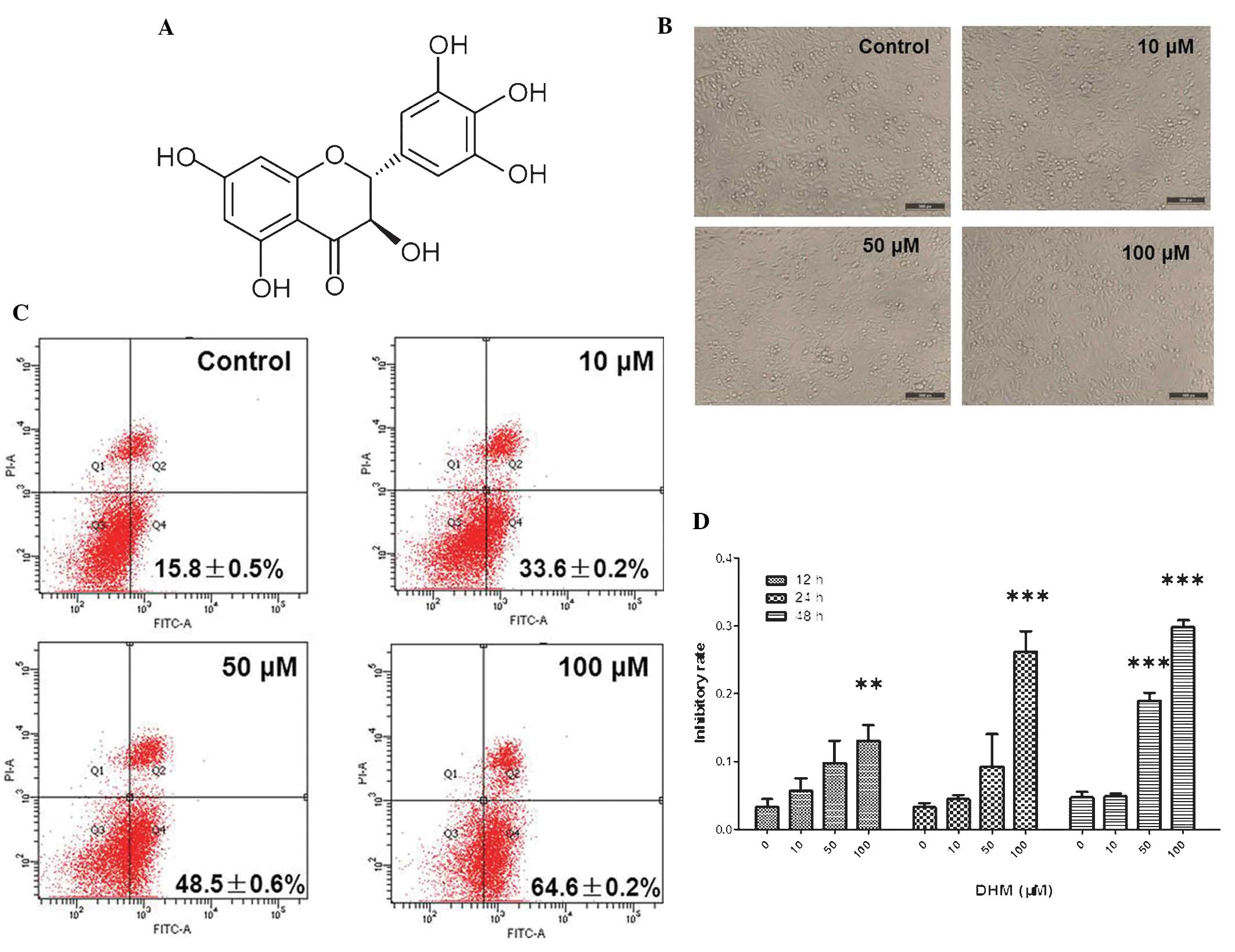
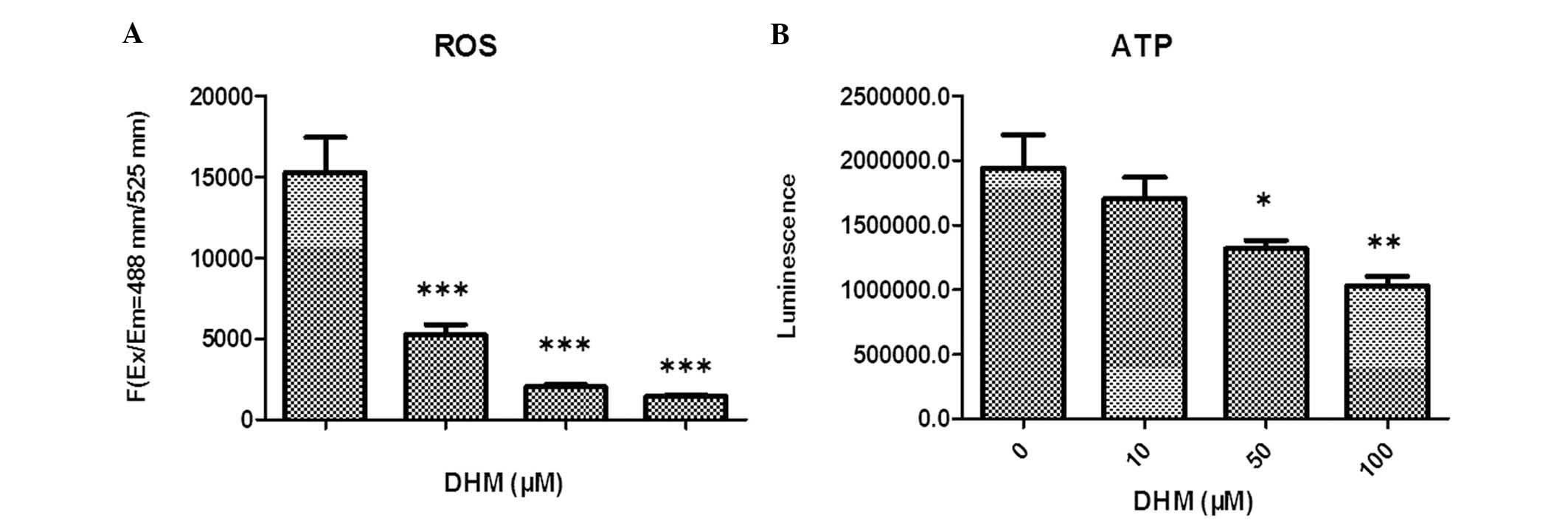
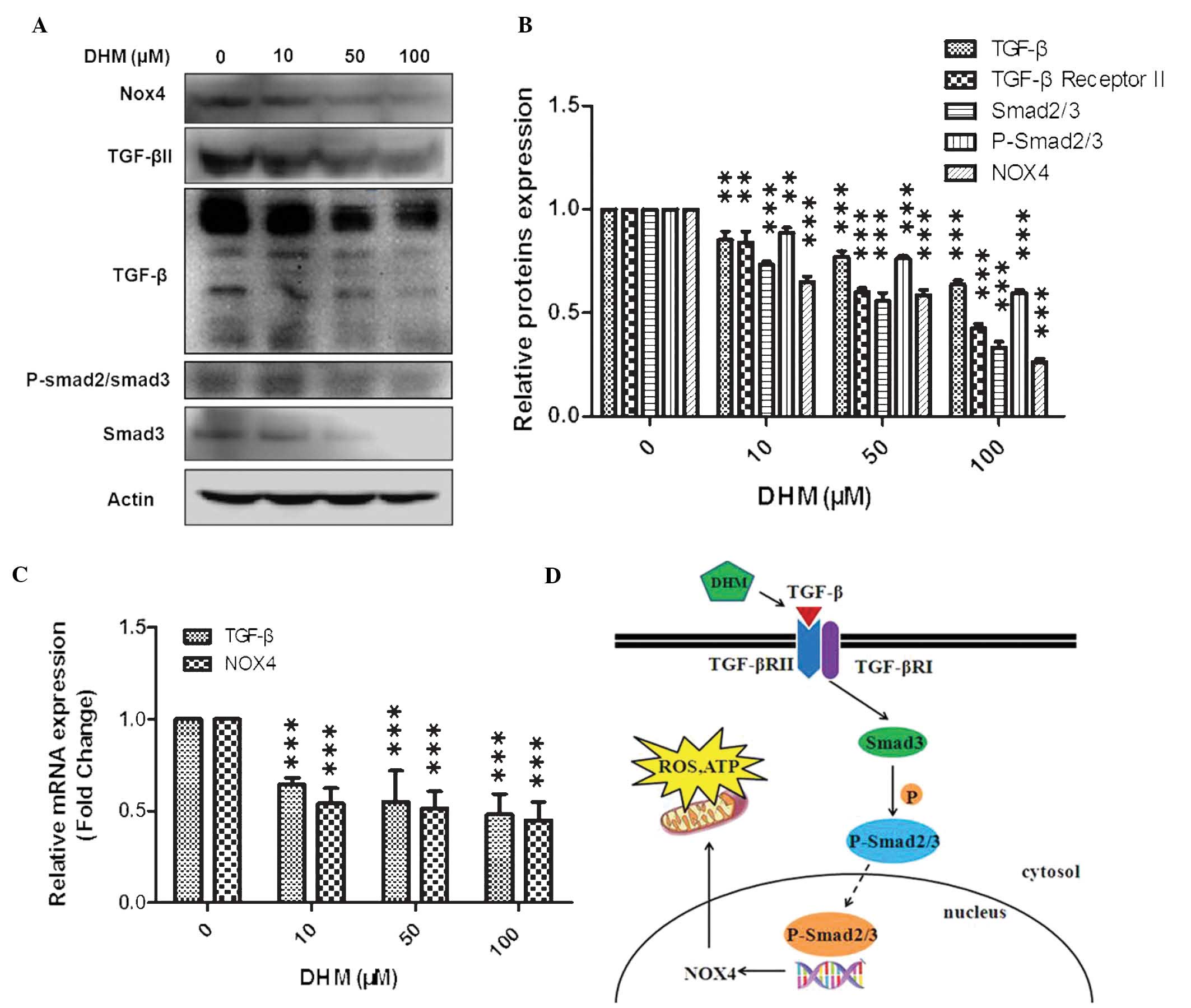
|
1
|
Wu S, Liu B, Zhang Q, et al:
Dihydromyricetin reduced Bcl-2 expression via p53 in human hepatoma
hepg2 cells. PLoS One. 8:e768862013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Li H, Li Y, Zhang Y, Shi H, Hu W and Zhang
Z: Comparison of refluxing, ultrasonic-and microwave-assisted
extraction of dihydromyricetin from Ampelopsis grossedentata. J
AOAC Int. 91:1278–1283. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Ye J, Guan Y, Zeng S and Liu D: Ampelopsin
prevents apoptosis induced by H2O2 in MT-4 lymphocytes. Planta Med.
