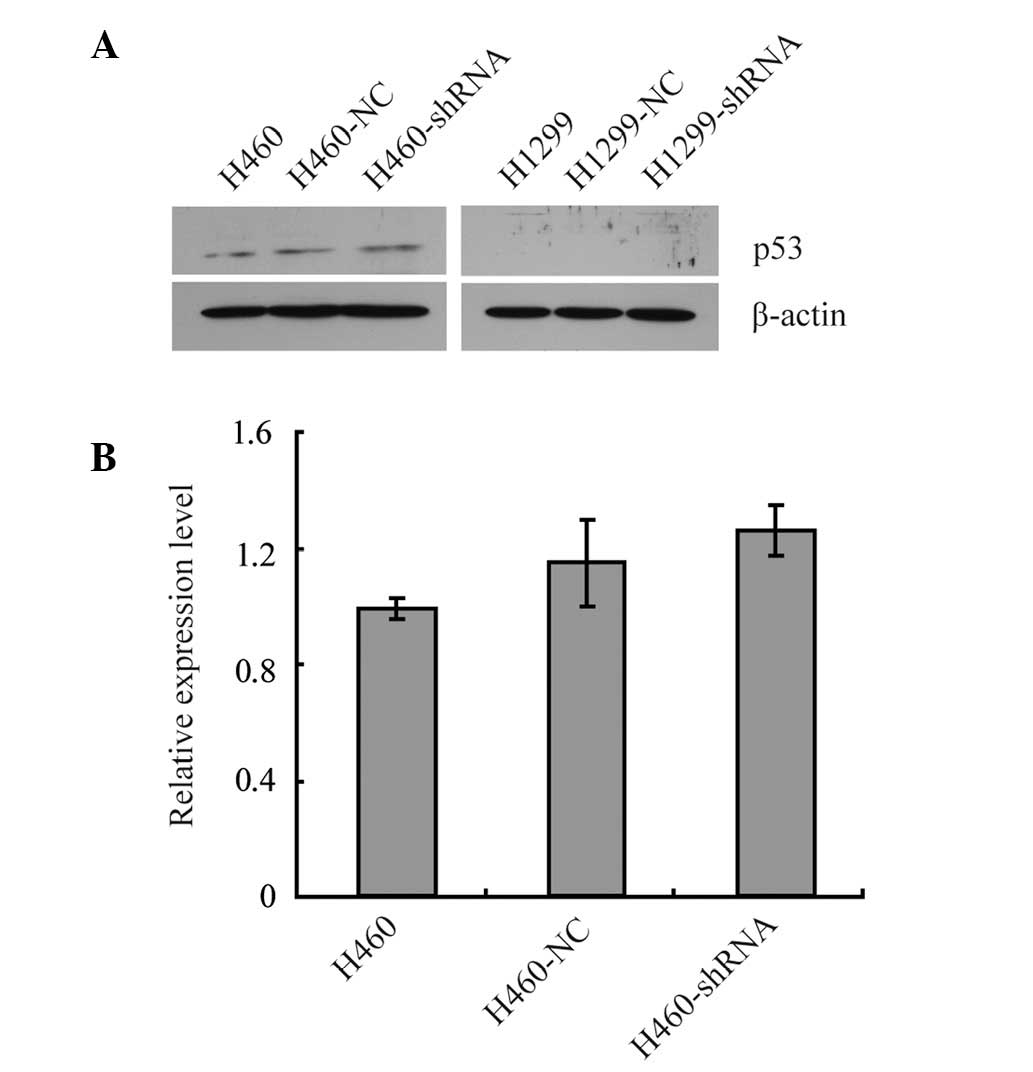
|
1
|
Pober BR: Williams-Beuren syndrome. New
Engl J Med. 362:239–252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bellugi U, Lichtenberger L, Mills D,
Galaburda A and Korenberg JR: Bridging cognition, the brain and
molecular genetics: evidence from Williams syndrome. Trends
Neurosci. 22:197–207. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Morris CA, Demsey SA, Leonard CO, Dilts C
and Blackburn BL: Natural history of Williams syndrome: physical
characteristics. J Pediatr. 113:318–326. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Merla G, Ucla C, Guipponi M and Reymond A:
Identification of additional transcripts in the Williams-Beuren
syndrome critical region. Hum Genet. 110:429–438. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Doll A and Grzeschik KH: Characterization
of two novel genes, WBSCR20 and WBSCR22, deleted in Williams-Beuren
syndrome. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 95:20–27. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng X: DNA modification by
methyltransferases. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 5:4–10. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Takebayashi S, Tamura T, Matsuoka C and
Okano M: Major and essential role for the DNA methylation mark in
mouse embryogenesis and stable association of DNMT1 with newly
replicated regions. Mol Cell Biol. 27:8243–8258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakazawa Y, Arai H and Fujita N: The novel
metastasis promoter Merm1/Wbscr22 enhances tumor cell survival in
the vasculature by suppressing Zac1/p53-dependent apoptosis. Cancer
Res. 71:1146–1155. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tiedemann RE, Zhu YX, Schmidt J, et al:
Identification of molecular vulnerabilities in human multiple
myeloma cells by RNA interference lethality screening of the
druggable genome. Cancer Res. 72:757–768. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li H and Yang BB: Friend or foe: the role
of microRNA in chemotherapy resistance. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
34:870–879. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Ding L and Sandford AJ: Selection
of reference genes for gene expression studies in human neutrophils
by real-time PCR. BMC Mol Biol. 6:42005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rho HW, Lee BC, Choi ES, et al:
