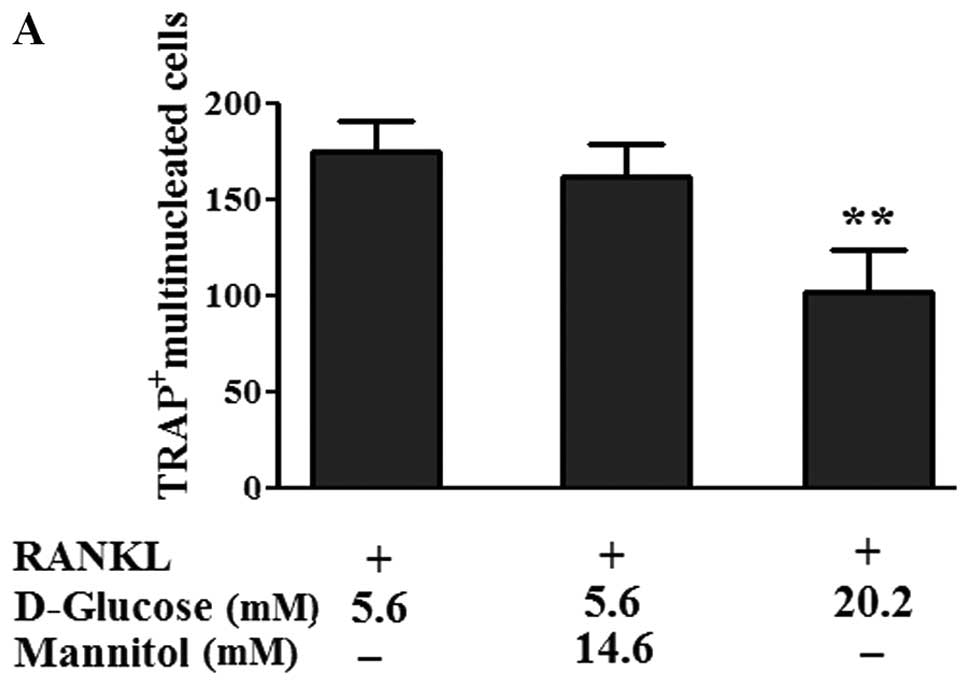
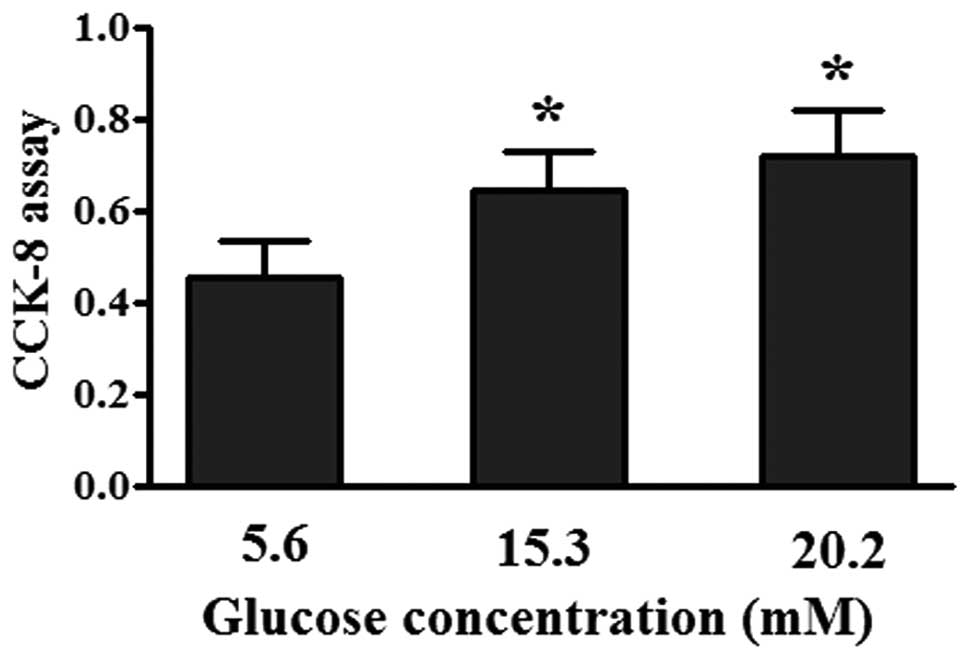
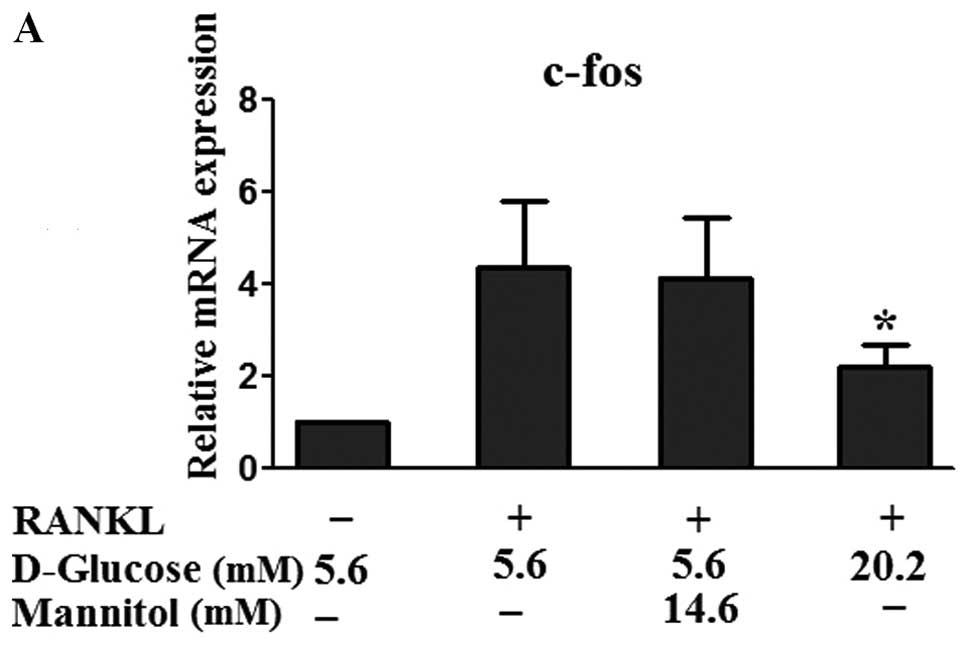
|
1
|
Xu Y, Wang L, He J, et al: Prevalence and
control of diabetes in Chinese adults. JAMA. 310:948–959. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khazai NB, Beck GR Jr and Umpierrez GE:
Diabetes and fractures: an overshadowed association. Curr Opin
Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 16:435–445. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hamada Y, Kitazawa S, Kitazawa R, Fujii H,
Kasuga M and Fukagawa M: Histomorphometric analysis of diabetic
osteopenia in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice: a possible role
of oxidative stress. Bone. 40:1408–1414. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fujii H, Hamada Y and Fukagawa M: Bone
formation in spontaneously diabetic Torii-newly established model
of non-obese type 2 diabetes rats. Bone. 42:372–379. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gaudio A, Privitera F, Battaglia K, et al:
Sclerostin levels associated with inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and reduced bone turnover in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:3744–3750. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wittrant Y, Gorin Y, Woodruff K, et al:
High d(+) glucose concentration inhibits RANKL-induced
osteoclastogenesis. Bone. 42:1122–1130. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu F, Ye YP, Dong YH, Guo FJ, Chen AM and
Huang SL: Inhibitory effects of high glucose/insulin environment on
osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 33:244–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaneko H, Sasaki T, Ramamurthy NS and
Golub LM: Tetracycline administration normalizes the structure and
acid phosphatase activity of osteoclasts in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Anat Rec. 227:427–436. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hamada Y, Fujii H, Kitazawa R, Yodoi J,