74:252–257. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kundaković K, Stanojković T, Milenković M,
Grubin J, Juranić Z, Stevanović B and Kovačević N: Cytotoxic,
antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities of Ampelopsis
brevipedunculata and Parthenocissus tricuspidata (Vitaceae). Arch
Biol Sci. 60:641–647. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhou Y, Shu F, Liang X, et al: Ampelopsin
induces cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in breast cancer cells
through ROS generation and endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway.
PLoS One. 9:e890212014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kou X, Shen K, An Y, Qi S, Dai WX and Yin
Z: Ampelopsin inhibits H2O2-induced apoptosis
by ERK and Akt signaling pathways and up-regulation of heme
oxygenase-1. Phytother Res. 26:988–994. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Qi S, Xin Y, Guo Y, Diao Y, Kou X, Luo L
and Yin Z: Ampelopsin reduces endotoxic inflammation via repressing
ROS-mediated activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. Int
Immunopharmacol. 12:278–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jeon SH, Chun W, Choi YJ and Kwon YS:
Cytotoxic constituents from the bark of Salix hulteni. Arch Pharm
Res. 31:978–982. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhou FZ, Zhang XY and Guo Y:
Anti-proliferation effect of combining dihydromyricetin and
adriamycin on MDA-MB-231 cell in vitro. Journal of Hubei University
for Nationalities (Medical Edition). 4:0012010.
|
|
10
|
Guo X, Zhu K, Zhang H and Yao H:
Anti-tumor activity of a novel protein obtained from tartary
buckwheat. Int J Mol Sci. 11:5201–5211. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang QY, Li R, Zeng GF, et al:
Dihydromyricetin inhibits migration and invasion of hepatoma cells
through regulation of MMP-9 expression. World J Gastroenterol.
20:10082–10093. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Busse A and Keilholz U: Role of TGF-β in
melanoma. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 12:2165–2175. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Perrot CY, Javelaud D and Mauviel A:
Insights into the transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway in
cutaneous melanoma. Ann Dermatol. 25:135–144. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moustakas A, Souchelnytskyi S and Heldin
CH: Smad regulation in TGF-beta signal transduction. J Cell Sci.
114(Pt 24): 4359–4369. 2001.
|
|
15
|
Varelas X, Samavarchi-Tehrani P, Narimatsu
M, et al: The Crumbs complex couples cell density sensing to
Hippo-dependent control of the TGF-β-SMAD pathway. Developmental
cell. 19:831–844. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Brown DI and Griendling KK: Nox proteins
in signal transduction. Free Radic Biol and Med. 47:1239–1253.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tobar N, Guerrero J, Smith PC and Martínez
J: NOX4-dependent ROS production by stromal mammary cells modulates
epithelial MCF-7 cell migration. Br J Cancer. 103:1040–1047. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Boudreau HE, Emerson SU, Korzeniowska A,
Jendrysik MA and Leto TL: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) proteins induce
NADPH oxidase 4 expression in a transforming growth factor
β-dependent manner: a new contributor to HCV-induced oxidative
stress. J Virol. 83:12934–12946. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Barnes JL and Gorin Y: Myofibroblast
differentiation during fibrosis: role of NAD(P)H oxidases. Kidney
Int. 79:944–956. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu R-M and Gaston Pravia K: Oxidative
stress and glutathione in TGF-β-mediated fibrogenesis. Free Radical
Biology and Medicine. 48:1–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Pike LS, Smift AL, Croteau NJ, Ferrick DA
and Wu M: Inhibition of fatty acid oxidation by etomoxir impairs
NADPH production and increases reactive oxygen species resulting in
ATP depletion and cell death in human glioblastoma cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1807.726–734. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Kisseleva T and Brenner DA: Mechanisms of
fibrogenesis. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 233:109–122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Pérez-Gómez E, Del Castillo G, Santibáñez
JF, Lopez-Novoa JM, Bernabéu C and Quintanilla M: The role of the
TGF-β coreceptor endoglin in cancer. Scientific World Journal.