Identification of valid reference genes for gene expression studies
of human stomach cancer by reverse transcription-qPCR. BMC Cancer.
10:2402010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Weglarz L, Molin I, Orchel A, Parfiniewicz
B and Dzierzewicz Z: Quantitative analysis of the level of p53 and
p21(WAF1) mRNA in human colon cancer HT-29 cells treated with
inositol hexaphosphate. Acta Bioch Pol. 53:349–356. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Carmichael J, DeGraff WG, Gazdar AF, Minna
JD and Mitchell JB: Evaluation of a tetrazolium-based semiautomated
colorimetric assay: assessment of chemosensitivity testing. Cancer
Res. 47:936–942. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takahashi T, Nau MM, Chiba I, et al: p53:
a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer.
Science. 246:491–494. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lin DL and Chang C: p53 is a mediator for
radiation-repressed human TR2 orphan receptor expression in MCF-7
cells, a new pathway from tumor suppressor to member of the steroid
receptor superfamily. J Biol Chem. 271:14649–14652. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vermeulen PB, Gasparini G, Fox SB, et al:
Second international consensus on the methodology and criteria of
evaluation of angiogenesis quantification in solid human tumours.
Eur J Cancer. 38:1564–1579. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hendrix MJ, Wood WR, Seftor EA, et al:
Retinoic acid inhibition of human melanoma cell invasion through a
reconstituted basement membrane and its relation to decreases in
the expression of proteolytic enzymes and motility factor receptor.
Cancer Res. 50:4121–4130. 1990.
|
|
19
|
Teng IW, Hou PC, Lee KD, et al: Targeted
methylation of two tumor suppressor genes is sufficient to
transform mesenchymal stem cells into cancer stem/initiating cells.
Cancer Res. 71:4653–4663. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kerr JF, Winterford CM and Harmon BV:
Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer.
73:2013–2026. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bak Y, Kim H, Kang JW, et al: A synthetic
naringenin derivative, 5-hydroxy-7,4′-diacetyloxyflavanone-N-phenyl
hydrazone (N101-43), induces apoptosis through up-regulation of
Fas/FasL expression and inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathways
in non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem.