Kitazawa S and Fukagawa M: Thioredoxin-1 overexpression in
transgenic mice attenuates streptozotocin-induced diabetic
osteopenia: a novel role of oxidative stress and therapeutic
implications. Bone. 44:936–941. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Reyes-García R, Rozas-Moreno P,
López-Gallardo G, García-Martín A, Varsavsky M, Avilés-Perez MD and
Muñoz-Torres M: Serum levels of bone resorption markers are
decreased in patients with type 2 diabetes. Acta Diabetol.
50:47–52. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Dienelt A and zur Nieden NI: Hyperglycemia
impairs skeletogenesis from embryonic stem cells by affecting
osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation. Stem Cells Dev.
20:465–474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim K, Lee SH, Ha Kim J, Choi Y and Kim N:
NFATc1 induces osteoclast fusion via up-regulation of Atp6v0d2 and
the dendritic cell-specific transmembrane protein (DC-STAMP). Mol
Endocrinol. 22:176–185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Suda T, Takahashi N, Udagawa N, Jimi E,
Gillespie MT and Martin TJ: Modulation of osteoclast
differentiation and function by the new members of the tumor
necrosis factor receptor and ligand families. Endocr Rev.
20:345–357. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Asagiri M and Takayanagi H: The molecular
understanding of osteoclast differentiation. Bone. 40:251–264.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamashita T, Yao Z, Li F, et al: NF-kappaB
p50 and p52 regulate receptor activator of NF-kappaB ligand (RANKL)
and tumor necrosis factor-induced osteoclast precursor
differentiation by activating c-Fos and NFATc1. J Biol Chem.
282:18245–18253. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Teitelbaum SL and Ross FP: Genetic
regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat Rev Genet.