10:2367–2384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Baek HJ, Pishvaian MJ, Tang Y, Kim TH,
Yang S, Zouhairi ME, Mendelson J, Shetty K, Kallakury B, Berry DL,
et al: Transforming growth factor-β adaptor, β2-spectrin, modulates
cyclin dependent kinase 4 to reduce development of hepatocellular
cancer. Hepatology. 53:1676–1684. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Taatjes DJ: The human Mediator complex: a
versatile, genome-wide regulator of transcription. Trends Biochem
Sci. 35:315–322. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moses H and Barcellos-Hoff MH: TGF-beta
biology in mammary development and breast cancer. Cold Spring
Harbor Perspect Biol. 3:a0032772011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wiercinska E, Naber HP, Pardali E, van der
Pluijm G, van Dam H and ten Dijke P: The TGF-β/Smad pathway induces
breast cancer cell invasion through the up-regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase 2 and 9 in a spheroid invasion model system.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:657–666. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Petersen M, Pardali E, Van Der Horst G,
Cheung H, van den Hoogen C, van der Pluijm G and Ten Dijke P: Smad2
and Smad3 have opposing roles in breast cancer bone metastasis by
differentially affecting tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene.
29:1351–1361. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dzwonek J, Preobrazhenska O, Cazzola S,
Conidi A, Schellens A, van Dinther M, Stubbs A, Klippel A,
Huylebroeck D, ten Dijke P and Verschueren K: Smad3 is a key
nonredundant mediator of transforming growth factor beta signaling
in Nme mouse mammary epithelial cells. Mol Cancer Res. 7:1342–1353.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Szatrowski TP and Nathan CF: Production of
large amounts of hydrogen peroxide by human tumor cells. Cancer
Res. 51:794–798. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: Gain or loss of
TGFbeta signaling in mammary carcinoma cells can promote
metastasis. Cell Cycle. 8:3319–3327. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bierie B, Chung CH, Parker JS, Stover DG,
Cheng N, Chytil A, Aakre M, Shyr Y and Moses HL: Abrogation of
TGF-beta signaling enhances chemokine production and correlates
with prognosis in human breast cancer. J Clin Invest.
119:1571–1582. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil
A, Aakre M, Carbone DP, Matrisian LM, Richmond A, Lin PC and Moses
HL: Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits
Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell.
13:23–35. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Giannelli G, Mazzocca A, Fransvea E, Lahn
M and Antonaci S: Inhibiting TGF-β signaling in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1815.214–223. 2011.
|
|
35
|
Aon MA, Cortassa S and O’Rourke B:
Redox-optimized ROS balance: a unifying hypothesis. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1797:865–877. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Parga J, Rodríguez-Pallares J, Joglar B,
Diaz-Ruiz C, Guerra M and Labandeira-Garcia JL: Effect of
inhibitors of NADPH oxidase complex and mitochondrial ATP-sensitive
potassium channels on generation of dopaminergic neurons from
neurospheres of mesencephalic precursors. Dev Dyn. 239:3247–3259.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li S, Tabar SS, Malec V, Eul BG, Klepetko
W, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Rose F and Hänze J: NOX4
regulates ROS levels under normoxic and hypoxic conditions,
triggers proliferation, and inhibits apoptosis in pulmonary artery
adventitial fibroblasts. Antioxid Redox Signal. 10:1687–1698. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu RM, Choi J, Wu JH, Gaston Pravia KA,
Lewis KM, Brand JD, Mochel NS, Krzywanski DM, Lambeth JD, Hagood
JS, et al: Oxidative modification of nuclear mitogen-activated
protein kinase phosphatase 1 is involved in transforming growth
factor beta1-induced expression of plasminogen activator inhibitor
1 in fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 285:16239–16247. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu R-M and Gaston Pravia K: Oxidative
stress and glutathione in TGF-β-mediated fibrogenesis. Free Radic
Biol Med. 48:1–15. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Hecker L, Vittal R, Jones T, Jagirdar R,
Luckhardt TR, Horowitz JC, Pennathur S, Martinez FJ and Thannickal
VJ: NADPH oxidase-4 mediates myofibroblast activation and
fibrogenic responses to lung injury. Nat Med. 15:1077–1081. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|