59:10286–10297. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim TH, Seo WD, Ryu HW, et al: Anti-tumor
effects by a synthetic chalcone compound is mediated by
c-Myc-mediated reactive oxygen species production. Chem Biol
Interact. 188:111–118. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rho JK, Choi YJ, Ryoo BY, et al: p53
enhances gefitinib-induced growth inhibition and apoptosis by
regulation of Fas in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res.
67:1163–1169. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lai SL, Perng RP and Hwang J: p53 gene
status modulates the chemosensitivity of non-small cell lung cancer
cells. J Biomed Sci. 7:64–70. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kawasaki M, Nakanishi Y, Kuwano K, et al:
The utility of p53 immunostaining of transbronchial biopsy
specimens of lung cancer: p53 overexpression predicts poor
prognosis and chemoresistance in advanced non-small cell lung
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 3:1195–1200. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kawasaki M, Nakanishi Y, Kuwano K, et al:
Immunohistochemically detected p53 and P-glycoprotein predict the
response to chemotherapy in lung cancer. Eur J Cancer.
34:1352–1357. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Osaki M, Tatebe S, Goto A, et al:
5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cell
lines: role of the p53 gene. Apoptosis. 2:221–226. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li YX, Lin ZB and Tan HR: Wild type p53
increased chemosensitivity of drug-resistant human hepatocellular
carcinoma Bel7402/5-FU cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:76–82.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu ZW, Zhao P, Liu M, et al: Reversal of
5-flouroucial resistance by adenovirus-mediated transfer of
wild-type p53 gene in multidrug-resistant human colon carcinoma
LoVo/5-FU cells. World J Gastroenterol. 10:1979–1983.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu HC, Chen GG, Vlantis AC, et al:
5-fluorouracil mediates apoptosis and G1/S arrest in laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma via a p53-independent pathway. Cancer J.
12:482–493. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Xing H, Weng D, et al: Inhibition
of Akt signaling by SN-38 induces apoptosis in cervical cancer.
Cancer Lett. 274:47–53. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Takeba Y, Sekine S, Kumai T, et al:
Irinotecan-induced apoptosis is inhibited by increased
P-glycoprotein expression and decreased p53 in human hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 30:1400–1406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Takeba Y, Kumai T, Matsumoto N, et al:
Irinotecan activates p53 with its active metabolite, resulting in
human hepatocellular carcinoma apoptosis. J Pharmacol Sci.
104:232–242. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vaziri SA, Hill J, Chikamori K, et al:
Sensitization of DNA damage-induced apoptosis by the proteasome
inhibitor PS-341 is p53 dependent and involves target proteins
14-3-3sigma and survivin. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1880–1890. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ueno M, Nonaka S, Yamazaki R, Deguchi N
and Murai M: SN-38 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human
testicular cancer. Eur Urol. 42:390–397. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xie X, Sasai K, Shibuya K, et al: P53
status plays no role in radiosensitizing effects of SN-38, a
camptothecin derivative. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 45:362–368.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Osaki S, Nakanishi Y, Takayama K, et al:
Alteration of drug chemosensitivity caused by the
adenovirus-mediated transfer of the wild-type p53 gene in human
lung cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther. 7:300–307. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boyer J, McLean EG, Aroori S, et al:
Characterization of p53 wild-type and null isogenic colorectal
cancer cell lines resistant to 5-fluorouracil, oxaliplatin, and
irinotecan. Clin Cancer Res. 10:2158–2167. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Oizumi S, Isobe H, Ogura S, et al:
Topoisomerase inhibitor-induced apoptosis accompanied by
down-regulation of Bcl-2 in human lung cancer cells. Anticancer
Res. 22:4029–4037. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
McDonald AC and Brown R: Induction of
p53-dependent and p53-independent cellular responses by
topoisomerase 1 inhibitors. Br J Cancer. 78:745–751. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang Y, Zhu S, Cloughesy TF, Liau LM and
Mischel PS: p53 disruption profoundly alters the response of human
glioblastoma cells to DNA topoisomerase I inhibition. Oncogene.
23:1283–1290. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|