4:638–649. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Sawatani Y, et al:
DC-STAMP is essential for cell-cell fusion in osteoclasts and
foreign body giant cells. J Exp Med. 202:345–351. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lee SH, Rho J, Jeong D, et al: v-ATPase V0
subunit d2-deficient mice exhibit impaired osteoclast fusion and
increased bone formation. Nat Med. 12:1403–1409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yagi M, Ninomiya K, Fujita N, et al:
Induction of DC-STAMP by alternative activation and downstream
signaling mechanisms. J Bone Miner Res. 22:992–1001. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suzuki K, Kurose T, Takizawa M, et al:
Osteoclastic function is accelerated in male patients with type 2
diabetes mellitus: the preventive role of osteoclastogenesis
inhibitory factor/osteoprotegerin (OCIF/OPG) on the decrease of
bone mineral density. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 68:117–125. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hie M, Yamazaki M and Tsukamoto I:
Curcumin suppresses increased bone resorption by inhibiting
osteoclastogenesis in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes.
Eur J Pharmacol. 621:1–9. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rio DC, Ares M Jr, Hannon GJ and Nilsen
TW: Purification of RNA using TRIzol (TRI reagent). Cold Spring
Harb Protoc. 2010.5439:2010
|
|
25
|
Matsuo K, Owens JM, Tonko M, Elliott C,
Chambers TJ and Wagner EF: Fosl1 is a transcriptional target of
c-Fos during osteoclast differentiation. Nat Genet. 24:184–187.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wagner EF and Karsenty G: Genetic control
of skeletal development. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 11:527–532. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsuo K, Galson DL, Zhao C, et al:
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) rescues
osteoclastogenesis in precursors lacking c-Fos. J Biol Chem.
279:26475–26480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ishida N, Hayashi K, Hoshijima M, et al:
Large scale gene expression analysis of osteoclastogenesis in vitro
and elucidation of NFAT2 as a key regulator. J Biol Chem.
277:41147–41156. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gandhi A, Doumas C, O’Connor JP, Parsons
JR and Lin SS: The effects of local platelet rich plasma delivery
on diabetic fracture healing. Bone. 38:540–546. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Verhaeghe J, Suiker AM, Visser WJ, Van
Herck E, Van Bree R and Bouillon R: The effects of systemic
insulin, insulinlike growth factor-I and growth hormone on bone
growth and turnover in spontaneously diabetic BB rats. J
Endocrinol. 134:485–492. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hamada Y, Fujii H, Kitazawa R, Yodoi J,
Kitazawa S and Fukagawa M: Thioredoxin-1 overexpression in
transgenic mice attenuates streptozotocin-induced diabetic
osteopenia: a novel role of oxidative stress and therapeutic
implications. Bone. 44:936–941. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fujii H, Hamada Y and Fukagawa M: Bone
formation in spontaneously diabetic Torii-newly established model
of nonobese type 2 diabetes rats. Bone. 42:372–379. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Dougall WC, Glaccum M, Charrier K, et al:
RANK is essential for osteoclast and lymph node development. Genes
Dev. 13:2412–2424. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kong YY, Yoshida H, Sarosi I, et al: OPGL
is a key regulator of osteoclastogenesis, lymphocyte development
and lymph-node organogenesis. Nature. 397:315–323. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wagner EF and Eferl R: Fos/AP-1 proteins
in bone and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 208:126–140. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang ZQ, Ovitt C, Grigoriadis AE,
Möhle-Steinlein U, Rüther U and Wagner EF: Bone and haematopoietic
defects in mice lacking c-fos. Nature. 360:741–745. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Grigoriadis AE, Wang ZQ, Cecchini MG,
Hofstetter W, Felix R, Fleisch HA and Wagner EF: c-Fos: a key
regulator of osteoclast-macrophage lineage determination and bone
remodeling. Science. 266:443–448. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Matsuo K, Galson DL, Zhao C, et al:
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells (NFAT) rescues
osteoclastogenesis in precursors lacking c-Fos. Biol Chem.
279:26475–26480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Teitelbaum SL: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yagi M, Miyamoto T, Toyama Y and Suda T:
Role of DC-STAMP in cellular fusion of osteoclasts and macrophage
giant cells. J Bone Miner Metab. 24:355–358. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Feng X and McDonald JM: Disorders of bone
remodeling. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:121–145. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Karsdal MA, Martin TJ, Bollerslev J,
Christiansen C and Henriksen K: Are nonresorbing osteoclasts
sources of bone anabolic activity? Bone Miner Res. 22:487–494.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Burr DB, Miller L, Grynpas M, et al:
Tissue mineralization is increased following 1-year treatment with
high doses of bisphosphonates in dogs. Bone. 33:960–969. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li J, Sato M, Jerome C, Turner CH, Fan Z
and Burr DB: Microdamage accumulation in the monkey vertebra does
not occur when bone turnover is suppressed by 50% or less with
estrogen or raloxifene. J Bone Miner Metab. 23:48–54. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ma L, Oei L, Jiang L, et al: Association
between bone mineral density and type 2 diabetes mellitus: a
meta-analysis of observational studies. Eur J Epidemiol.
27:319–332. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vestergaard P: Discrepancies in bone
mineral density and fracture risk in patients with type 1 and type
2 diabetes-a meta-analysis. Osteoporos Int. 18:427–444. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Janghorbani M, Van Dam RM, Willett WC and
Hu FB: Systematic review of type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus and
risk of fracture. Am J Epidemiol. 166:495–505. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|